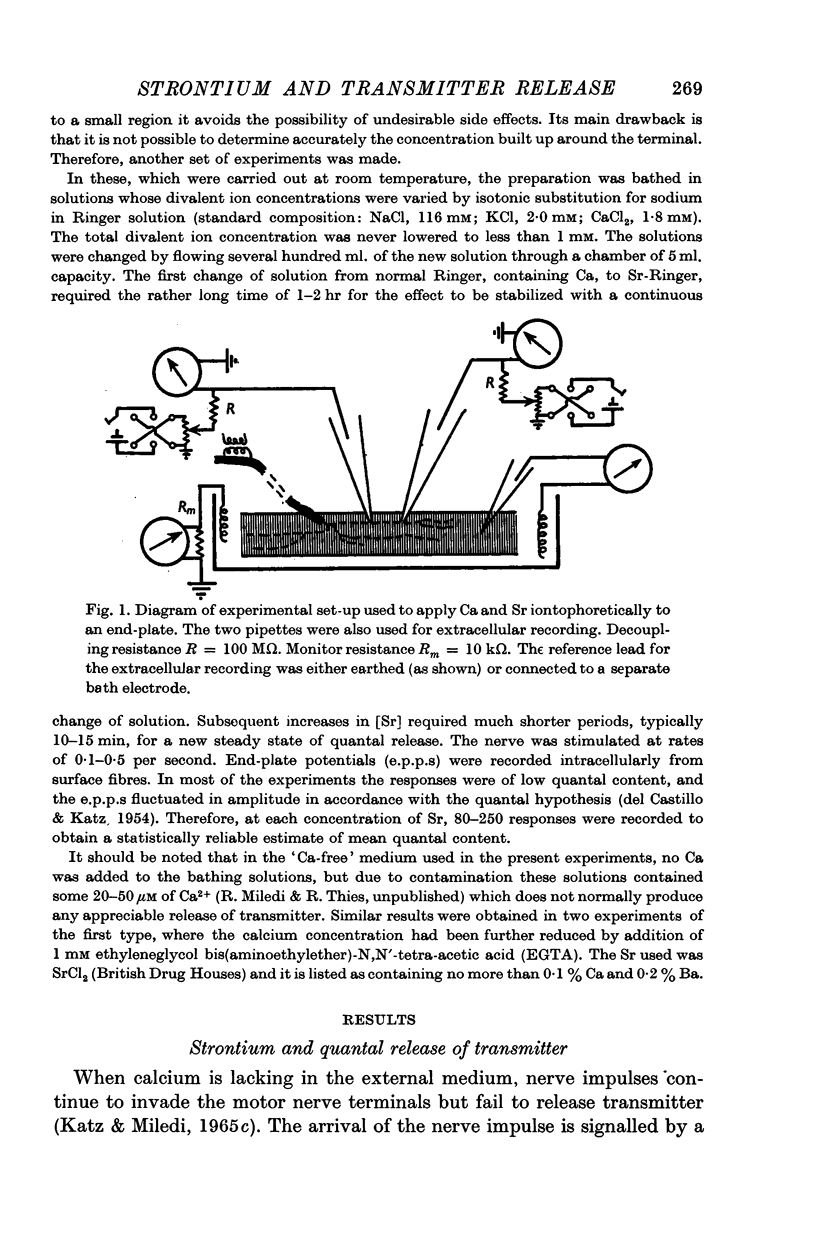
Abstract
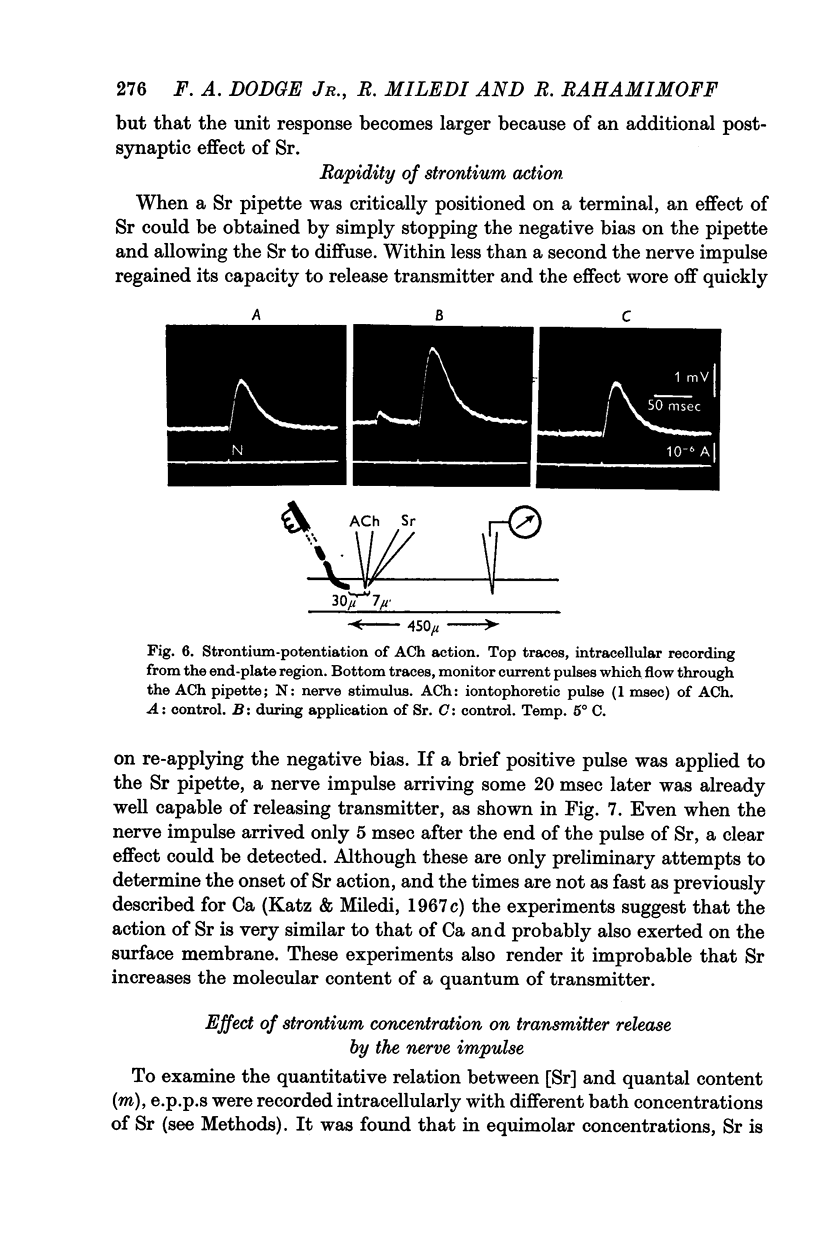
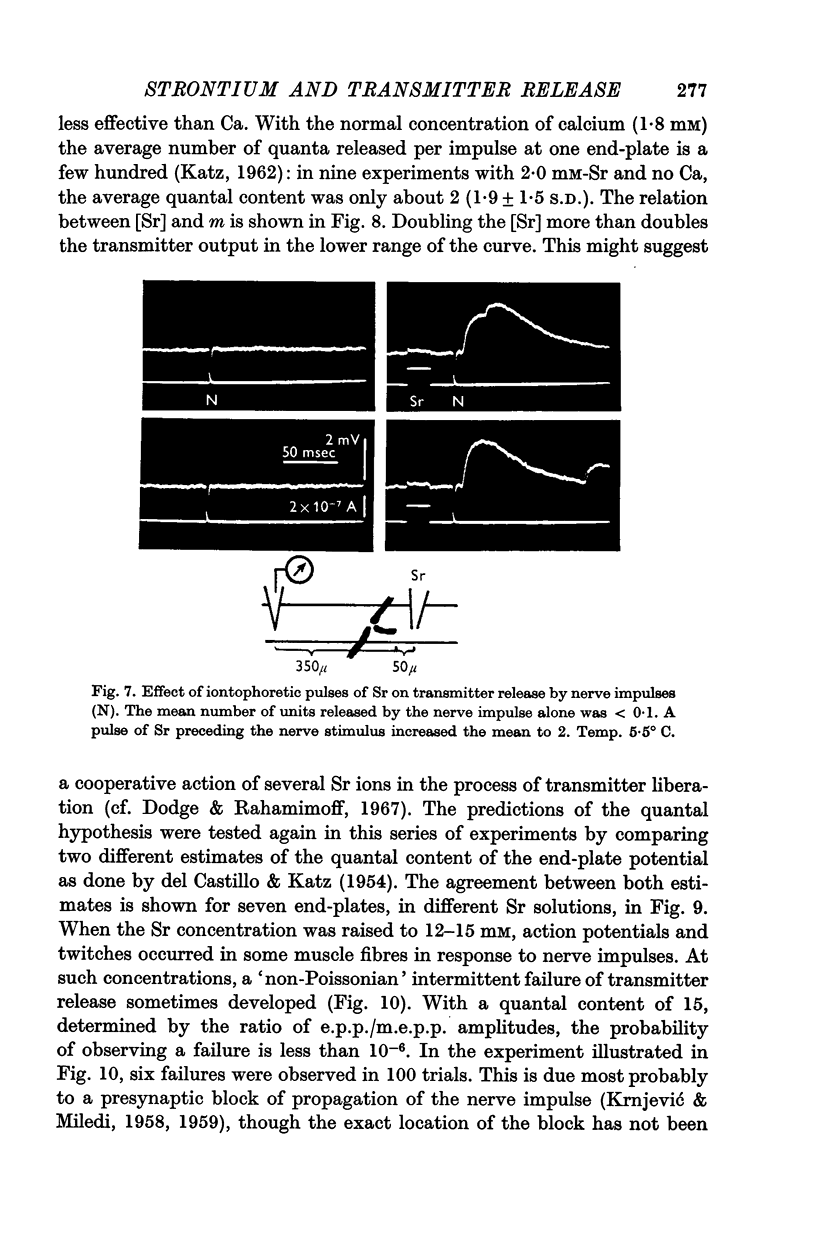
1. Previous work has shown that in calcium-free solutions nerve