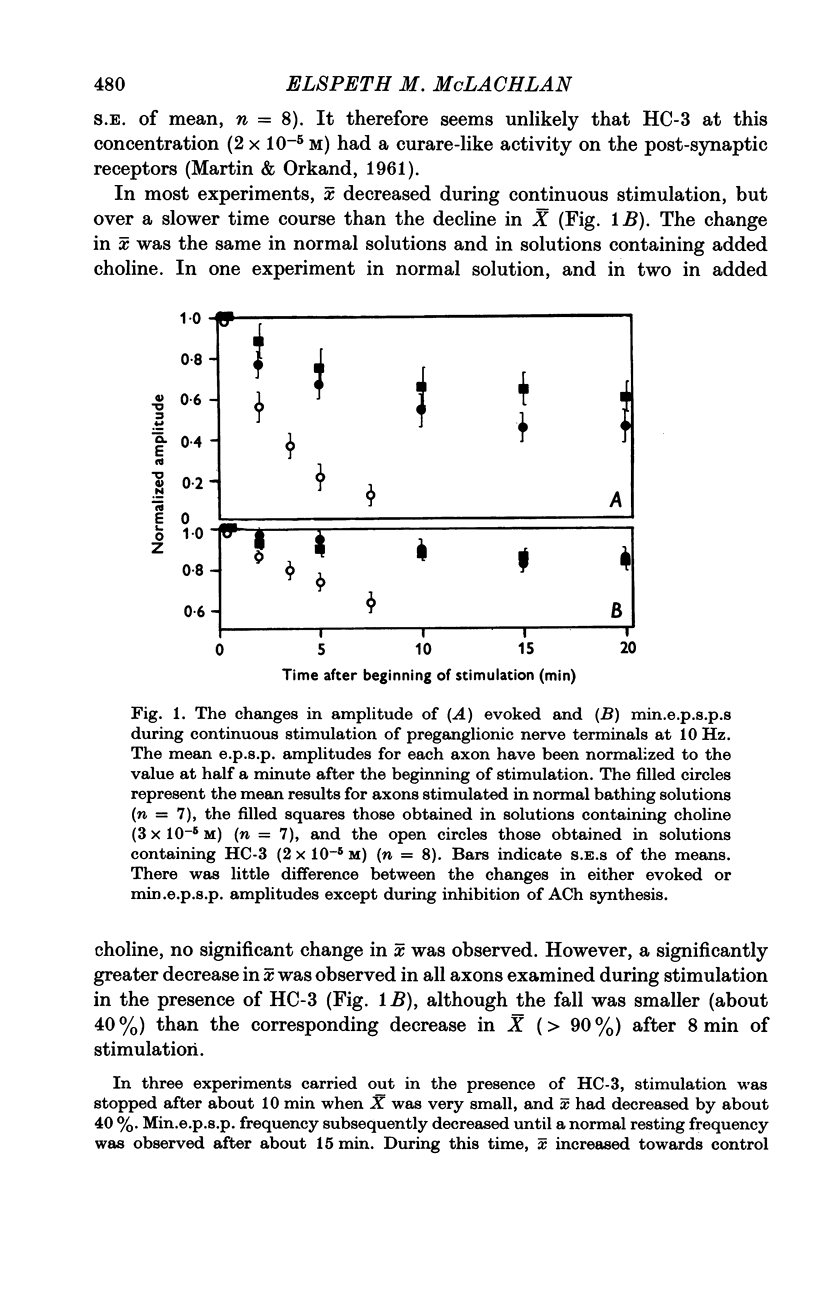
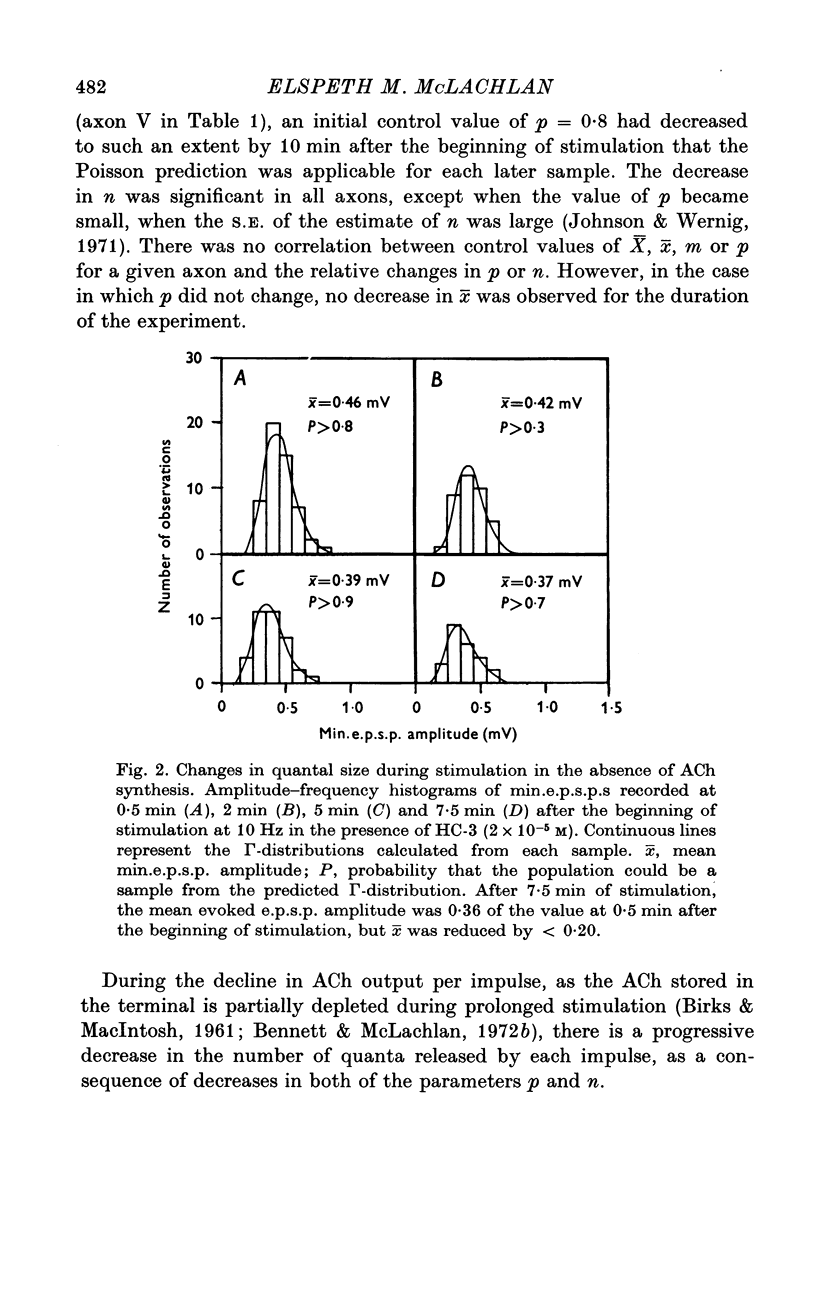
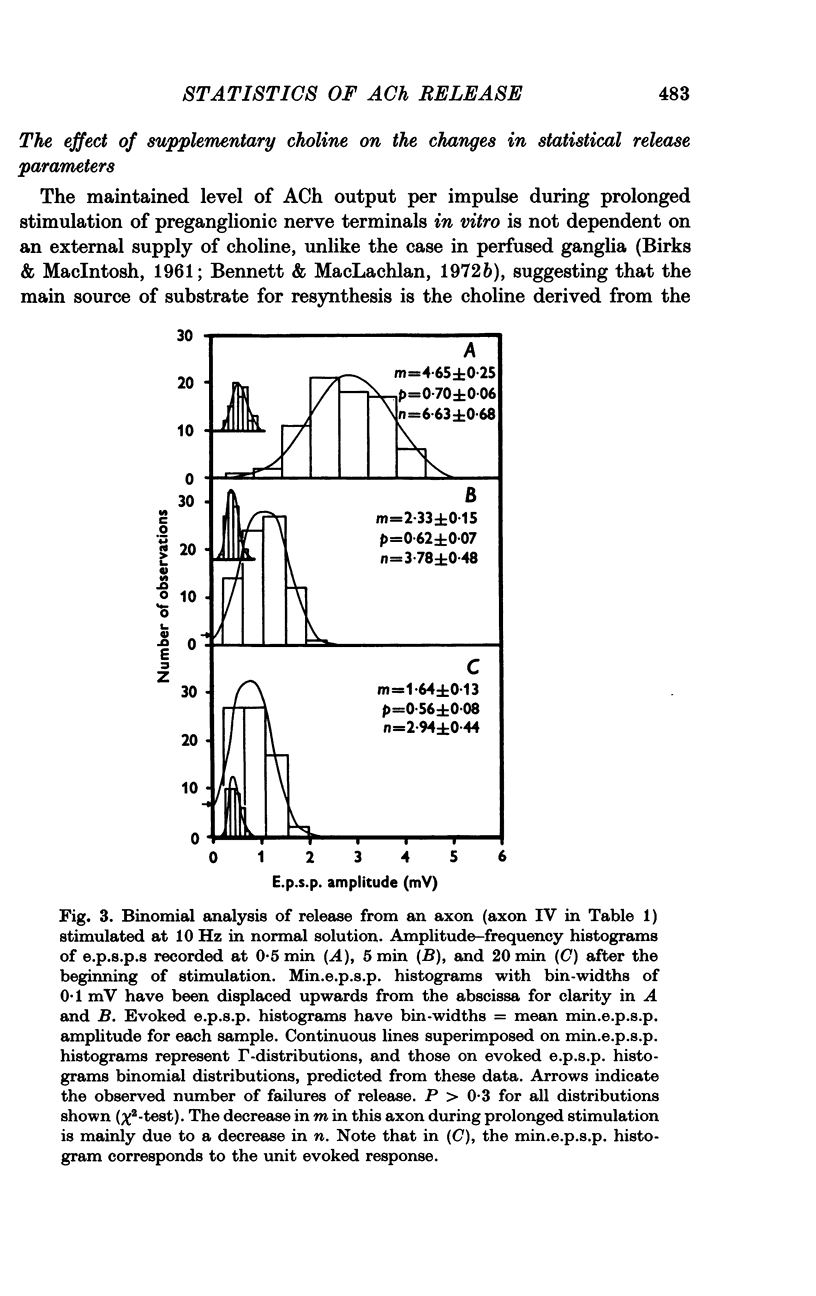
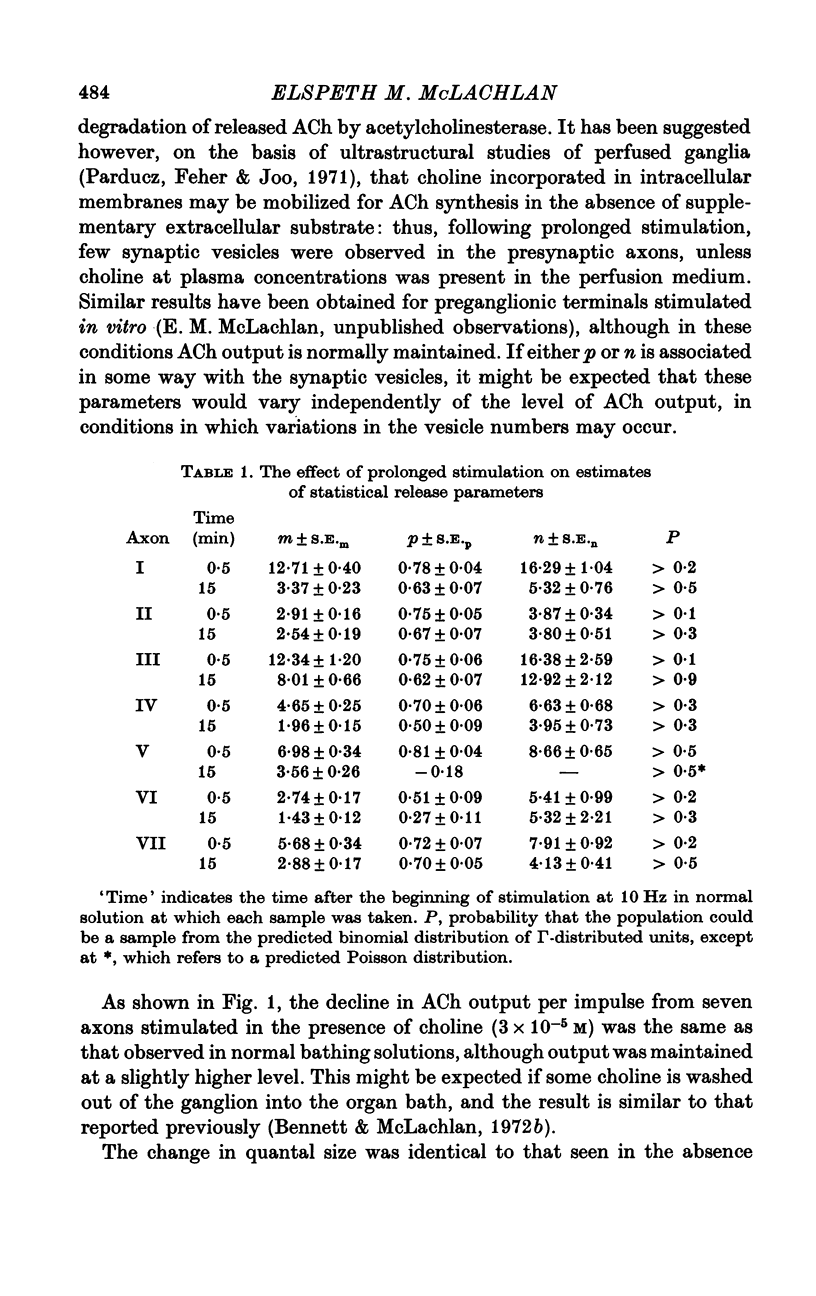
Abstract
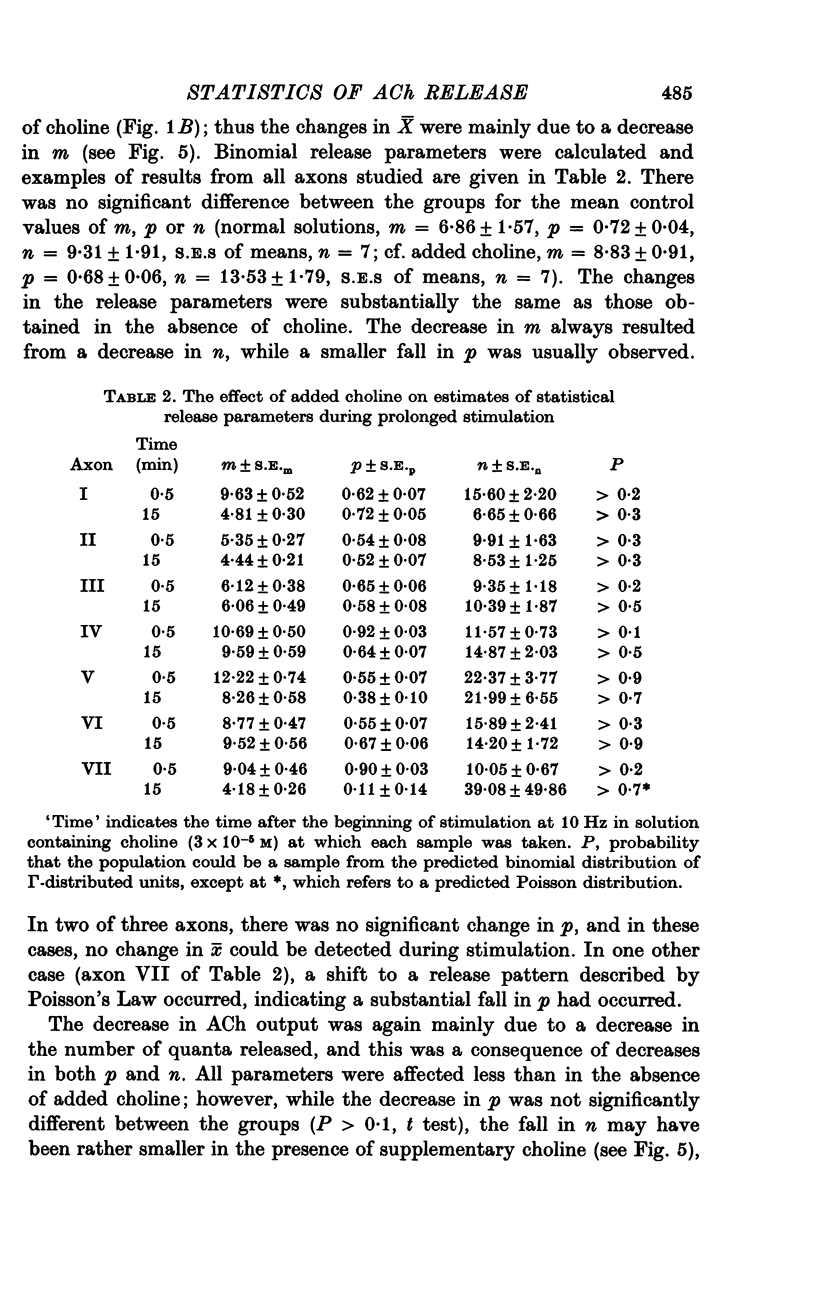
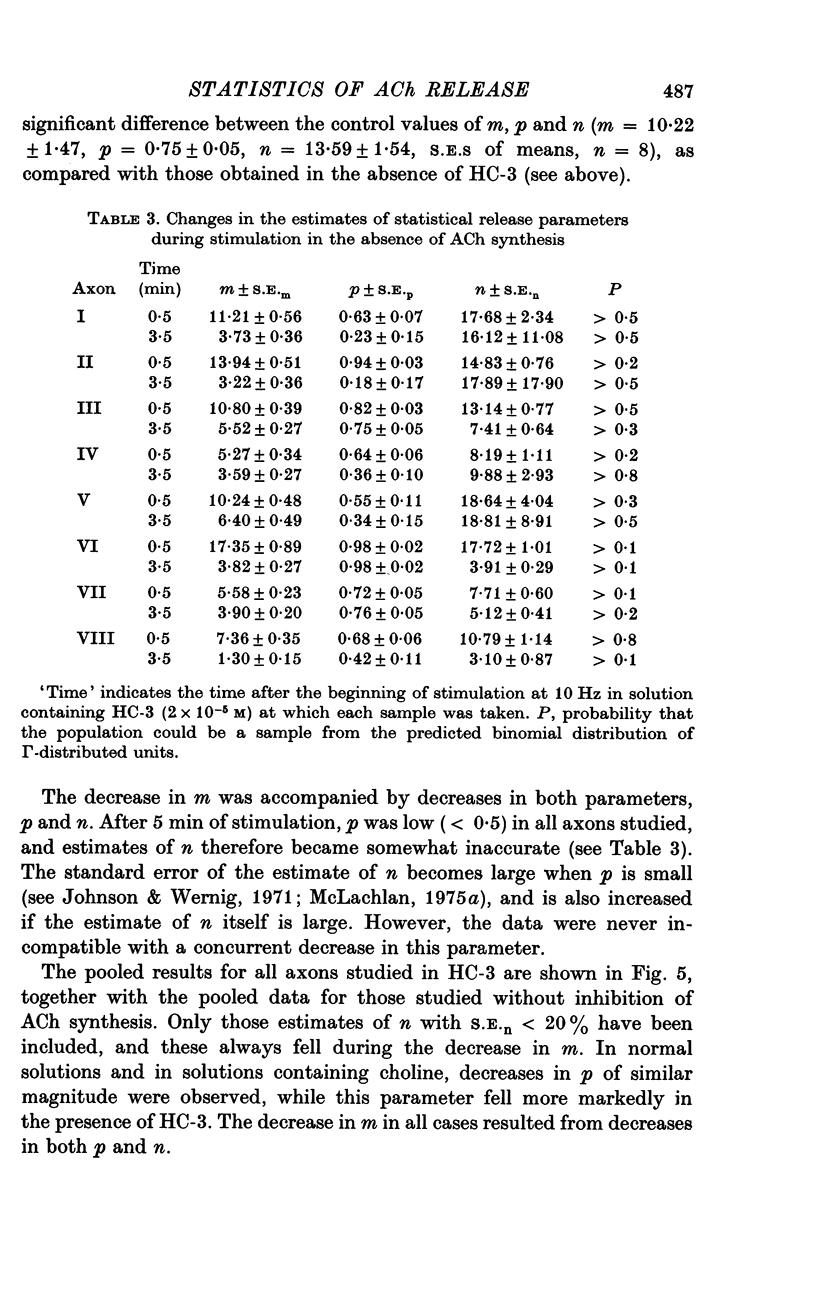
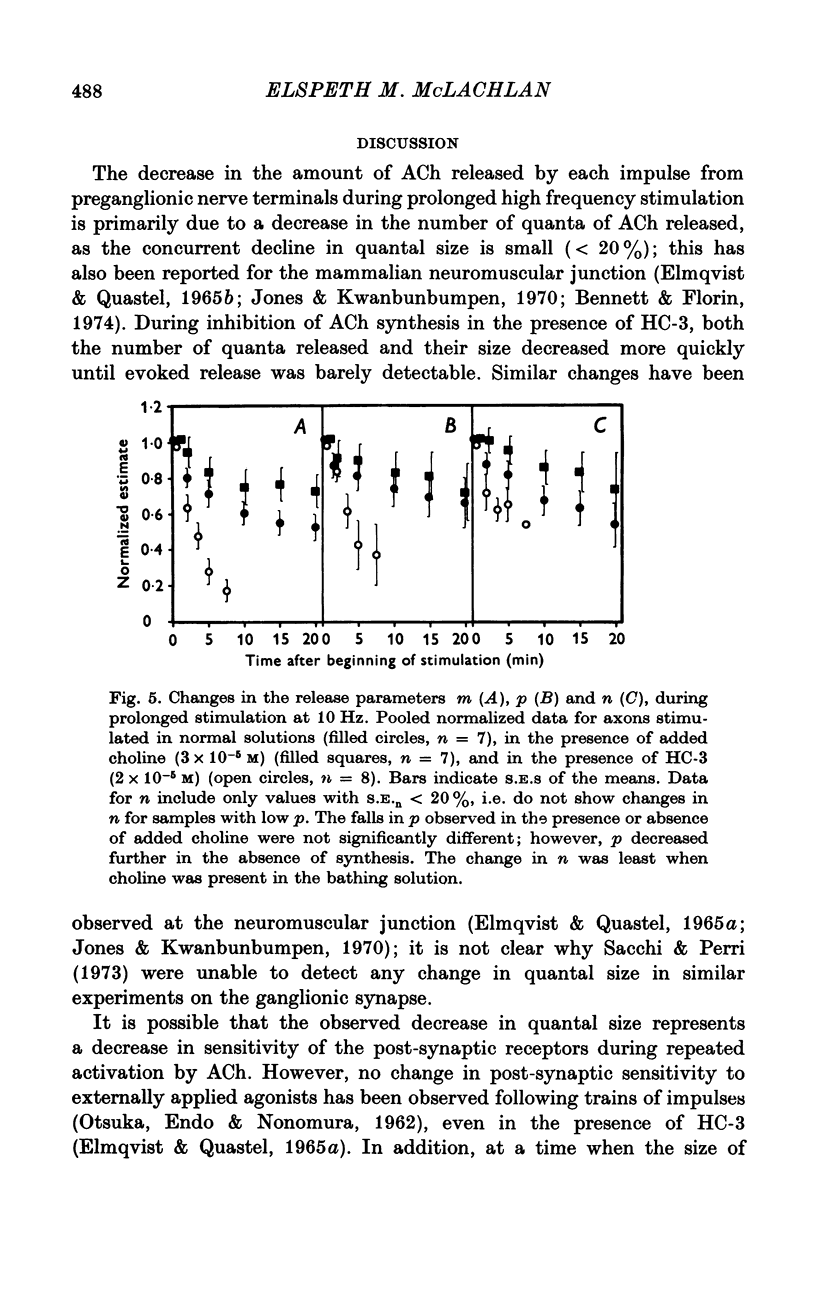
1. An analysis has been made of the release of acetylcholine (ACh) from the preganglionic nerve terminals of the isolated superior cervical ganglion of the guinea-pig during prolonged repetitive stimulation (10 Hz), using the amplitude of the excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.) as a measure of the amount of ACh released. 2. The decline in the mean amount of ACh released by each impulse over 20 min of continuous stimulation was accompanied by a small decrease in the mean miniature (min.) e.p.s.p. amplitude (less than 20%), both in the presence and absence of supplementary choline (3 x 10(-5) M). During stimulation in the presence of hemicholinium-3 (HC-3) (2 x 10(-5) M), the fall in min.e.p.s.p. amplitude was significantly larger. 