Abstract
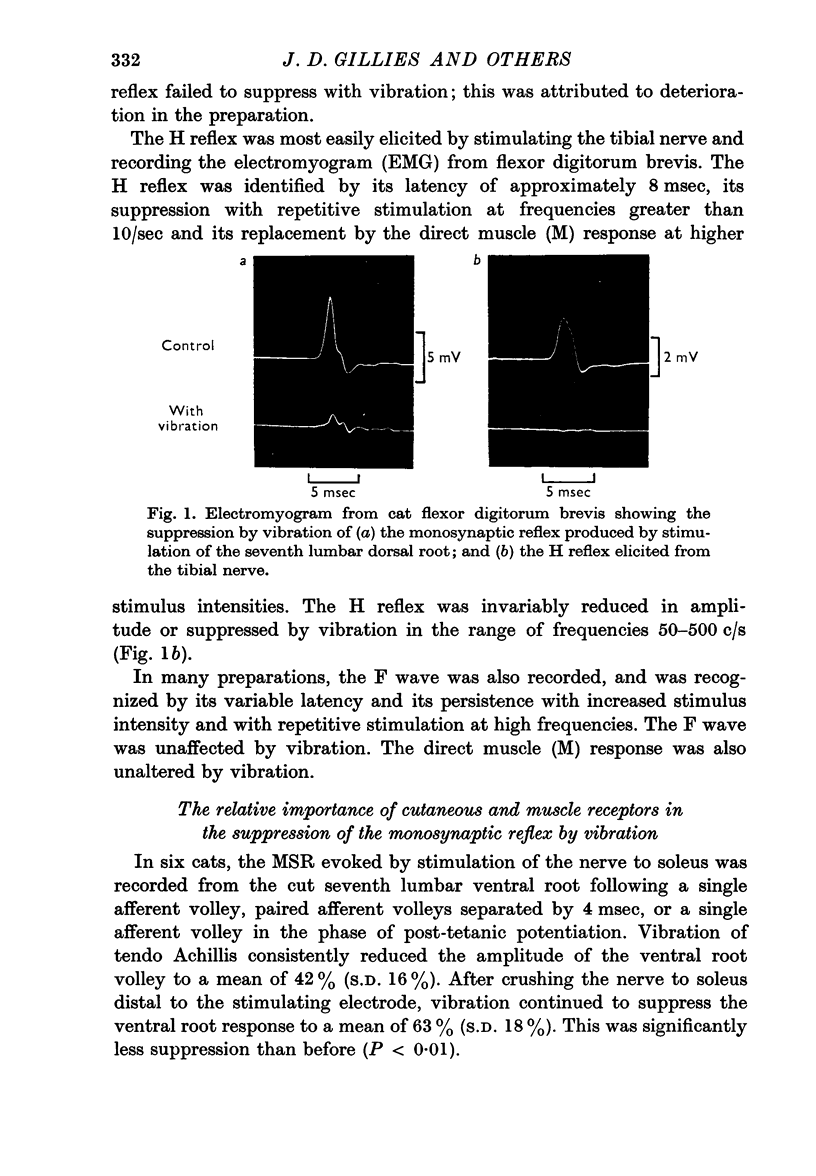
In cats, the monosynaptic reflex (MSR) elicited from L7 or S1 dorsal roots, or from the tibial nerve (H reflex) was suppressed by vibration at 50-500 c/s of the hind limb with innervation intact. The MSR was not suppressed by selective vibration of cutaneous receptors, and suppression was still observed after the hind limb was skinned. In contrast, the phenomenon disappeared when all muscle nerves were crushed.
