Abstract
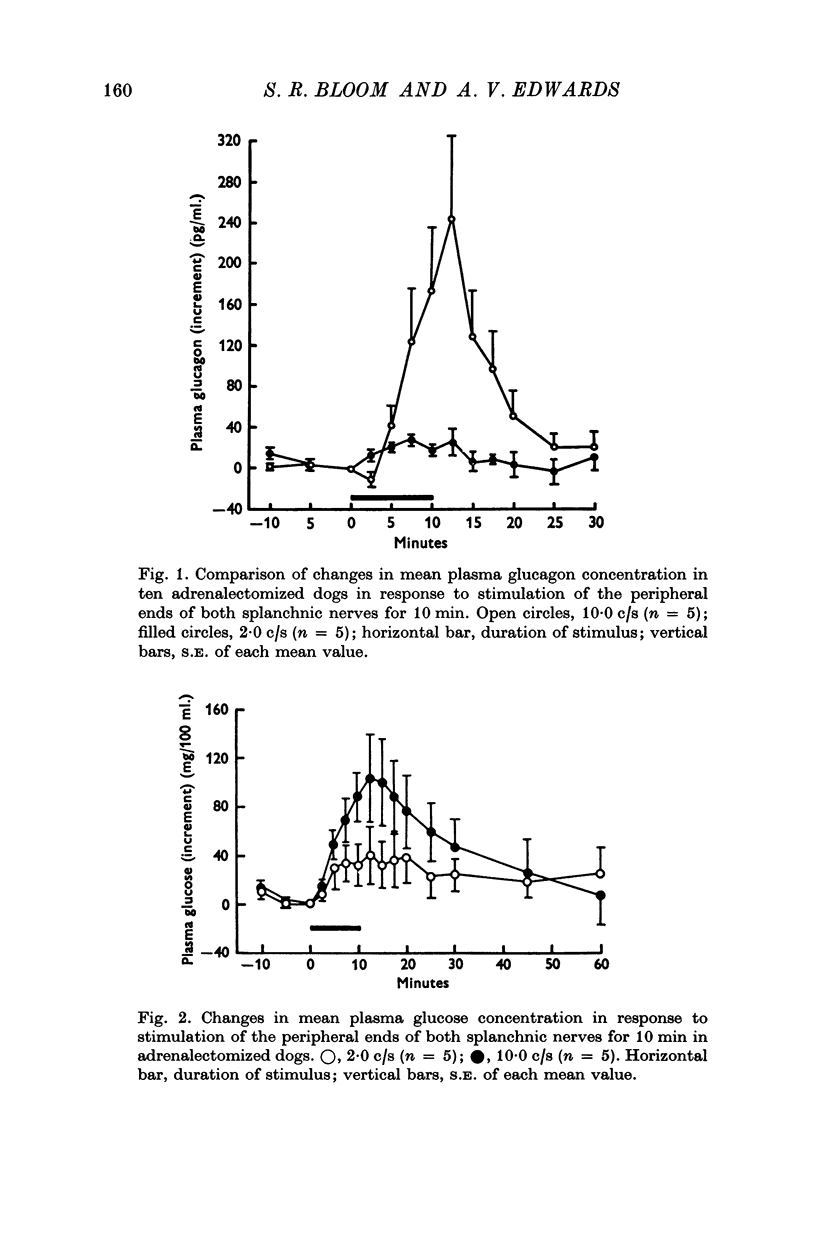
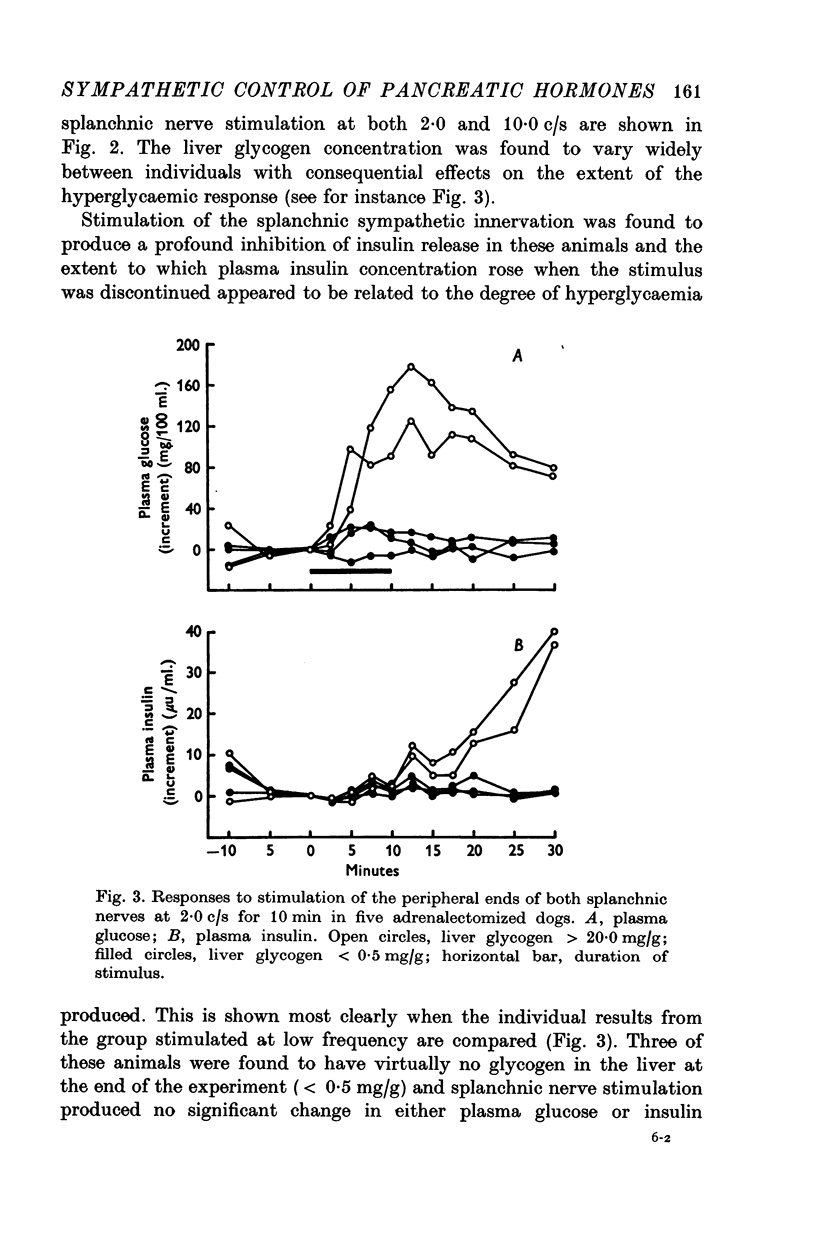
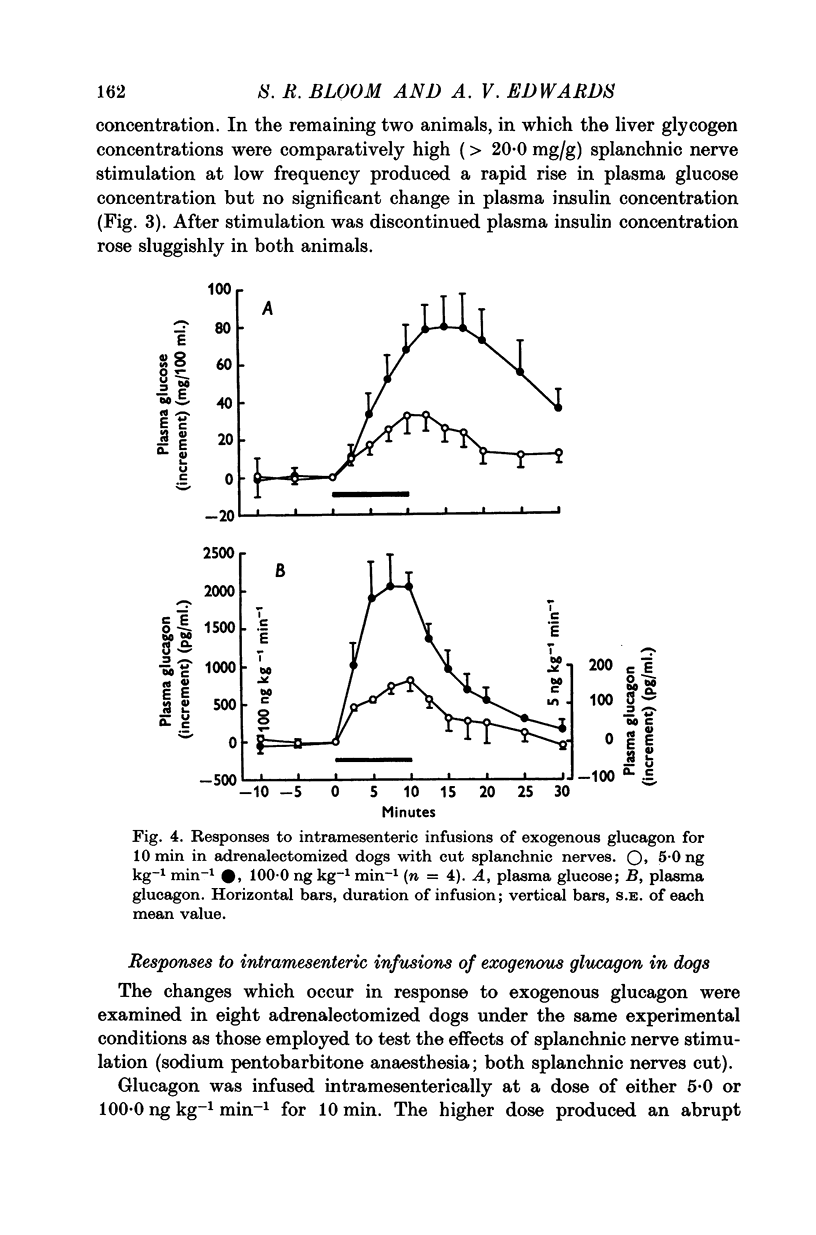
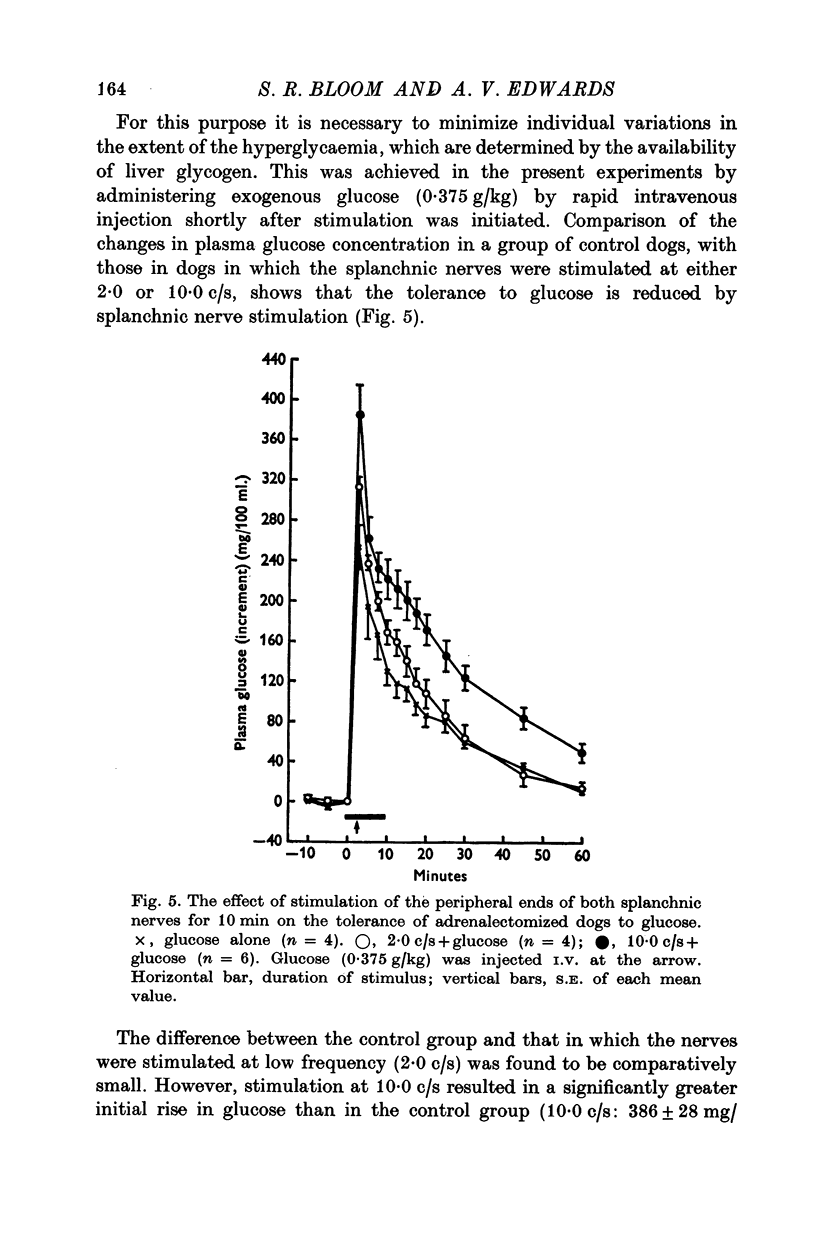
The changes in the concentration of glucagon and insulin in arterial plasma which occur in response to splanchnic nerve stimulation have been investigated in adrenalectomized dogs, cats and sheep. 2. In dogs, stimulation of both splanchnic nerves at a low frequency (2-0 c/s) for 10 min produced a small but statistically significant increase in plasma glucagon concentration and appeared to inhibit the release of insulin. Stimulation at a higher frequency (10-0 c/s) produced a much greater increase in plasma glucagon concentration, which was normally accompanied by a rise in plasma glucose concentration. 3. Qualitatively similar changes in plasma glucagon and insulin concentration were observed in both sheep and cats in response to adrenergic stimulation. 4. Intramesenteric infusions of glucagon at a dose of 5-0 ng kg-1 min-1 in dogs produced a comparable rise in plasma glucagon concentration to that elicited by splanchnic nerve stimulation at high frequency (10-0 c/s) and invariably caused a rise in plasma glucose concentration. 5. In dogs given exogenous glucose, release of glucagon in response to splanchnic nerve stimulation was unaffected by induced hyperglycaemia. Secretion of insulin was partially inhibited by stimulation at 2-0 c/s and completely suppressed at higher frequency (10-0c/s). 