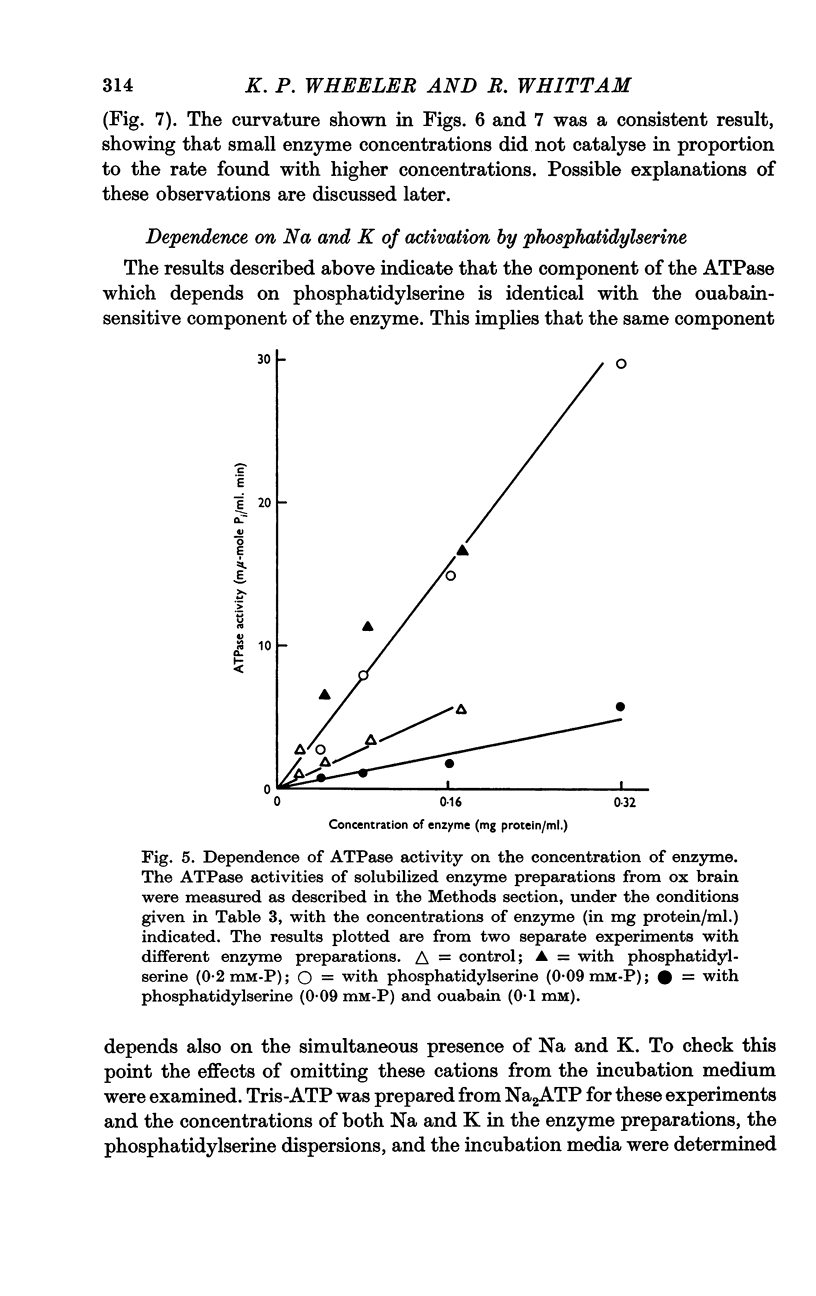
Abstract
1. A study has been made to see whether the ATPase of the Na pump is activated by phospholipids.
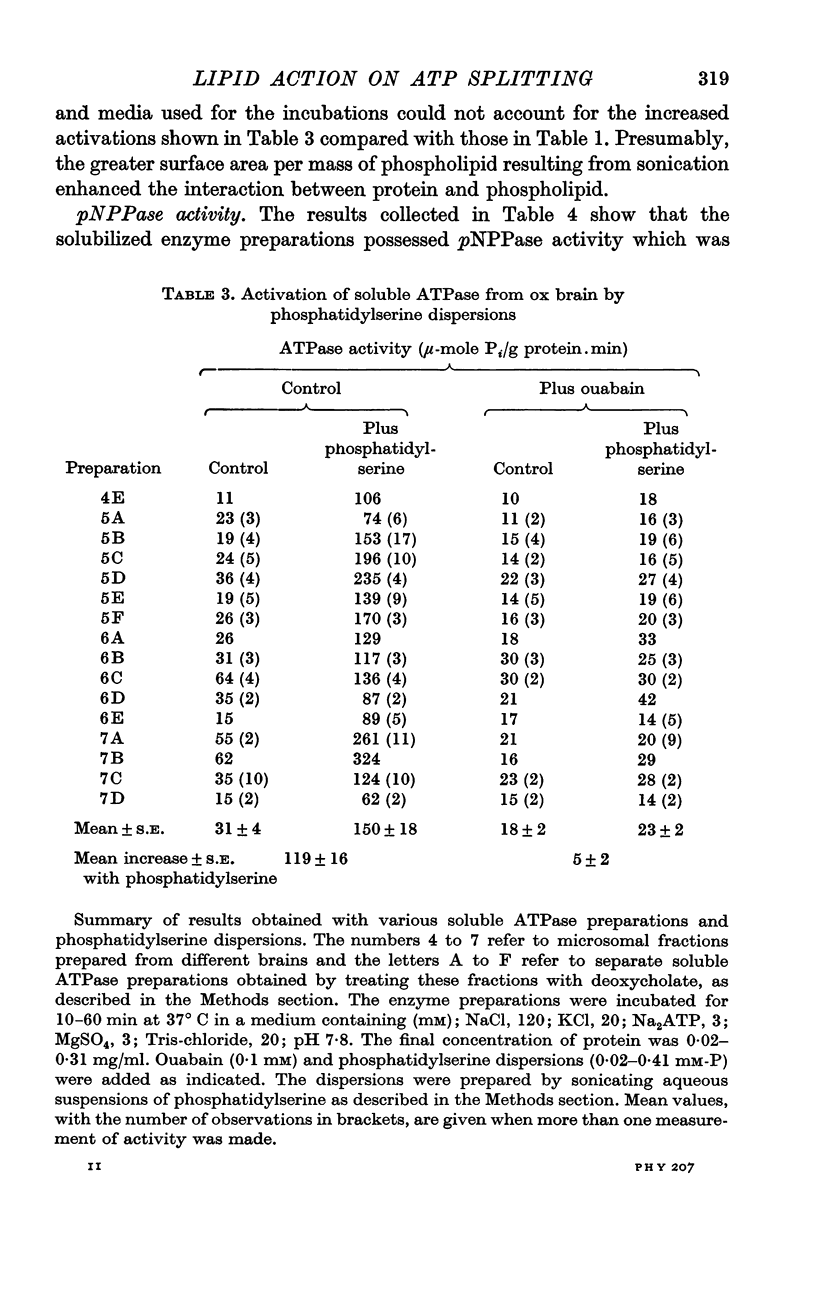
2. Solubilization of a membrane-containing (microsomal) fraction from ox brain cortex with deoxycholate removed most or all of the ouabain-inhibited ATPase and p-nitrophenylphosphatase (pNPPase) activities. Addition of sonicated dispersions of crude commercial samples of phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol or phosphatidylserine stimulated both enzymic activities, but neither phosphatidylcholine nor phosphatidylethanolamine affected them. After partial purification by chromatography, however, definite activation was demonstrated only with that component of crude samples which migrated like phosphatidylserine.