impulses invade the motor nerve terminals at the neuromuscular junction, but fail to release transmitter. In these conditions, strontium ions applied iontophoretically to a minute part of a junction, or to the whole muscle by bath application, restore to the nerve impulse its ability to release transmitter.
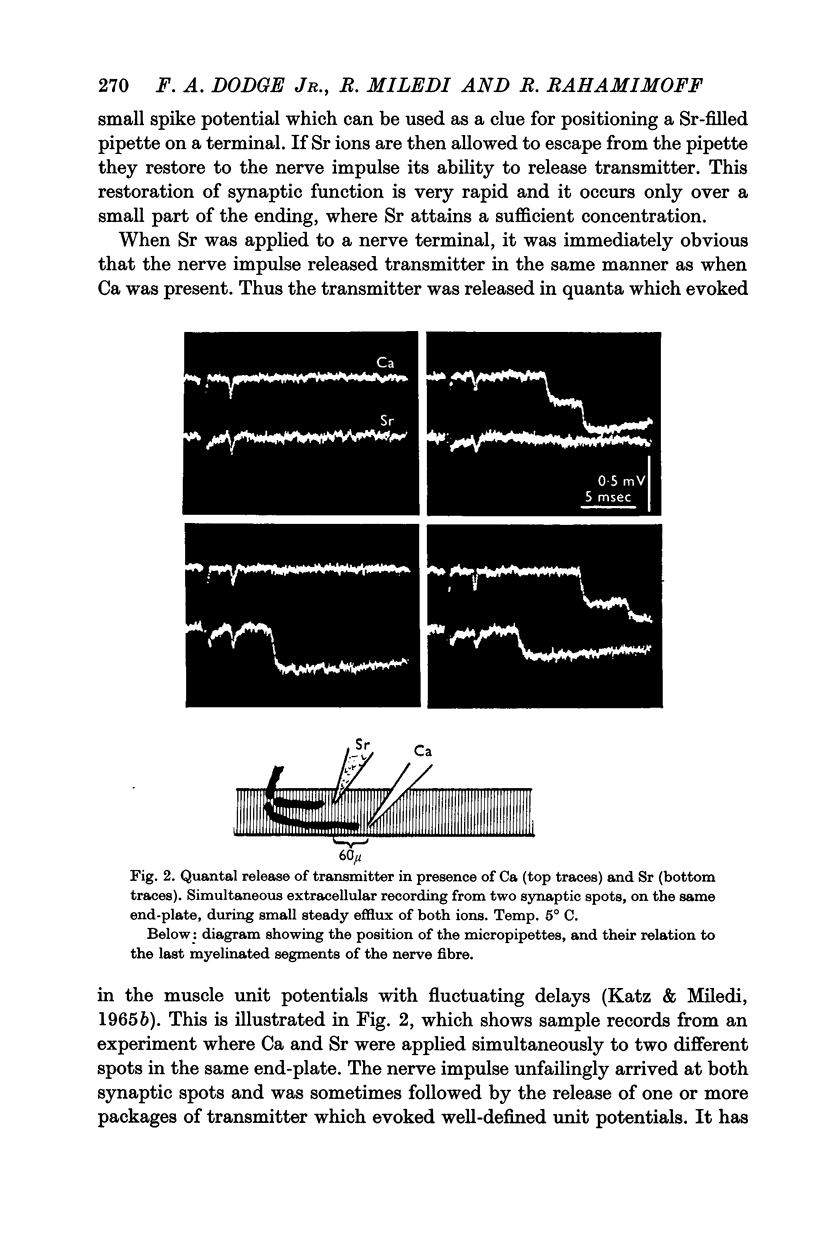
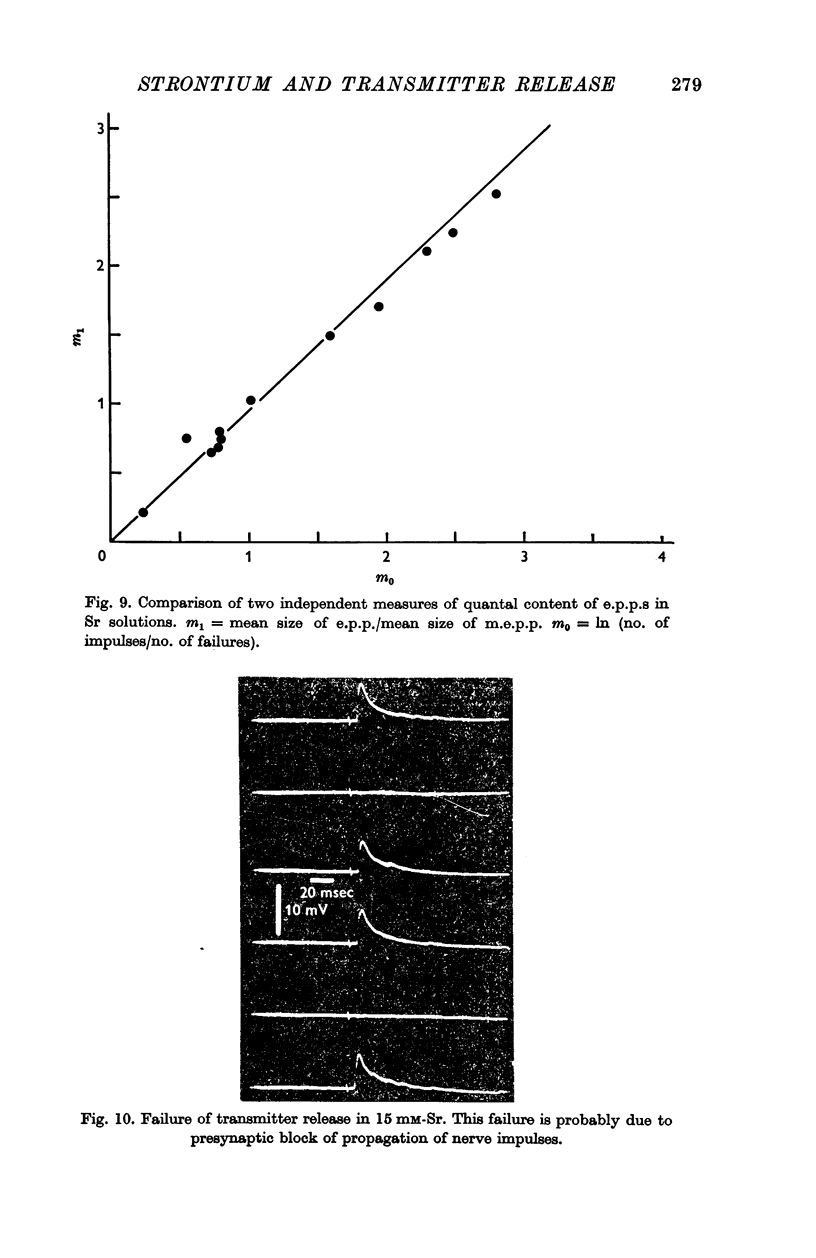
