Abstract
1. Micro-electrodes were used to examine transmission from intrinsic and extrinsic nerves to single cells of the longitudinal and circular muscle coats of colons from guinea-pigs and rabbits.
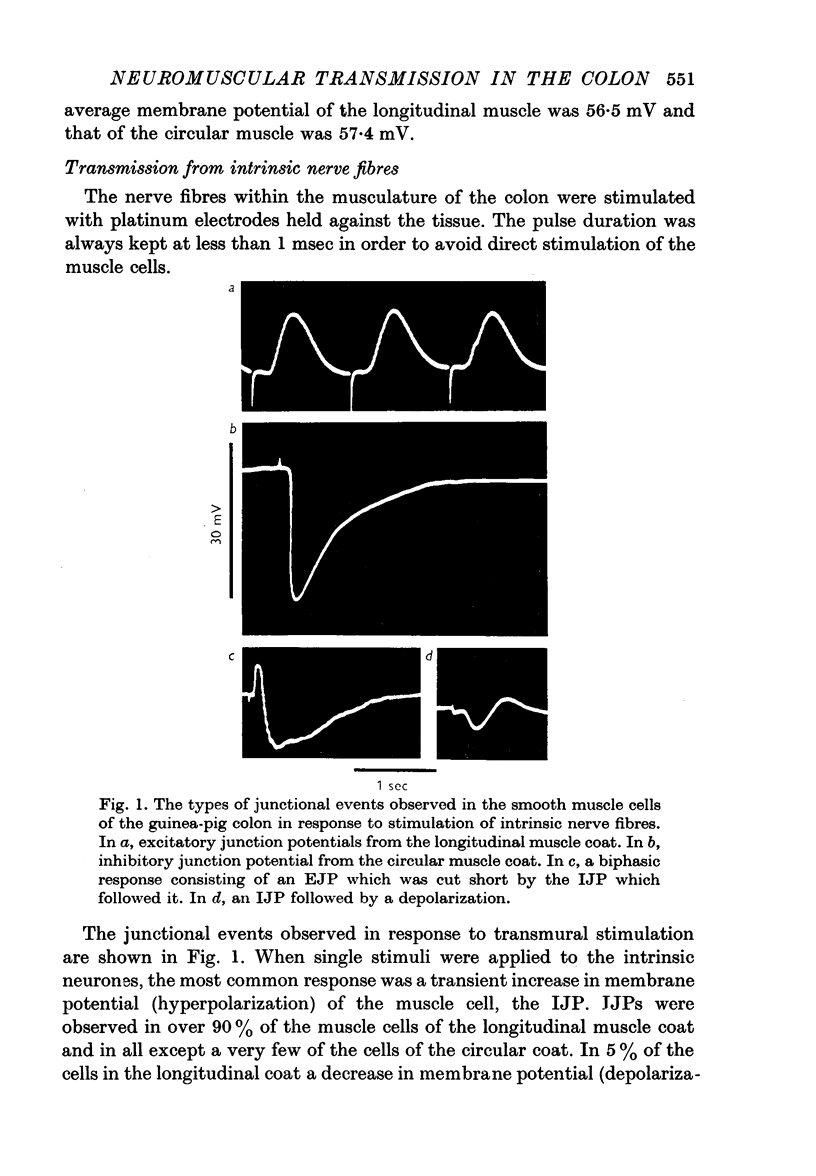
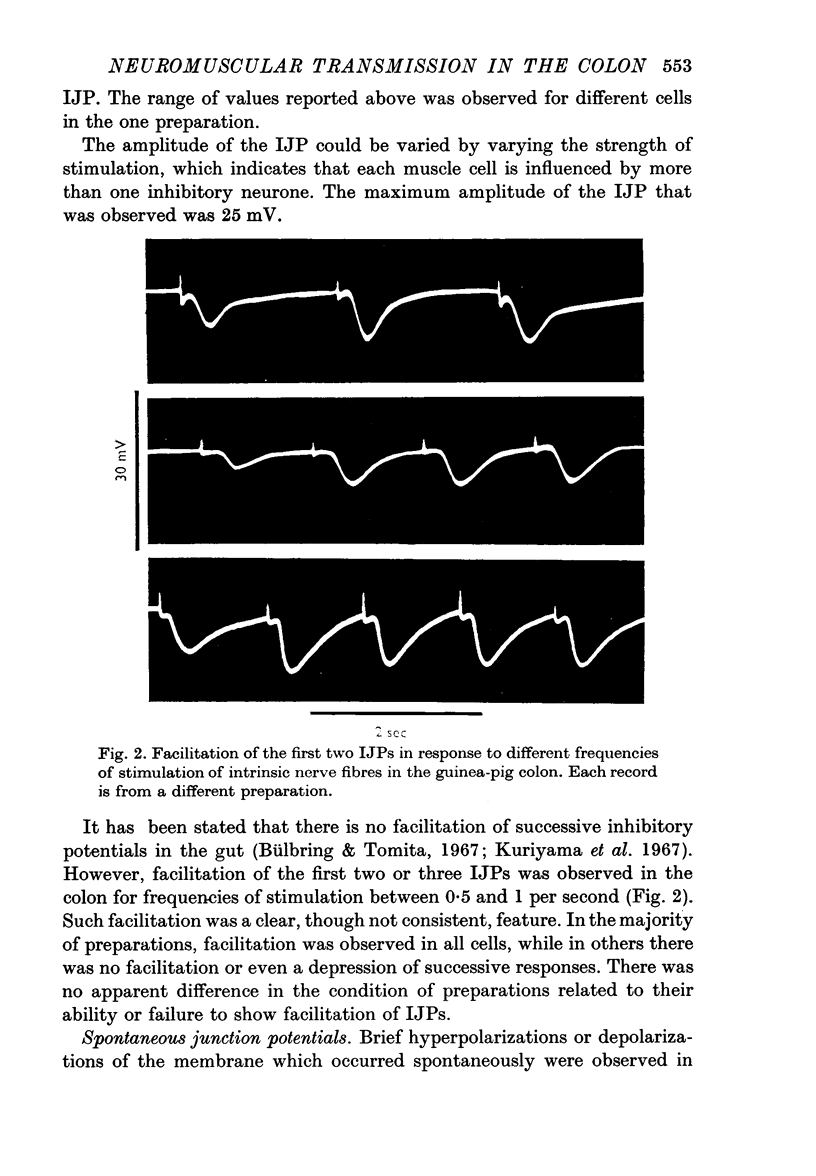
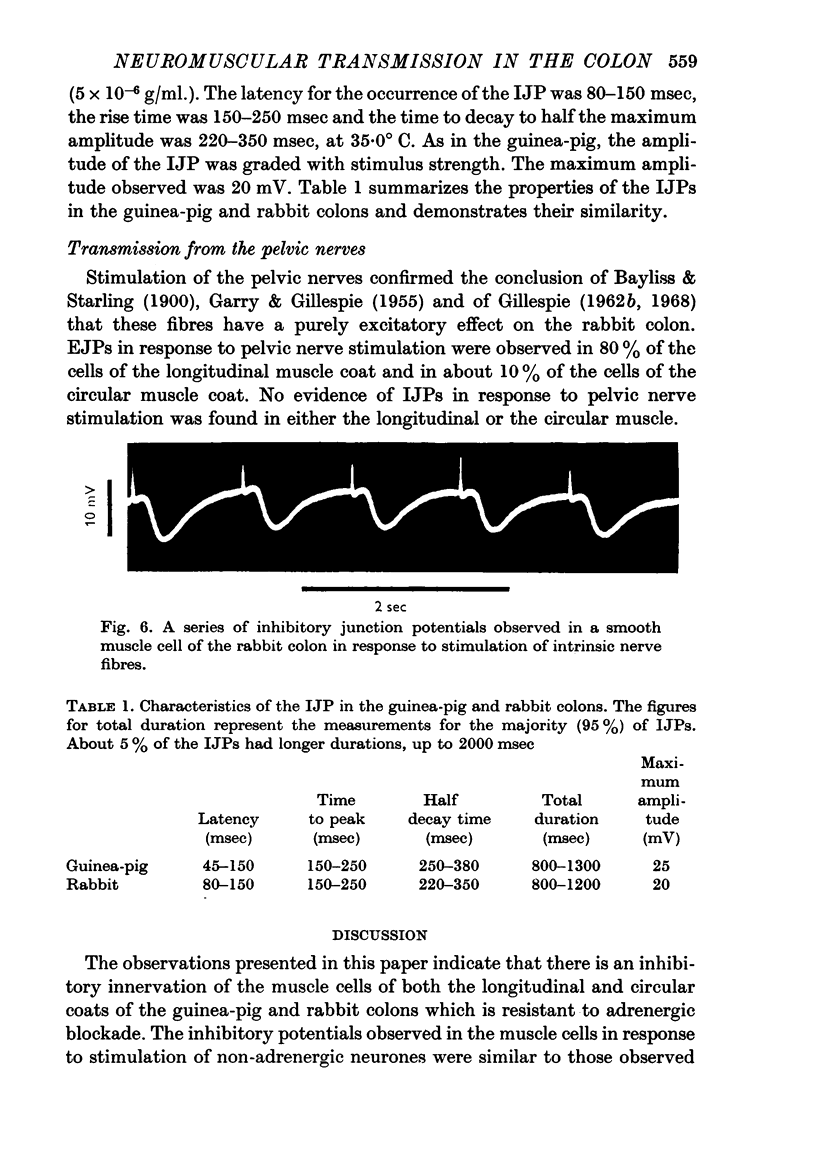
