Abstract
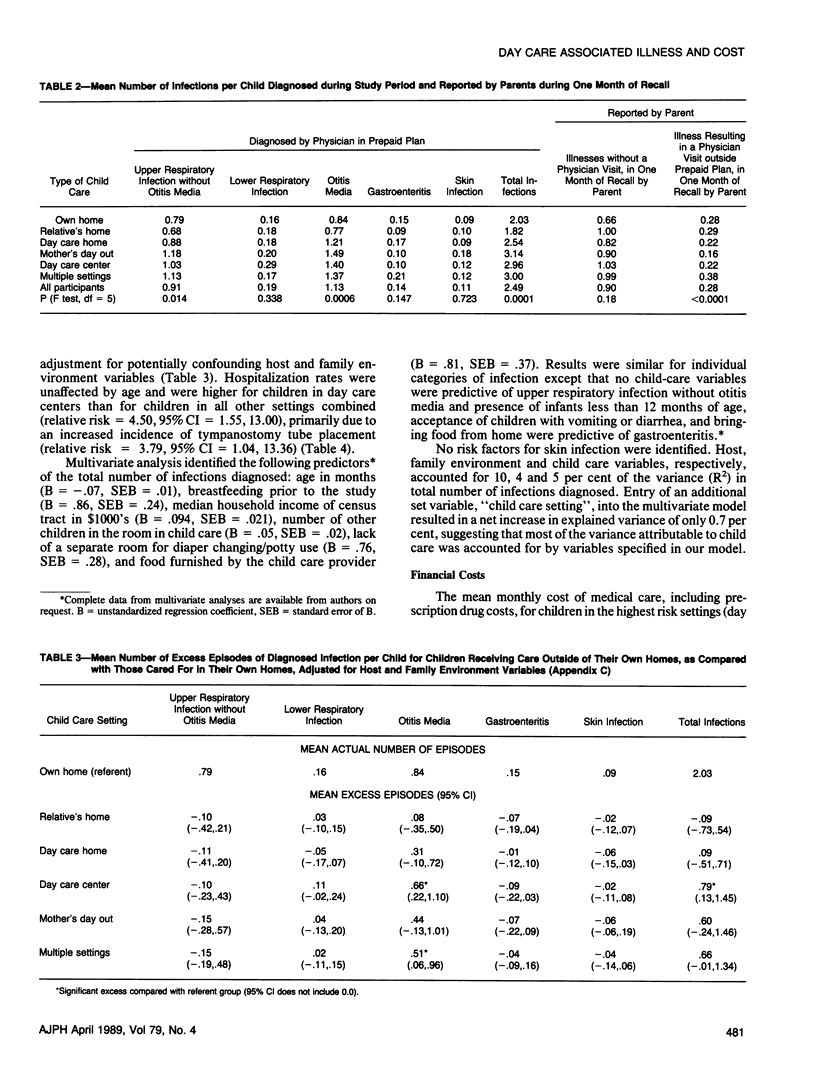
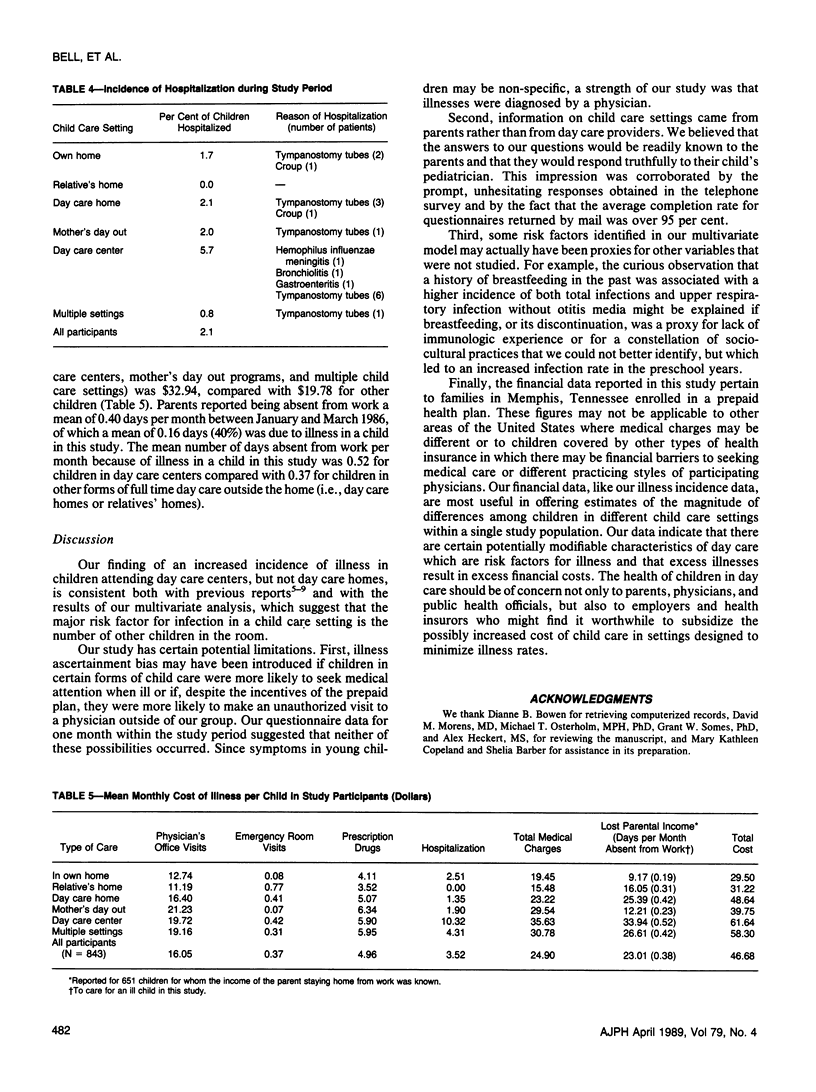
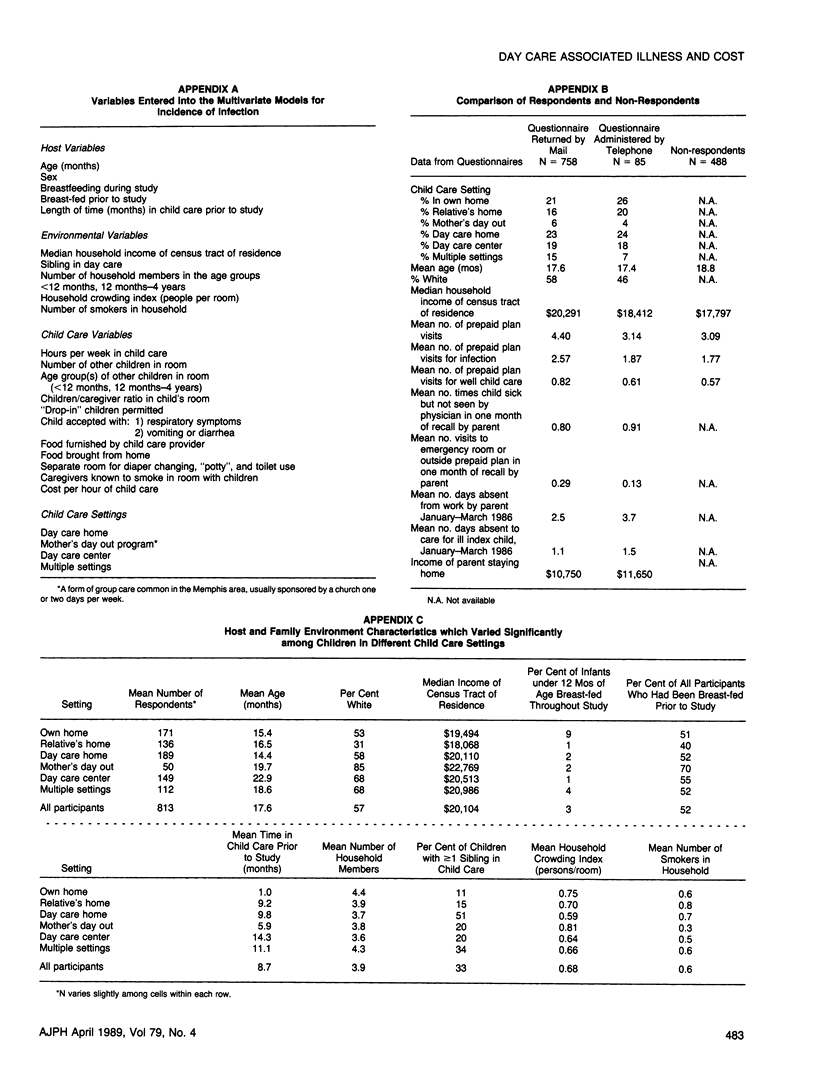
We studied 843 children under 36 months of age enrolled in a prepaid health plan from September 1985 through March 1986, to identify characteristics of day care which might be risk factors for infection and to describe the resulting economic costs. Children cared for in their own home had a mean of 2.03 infections diagnosed during the study period. Adjusted rates of excess infection (95 per cent CI) for children cared for in other settings were: -.09 (-.73, .54) in relatives' homes; .10 (-.51, .71) in day care homes; .79 (.13, 1.45) in day care centers; .60 (-.24, 1.46) in mother's day out programs; and .66 (-.01, 1.34) in multiple settings. Children in day care centers were 4.5 times more likely to be hospitalized than those in other settings (95 per cent CI = 1.55, 13.00), primarily due to an increased rate of tympanostomy tube placement (relative risk 3.79, 95 per cent CI = 1.04, 13.36). The strongest predictor of illness risk was the number of other children in the room. The mean monthly cost of medical care was $32.94 for children in the highest risk settings compared with $19.78 for those in other settings. Illness in a child in our study accounted for 40 per cent of parental absenteeism from work; the mean number of days lost per month was 0.52 for parents of children in day care centers compared with 0.37 for those of children in other forms of full time care outside the home.