Abstract
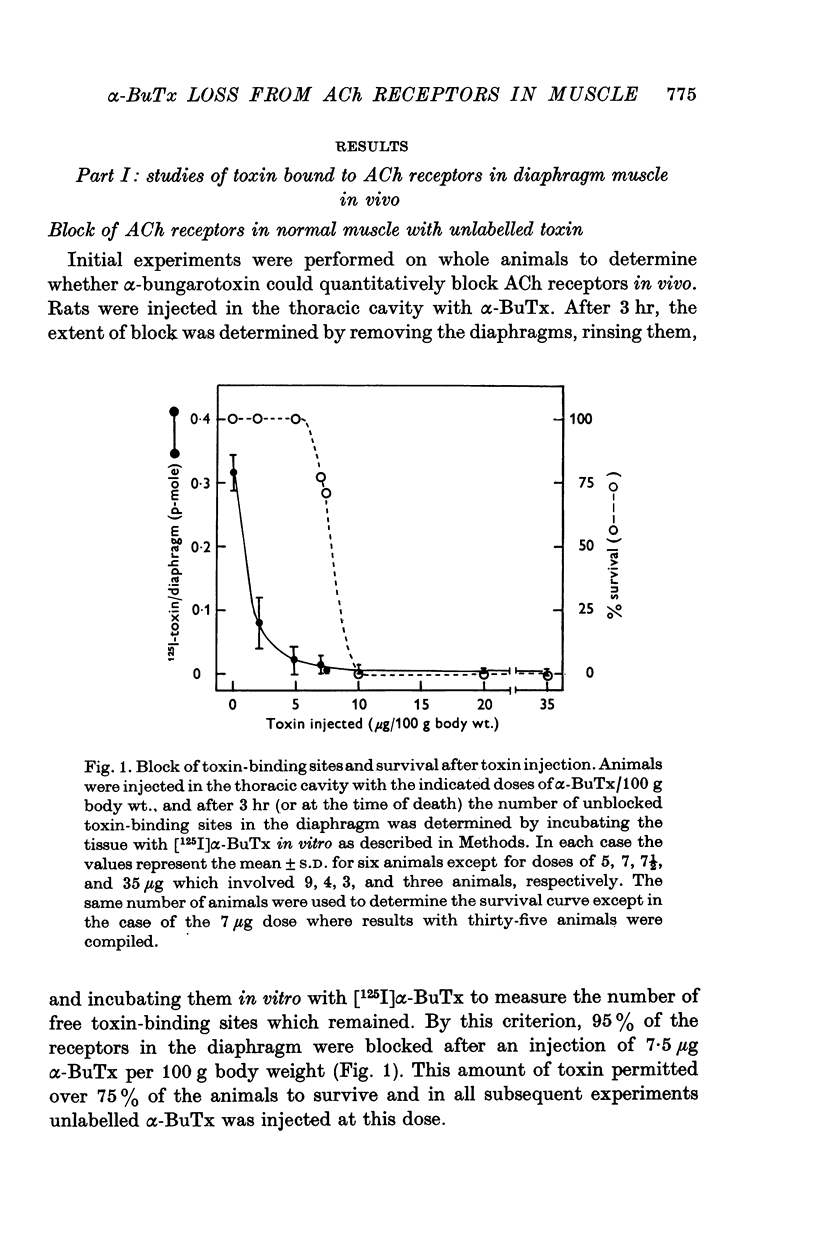
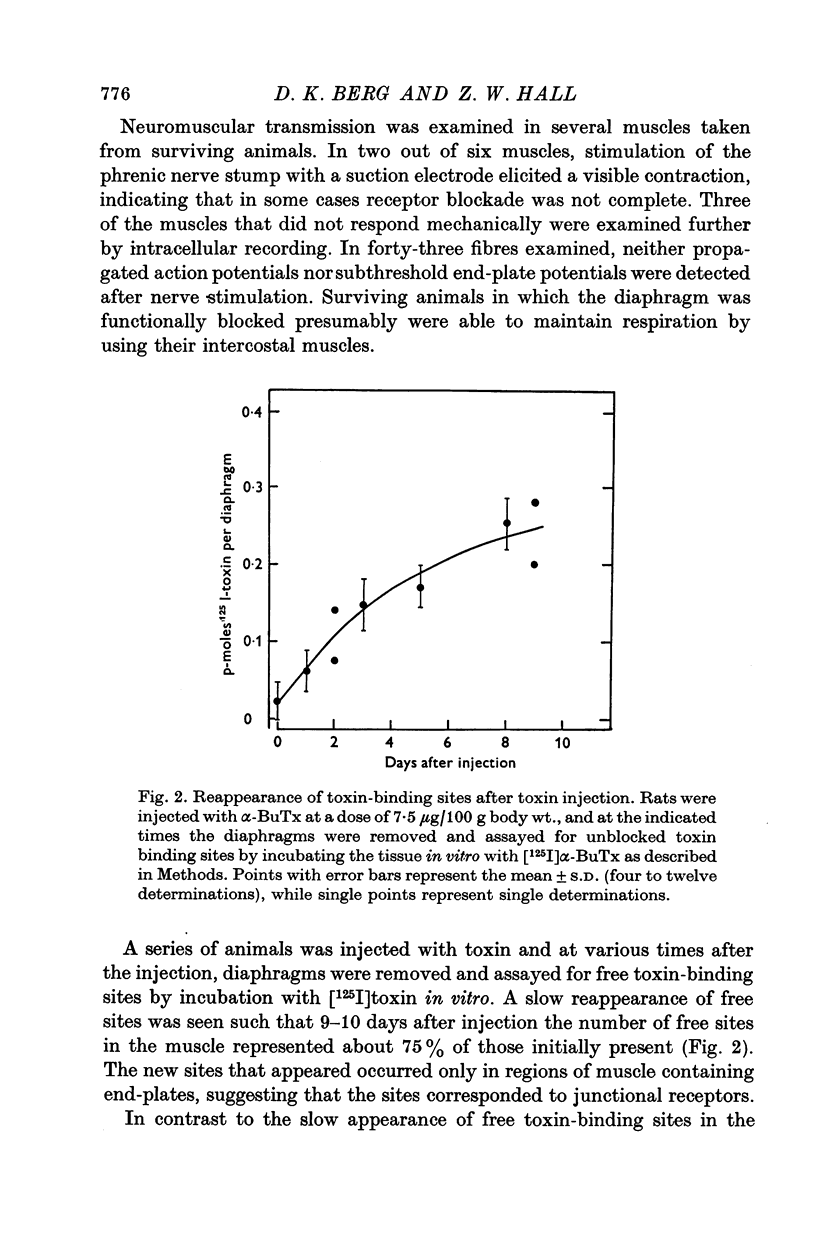
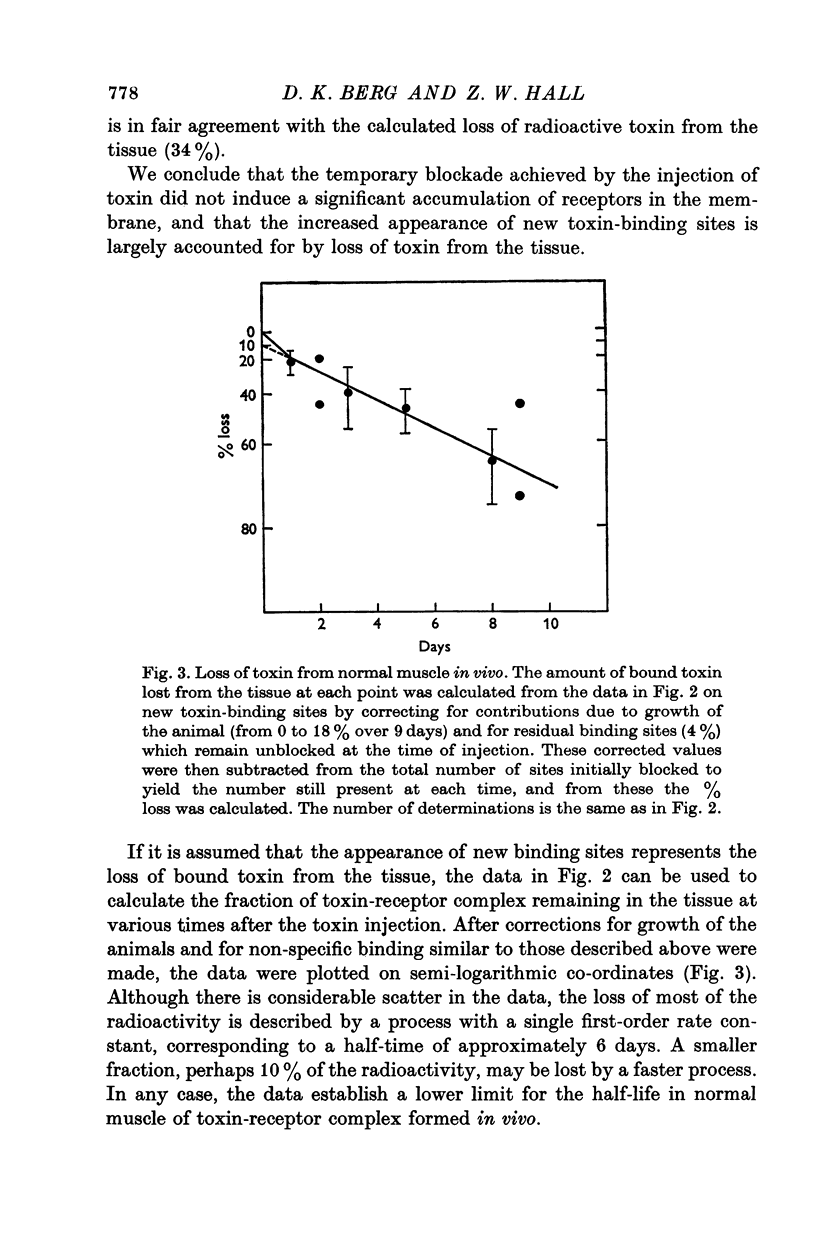
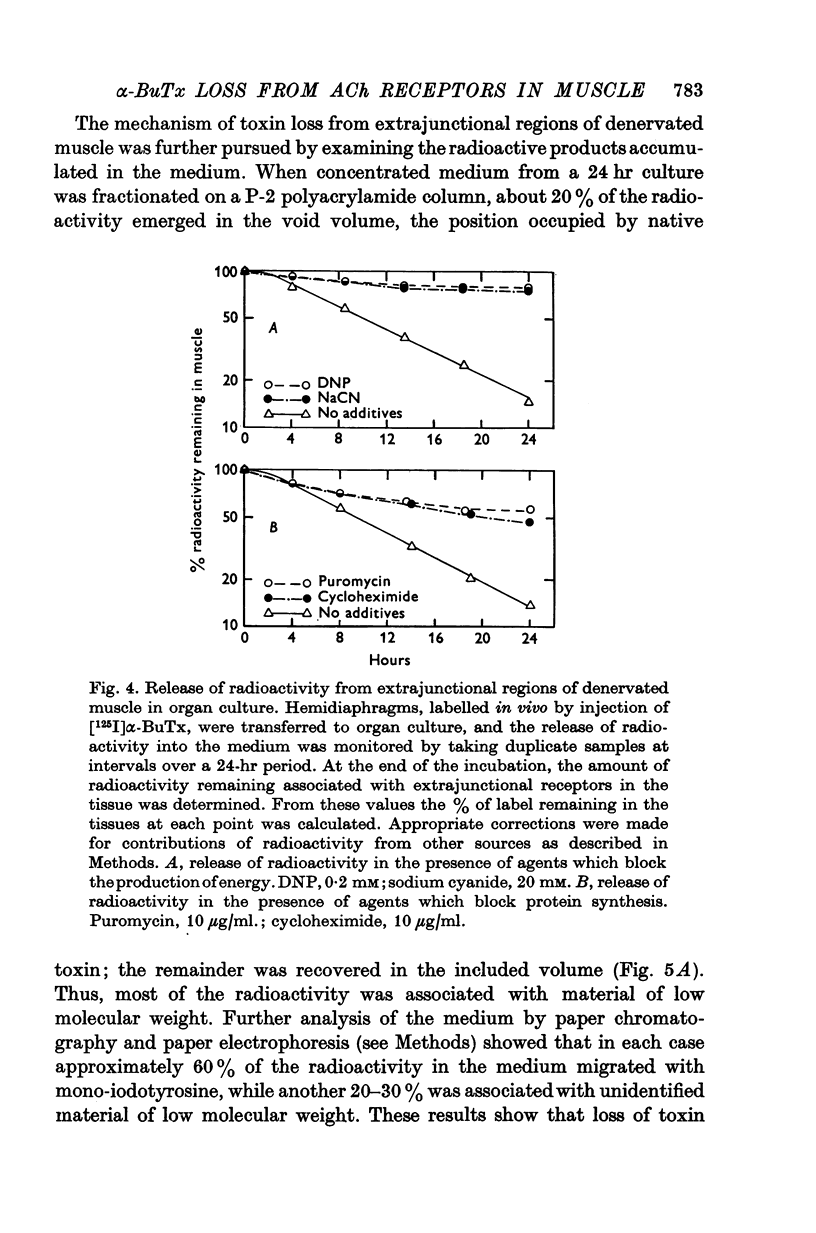
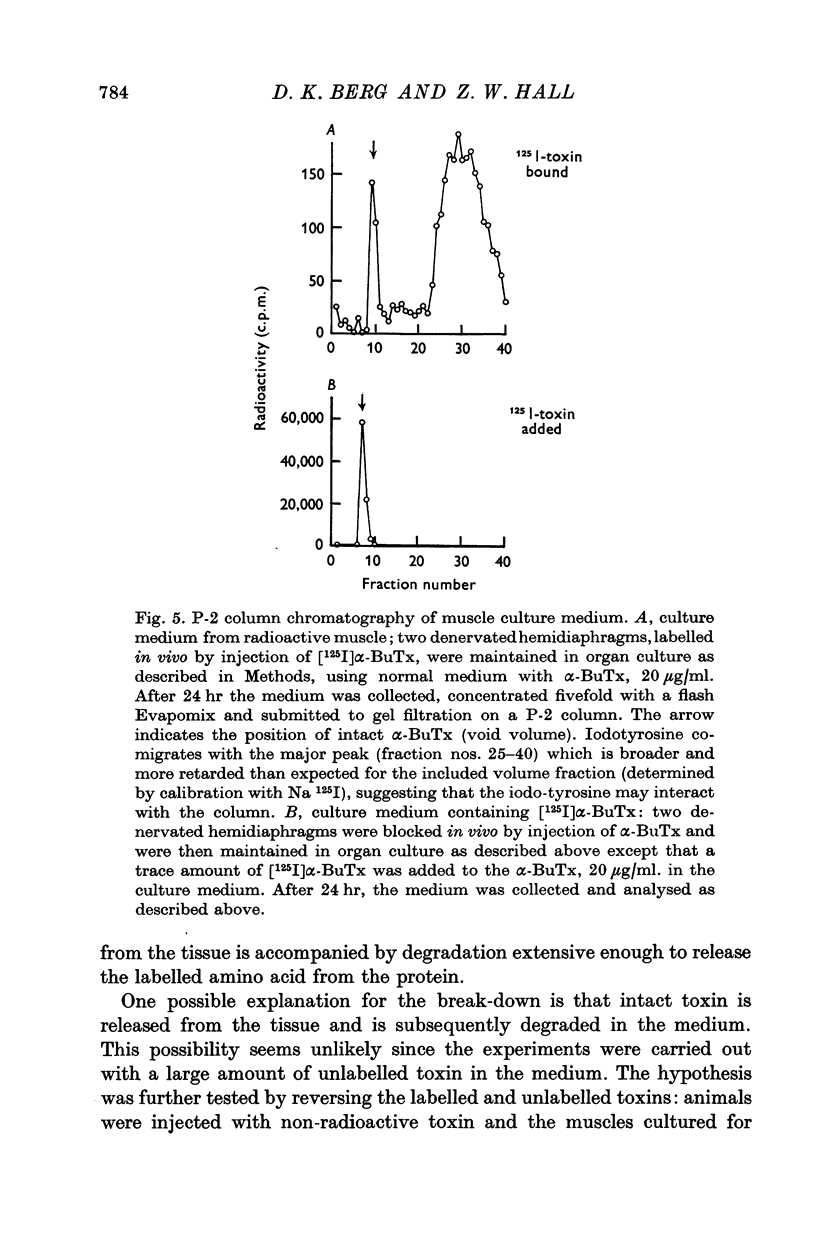
Acetylcholine (ACh) receptors in rat diaphragm muscle were blocked by intrathoracic injection of alpha-bungarotoxin (alpha-BuTx) or [125I]alpha-bungarotoxin ([125I]alpha-BuTx). The stability in vivo of the toxin-receptor complex formed by receptors in normal muscles and receptors in extrajunctional regions of denervated muscles was compared. Toxin was lost from junctional regions of normal muscles with a half-time of approximately 6 days. The loss of toxin was accompanied by a corresponding increase in the number of free toxin-binding sites. In contrast, 65% of the toxin bound to extrajunctional regions of denervated muscle was lost in 24 hr. 2. In a second series of experiments, animals were injected with [125I]alpha-BuTx and the muscle subsequently cultured for 24 hr. Loss of toxin again occurred more rapidly from