Abstract
1. A permeability barrier in or around the seminiferous tubules of rams has been demonstrated by studying the rate of passage of a variety of substances from blood plasma into fluid collected from the rete testis and into testicular lymph.
2. All substances studied passed readily into testicular lymph.
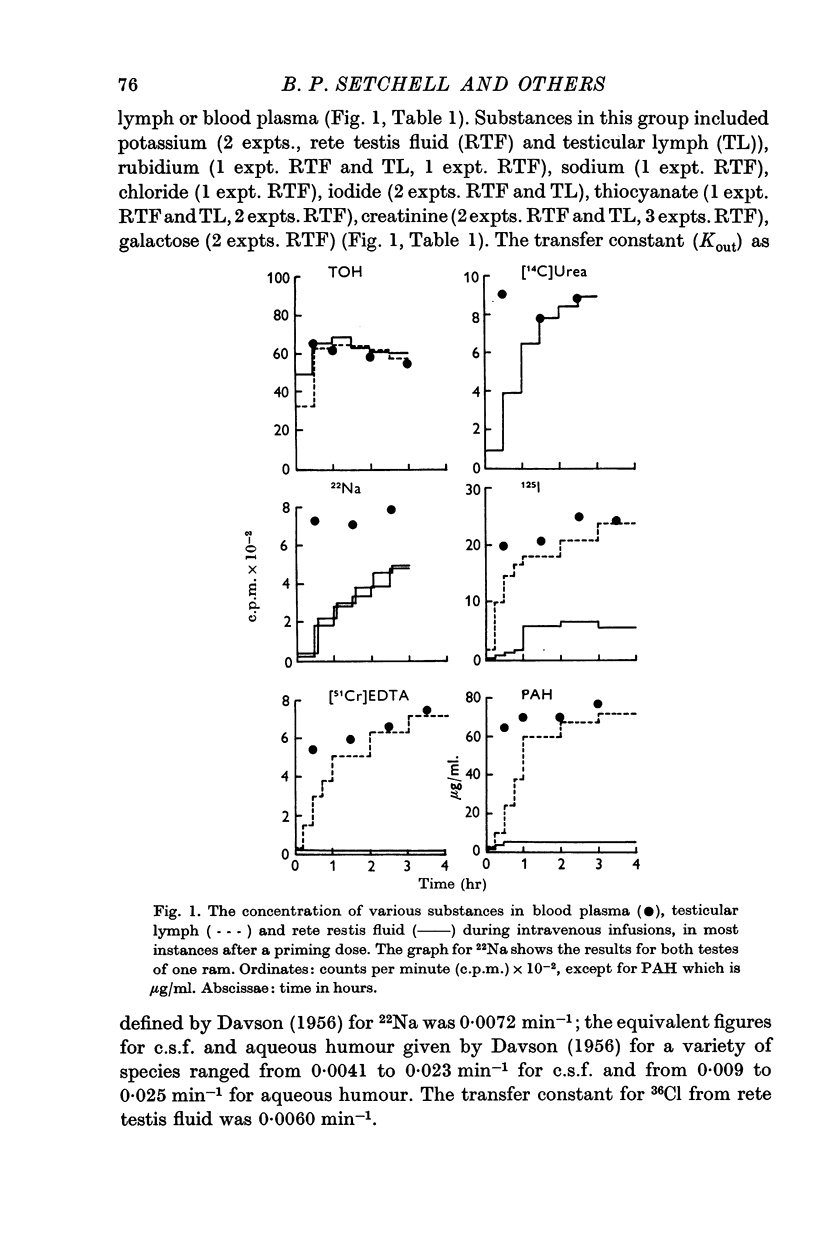
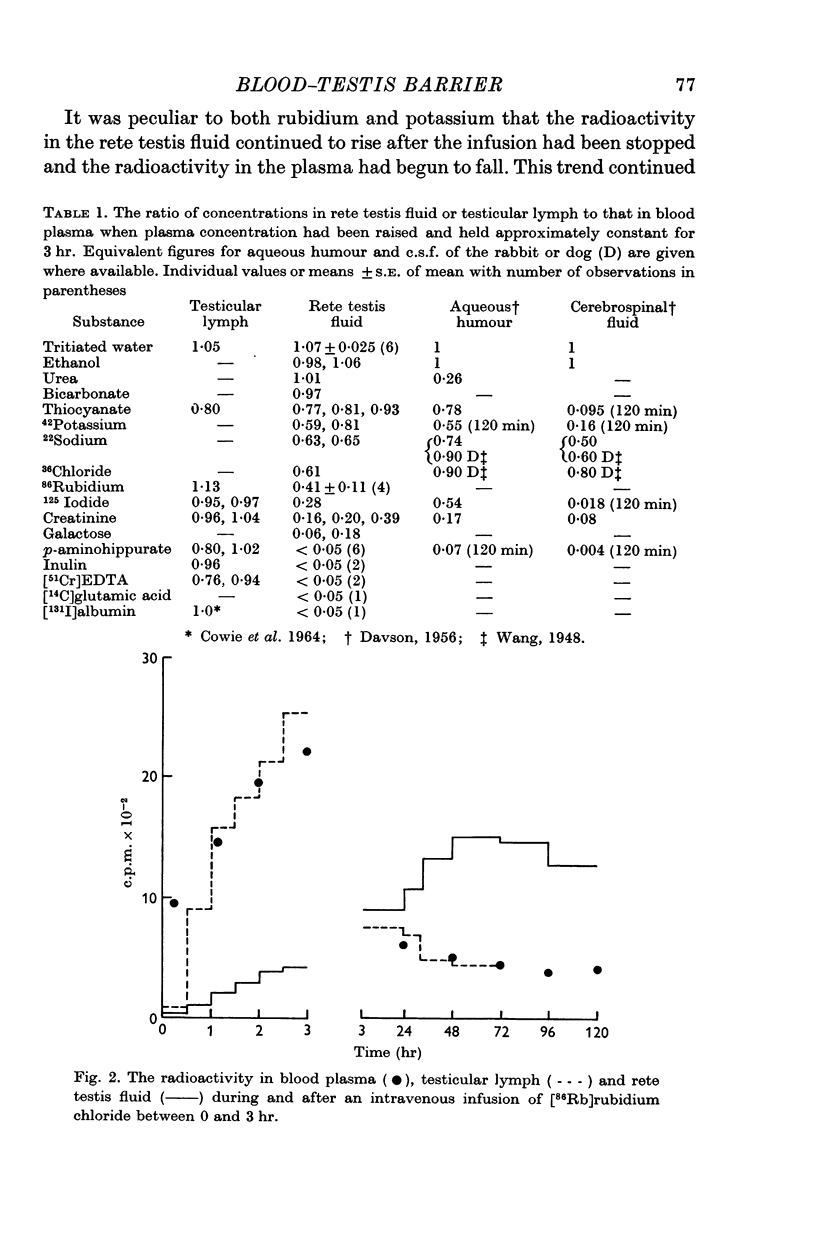
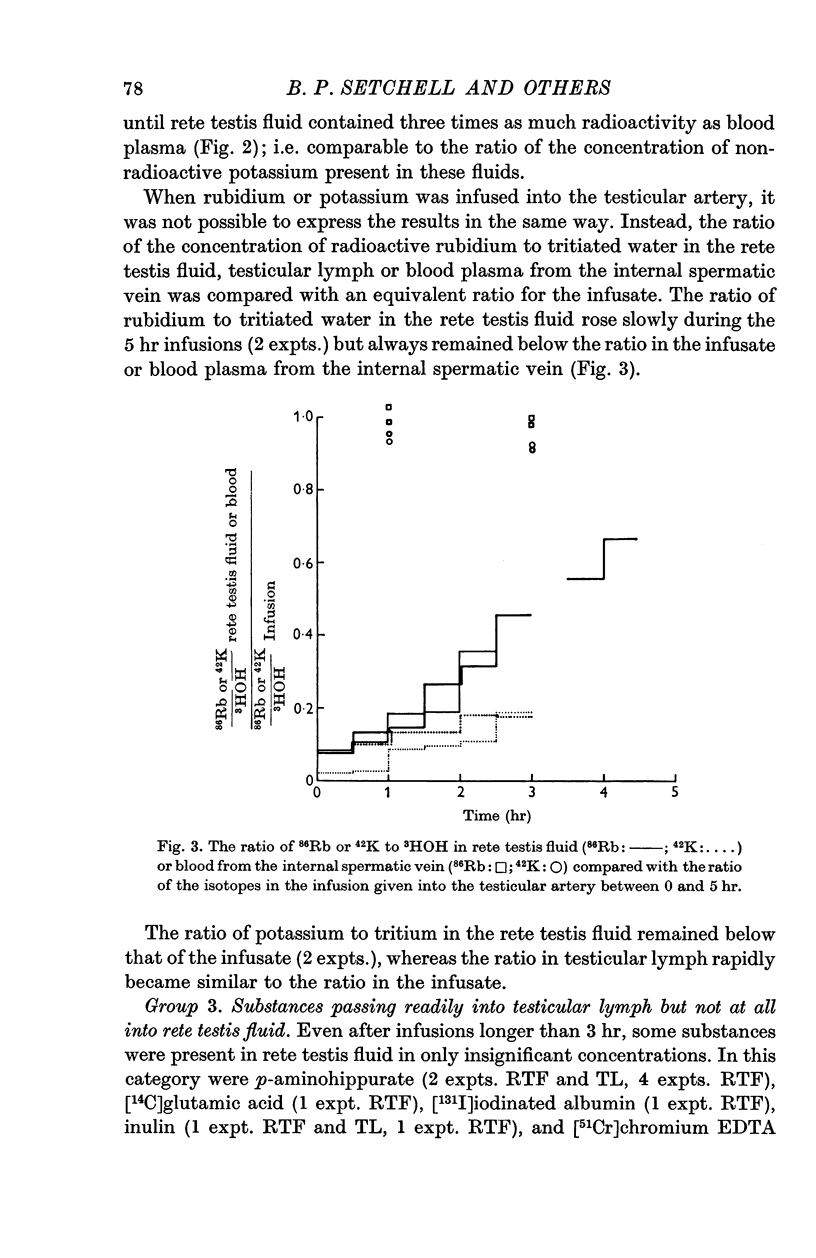
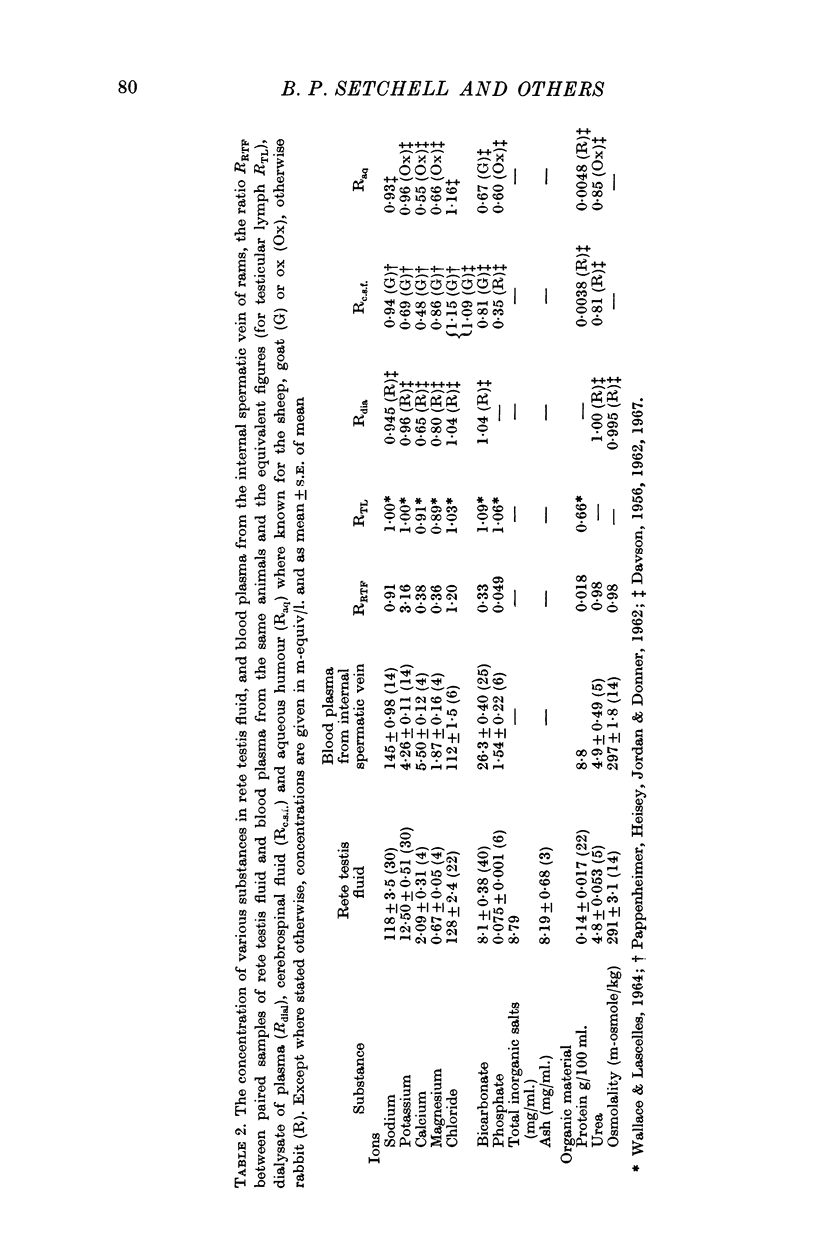
3. Tritiated water, urea, ethanol and bicarbonate in rete testis fluid equilibrated with blood plasma within 3 hr; Na+, K+, Rb+, Cl-, I-, CNS-, creatinine and galactose entered slowly and p-aminohippurate (PAH), glutamate, iodinated albumin, inulin and [51Cr]EDTA did not appear in rete testis fluid at all.
