Abstract
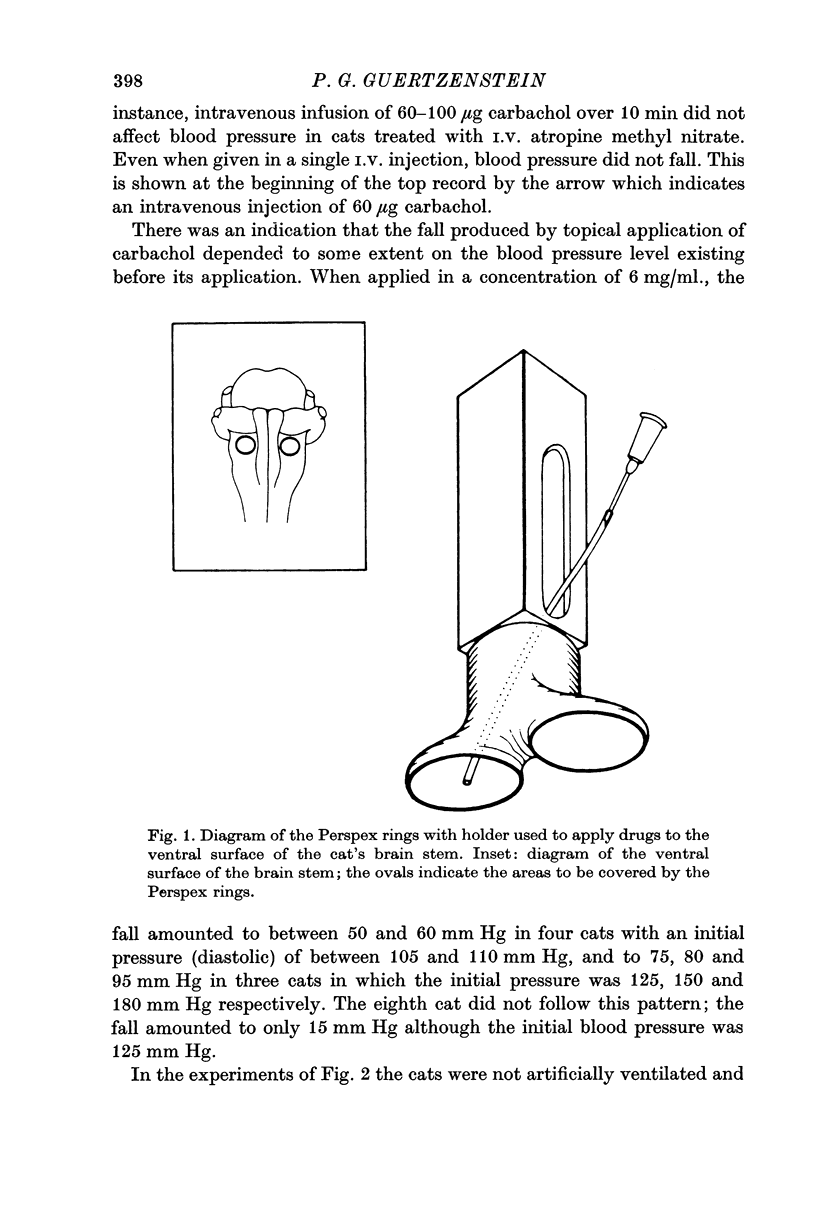
1. In cats anaesthetized with pentobarbitone sodium the effect on arterial blood pressure was examined of substances applied bilaterally to the exposed ventral surface of the brain stem by means of Perspex rings placed lateral to the pyramids and caudal to the trapezoid bodies. Routinely, atropine methyl nitrate, which does not pass the blood—brain barrier, was injected I.V.