2. As with calcium, the transmitter released in the presence of strontium is in the form of packages (quanta) whose release can be predicted from Poisson's Theorem.
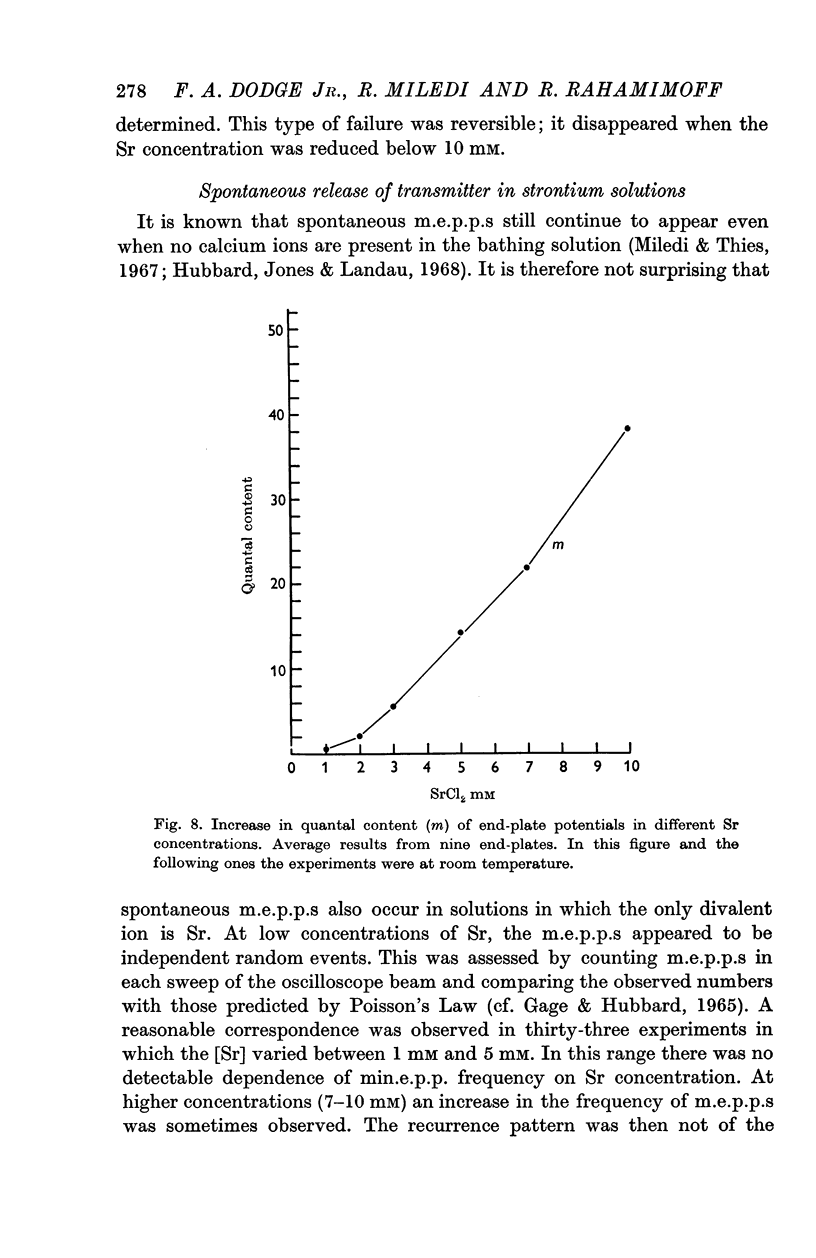
3. The mean number of quanta released by a nerve impulse increases with the concentration of strontium. Strontium is much less effective than calcium in equimolar concentrations.
