Abstract
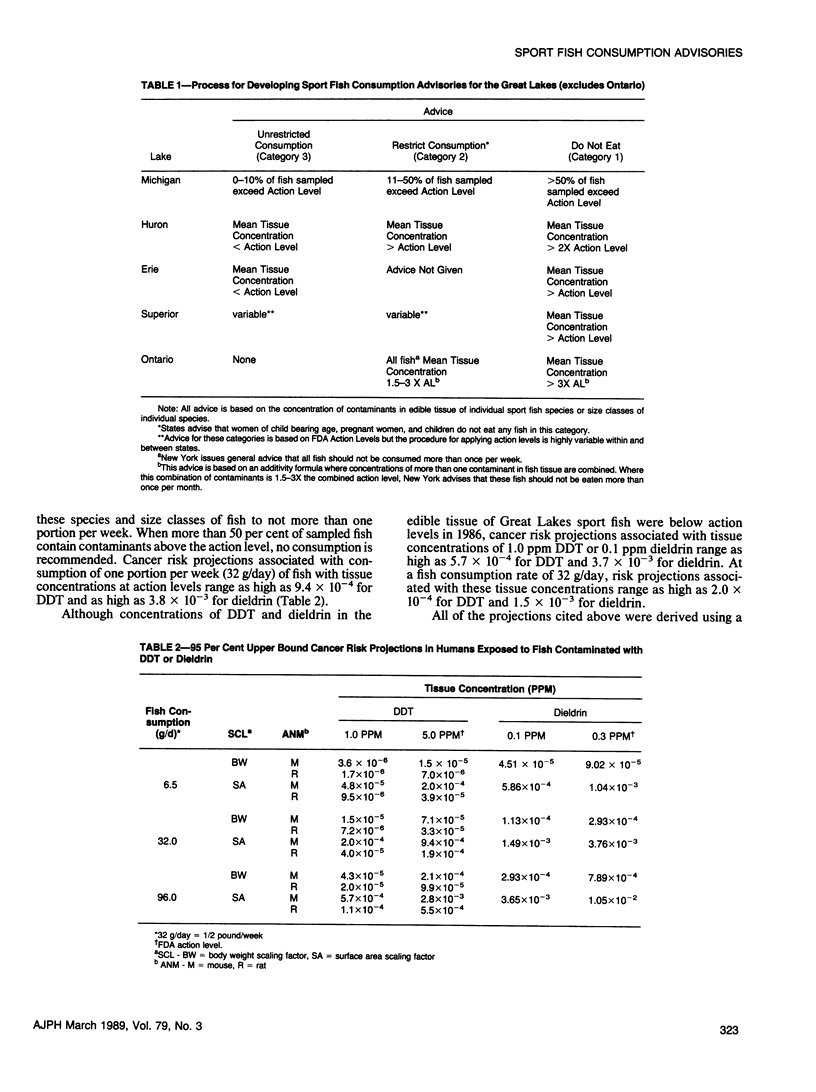
Because Great Lakes sport fish are contaminated with several toxicants, the Great Lakes states individually issue advisories, principally based on Food and Drug Administration (FDA) action levels, that suggest limiting or eliminating consumption of contaminated fish. We describe the procedures the states use to determine when to issue consumption advisories and we evaluate the associated cancer risks using EPA-IARC-OSTP risk assessment procedures. Projected cancer risks are high for consumers of small quantities of sport fish contaminated with DDT or dieldrin at their respective action levels. Projected risks at concentrations that are common but below the action levels are also substantial. We propose that sport fish with tissue concentrations of DDT or dieldrin one-fifth and one-third of the action levels should be covered by consumption advisories to warn consumers of the potential adverse health impacts.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cabral J. R., Hall R. K., Rossi L., Bronczyk S. A., Shubik P. Effects of long-term intake of DDT on rats. Tumori. 1982 Feb 28;68(1):11–17. doi: 10.1177/030089168206800103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodin U., Fredriksson M., Persson B., Axelson O. Chronic lymphatic leukaemia and engine exhausts, fresh wood, and DDT: a case-referent study. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Jan;45(1):33–38. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S. W., Fein G. G., Jacobson J. L., Schwartz P. M., Dowler J. K. The effect of intrauterine PCB exposure on visual recognition memory. Child Dev. 1985 Aug;56(4):853–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Hino O., Nomura K., Sugano H. Dose-response studies on promoting and anticarcinogenic effects of phenobarbital and DDT in the rat hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Dec;5(12):1653–1656. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.12.1653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maronpot R. R., Haseman J. K., Boorman G. A., Eustis S. E., Rao G. N., Huff J. E. Liver lesions in B6C3F1 mice: the National Toxicology Program, experience and position. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1987;10:10–26. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71617-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds S. H., Stowers S. J., Patterson R. M., Maronpot R. R., Aaronson S. A., Anderson M. W. Activated oncogenes in B6C3F1 mouse liver tumors: implications for risk assessment. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1309–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.3629242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp E. M., Miller F. I., Baes C. F., 3rd Some results of recent surveys of fish and shellfish consumption by age and region of U.S. residents. Health Phys. 1980 Aug;39(2):165–175. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198008000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennekes H. A., Edler L., Kunz H. W. Dose-response analysis of the enhancement of liver tumour formation in CF-1 mice by dieldrin. Carcinogenesis. 1982;3(8):941–945. doi: 10.1093/carcin/3.8.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorslund T. W., Brown C. C., Charnley G. Biologically motivated cancer risk models. Risk Anal. 1987 Mar;7(1):109–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.1987.tb00974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomatis L., Turusov V., Day N., Charles R. T. The effect of long-term exposure to DDT on CF-1 MICE. Int J Cancer. 1972 Nov;10(3):489–506. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A. I., Thorpe E., Stevenson D. E. The toxicology of dieldrin (HEOD). I. Long-term oral toxicity studies in mice. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1973 Jun;11(3):415–432. doi: 10.1016/0015-6264(73)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. M., Numoto S. Promotion of mouse liver neoplasms by the organochlorine pesticides chlordane and heptachlor in comparison to dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Dec;5(12):1689–1696. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.12.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