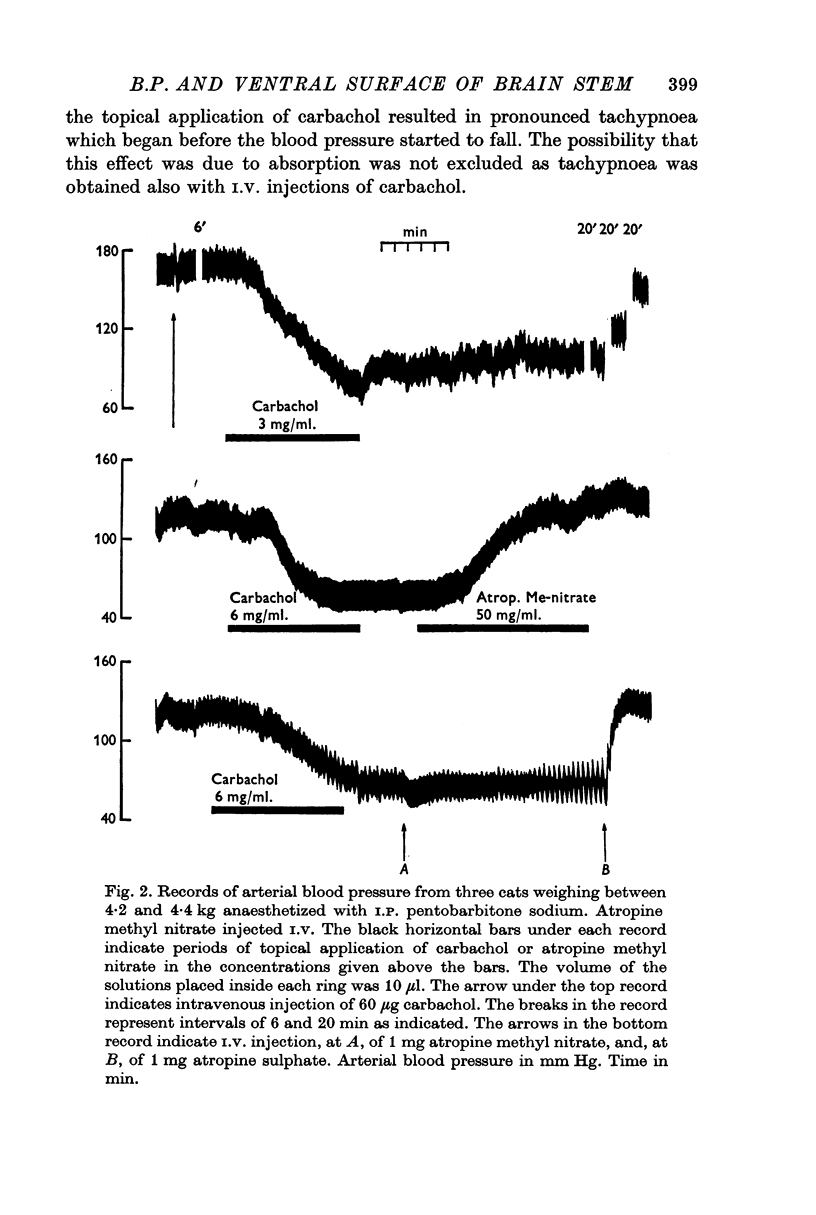
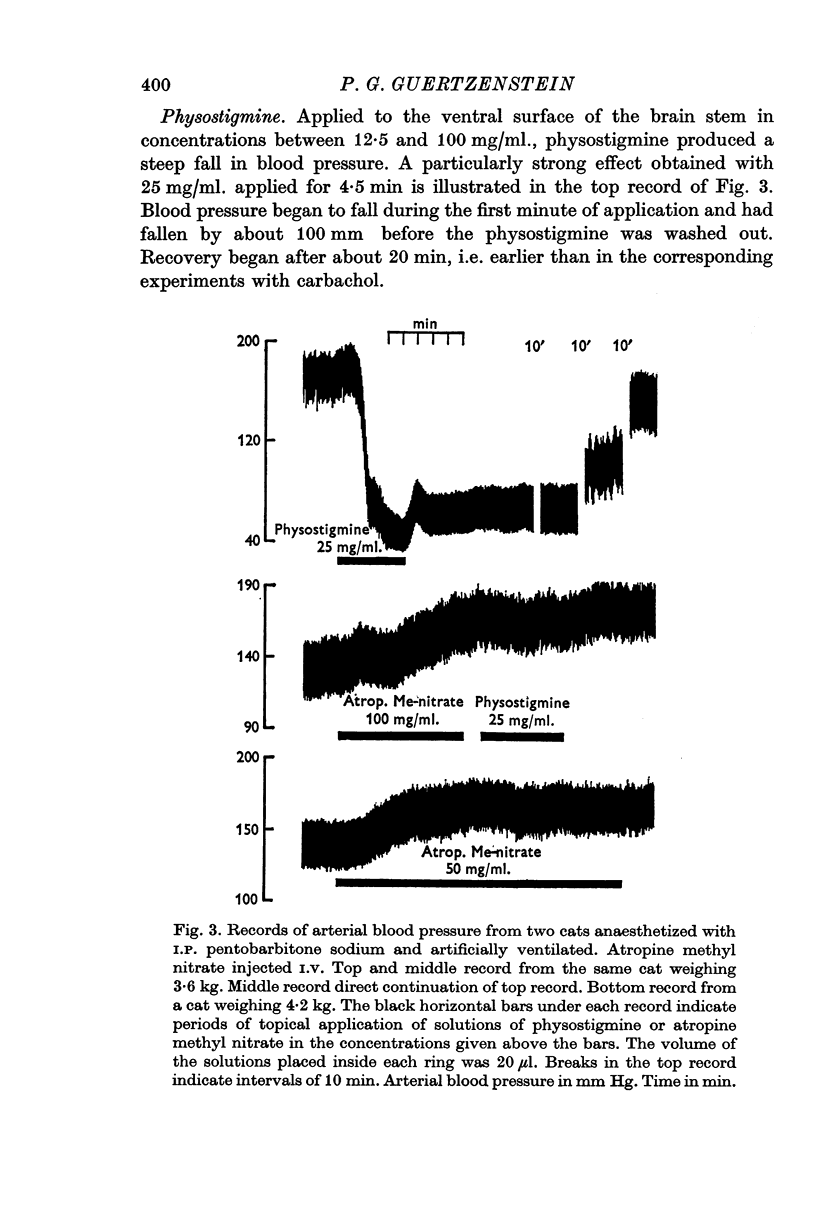
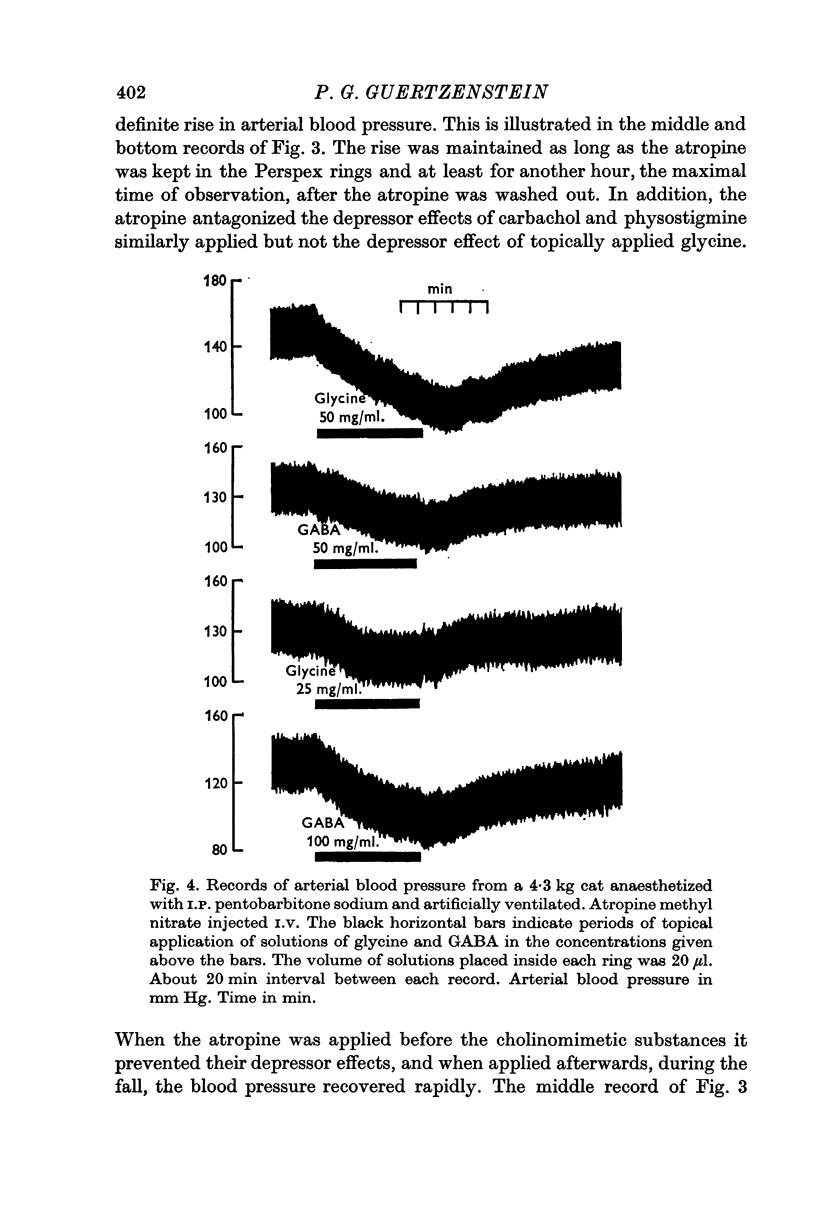
2. The cholinomimetic substances carbachol and physostigmine, and the amino acids glycine and GABA, caused a fall in arterial blood pressure.
3. Atropine produced a small but definite rise in arterial blood pressure, antagonized the depressor effects of the cholinomimetic substances, but not those of the amino acids.
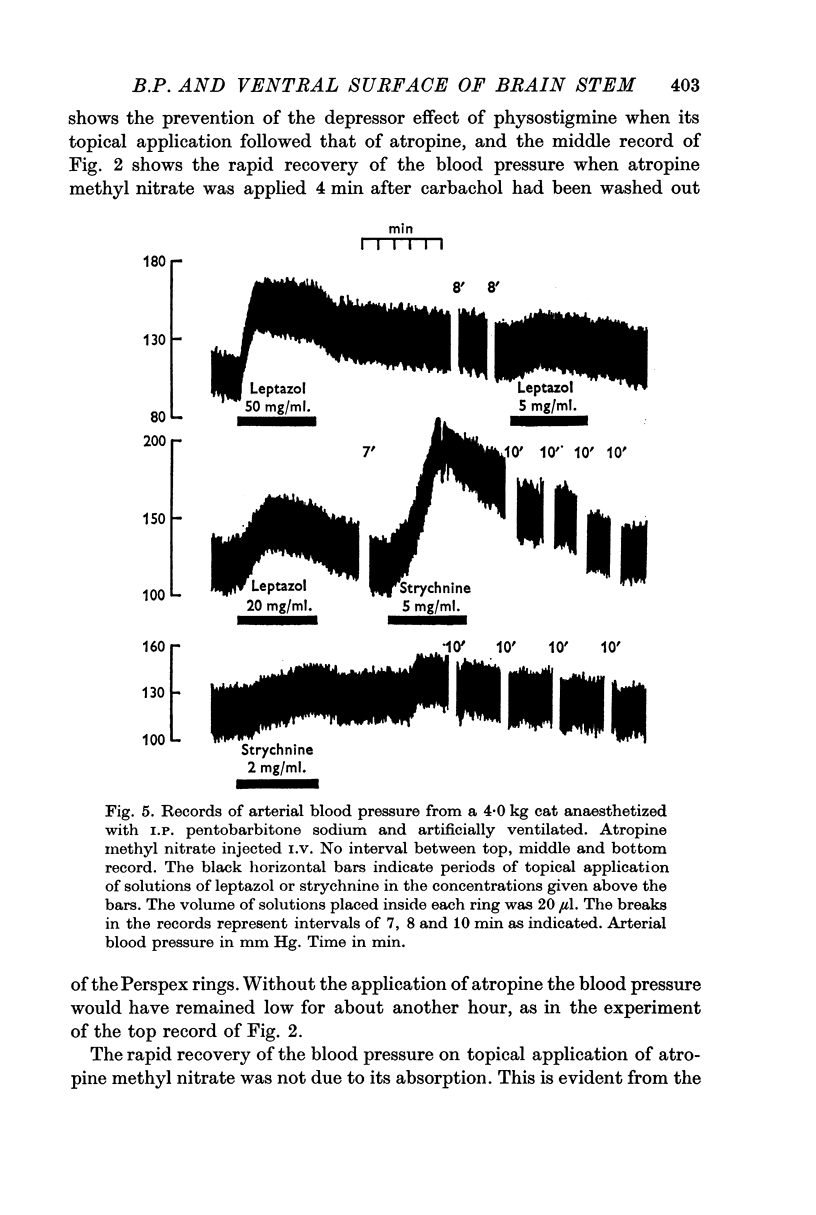
4. Strychnine, leptazol and tubocurarine, caused a rise in arterial blood pressure.
5. The depressor and pressor effects are due to changes in vasomotor tone. They are central effects brought about by penetration of the substances into the brain tissue from the ventral surface of the brain stem. They are not due to their absorption into the blood stream.
6. The depressor effects of the cholinomimetic substances may imitate the action of cholinergic neurones, and those of the amino acids that of central inhibitory neurones ending on