3. Amplitude-frequency histograms of e.p.s.p.s evoked at different times after the beginning of stimulation were usually well predicted by binomial statistics, using the min.e.p.s.p.s released during each sample period as a measure of the quantal unit. In the other cases, histograms could be predicted using Poisson's Law. 4. A decline in quantal content, m, occurred in all experiments. In the presence of synthesis, with or without added choline, this was always associated with a decrease in the binomial parameter, n, and, in many cases, with a decrease in the binomial parameter, p. During stimulation in the presence of HC-3, a larger fall in p was observed in all experiments. 5. The results suggest that depletion of the ACh stored in the terminal decreases both the size and number of quanta available for release, and that the decrease in the amount of ACh in each quantum reduces the probability of its release.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIRKS R. I., MACINTOSH F. C., SASTRY P. B. Pharmacological inhibition of acetylcholine synthesis. Nature. 1956 Nov 24;178(4543):1181–1181. doi: 10.1038/1781181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T. A statistical analysis of the release of acetylcholine at newly formed synapses in striated muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):93–107. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M. An electrophysiological analysis of the storage of acetylcholine in preganglionic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):657–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M. An electrophysiological analysis of the synthesis of acetylcholine in preganglionic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):669–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman J. G., Purves R. D. Intracellular recordings from ganglia of the thoracic sympathetic chain of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):173–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P., Mauro A. Depletion of vesicles from frog neuromuscular junctions by prolonged tetanic stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jul;54(1):30–38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMQVIST D., QUASTEL D. M. PRESYNAPTIC ACTION OF HEMICHOLINIUM AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. J Physiol. 1965 Apr;177:463–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Quastel D. M. A quantitative study of end-plate potentials in isolated human muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Jun;178(3):505–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier D. T. Effect of hemicholinium no. 3 on amphibian nerve. Exp Neurol. 