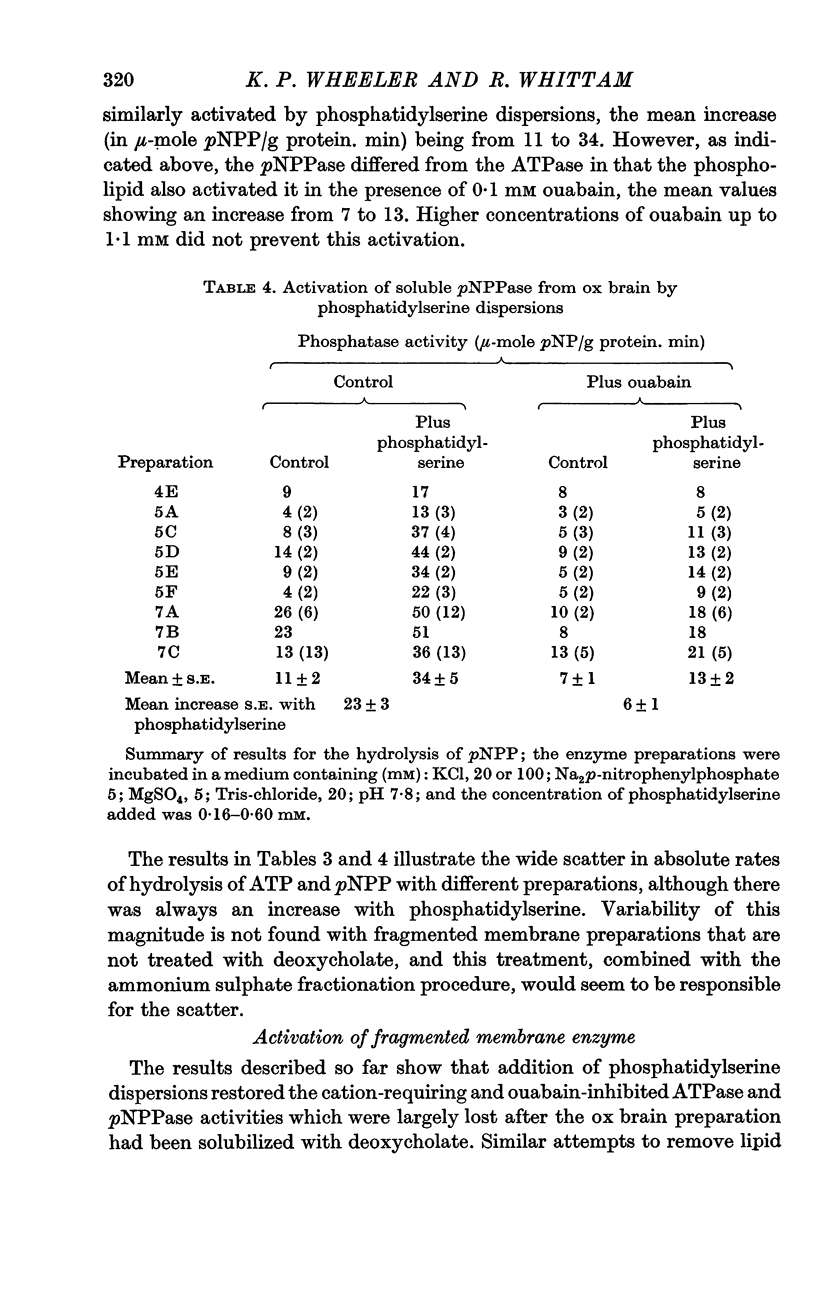
3. The ATPase activity dependent on phosphatidylserine was eliminated by removal of Na and K or by addition of ouabain and was substantially inhibited by oligomycin. The corresponding component of pNPPase activity was partially inhibited by ouabain or by removal of most of the K, but was little affected by oligomycin. The phosphatidylserine-dependent enzyme(s) therefore exhibited properties characteristic of the ATPase of the Na pump.
4. Phosphatidylserine dispersions similarly activated both the ATPase and the pNPPase of the particulate enzyme preparations, untreated with deoxycholate.
5. The results suggest that the system for active transport of Na and K involves a complex unit of phosphatidylserine and the protein of the ATPase.