2. When intrinsic nerves were stimulated, inhibitory junction potentials (IJPs) were observed in over 90% of the cells of the longitudinal coat and nearly all of the cells of the circular coat. The characteristics of IJPs in the guinea-pig and rabbit were similar. Facilitation of two or three successive IJP's was sometimes observed. The IJPs were unaffected by guanethedine but were blocked by procaine. IJPs could not be elicited by stimulation of either the pelvic parasympathetic or periarterial sympathetic nerves. In some cells, the IJP was preceded by a brief depolarization, which probably results from the stimulation of excitatory nerves to the same cell.
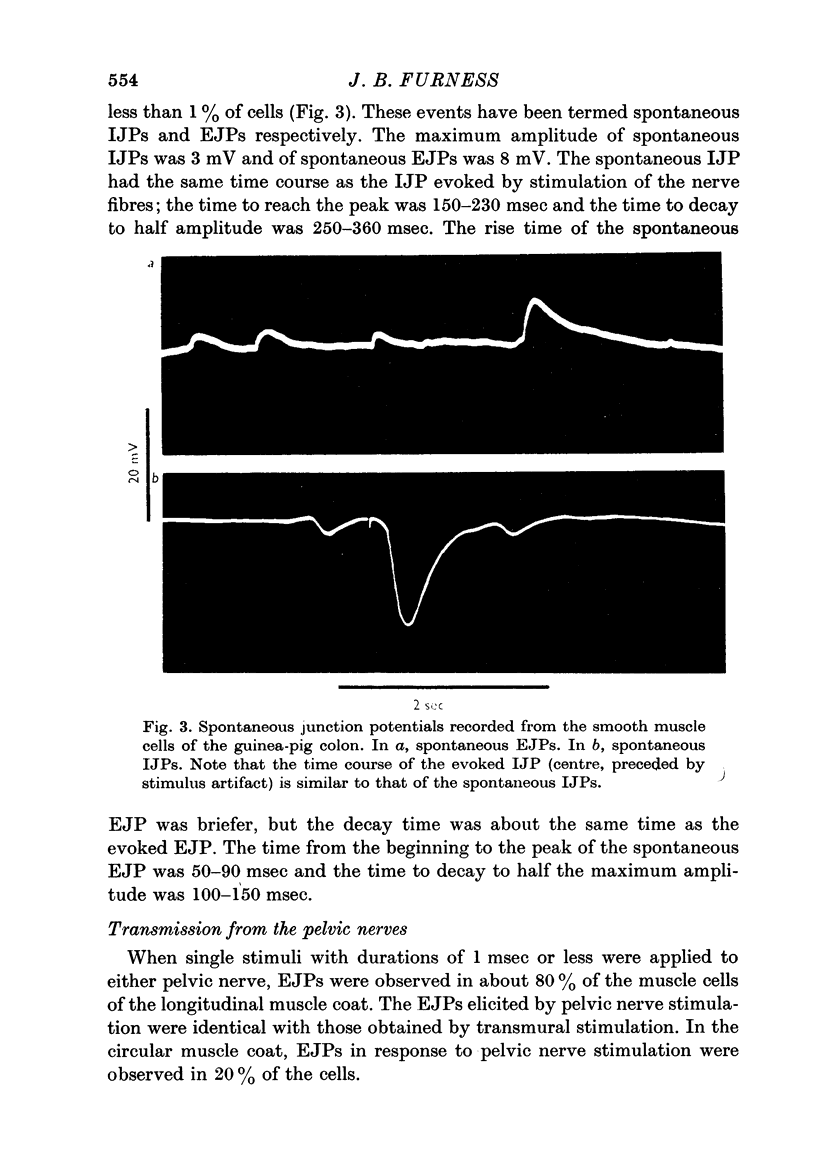
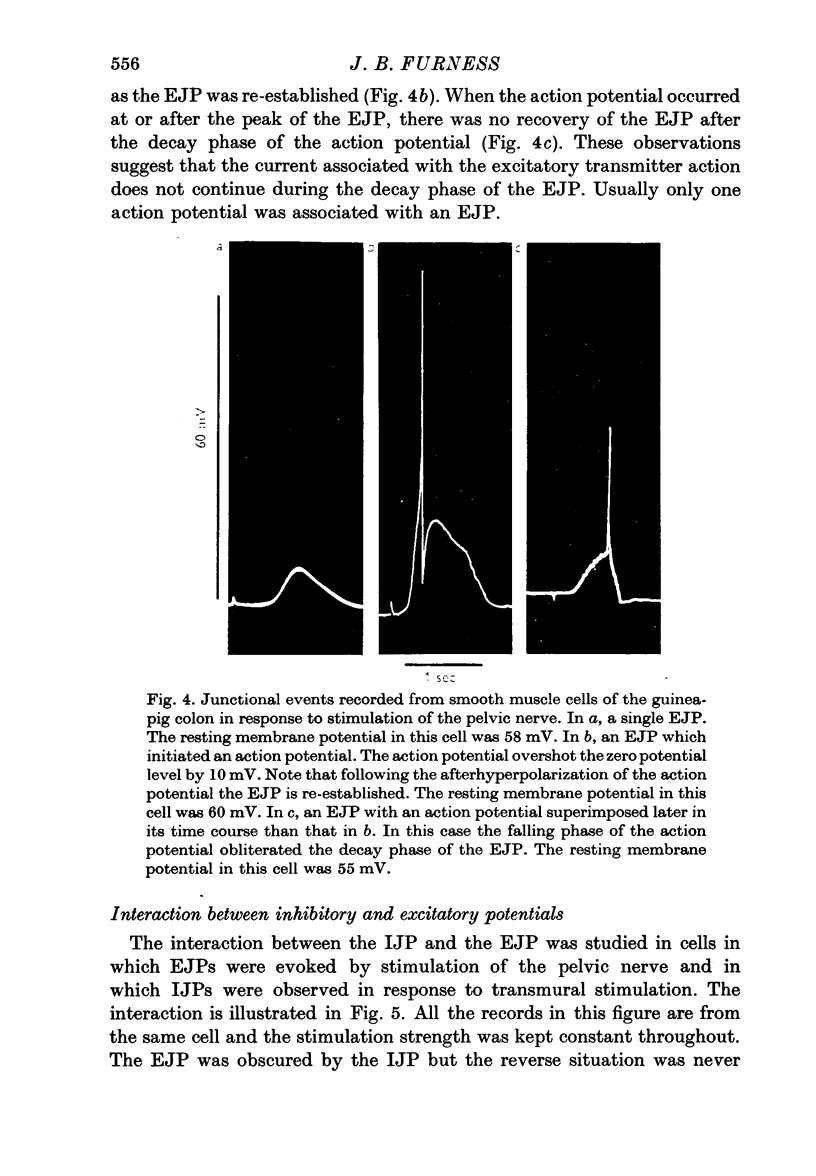
3. Excitatory junction potentials (EJPs) were observed in about 5% of cells of the longitudinal coat in response to stimulation of the intramural nerves. When the pelvic nerves were stimulated, EJPs were observed in most cells of both the longitudinal and circular muscle coats. The EJP in the guinea-pig colon was blocked by hyoscine.