1968 Feb;20(2):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. W., Wernig A. The binomial nature of transmitter release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):757–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. F., Kwanbunbumpen S. Some effects of nerve stimulation andhemicholinium on quantal transmitter release at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):51–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACINTOSH F. C. Formation, storage, and release of acetylcholine at nerve endings. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Feb;37(2):343–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., ORKAND R. K. Postsynaptic effects of HC-3 at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Feb;39:343–349. doi: 10.1139/o61-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan E. M. An analysis of the release of acetylcholine from preganglionic nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):447–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKA M., ENDO M., NONOMURA Y. Presynaptic nature of neuromuscular depression. Jpn J Physiol. 1962 Dec 15;12:573–584. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.12.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Párducz A., Fehér O., Joó F. Effects of stimulation and hemicholinium (HC-3) on the fine structure of nerve endings in the superior cervical ganglion of the cat. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90351-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. A new kind of drug antagonism: evidence that agonists cause a molecular change in acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;5(4):394–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi O., Perri V. Quantal mechanism of transmitter release during progressive depletion of the presynaptic stores at a ganglionic synapse. The action of hemicholinium-3 and thiamine deprivation. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):342–360. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silinsky E. M. On the association between transmitter secretion and the release of adenine nucleotides from mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):145–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. Changes in statistical parameters during facilitation at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):751–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. Estimates of statistical release parameters from crayfish and frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):207–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. The effects of calcium and magnesium on statistical release parameters at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):761–768. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Changes in the statistics of transmitter release during facilitation. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):787–810. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