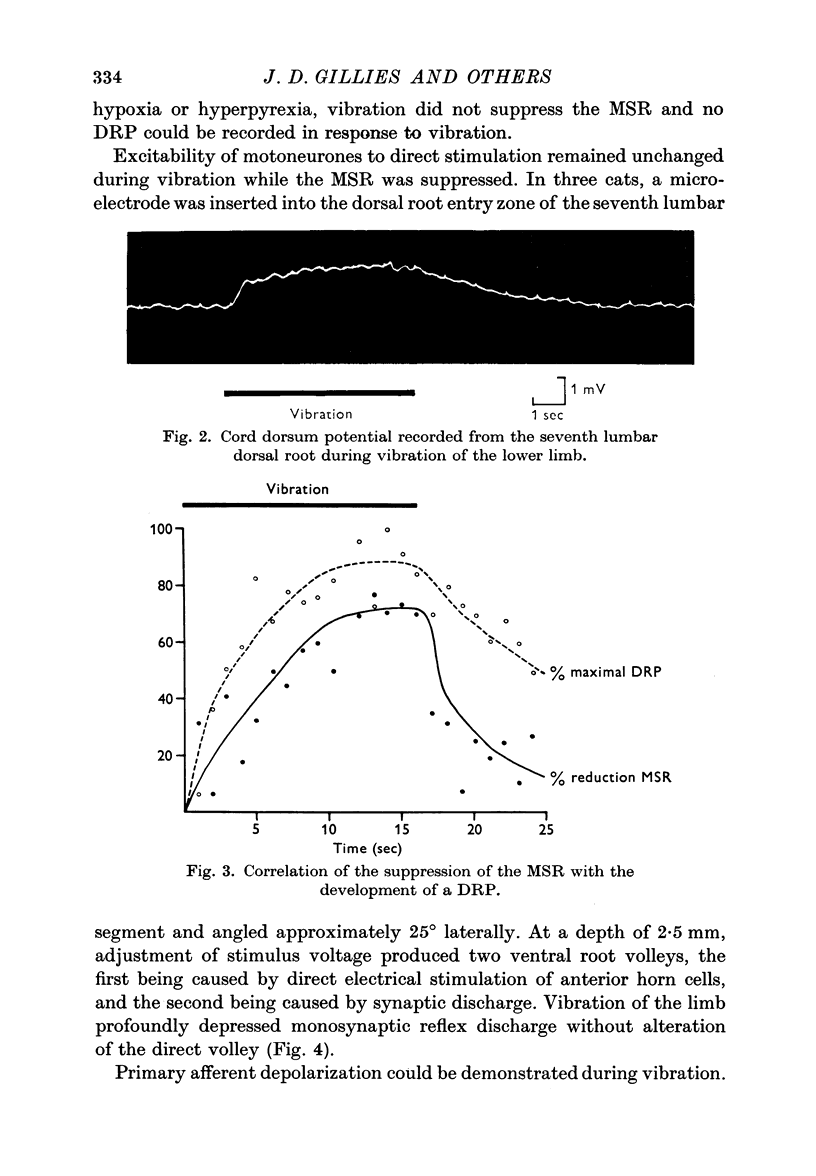
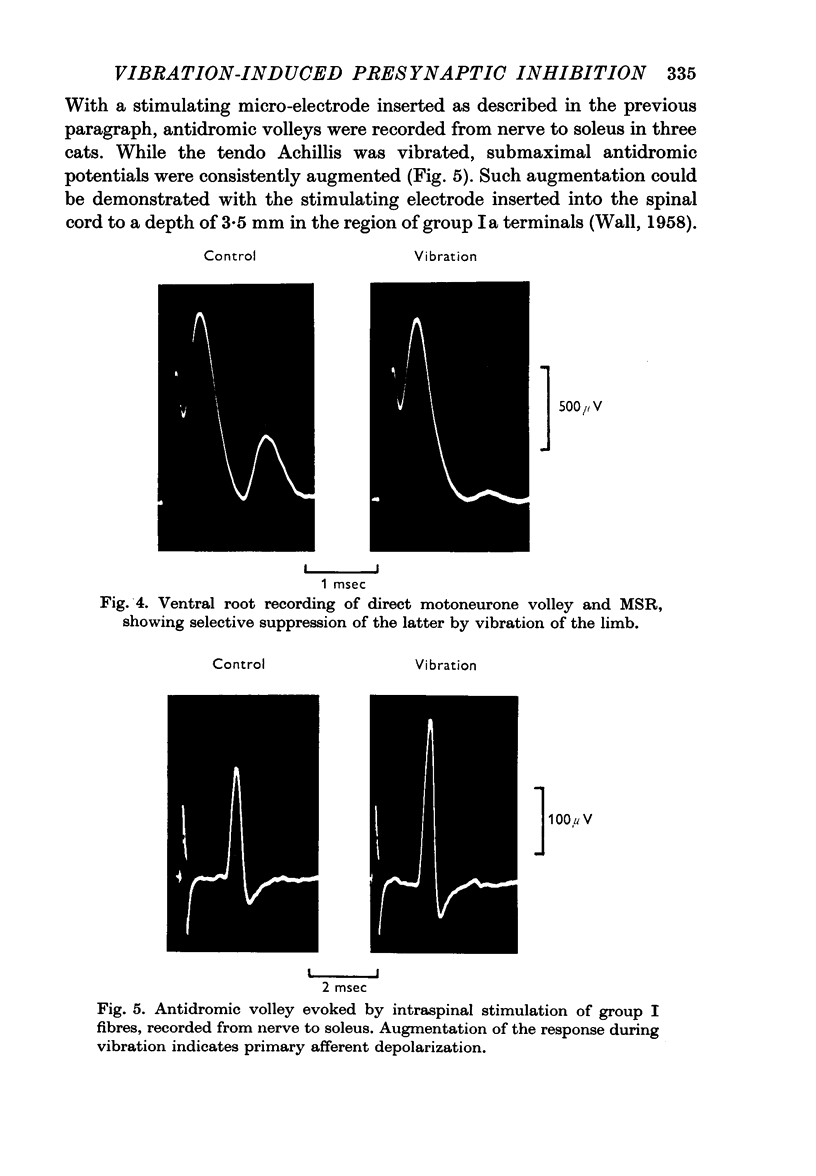
Suppression of the MSR by vibration was shown to be mediated by presynaptic inhibition by the following methods: correlation with onset of the dorsal root potential (DRP) evoked by vibration, and abolition of both DRP and reflex suppression by picrotoxin; demonstration of primary afferent depolarization and normal excitability of motoneurones to direct stimulation.
Reasons are given for deducing that the muscle afferent fibres responsible for the presynaptic inhibition induced by vibration are group Ia rather than groups Ib or II, or afferent fibres from Pacinian corpuscles.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIANCONI R., van der MEULEN J. The response to vibration of the end organs of mammalian muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jan;26:177–190. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Engberg I., Matthews P. B. The relative sensitivity to vibration of muscle receptors of the cat. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):773–800. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK W. A., Jr, NEILSON D. R., Jr, BROOKHART J. M. PRIMARY AFFERENT DEPOLARIZATION AND MONOSYNAPTIC REFLEX DEPRESSION FOLLOWING SUCCINYLCHOLINE ADMINISTRATION. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Mar;28:290–311. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Gail P., Lance J. W., Neilson P. D. Differential effects on tonic and phasic reflex mechanisms produced by vibration of muscles in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devanandan M. S., Eccles R. M., Yokota T. Depolarization of afferent terminals evoked by muscle stretch. J Physiol. 1965 Aug;179(3):417–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devanandan M. S., Eccles R. M., Yokota T. Muscle stretch and the presynaptic inhibition of the group Ia pathway to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1965 Aug;179(3):430–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., SCHMIDT R. F., WILLIS W. D. Presynaptic inhibition of the spinal monosynaptic reflex pathway. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:282–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echlin F., Fessard A. Synchronized impulse discharges from receptors in the deep tissues in response to a vibrating stimulus. J Physiol. 