4. Rubidium was excluded relative to iodoantipyrine from the testes of control and hypophysectomized rats and from rat testes heated to 37, 40, 43 and 45° C; no such exclusion was seen in testes of rats which had been given cadmium chloride 5 months earlier so as to destroy the seminiferous tubules.
5. It is suggested that this permeability barrier will regulate the access to the seminiferous epithelium of some constituents of blood plasma, isolate the germinal cells immunologically and help to maintain the concentration differences between rete testis fluid and lymph or blood plasma.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAWA S. R. FINE STRUCTURE OF THE SERTOLI CELL OF THE HUMAN TESTIS. J Ultrastruct Res. 1963 Dec;52:459–474. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(63)80078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROKELMANN J. Fine structure of germ cells and Sertoli cells during the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1963;59:820–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowler R. G. The determination of thiocyanate in blood serum. Biochem J. 1944;38(5):385–388. doi: 10.1042/bj0380385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLERMONT Y. Contractile elements in the limiting membrane of the seminiferous tubules of the rat. Exp Cell Res. 1958 Oct;15(2):438–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(58)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWIE A. T., LASCELLES A. K., WALLACE J. C. FLOW AND PROTEIN CONTENT OF TESTICULAR LYMPH IN CONSCIOUS RAMS. J Physiol. 1964 May;171:176–187. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRABO B. FINE STRUCTURE OF THE INTERSTITIAL CELLS OF THE RABBIT TESTES. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1963 Dec 3;61:587–604. doi: 10.1007/BF00344002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg E. J., Carr I. Changes in the blood vessels of the rat testis and epididymis produced by cadmium chloride. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):317–322. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVSON H. A comparative study of the aqueous humour and cerebrospinal fluid in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1955 Jul 28;129(1):111–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVSON H. THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID. Ergeb Physiol. 1963;52:20–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNES A. M., MCDONALD I. W. THE CHROMIUM-51 COMPLEX OF ETHYLENEDIAMINE TETRAACETIC ACID AS A SOLUBLE RUMEN MARKER. Br J Nutr. 1964;18:153–162. doi: 10.1079/bjn19640015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flickinger C., Fawcett D. W. The junctional specializations of Sertoli cells in the seminiferous epithelium. Anat Rec. 1967 Jun;158(2):207–221. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091580210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER P. J., HOLYOKE E. A. FINE STRUCTURE OF THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULE OF THE SWISS MOUSE. I. THE LIMITING MEMBRANE, SERTOLI CELL, SPERMATOGONIA, AND SPERMATOCYTES. Anat Rec. 1964 Dec;150:391–404. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091500407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDACRE R. J., SYLVEN B. A rapid method for studying tumour blood supply using systemic dyes. Nature. 1959 Jul 4;184:63–64. doi: 10.1038/184063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDACRE R. J., SYLVEN B. On the access of blood-borne dyes to various tumour regions. Br J Cancer. 1962 Jun;16:306–322. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1962.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARE R. S. Endogenous creatinine in serum and urine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 May;74(1):148–151. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-17837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGETT A. S., NIXON D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet. 1957 Aug 24;273(6991):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinks N. T., Mills S. C., Setchell B. P. A simple method for the determination of the specific activity of carbon dioxide in blood. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):551–553. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kormano M. Distribution of injected L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-dopa) in the adult rat testis and epididymis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Sep;71(1):125–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kormano M. Dye permeability and alkaline phosphatase activity of testicular capillaries in the postnatal rat. Histochemie. 1967;9(4):327–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00305816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kormano M. Penetration of intravenous trypan blue into the rat testis and epididymis. Acta Histochem. 