Abstract
1. In the halothane anaesthetized baboon the threshold for cortically elicited primary and secondary spindle afferent discharge was compared to the threshold at the `best point' for a cortically elicited tibialis anticus tension change.
2. The cortical threshold for eliciting a tension change was greater than the cortical threshold for eliciting spindle afferent discharge for some afferents and less for other afferents.
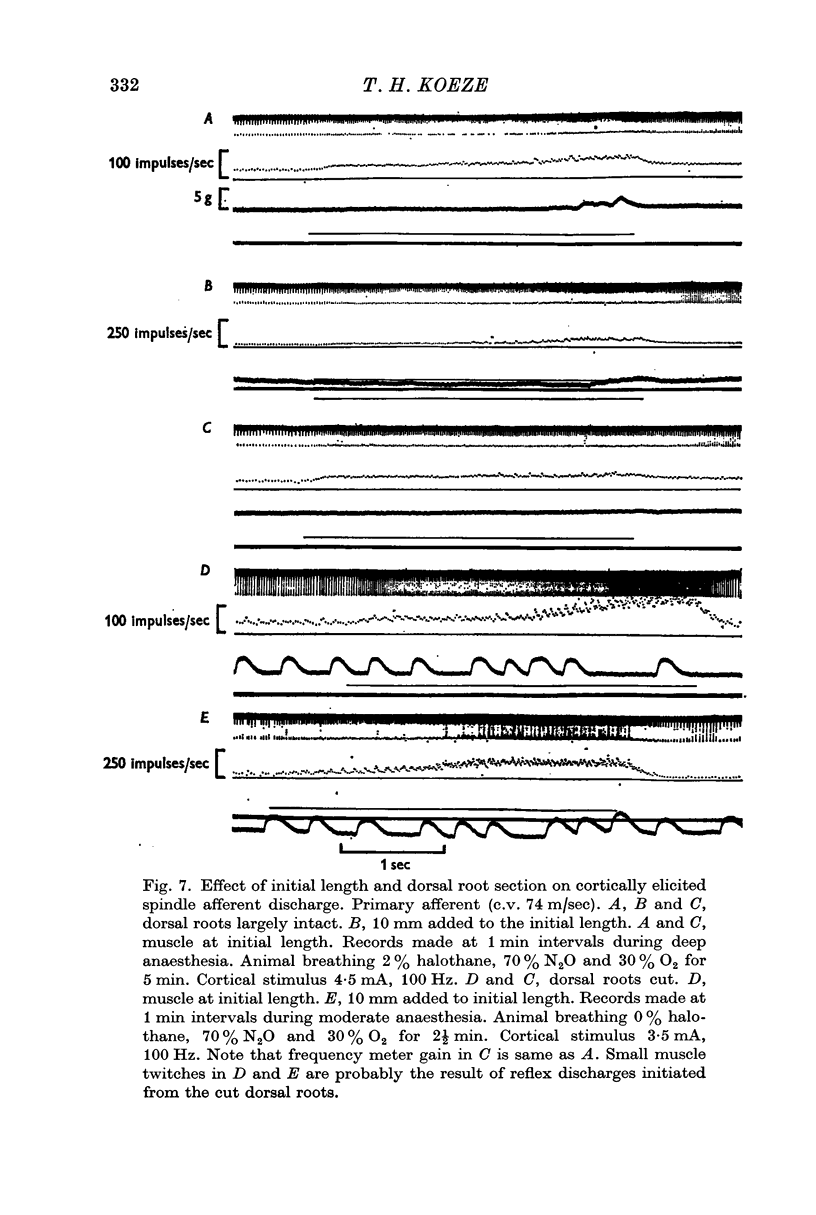
3. The pattern of cortically elicited spindle afferent discharge during muscle stretch suggested static γ-motoneurone activation. No convincing evidence of dynamic γ-motoneurone activation was seen.
