Abstract
1. Sacs 20 cm long were obtained from the upper half of the small intestine of bile fistula rats (bile duct cannulated 48 hours previously). The sacs were everted, filled with oxygenated phosphate buffer and incubated 1 hr at 37° C in 25 ml. of a buffered micellar solution of oleic acid (0·6 mM), mono-olein (0·3 mM), sodium taurocholate (4·8 mM) and 3H-labelled cholesterol (0·15 mM) plus glucose (28 mM).
2. After incubation the amount of [3H]cholesterol taken up by the mucosal tissue was measured. It averaged 200 n-mole/hr.g tissue wet wt. ± 6 (S.E.).
3. Adding 3 ml. whole rate bile with other factors unchanged caused cholesterol uptake to decrease by 50% in confirmation of previous studies.
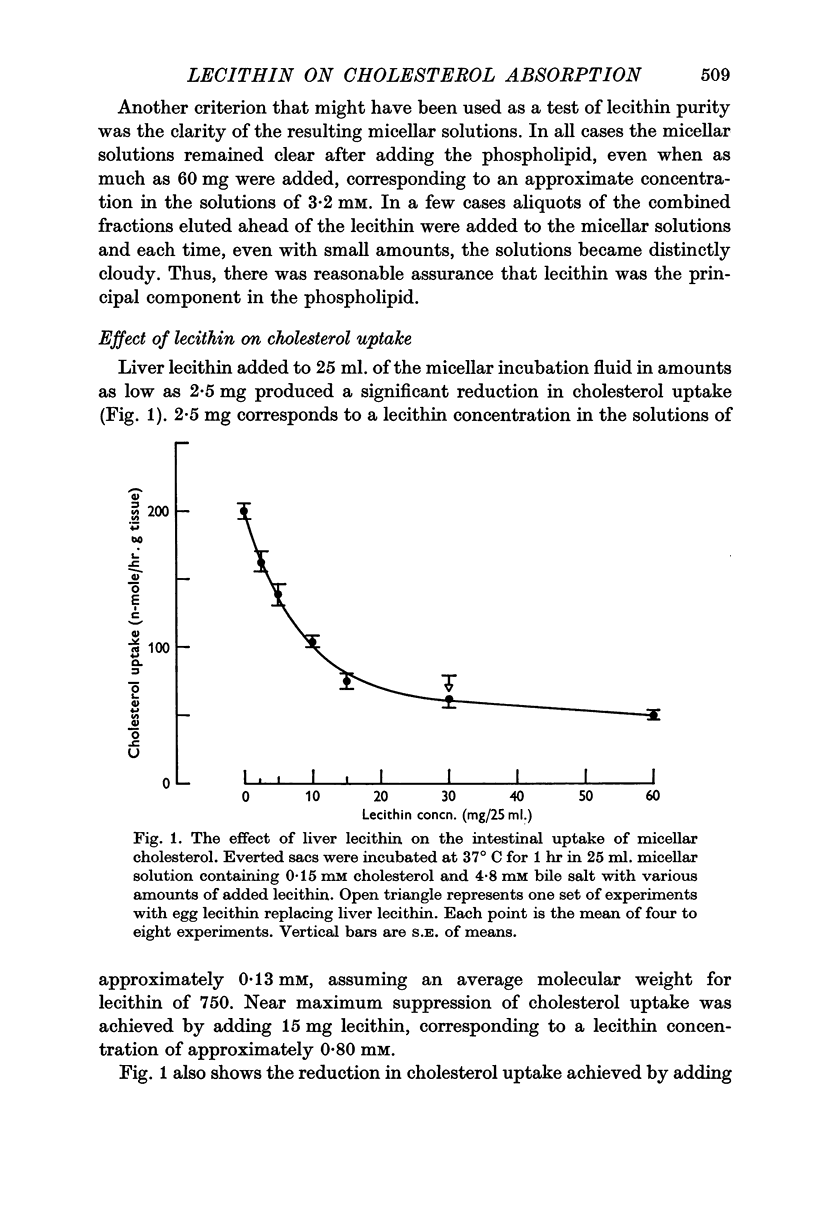
4. Adding purified lecithin obtained from rat liver tissue, and from egg yolks, similarly decreased cholesterol uptake. A significant response was obtained with 2·5 mg liver lecithin (concentration 0·13 mM) and a near maximum response with 15 mg (concentration 0·80 mM). 10 mg lecithin decreased uptake by an amount equivalent to that obtained with 3 ml. whole bile.
