Abstract
1. Methods for the estimation of radioactive aniline in body fluids are described. The recovery of aniline added to blood, plasma and gastric juice was over 90% of the recovery from saline.
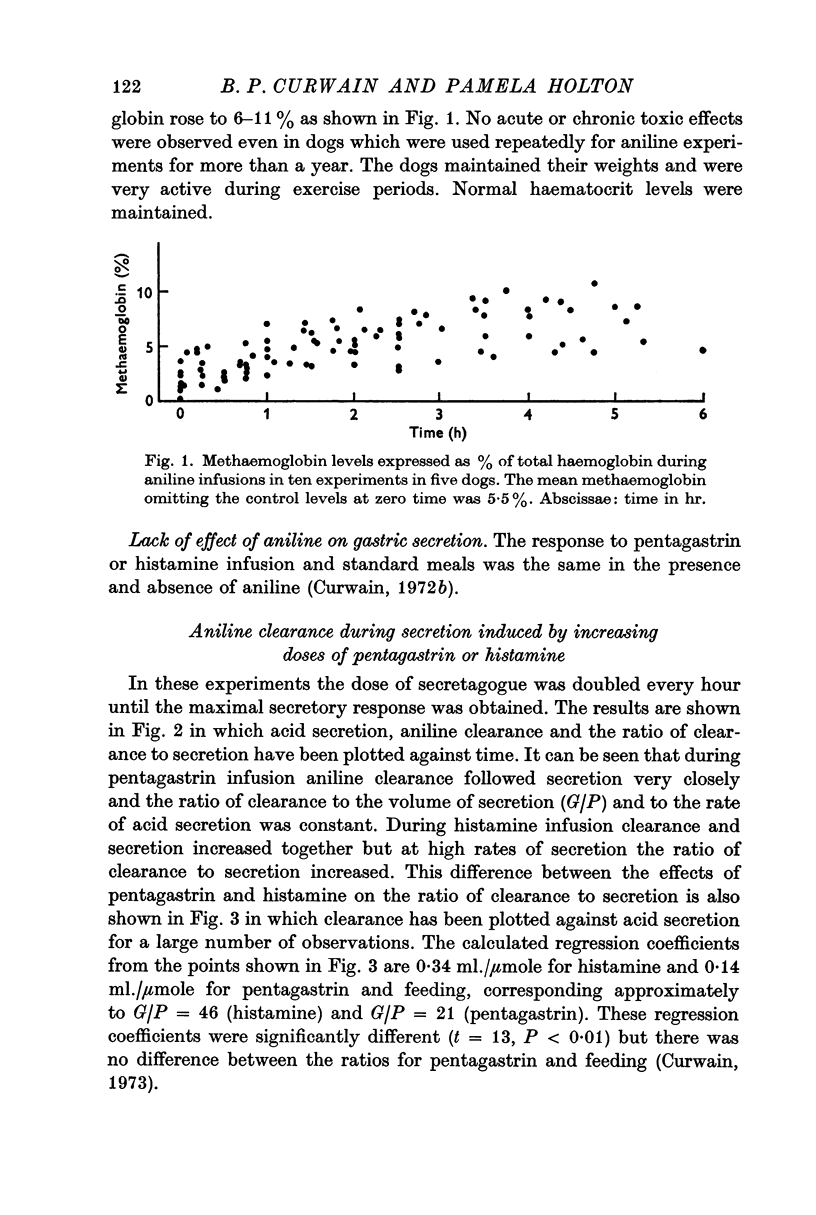
2. In the doses used aniline caused methaemoglobinaemia of 5-11% of total haemoglobin. No other effect was detected. Gastric secretion was also unaffected.
