Abstract
1. The spatial properties of edge detectors were measured psychophysically with the technique of subthreshold addition. Subthreshold patterns used to add to an edge were lines, sine gratings, Gaussian edges, and ramps.
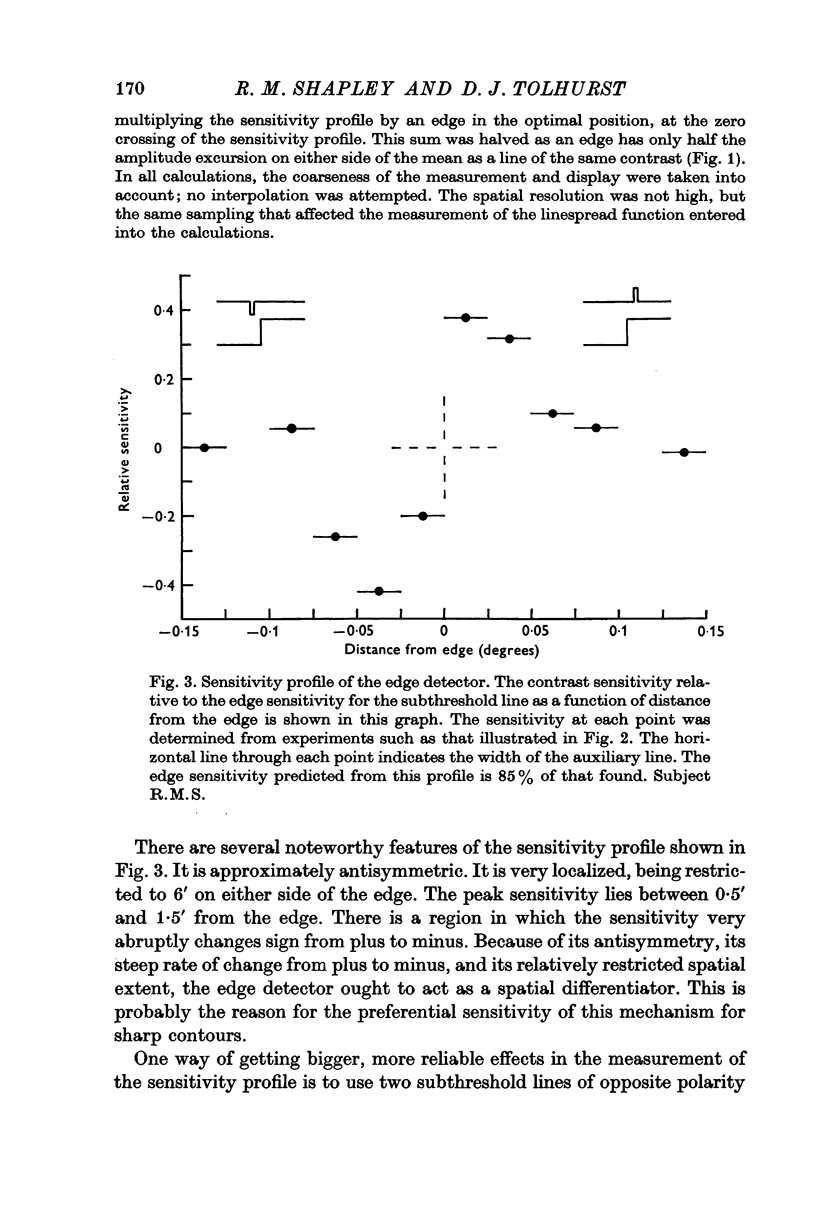
2. The sensitivity profile, determined from experiments on subthreshold addition of lines to an edge was an antisymmetric function, with peak sensitivity approximately ± 1·5′ from its midpoint. Its total extent was about ± 6′.
3. The spatial frequency response of edge detectors was measured in experiments on subthreshold addition of sine gratings to an edge. The spatial frequency response was peaked at about 3 c/deg, and was broadly tuned in frequency. It was approximately equal to the Fourier transform of the sensitivity profile, implying linearity of edge detectors.