5. Lecithin is an active component of whole bile causing reduced intestinal cholesterol uptake from micelles.
6. The decreased uptake of cholesterol in the presence of lecithin may have been the result of expansion of the cholesterol-containing micelles with consequent reduction in cholesterol permeability.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucrot P. Is there an entero-hepatic circulation of the bile phospholipids? Lipids. 1972 May;7(5):282–288. doi: 10.1007/BF02532645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgès M., Small D. M., Dervichian D. G. Biophysics of lipid associations. 3. The quaternary systems lecithin-bile salt-cholesterol-water. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):189–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O., SHIBATA E. Observations concerning the production and excretion of cholesterol in mammals. X. Factors affecting the absorption and fate of ingested cholesterol. J Exp Med. 1953 Aug;98(2):107–117. doi: 10.1084/jem.98.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A. C., Schulman J. H., Stewart H. C. Emulsification of fat in the intestine of the rat and its relationship to absorption. J Physiol. 1944 Dec 15;103(3):306–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1944.sp004079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J., AHRENS E. H., Jr The separation of complex lipide mixtures by the use of silicic acid chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):311–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., BORGSTROEM B. THE INTRALUMINAL PHASE OF FAT DIGESTION IN MAN: THE LIPID CONTENT OF THE MICELLAR AND OIL PHASES OF INTESTINAL CONTENT OBTAINED DURING FAT DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION. J Clin Invest. 1964 Feb;43:247–257. doi: 10.1172/JCI104909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., BORGSTROM B. Physico-chemical state of lipids in intestinal content during their digestion and absorption. Fed Proc. 1962 Jan-Feb;21:43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison F. A., Leat W. M. Adsorption of palmitic, stearic and oleic acids in the sheep in the presence or absence of bile and-or pancreatic juice. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(3):565–576. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E. The relationship between uptake in vitro of oleic acid and micellar solubilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. A physicochemical approach to the intraluminal phase of fat absorption. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jan;50(1):56–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAKSSON B. On the dissolving power of lecithin and bile salts for cholesterol in human bladder bile. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1954 Sep 30;59(5-6):296–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVY A. C., SUZUKI R., RAM PRASAD C. Obligatory function of a continuous flow of normal bile for cholesterol absorption. Am J Physiol. 1958 Jun;193(3):521–524. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON J. M., BORGSTROEM B. THE INTESTINAL ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF MICELLAR SOLUTIONS OF LIPIDS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 5;84:412–423. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz I., Keeney M. The lipids of some rumen holotrich protozoa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 8;144(1):102–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAYAMA F., MIYAKE H. CHOLESTEROL COMPLEXING BY MACROMOLECULAR FRACTIONS IN HUMAN GALL BLADDER BILE. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Apr;65:638–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiderhiser D. H., Roth H. P., Webster L. T., Jr Studies on the importance of lecithin for cholesterol solubilization in bile. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jul;68(1):90–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampone A. J. Bile salt and non-bile salt components in bile affecting micellar cholesterol uptake by rat intestine in vitro. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):889–898. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampone A. J. Studies on micellar fatty acid uptake by rat intestine in vitro with reference to the role of bile. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):495–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampone A. J. The effects of bile salt and raw bile on the intestinal absorption of micellar fatty acid in the rat in vitro. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):679–690. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIPERSTEIN M. D., CHAIKOFF I. L., REINHARDT W. O. C14-Cholesterol. V. Obligatory function of bile in intestinal absorption of cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPITZER H. L., KYRIAKIDES E. C., BALINT J. A. BILIARY PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN VARIOUS SPECIES. Nature. 1964 Oct 17;204:288–288. doi: 10.1038/204288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWELL L., TROUT E. C., Jr, HOPPER J. R., FIELD H., Jr, TREADWELL C. R. Specific function of bile salts in cholesterol absorption. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 May;98(1):174–176. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-23979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THUREBORN E. A water-soluble lipid complex obtained in the macromolecular phase by gel-filtration of human bile. Nature. 1963 Mar 30;197:1301–1302. doi: 10.1038/1971301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAHOUNY G. V., BORJA C. R., TREADWELL C. R. ABSORPTION AND ESTERIFICATION OF MICELLAR FREE AND ESTERIFIED CHOLESTEROL-4-C14. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:440–446. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER H., HOERHAMMER L., WOLFF P. [Thin layer chromatography of phosphatides and glycolipids]. Biochem Z. 1961;334:175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