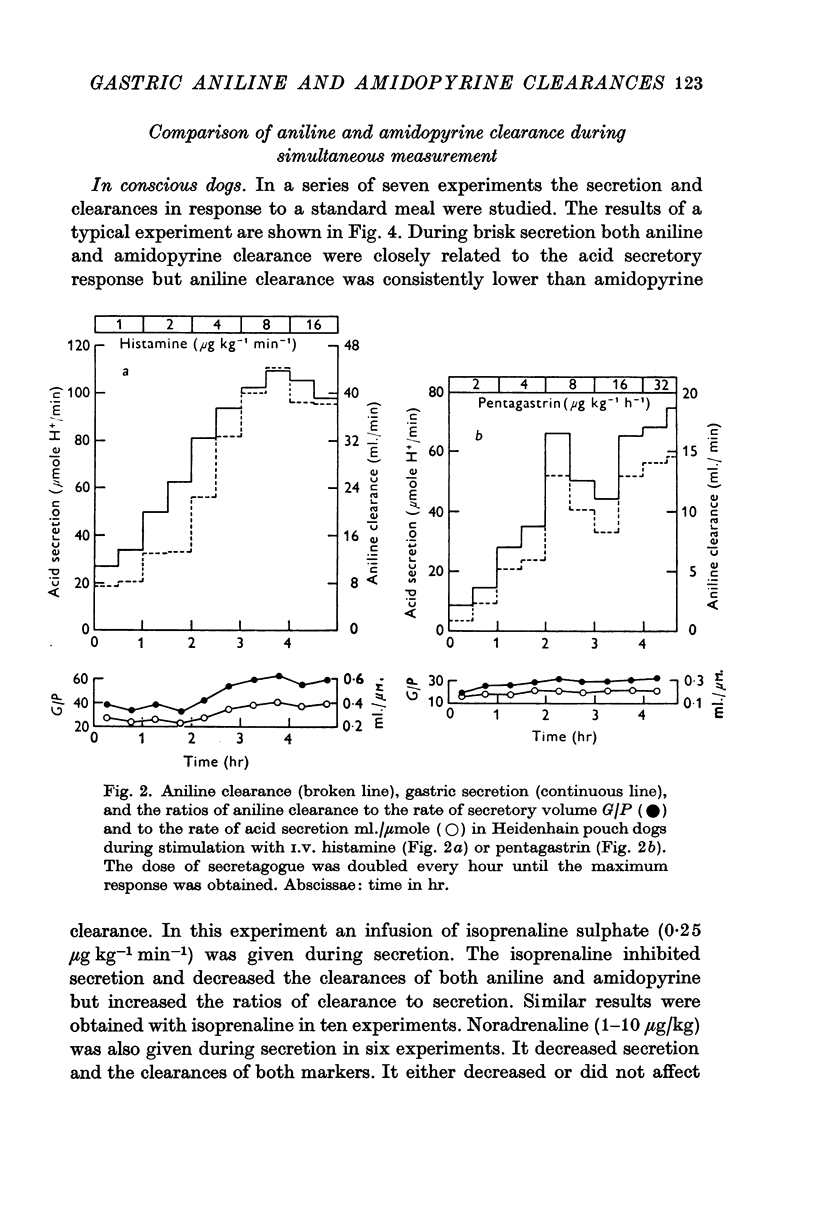
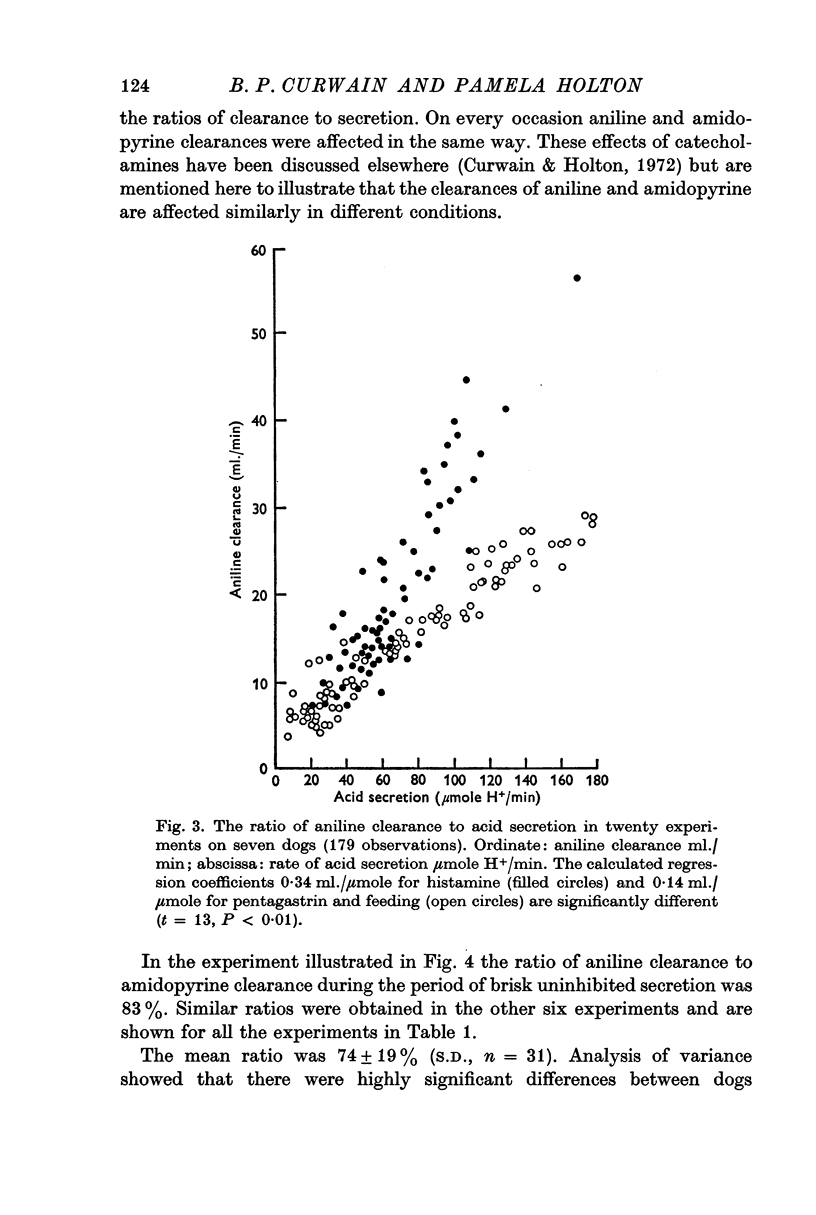
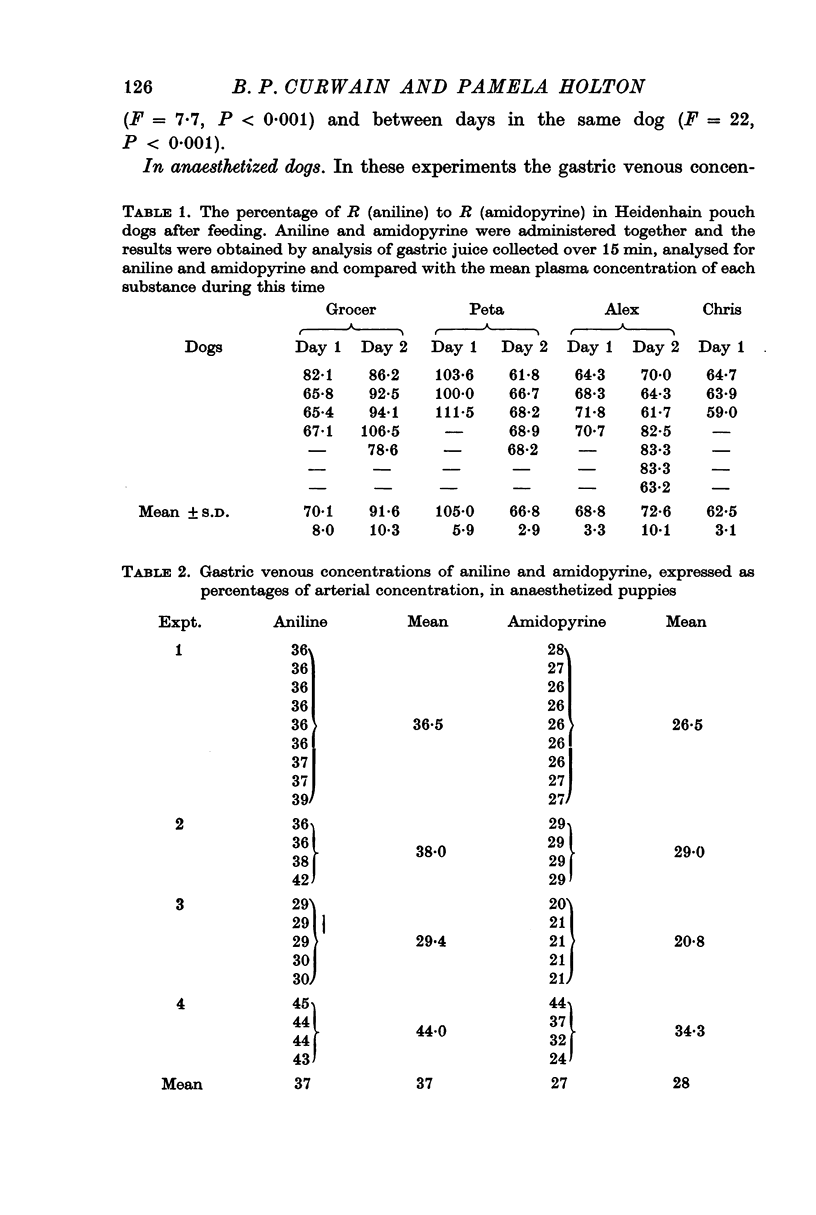
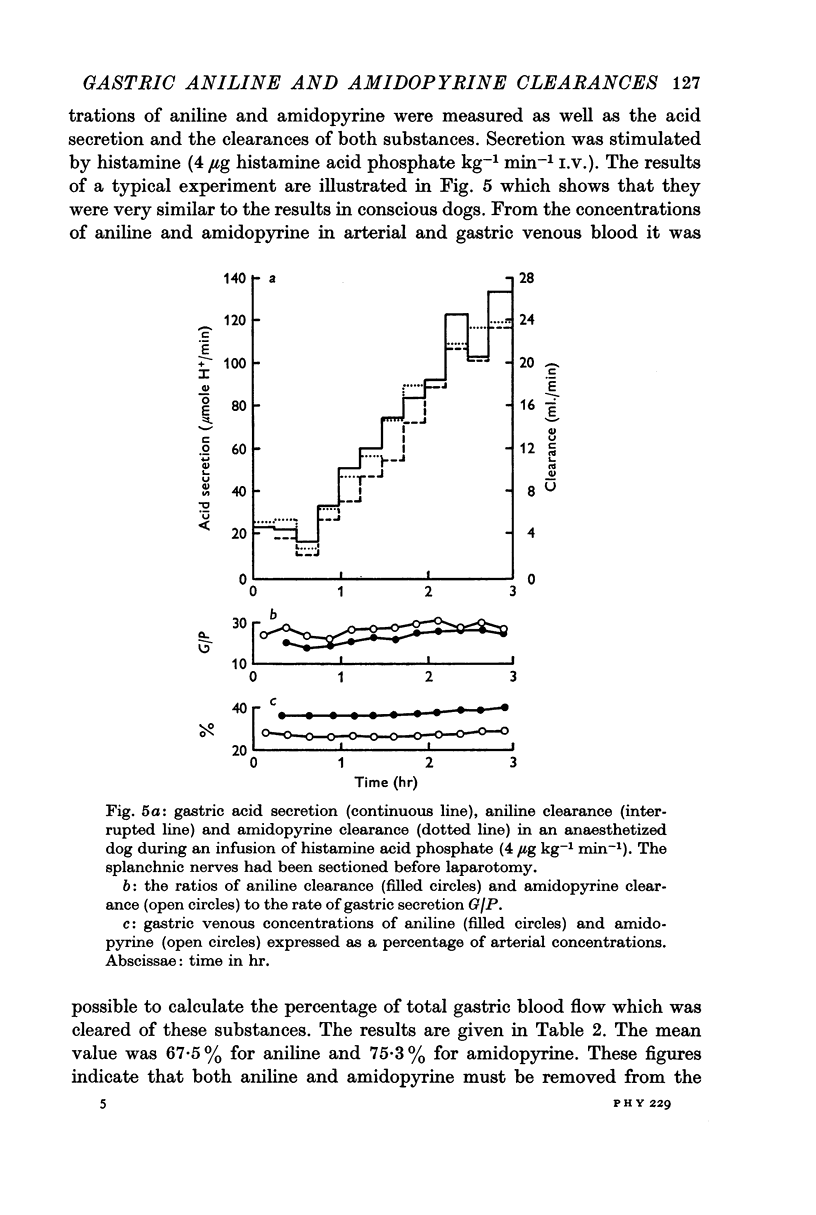
3. Aniline clearance increased in parallel with acid secretion from Heidenhain pouches in conscious dogs and in anaesthetized dogs. In conscious dogs the ratio of aniline clearance to acid secretion was significantly higher for histamine stimulation than for pentagastrin stimulation.
