Abstract
1. The intestinal absorption of [131I]porcine and bovine serum γ-globulin after oral administration has been investigated in conscious pigs less than 20 hr old. Absorption was measured by the concentration of 131I in venous blood during the 6 hr after feeding and also by the distribution of 131I between homogenates of the alimentary tract and the rest of the animal at the end of the experiment.
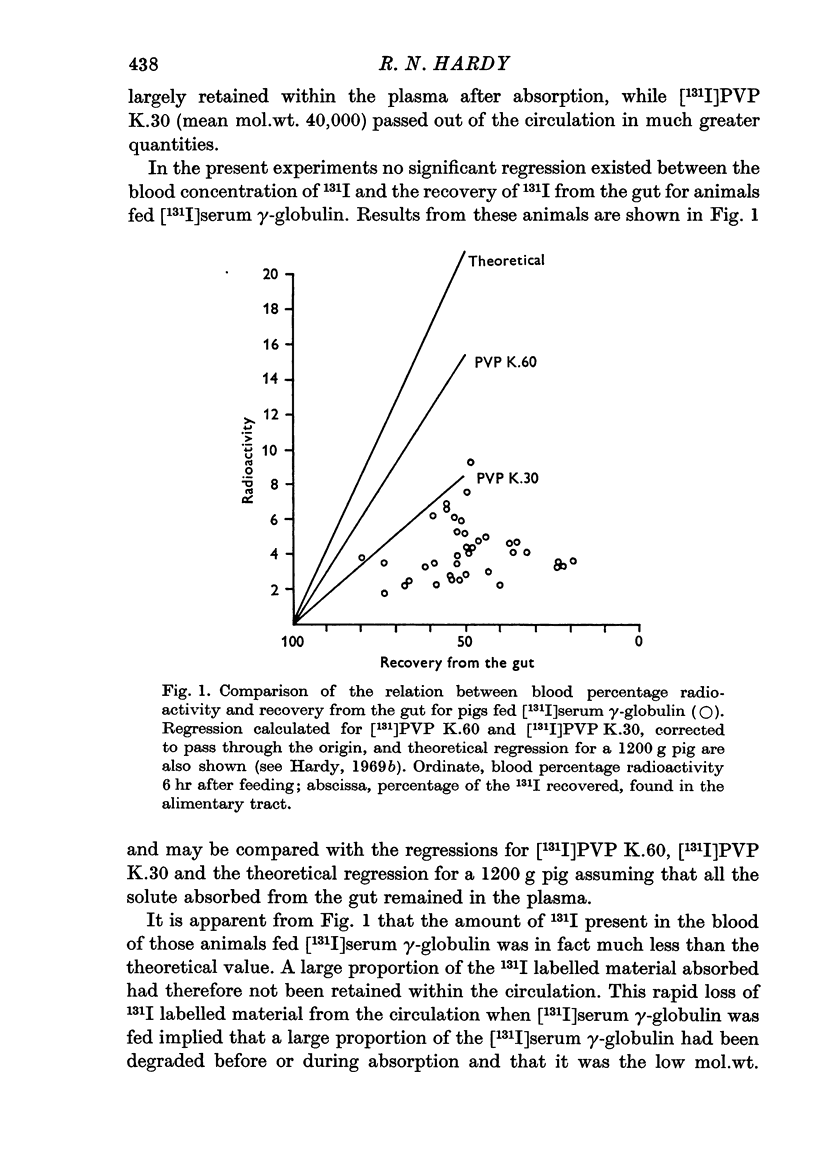