1938 Sep 16;93(4):312–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg I., Lundberg A., Ryall R. W. Reticulospinal inhibition of transmission in reflex pathways. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):201–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HENATSCH H. D., STEG G. Tonic and phasic ventral horn cells differentiated by post-tetanic potentiation in cat extensors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Sep 26;37(2-3):114–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1956.tb01347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. On the nature of vibration receptors in the hind limb of the cat. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:175–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. The effect of stretch receptors from muscle on the discharge of motorneurons. J Physiol. 1952 Jul;117(3):359–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A. SUPRASPINAL CONTROL OF TRANSMISSION IN REFLEX PATHS TO MOTONEURONES AND PRIMARY AFFERENTS. Prog Brain Res. 1964;12:197–221. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60624-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance J. W., Neilson P. D., Tassinari C. A. Suppression of the H reflex by peripheral vibration. Proc Aust Assoc Neurol. 1968;5(1):45–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance J. W. The mechanism of reflex irradiation. Proc Aust Assoc Neurol. 1965;3:77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance J. W. The reflex effects of muscle vibration. Proc Aust Assoc Neurol. 1966;4:49–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. B. The reflex excitation of the soleus muscle of the decerebrate cat caused by vibbration applied to its tendon. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):450–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Wray S. H. An experimental study of the F wave in the baboon. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Jun;29(3):196–200. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.3.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Excitability changes in afferent fibre terminations and their relation to slow potentials. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


