Abstract
1. In dogs under chloralose-urethane anaesthesia the submaxillary duct was cannulated and connected either to an open outflow system, in which saliva displaced water, or to a closed pressure recording system.
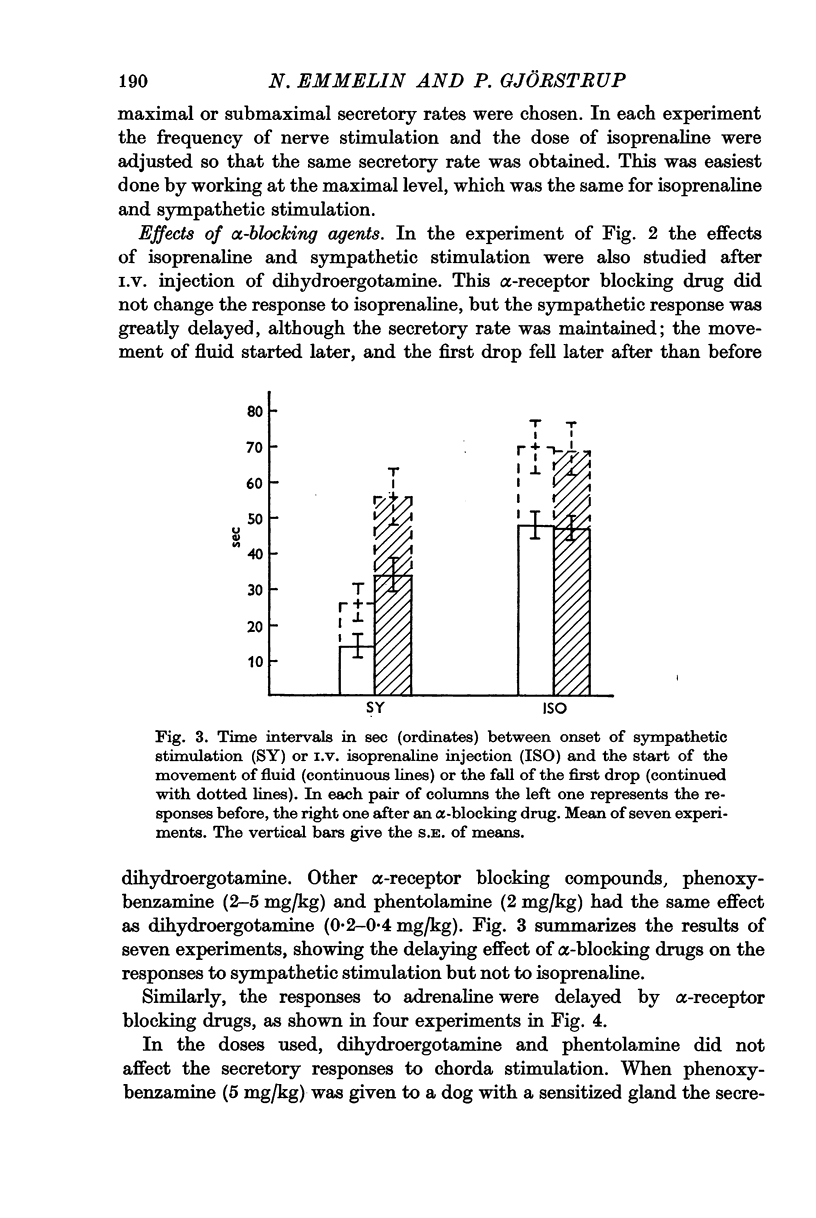
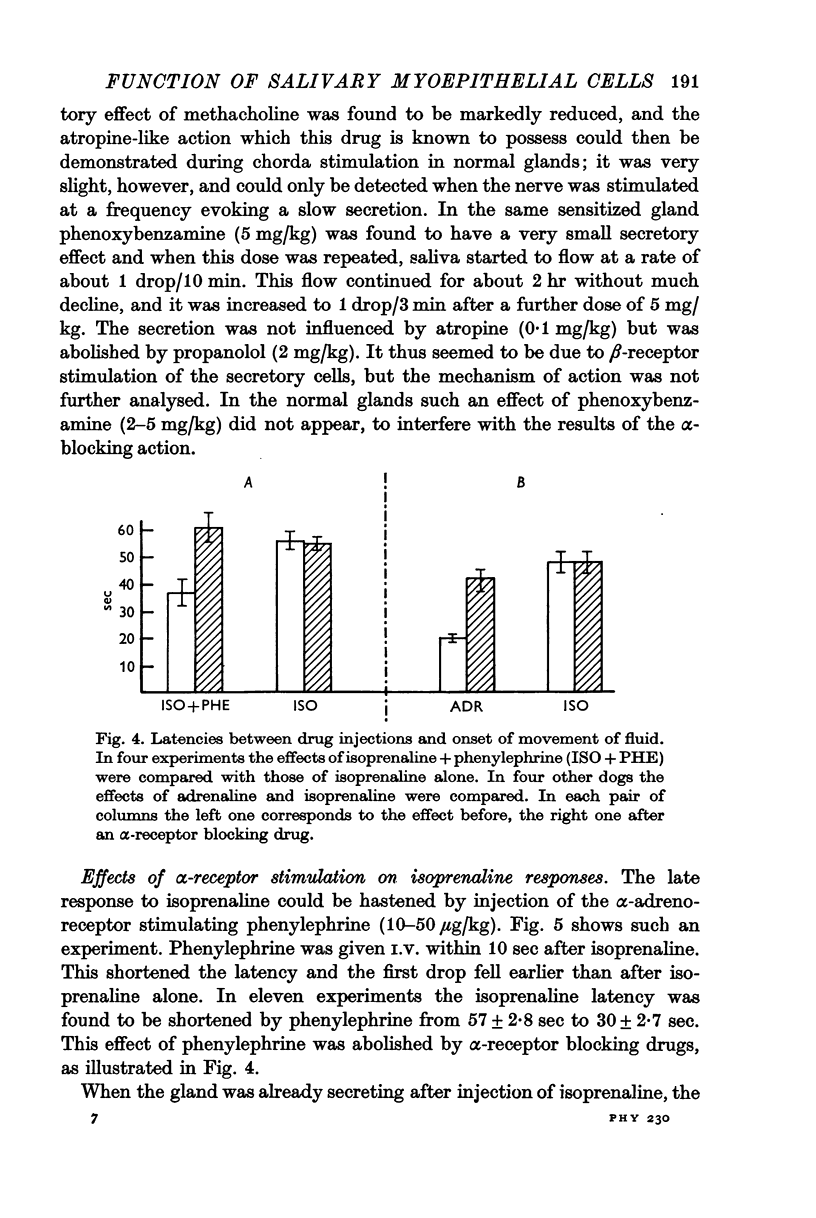
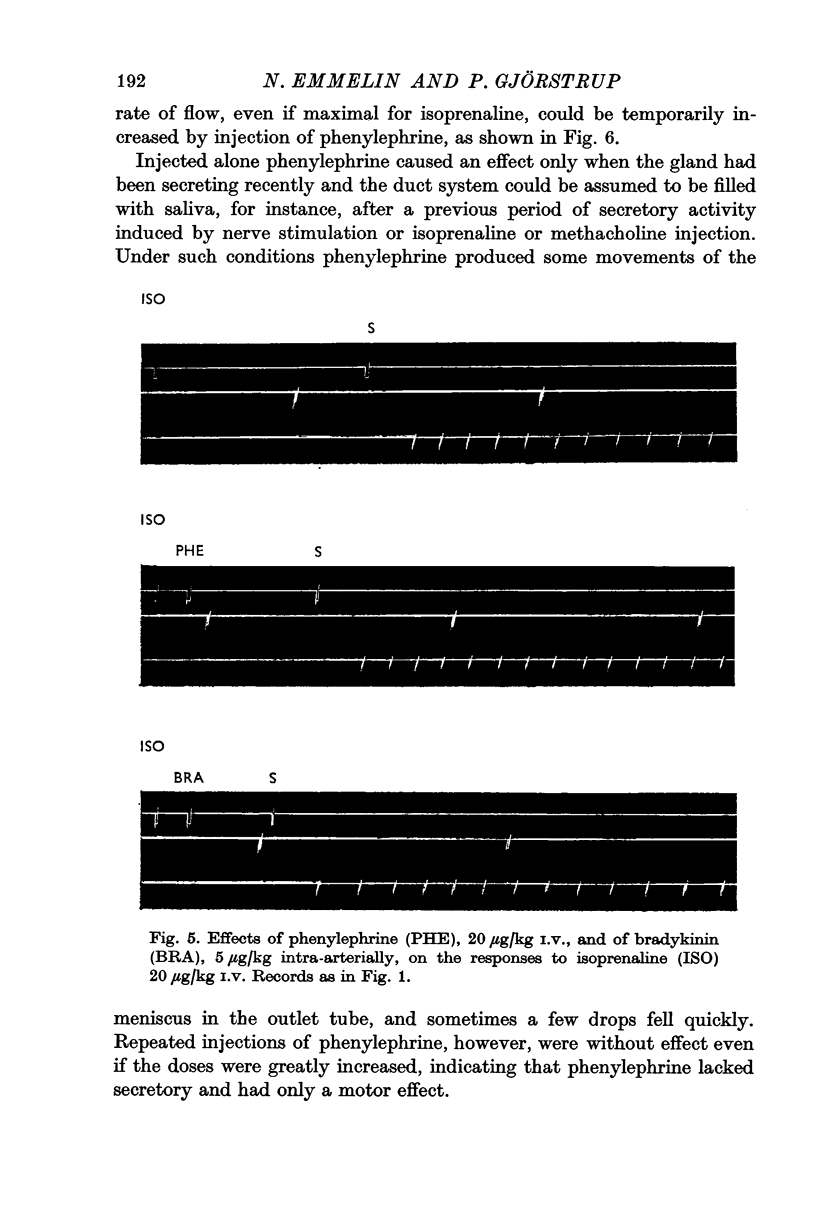
2. The secretory cells, which are supplied with β-adrenoreceptors, were stimulated with isoprenaline, adrenaline or sympathetic nerve stimulation. Myoepithelial cells, supplied with α-receptors, were activated with phenylephrine, adrenaline or sympathetic stimulation, and also with bradykinin. To abolish α-receptor stimulating effects of adrenaline and sympathetic nerve stimulation, dihydroergotamine, phenoxybenzamine and phentolamine were used.