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. J., Parker R. A., Strikas R. A., Farrar J. A., Gangarosa E. J., Keyserling H. L., Sikes R. K. Day-care center attendance and hospitalization for lower respiratory tract illness. Pediatrics. 1988 Sep;82(3):300–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson S. S., Osterholm M. T. Infectious diseases in child day care: management and prevention. Summary of the symposium and recommendations. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;8(4):672–679. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.4.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett A. V., Moore M., Gary G. W., Starko K. M., Erben J. J., Meredith B. A. Diarrheal illness among infants and toddlers in day care centers. I. Epidemiology and pathogens. J Pediatr. 1985 Oct;107(4):495–502. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett A. V., Moore M., Gary G. W., Starko K. M., Erben J. J., Meredith B. A. Diarrheal illness among infants and toddlers in day care centers. II. Comparison with day care homes and households. J Pediatr. 1985 Oct;107(4):503–509. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Dykes A. C., Anderson K. E., Wells J. G., Sinclair S. P., Gary G. W., Jr, Hatch M. H., Gangarosa E. J. Handwashing to prevent diarrhea in day-care centers. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Apr;113(4):445–451. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., Hightower A. W., Broome C. V. Childhood upper respiratory tract infections: to what degree is incidence affected by day-care attendance? Pediatrics. 1987 Jan;79(1):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler S. C., Erben J. J., Francis D. P., Webster H. M., Maynard J. E. Risk factors for hepatitis A in day-care centers. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):255–261. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins R., Kotch J. Day care and illness: evidence, cost, and public policy. Pediatrics. 1986 Jun;77(6 Pt 2):951–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen A. S., Leibowitz A., Waite L. J. Child care and children's illness. Am J Public Health. 1988 Sep;78(9):1175–1177. doi: 10.2105/ajph.78.9.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemp G. F., Woodward W. E., Pickering L. K., Sullivan P. S., DuPont H. L. The relationship of staff to the incidence of diarrhea in day-care centers. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Nov;120(5):750–758. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strangert K. Respiratory illness in preschool children with different forms of day care. Pediatrics. 1976 Feb;57(2):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R., Dashefsky B., Byers C., Guerra N., Taylor F. Frequency and severity of infections in day care. J Pediatr. 1988 Apr;112(4):540–546. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