cells near the ventral surface of the brain stem and exerting an inhibitory influence on vasomotor tone. The pressor effects of strychnine and tubocurarine may in part result from `disinhibition', i.e. from an antagonistic action produced by these drugs on the amino acids released from the central inhibitory neurones.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage A. K., Hall G. H. Further evidence relating to the mode of action of nicotine in the central nervous system. Nature. 1967 Jun 3;214(5092):977–979. doi: 10.1038/214977a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee U., Feldberg W., Georgiev V. P. Microinjections of tubocurarine, leptazol, strychnine and picrotoxin into the cerebral cortex of anaesthetized cats. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Sep;40(1):6–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobbin R. P., Guth P. S. Evidence that gamma-aninobutyric acid is not the inhibitory transmitter at the crossed olivocochlear nerve-hair cell junction. Neuropharmacology. 1970 Nov;9(6):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(70)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Dhawan B. N., Wolstencroft J. H. Pharmacological properties of cholinoceptive neurones in the medulla and pons of the cat. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):658–674. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., FLEISCHAUER K. Scratching movements evoked by drugs applied to the upper cervical cord. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:502–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., FLEISCHHAUER K. The site of origin of the seizure discharge produced by tubocurarine acting from the cerebral ventricles. J Physiol. 1962 Feb;160:258–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Guertzenstein P. G. A vasodepressor effect of pentobarbitone sodium. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):83–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guertzenstein P. G. Vasodepressor and pressor responses to drugs topically applied to the ventral surface of the brain stem. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):84P–85P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. G., Katzman R. K 42 distribution in brain during simultaneous ventriculocisternal and subarachnoid perfusion. Brain Res. 1972 Mar 10;38(1):49–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90589-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovický P. Uber die Glia marginalis und oberglächliche Nervenzellen im Hirmstamm der Katze. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1968 Nov 4;127(3):221–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., York D. H. Pharmacological studies on a cholinergic inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1968 Sep;10(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., York D. H. Strychnine block of neural and drug-induced inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):922–923. doi: 10.1038/216922a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