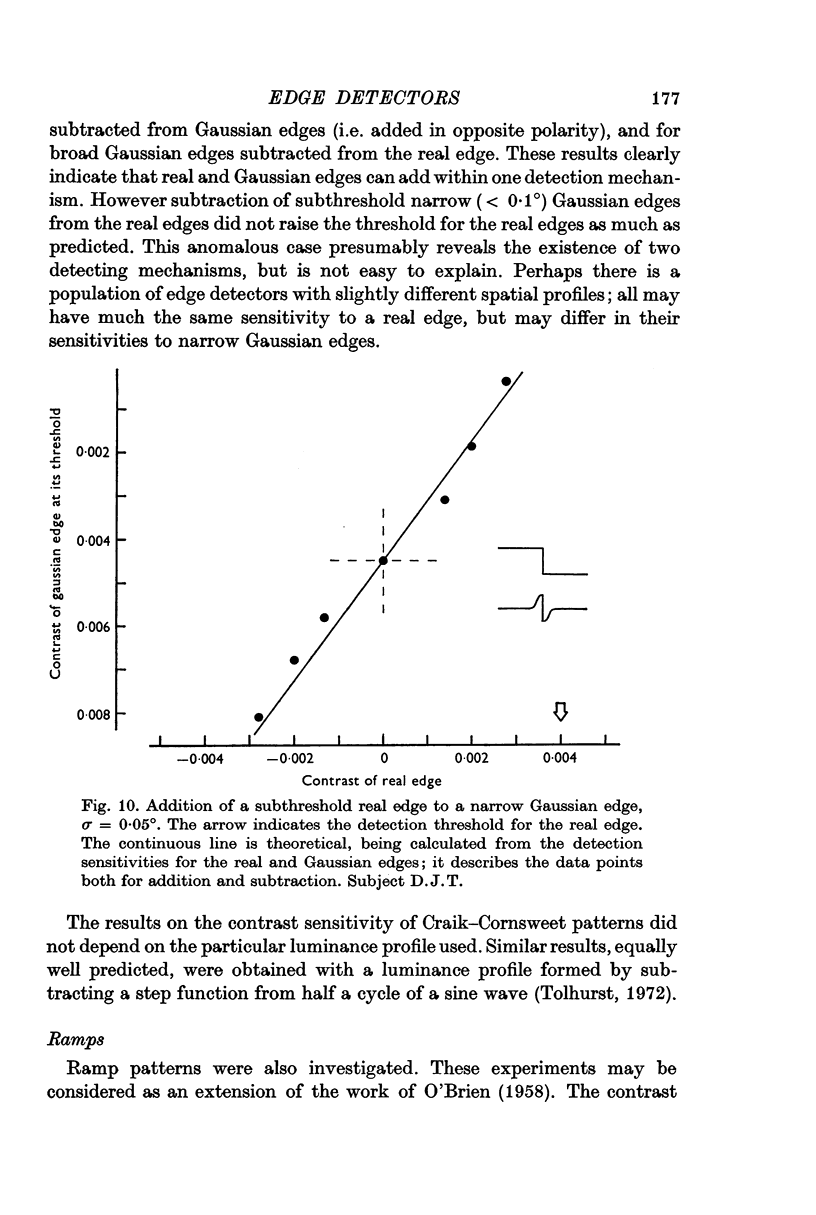
4. The visibility of Gaussian edges and ramps could be explained largely in terms of the activation of edge detector neurones.
5. The role of edge detectors in perception, in creating apparent brightness, and as an explanation of contour illusions, is discussed.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blakemore C., Campbell F. W. On the existence of neurones in the human visual system selectively sensitive to the orientation and size of retinal images. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):237–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell F. W., Howell E. R., Robson J. G. The appearance of gratings with and without the fundamental Fourier component. J Physiol. 1971;217 (Suppl):17P–18P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell F. W., Robson J. G. Application of Fourier analysis to the visibility of gratings. J Physiol. 1968 Aug;197(3):551–566. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham N., Nachmias J. Detection of grating patterns containing two spatial frequencies: a comparison of single-channel and multiple-channels models. Vision Res. 1971 Mar;11(3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Growney R., Weisstein N. Spatial characteristics of metacontrast. J Opt Soc Am. 1972 May;62(5):690–696. doi: 10.1364/josa.62.000690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:106–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY E. M., DEPALMA J. J. Sine-wave response of the visual system. I. The Mach phenomenon. J Opt Soc Am. 1961 Jul;51:740–746. doi: 10.1364/josa.51.000740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. B., Nachmias J., Robson J. G. Spatial-frequency channels in human vision. J Opt Soc Am. 1971 Sep;61(9):1176–1186. doi: 10.1364/josa.61.001176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. P., Kovar C. W. The effect of contour sharpness on perceived brightness. Vision Res. 1965 Oct;5(9):559–564. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(65)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolhurst D. J. On the possible existance of edge detector neurones in the human visual system. Vision Res. 1972 May;12(5):797–804. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(72)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