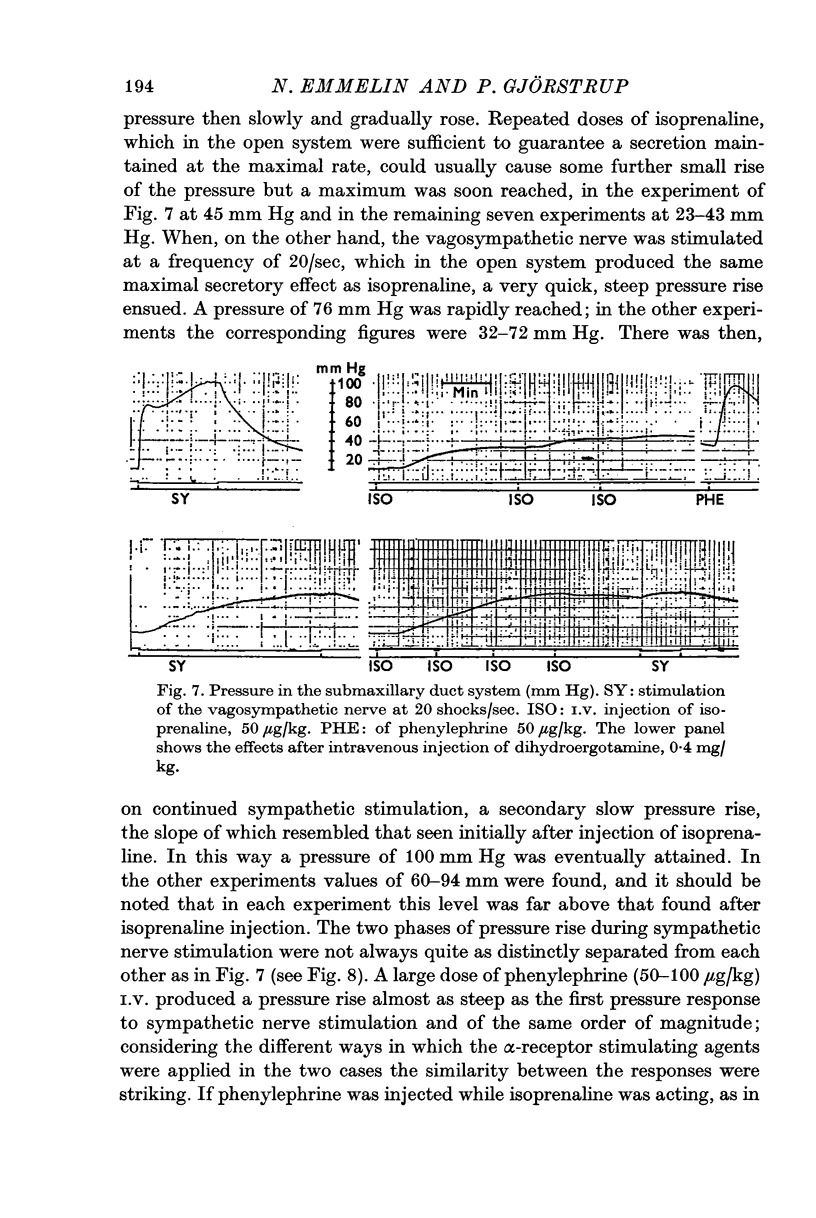
3. When the secretory cells were activated alone, saliva flowed from the salivary duct, but the flow started late and only a moderately high pressure could be produced in the closed system. Saliva appeared much earlier in the duct when secretion was combined with myoepithelial contraction, and a much higher pressure could be built up in the duct system.
4. It is concluded that rapid emptying of saliva in the mouth and a maintained flow at a high rate of the viscous saliva is promoted by contractions of the myoepithelial cells.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Emmelin N., Lenninger S. The "direct" effect of physalaemin on salivary gland cells. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Aug;30(3):676–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02174.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmelin N., Ohlin P., Thulin A. The pharmacology of salivary myoepithelial cells in dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Nov;37(3):666–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