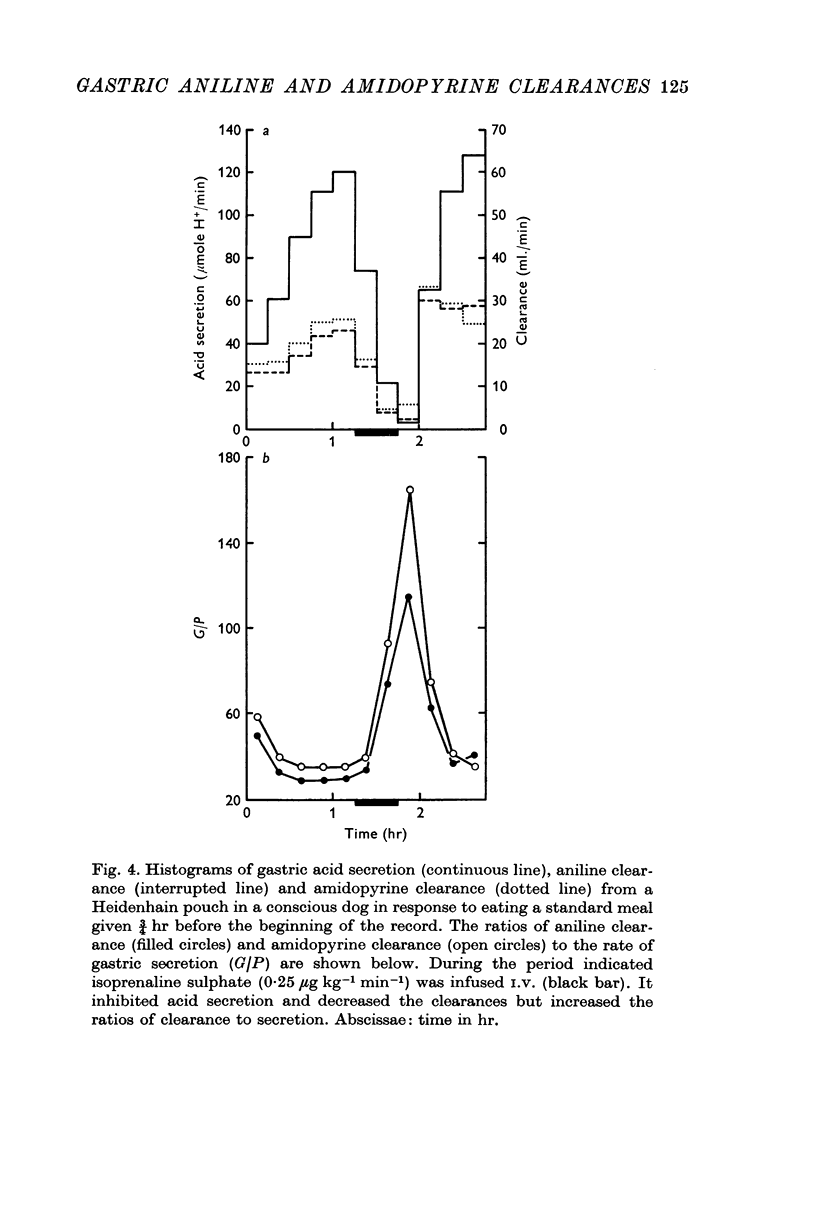
4. Aniline and amidopyrine clearances were compared simultaneously in the same dogs. Aniline clearance was about 80% of amidopyrine clearance.