6. It is concluded that stimulation of the sympathetic innervation to the pancreatic islets, at frequencies within thephysiological range, stimulates the release of glucagon and inhibits that of insulin in each of these species.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alric R., Loubatières-Mariani M. M., Loubatières A. L., Puech R. Récepteurs cholinergiques et sécrétion de glucagon. Etude sur le pancréas isolé et perfusé du rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1972;166(8):1030–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Daniel P. M., Johnston D. I., Ogawa O., Pratt O. E. Release of glucagon, induced by stress. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1973 Jan;58(1):99–108. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1973.sp002195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K. W., Silver M. Endocrine responses to insulin hypoglycaemia in the young calf. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(3):783–803. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K. W., Silver M. Responses to feeding in the conscious unweaned calf. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):34P–35P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Vaughan N. J. The role of the autonomic innervation in the control of glucagon release during hypoglycaemia in the calf. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):611–623. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Vaughan N. J. The role of the sympathetic innervation in the control of plasma glucagon concentration in the calf. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(2):457–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V. The glycogenolytic response to stimulation of the splanchnic nerves in adrenalectomized calves, sheep, dogs, cats and pigs. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):741–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V. The hyperglycaemic response to stimulation of the hepatic sympathetic innervation in adrenalectomized cats and dogs. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;220(3):697–710. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V. The sensitivity of the hepatic glycogenolytic mechanism ot stimulation of the splanchnic nerves. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(2):315–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterhuizen A. C., Howell S. L. Ultrastructure of the A-cells of cat islets of Langerhans following sympathetic stimulation of glucagon secretion. J Cell Biol. 1970 Sep;46(3):593–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. A., Gill J. R., Lever J. D., Randle P. J., Spriggs T. L. Increased insulin output following stimulation of the vagal supply to the perfused rabbit pancreas. J Anat. 1969 May;104(Pt 3):580–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen J. Effect of acetyl choline on the secretion of glucagon and insulin from the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. Diabetes. 1973 May;22(5):381–387. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.5.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järhult J., Hillman J., Mellander S. Circulatory effects evoded by 'physiological' increases of arterial osmolality. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Jan;93(1):129–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järhult J. Role of the symphato-adrenal system in hemorrhagic hyperglycemia. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Jan;93(1):25–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kosaka K. Stimulation of glucagon and insulin secretion by acetylcholine infused intrapancreatically. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):676–681. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Girardier L., Seydoux J., Kanazawa Y., Posternak J. Neural regulation of insulin secretion in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):210–214. doi: 10.1172/JCI107168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Porte D., Jr Neural control of the endocrine pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jul;54(3):596–619. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