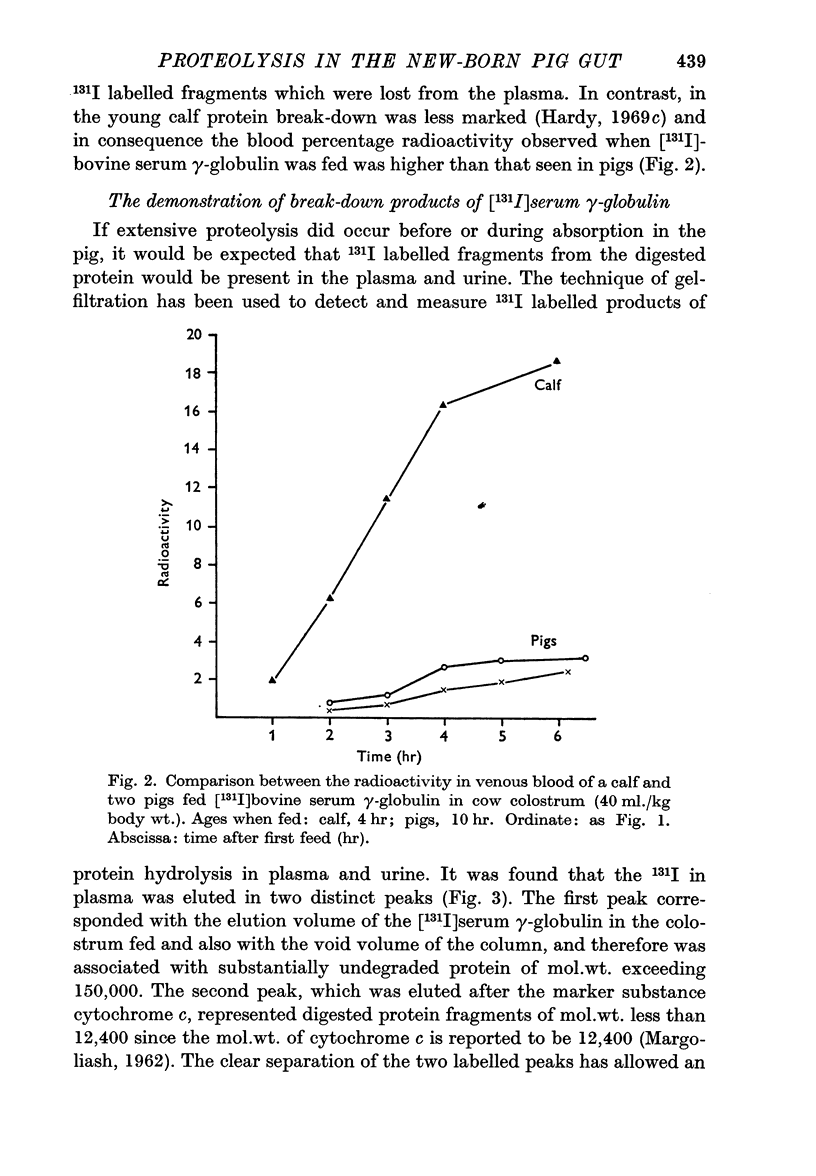
2. The concentration of 131I in the blood was always low after feeding [131I]γ-globulin, although a large proportion of the isotope fed was found to have left the alimentary tract. This indicated that much of the [131I]-γ-globulin had been hydrolysed into fragments of low mol.wt. which were not retained in the plasma. There were no significant differences between results obtained with homologous and heterologous γ-globulin.