Full text
PDF






















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON D., BLECHER M. QUANTITATIVE TWO-DIMENSIONAL THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF NATURALLY OCCURRING PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:628–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALBERS R. W., RODRIGUEZDE LORES, DEROBERTIS E. SODIUM-POTASSIUM-ACTIVATED ATPASE AND POTASSIUM-ACTIVATED P-NITROPHENYLPHOSPHATASE: A COMPARISON OF THEIR SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATIONS IN RAT BRAIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Mar;53:557–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKARI A., FRATANTONI J. C. EFFECT OF MONOVALENT CATIONS ON THE ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATASE OF SONICATED ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 23;92:132–141. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers R. W., Koval G. J. Sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of Electrophorus electric organ. 3. An associated potassium-activated neutral phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1896–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askari A., Koyal D. Different oligomycin sensitivities of the Na++K+-activated adenosinetriphosphatase and its partial reactions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader H., Post R. L., Bond G. H. Comparison of sources of a phosphorylated intermediate in transport ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 3;150(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., LIONETTI F., SOLOMON A. K. Possible cation-carrier substances in blood. Nature. 1956 Sep 15;178(4533):582–583. doi: 10.1038/178582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. Studies on the hydrolysis of lecithin by a Penicillium notatum phospholipase B preparation. Biochem J. 1958 Dec;70(4):559–570. doi: 10.1042/bj0700559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmelot P., Bos C. J. Studies on plasma membranes. V. On the lipid dependence of some phosphohydrolases of isolated rat-liver plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):341–353. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenster L. J., Copenhaver J. H., Jr Phosphatidyl serine requirement of (Na+-K+)-activated adenosine triphosphatase from rat kidney and brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):406–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formby B., Clausen J. Comparative studies on K -p-nitrophenylphosphatase, K -acylphosphatase and (Na + K)adenosinetriphosphatase in synaptosomes of rat brain. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Jul;349(7):909–919. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1968.349.2.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita M., Nakao T., Tashima Y., Mizuno N., Nagano K., Nakao M. Potassium-ion stimulated p-nitrophenylphosphatase activity occurring in a highly specific adenosine triphosphatase preparation from rabbit brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):42–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M., SLAYMAN C. W., EICHBERG J., DAWSON R. M. THE ADENOSINE-TRIPHOSPHATASE SYSTEM RESPONSIBLE FOR CATION TRANSPORT IN ELECTRIC ORGAN: EXCLUSION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS AS INTERMEDIATES. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:692–699. doi: 10.1042/bj0940692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase and cation transport. Br Med Bull. 1968 May;24(2):165–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel Y., Titus E. A comparison of microsomal (Na+ + K+)-ATPase with K+-acetylphosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 11;139(2):450–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARNEFELT J. Sodium-stimulated adenosinetriphosphatase in microsomes from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Mar 18;48:104–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90520-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSCHNER L. B. The cation content of phospholipides from swine erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Nov 20;42(2):231–241. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa Y., Racker E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. 8. Properties of a factor conferring oligomycin sensitivity on mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2461–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa T., Saito M., Tonomura Y. [Properties of a phosphorylated protein as a reaction intermediate of Na+-K+ sensitive ATPase]. J Biochem. 1967 May;61(5):555–566. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OHNISHI T., KAWAMURA H. R OLE DES PHOSPHATIDES DANS L'AD'ENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE SENSITIVE 'A L'OUABAINE LOCALIS'EE DANS LES MEMBRANES D'ERYTHROCYTE. J Biochem. 1964 Oct;56:377–378. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Bangham A. D. Biophysical properties of phospholipids. II. Permeability of phosphatidylserine liquid crystals to univalent ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep 5;126(1):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROJAS E., TOBIAS J. M. MEMBRANE MODEL: ASSOCIATION OF INORGANIC CATIONS WITH PHOSPHOLIPID MONOLAYERS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 29;94:394–404. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZMANN H. J. Lipoprotein nature of red cell adenosine triphosphatase. Nature. 1962 Nov 17;196:677–677. doi: 10.1038/196677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEKUZU I., JURTSHUK P., Jr, GREEN D. E. Studies on the electron transfer system. LI. Isolation and characterization of the D-(--)-beta-hydroxybutyric apodehydrogenase from beef heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:975–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA R., ABOOD L. G. PHOSPHOLIPID REQUIREMENT OF NA+,K+-ACTIVATED ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE FROM RAT BRAIN. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Oct;108:47–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90353-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R., Mitsumata T. P-nitrophenyl phosphatases of a membrane fraction from bovine cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1969 Jul;16(7):1163–1171. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R., Strickland K. P. Role of phospholipid in the activation of Na+, Ka+-activated adenosine triphosphatase of beef brain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Sep;111(3):583–592. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler K. P., Whittam R. Structural and enzymic aspects of the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate by membranes of kidney cortex and erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):349–363. doi: 10.1042/bj0930349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