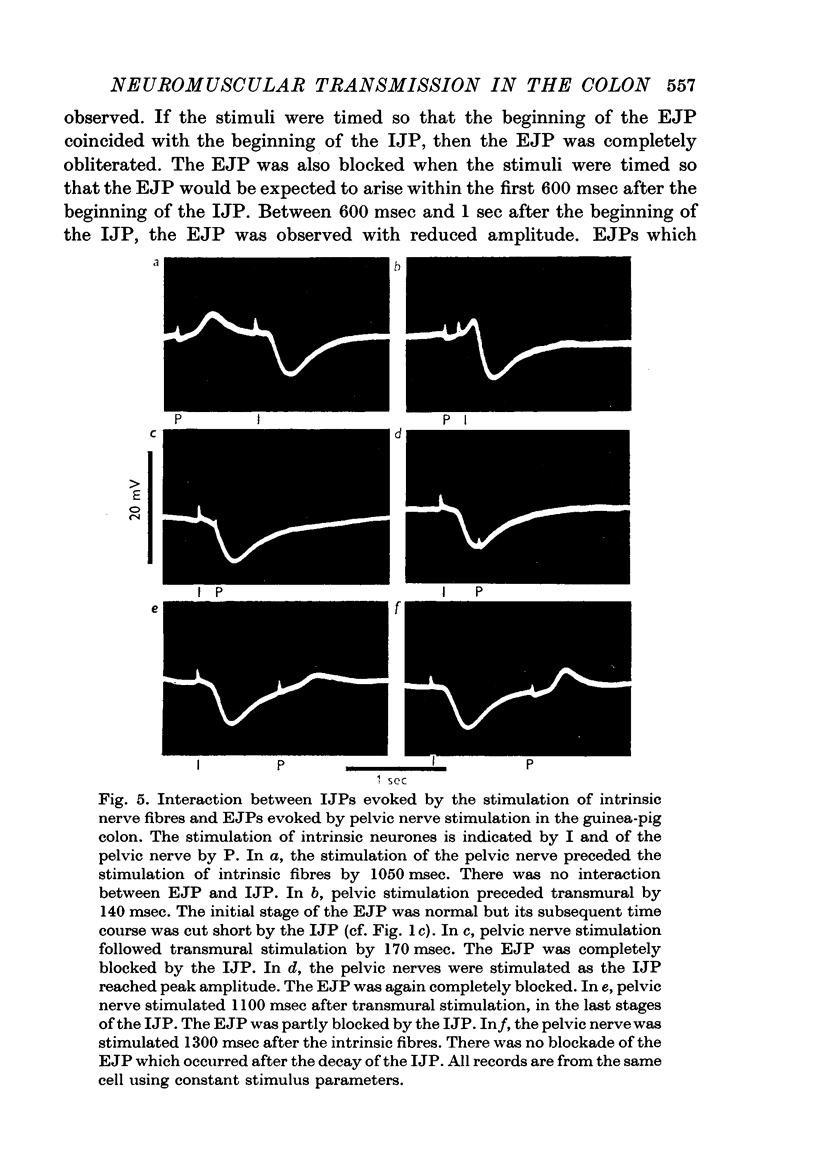
4. The interaction of the IJP evoked by intrinsic nerve stimulation and the EJP evoked by pelvic nerve stimulation was examined. When both nerve supplies were stimulated together, only an IJP was observed.