1968;30(1):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACY D., ROTBLAT J. Study of normal and irradiated boundary tissue of the seminiferous tubules of the rat. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Oct;21:49–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEESON C. R., LEESON T. S. THE POSTNATAL DEVELOPMENT AND DIFFERENTIATION OF THE BOUNDARY TISSUE OF THE SEMINIFEROUS TUBULE OF THE RAT. Anat Rec. 1963 Oct;147:243–259. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091470208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy D. The seminiferous tubule in mammals. Endeavour. 1967 May;26(98):101–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANCINI R. E., VILAR O., ALVAREZ B., SEIGUER A. C. EXTRAVASCULAR AND INTRATUBULAR DIFFUSION OF LABELED SERUM PROTEINS IN THE RAT TESTIS. J Histochem Cytochem. 1965 May-Jun;13:376–385. doi: 10.1177/13.5.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am interstitiellen Gewebe des Rattenhodens, unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Leydigschen Zwischenzellen. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;72(2):139–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ro T. S., Busch H. Concentration of [14C]actinomycin D in various tissues following intravenous injection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 11;108(2):317–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. H., Long I. R. Contractile cells in human seminiferous tubules. Science. 1966 Sep 9;153(3741):1271–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3741.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. H. The fine structure and development of the peritubular contractile cell component in the seminiferous tubules of the mouse. Am J Anat. 1967 Nov;121(3):523–557. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT F. C. LICHT- UND ELEKTRONENMIKROSKOPISCHE UNTERSUCHUNGEN AM MENSCHLICHEN HODEN UND NEBENHODEN. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1964 Aug 18;63:707–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell B. P., Hinks N. T. The importance of glucose in the oxidative metabolism of the testis of the conscious ram and the role of the pentose cycle. Biochem J. 1967 Feb;102(2):623–630. doi: 10.1042/bj1020623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell B. P., Hinks N. T., Voglmayr J. K., Scott T. W. Amino acids in ram testicular fluid and semen and their metabolism by spermatozoa. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1061–1065. doi: 10.1042/bj1051061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacy B. D., Thorburn G. D. Chromium-51 ethylenediaminetetraacetate for estimation of globerular filtration rate. Science. 1966 May 20;152(3725):1076–1077. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3725.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voglmayr J. K., Scott T. W., Setchell B. P., Waites G. M. Metabolism of testicular spermatozoa and characteristics of testicular fluid collected from conscious rams. J Reprod Fertil. 1967 Aug;14(1):87–99. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0140087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voglmayr J. K., Waites G. M., Setchell B. P. Studies on spermatozoa and fluid collected directly from the testis of the conscious ram. Nature. 1966 May 21;210(5038):861–863. doi: 10.1038/210861b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE J. C., LASCELLES A. K. COMPOSITION OF TESTICULAR AND EPIDIDYMAL LYMPH IN THE RAM. J Reprod Fertil. 1964 Oct;8:235–242. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0080235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS L. A., LINN R. A., ZAK B. Determination of ethanol in fingertip quantities of blood. Clin Chim Acta. 1958 Mar;3(2):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(58)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waites G. M., Setchell B. P. Changes in blood flow and vascular permeability of the testis, epididymis and accessory reproductive organs of the rat after the administration of cadmium chloride. J Endocrinol. 1966 Mar;34(3):329–342. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0340329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Merker H. J. Ultrastruktur und Bildung von Poren im Endothel von porösen und geschlossenen Kapillaren. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;73(2):174–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZACHARIAE F. Studies on the mechanism of ovulation: permeability of the blood-liquor barrier. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1958 Mar;27(3):339–342. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0270339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de BRUYN P. P. H., ROBERTSON R. C., FARR R. S. In vivo affinity of diaminoacridines for nuclei. Anat Rec. 1950 Oct;108(2):279–307. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