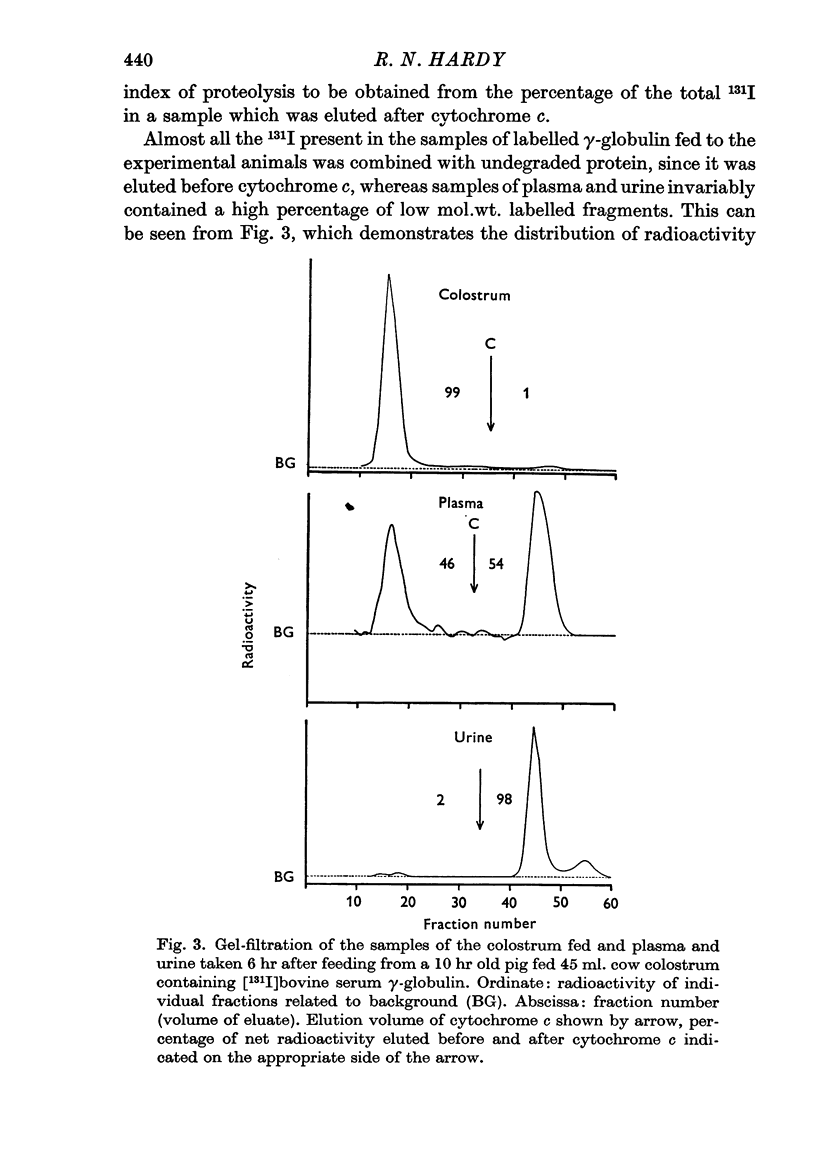
3. Examination by gel-filtration confirmed that, after feeding [131I]-serum γ-globulin, much of the 131I in the plasma was associated with material of mol.wt. less than 12,400 and demonstrated that the break-down of bovine γ-globulin was comparable with that of homologous γ-globulin.
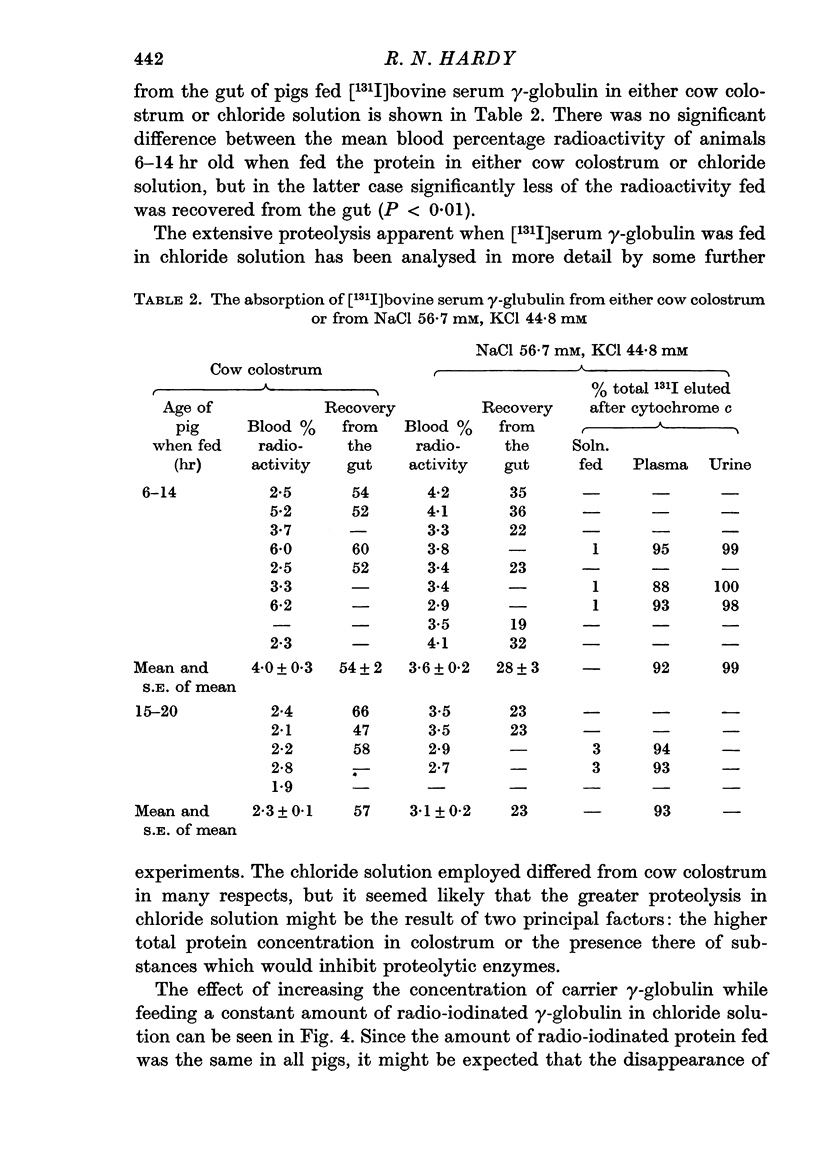
4. Comparison of the absorption of [131I]serum γ-globulin from colostrum with that from a chloride solution with a similar Na+ and K+ concentration showed that, although the blood concentration remained low, colostrum reduced the hydrolysis of the labelled protein.
5. This effect of colostrum could be simulated by the addition to the chloride solution of either the synthetic trypsin inhibitor Trasylol or a higher concentration of unlabelled protein.
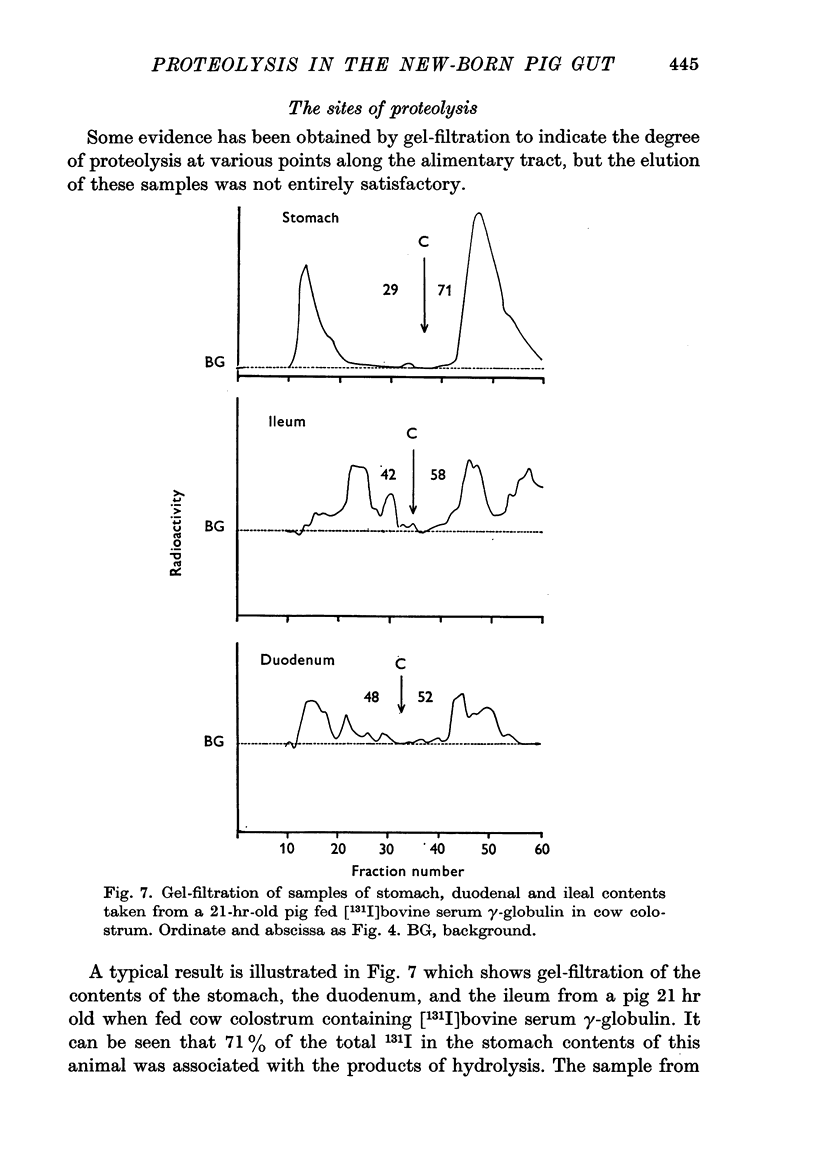
6. Gel-filtration of samples of the contents of the stomach, duodenum and terminal ileum after feeding [131I]serum γ-globulin showed that proteolysis occurred at all these sites.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balfour W. E., Comline R. S. Acceleration of the absorption of unchanged globulin in the new-born calf by factors in colostrum. J Physiol. 1962 Feb;160(2):234–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Smith M. W., Witty R. Interdependence of albumin and sodium transport in the foetal and new-born pig intestine. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(2):365–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain A. G., Perry G. C., Jones R. E. Effect of trypsin inhibitor isolated from sows' colostrum on the absorption of gamma-globulin by piglets. Nature. 1965 Jul 24;207(995):429–429. doi: 10.1038/207429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. M., Hardy R. N. The use of [125-I] polyvinyl pyrrolidone K. 60 in the quantitative assessment of the uptake of macromolecular substances by the intestine of the young rat. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):113–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUTSCH H. F., SMITH V. R. Intestinal permeability to proteins in the newborn herbivore. Am J Physiol. 1957 Nov;191(2):271–276. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.191.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. N. Proteolytic activity during the absorption of 131-I-gamma-globulin in the new-born calf. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(2):453–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. N. The absorption of polyvinyl pyrrolidone by the new-born pig intestine. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):633–651. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. N. The influence of specific chemical factors in the solvent on the absorption of macromolecular substances from the small intestine of the new-born calf. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):607–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAEBERIE M. L., SEGRE D. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF HOMOLOGOUS AND HETEROLOGOUS SERUM GLOBULINS BY THE NEWBORN PIG. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Jul;25:1096–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKOWSKI M., Jr, LASKOWSKI M. Crystalline trypsin inhibitor from colostrum. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jun;190(2):563–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKOWSKI M., KASSELL B., HAGERTY G. A crystalline trypsin inhibitor from swine colostrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 May;24(2):300–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKE R. F., MYERS W. L., SEGRE D. THE IMMUNOLOGIC BEHAVIOR OF BABY PIGS. IV. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION AND PERSISTANCE OF 6.6S AND 18S ANTIBODIES OF OVINE ORIGIN AND THEIR ROLE IN THE IMMUNOLOGIC COMPETENCE OF BABY PIGS. J Immunol. 1964 Oct;93:576–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E. Amino acid sequence of chymotryptic peptides from horse heart cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2161–2174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDBRING F., OLSSON B. Electrophoretic and immunological studies on sera of young pigs. II. The effect of feeding bovine trypsin inhibitor with porcine colostrum on the absorption of antibodies and immune globulins. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1958;63(1-2):25–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDBRING F., OLSSON B. Electrophoretic and immunological studies on sera of young pigs. III. Transfer of protein fractions and antibodies to the newborn pig by ingestion of porcine serum with a study of the effect of bovine trypsin inhibitor. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1958;63(1-2):41–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAYNE L. C., MARSH C. L. Gamma globulin absorption in the baby pig: the nonselective absorption of heterologous globulins and factors influencing absorption time. J Nutr. 1962 Feb;76:151–158. doi: 10.1093/jn/76.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce A. E., Smith M. W. The in vitro transfer of bovine immune lactoglobulin across the intestine of new-born pigs. J Physiol. 1967 May;190(1):19–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce A. E., Smith M. W. The intestinal absorption of pig and bovine immune lactoglobulin and human serum albumin by the new-born pig. J Physiol. 1967 May;190(1):1–18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