extrajunctional receptors than from junctional receptors. The loss from extrajunctional receptors was described by a single first-order rate constant whose corresponding half-time was 8-11 hr. Loss was almost completely blocked by sodium cyanide and dinitrophenol and was inhibited by puromycin and cycloheximide. The radioactivity recovered in the medium was largely monoiodotyrosine. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that toxin loss reflects intracellular degradation of toxin-receptor complex. 3. Neonatal rats were injected with [125I]alpha-BuTx and the diaphragms cultured. Radioactive toxin was lost rapidly from extrajunctional regions of muscle and more slowly from regions containing end-plates. 4. These results could be explained by a difference in turnover rates for junctional and extrajunctional receptors.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. A study of supersensitivity in denervated mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 23;147(1):178–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Wieckowski J., Chiu T. H. Cholinergic receptor molecules and cholinesterase molecules at mouse skeletal muscle junctions. Nature. 1971 Nov 26;234(5326):207–209. doi: 10.1038/234207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Hall Z. W. Fate of alpha-bungarotoxin bound to acetylcholine receptors of normal and denervated muscle. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):473–475. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Hall Z. W. Increased extrajunctional acetylcholine sensitivity produced by chronic acetylcholine sensitivity produced by chronic post-synaptic neuromuscular blockade. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(3):659–676. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Kelly R. B., Sargent P. B., Williamson P., Hall Z. W. Binding of -bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors in mammalian muscle (snake venom-denervated muscle-neonatal muscle-rat diaphragm-SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Hall Z. W. Acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated rat diaphragm muscle. I. Purification and interaction with [125I]-alpha-bungarotoxin. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2092–2099. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Hall Z. W. Acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated rat diaphragm muscle. II. Comparison of junctional and extrajunctional receptors. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2100–2106. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Hall Z. W. Synthesis of acetylcholine receptor by denervated rat diaphragm muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1368–1372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Huang M. C. Turnover of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors of the rat diaphragm. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):643–644. doi: 10.1038/253643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND J., MILEDI R. A study of foetal and new-born rat muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:393–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptor turnover in membranes of developing muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1975 May;65(2):335–358. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB C. O., KRNJEVIC K., SILVER A. ACETYLCHOLINE AND CHOLINE ACETYLTRANSFERASE IN THE DIAPHRAGM OF THE RAT. J Physiol. 1964 Jun;171:504–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptors. Distribution and extrajunctional density in rat diaphragm after denervation correlated with acetylcholine sensitivity. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Sep;60(3):248–262. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Tseng L. F., Chiu T. H. Influence of denervation on localization of neurotoxins from clapid venoms in rat diaphragm. Nature. 1967 Sep 9;215(5106):1177–1178. doi: 10.1038/2151177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Rosenthal J. Control of ACh sensitivity by muscle activity in the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):493–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