5. The proportion of aniline bound to plasma proteins was measured by two methods and found to be 25%. When aniline clearance was corrected for plasma binding, aniline and amidopyrine clearances were equal.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRODIE B. B., AXELROD J. The fate of aminopyrine (pyramidon) in man and methods for the estimation of aminopyrine and its metabolites in biological material. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1950 Jun;99(2):171–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN-GRANT K., CUMMING J. D., HAIGH A. L., HARRIES E. H. THE SECRETION OF RADIOACTIVE IODIDE BY THE STOMACH OF THE ANAESTHETIZED DOG IN RELATION TO TOTAL GASTRIC BLOOD FLOW AND TO ACID SECRETION. J Physiol. 1965 Apr;177:337–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley D. J., Code C. F. Effects of secretory inhibitors on mucosal blood flow in nonsecreting stomach of conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jan;218(1):270–274. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.1.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curwain B. P. Comparison of the plasma clearances of ( 14 C)aniline and amidopyrine for the measurement of gastric mucosal blood flow. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):1P–3P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curwain B. P., Holton P. Radioactive aniline clearance from canine gastric pouches for the measurement of gastric mucosal blood flow. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Feb;41(2):384P–384P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curwain B. P., Holton P. The effects of isoprenaline and noradrenaline on pentagastrin-stimulated gastric acid secretion and mucosal blood flow in the dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Oct;46(2):225–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. A., Reed J. D., Smy J. R. Gastric blood flow in anaesthetized cats. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):795–807. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Chang A. C. Comparison of gastrin and histamine on gastric mucosal blood flow. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):484–486. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D. Clearances of the gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1968 Mar;54(3):434–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D. Comparison of prostaglandin E1 and norepinephrine on the gastric mucosal circulation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):516–519. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Eisenberg M. M., Swan K. G. Effects of histamine on gastric blood flow in conscious dogs. Gastroenterology. 1966 Oct;51(4):466–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Linford R. H., Grossman M. I. Gastric secretion in relation to mucosal blood flow studied by a clearance technic. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):1–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI105313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Price W. E. Effect of hydrocortisone on gastric mucosal blood flow and secretion. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jul;57(1):36–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Swan K. G., Grossman M. I. Blood flow and secretion in the stomach. Gastroenterology. 1967 Feb;52(2):414–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Main I. H., Whittle B. J. Proceedings: Effects of prostaglandin E2 on rat gastric mucosal blood flow, as determined by 14C-aniline clearance. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;44(2):331P–332P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody F. G. Oxygen consumption during thiocyanate inhibition of gastric acid secretion in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):127–131. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OBRINK K. J. Bonedust-meat mixture as a test meal for continuous gastric secretion. Acta Physiol Scand. 1954;30(2-3):275–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. D., Sanders D. J. Pepsin secretion, gastric motility and mucosal blood flow in the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(1):159–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. D., Sanders D. J. Splanchnic nerve inhibition of gastric acid secretion and mucosal blood flow in anaesthetized cats. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):555–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. D., Smy J. R. Mechanisms relating gastric acid secretion and mucosal blood flow during gastrin and histamine stimulation. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):571–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., BRODIE B. B., HOGBEN C. A. The gastric secretion of drugs: a pH partition hypothesis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Mar;119(3):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORIBARA T. Y., TEREPKA A. R., DEWEY P. A. The ultrafiltrable calcium of human serum. I. Ultrafiltration methods and normal values. J Clin Invest. 1957 May;36(5):738–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI103477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