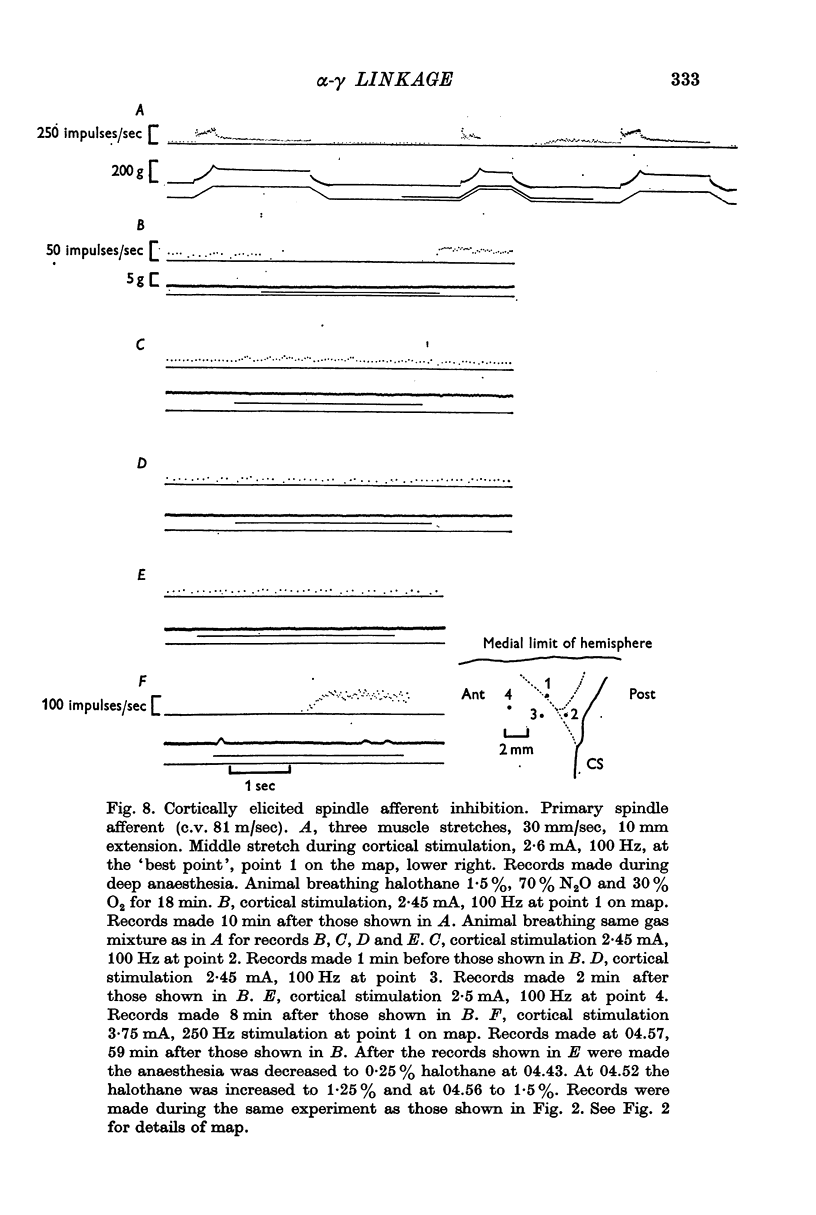
4. Inhibition of spindle afferent discharge was occasionally found and the `best point' was the same as the cortical `best point' for eliciting monosynaptic α-motoneurone activity. This result suggested that the cortical projections which inhibit the pre-existent activity of static γ-motoneurones are in a close anatomical relation to those cortical projections which elicit activity of α- and static γ-motoneurones.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALNAES E., JANSEN J. K., RUDJORD T. FUSIMOTOR ACTIVITY IN THE SPINAL CAT. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Mar;63:197–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Bessou P., Laporte Y. Action of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres on secondary endings of cat's spindles. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):160–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Pagès B. Spindle secondary ending responses elicited by stimulation of static fusimotor axons. J Physiol. 1969 Jun;202(3):569–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidone S. J., Preston J. B. Patterns of motor cortex control of flexor and extensor cat fusimotor neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Mar;32(2):103–115. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KAADA B. R. Influence of stimulation of central nervous structures on muscle spindles in cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;27(2-3):130–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigg P., Preston J. B. Baboon flexor and extensor fusimotor neurons and their modulation by motor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1971 May;34(3):428–436. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.3.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERN J. E., LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Selective excitation of corticofugal neurones by surface-anodal stimulation of the baboon's motor cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:73–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeze T. H. Muscle spindle afferent studies in the baboon. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):297–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeze T. H., Phillips C. G., Sheridan J. D. Thresholds of cortical activation of muslce spindles and alpha motoneurones of the baboon's hand. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):419–449. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeze T. H. The independence of corticomotoneuronal and fusimotor pathways in the production of muscle contraction by motor cortex stimulation. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(1):87–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Cortical fields of origin of the monosynaptic pyramidal pathways to some alpha motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:112–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Minimal synaptic actions of pyramidal impulses on some alpha motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:91–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON J. B., WHITLOCK D. G. Intracellular potentials recorded from motoneurons following precentral gyrus stimulation in primate. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Jan;24:91–100. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON J. B., WHITLOCK D. G. Precentral facilitation and inhibition of spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1960 Mar;23:154–170. doi: 10.1152/jn.1960.23.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara N., Fuller D. R., Brooks V. B. Collateral pyramidal influences on the corticorubrospinal system. J Neurophysiol. 1968 May;31(3):467–484. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.3.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedel J. P. Mise en évidence d'un contrôle cortical de l'activité des fibres fusimotrices dynamiques chez le chat par la voie pyramidale. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1966 Feb 21;262(8):908–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedel J. P., Mouillac-Baudevin J. Contrôle pyramidal de l'activité des fibres fusimotrices dynamiques et statiques chez le chat. Exp Brain Res. 1970;10(1):39–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00340518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Voorhoeve P. E. Pyramidal control of fusimotor neurons supplying extensor muscles in the cat's forelimb. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):96–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00238324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