5. The nature of the innervation of the colon and the origin of intrinsic non-adrenergic inhibitory neurones is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNSTOCK G., CAMPBELL G., BENNETT M., HOLMAN M. E. INHIBITION OF THE SMOOTH MUSCLE ON THE TAENIA COLI. Nature. 1963 Nov 9;200:581–582. doi: 10.1038/200581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNSTOCK G., CAMPBELL G., BENNETT M., HOLMAN M. E. INNERVATION OF THE GUINEA-PIG TAENIA COLI: ARE THERE INTRINSIC INHIBITORY NERVES WHICH ARE DISTINCT FROM SYMPATHETIC NERVES? Int J Neuropharmacol. 1964 May;3:163–166. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(64)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss W. M., Starling E. H. The movements and the innervation of the large intestine. J Physiol. 1900 Dec 31;26(1-2):107–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1900.sp000825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Burnstock G., Holman M. E. Transmission from perivascular inhibitory nerves to the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):527–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Burnstock G., Holman M. Transmission from intramural inhibitory nerves to the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):541–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R. Rebound excitation of the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli after stimulation of intramural inhibitory nerves. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):124–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R. Transmission from intramural excitatory nerves to the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):132–147. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C., Beani L., Frigo G. M., Crema A. Further evidence for the presence of non-adrenergic inhibitory structures in the guinea-pig colon. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Aug;4(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Campbell G., Rand M. J. The inhibitory innervation of the taenia of the guinea-pig caecum. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):504–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Properties of the inhibitory potential of smooth muscle as observed in the response to field stimulation of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):299–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUELGRAFF G., SCHMIDT L. UBER DIE HEMMUNG EINER ATROPINRESISTENTEN, NICHT ADRENERGISCHEN NEUROMUSKULAEREN UBERTRAGUNG DURCH GUANETHIDIN. Med Exp Int J Exp Med. 1963;9:371–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARRY R. C., GILLESPIE J. S. The responses of the musculature of the colon of the rabbit to stimulation, in vitro, of the parasympathetic and of the sympathetic outflows. J Physiol. 1955 Jun 28;128(3):557–576. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE J. S. Spontaneous mechanical and electrical activity of stretched and unstretched intestinal smooth muscle cells and their response to sympathetic-nerve stimulation. J Physiol. 1962 Jun;162:54–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE J. S. The electrical and mechanical responses of intestinal smooth muscle cells to stimulation of their extrinsic parasympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1962 Jun;162:76–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMAN M. E., HUGHES J. R. INHIBITION OF INTESTINAL SMOOTH MUSCLE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Jun;43:277–290. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Osa T., Toida N. Nervous factors influencing the membrane activity of intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):257–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN R. J., NEWEY H., SMYTH D. H. THE EFFECTS OF ADRENALECTOMY AND FASTING ON INTESTINAL FUNCTION IN THE RAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:58–73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D., VANE J. R. Analysis of he responses of the isolated stomach to electrical stimulation and to drugs. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165:10–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND M. J., RIDEHALGH A. ACTIONS OF HEMICHOLINIUM AND TRIETHYLCHOLINE ON RESPONSES OF GUINEA-PIG COLON TO STIMULATION OF AUTONOMIC NERVES. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 Mar;17:144–156. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read J. B., Burnstock G. Adrenergic innervation of the gut musculature in vertebrates. Histochemie. 1969;17(3):263–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00309871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