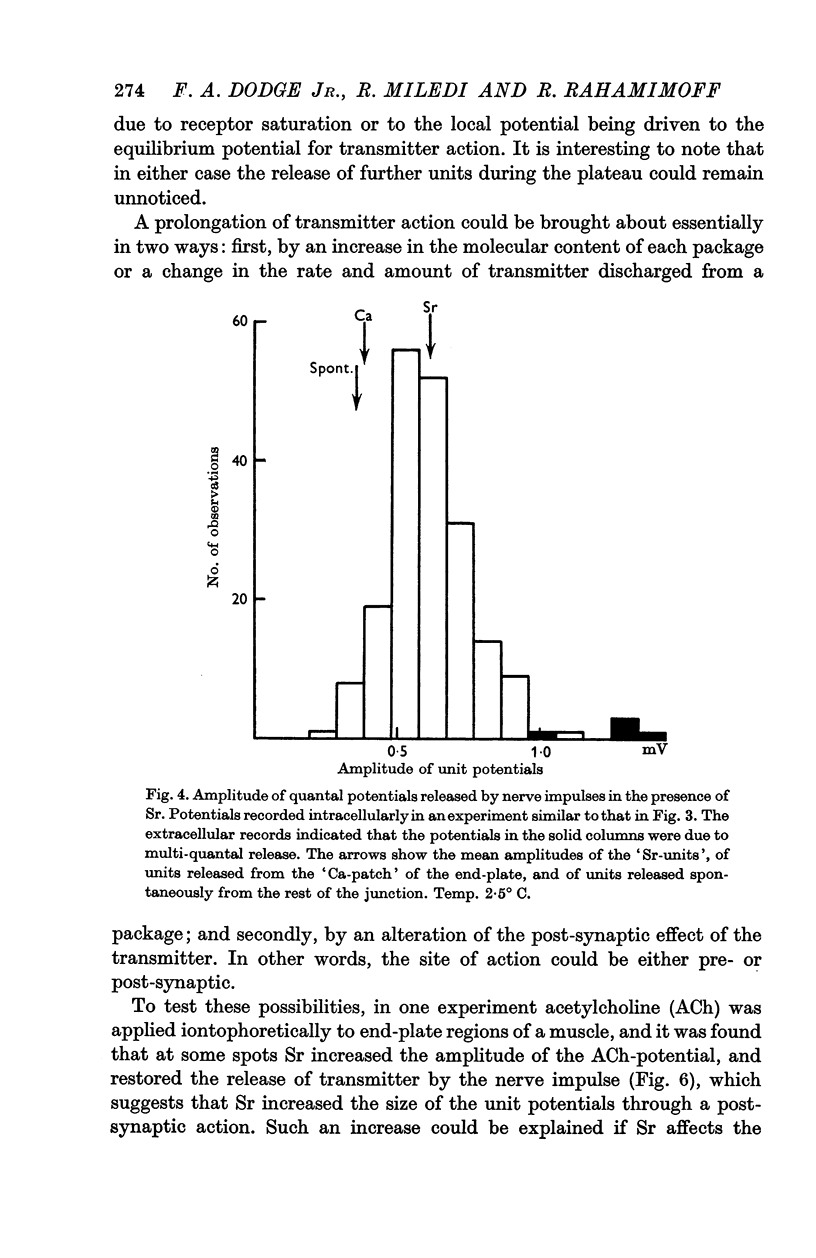
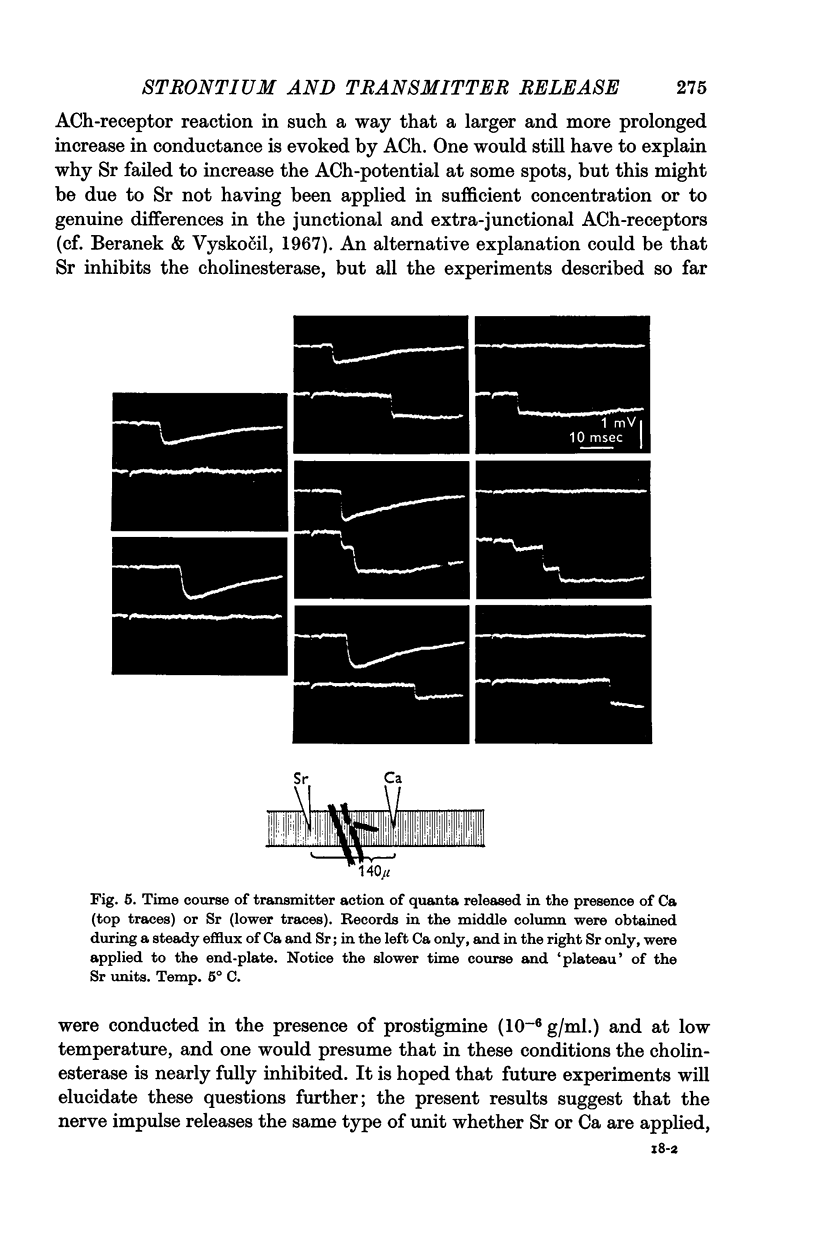
4. Transmitter quanta released in the presence of strontium evoke larger unit potentials than quanta released in the presence of calcium. The larger size of the Sr-unit potentials is caused by a prolongation of transmitter action, presumably due to a post-synaptic effect of strontium.
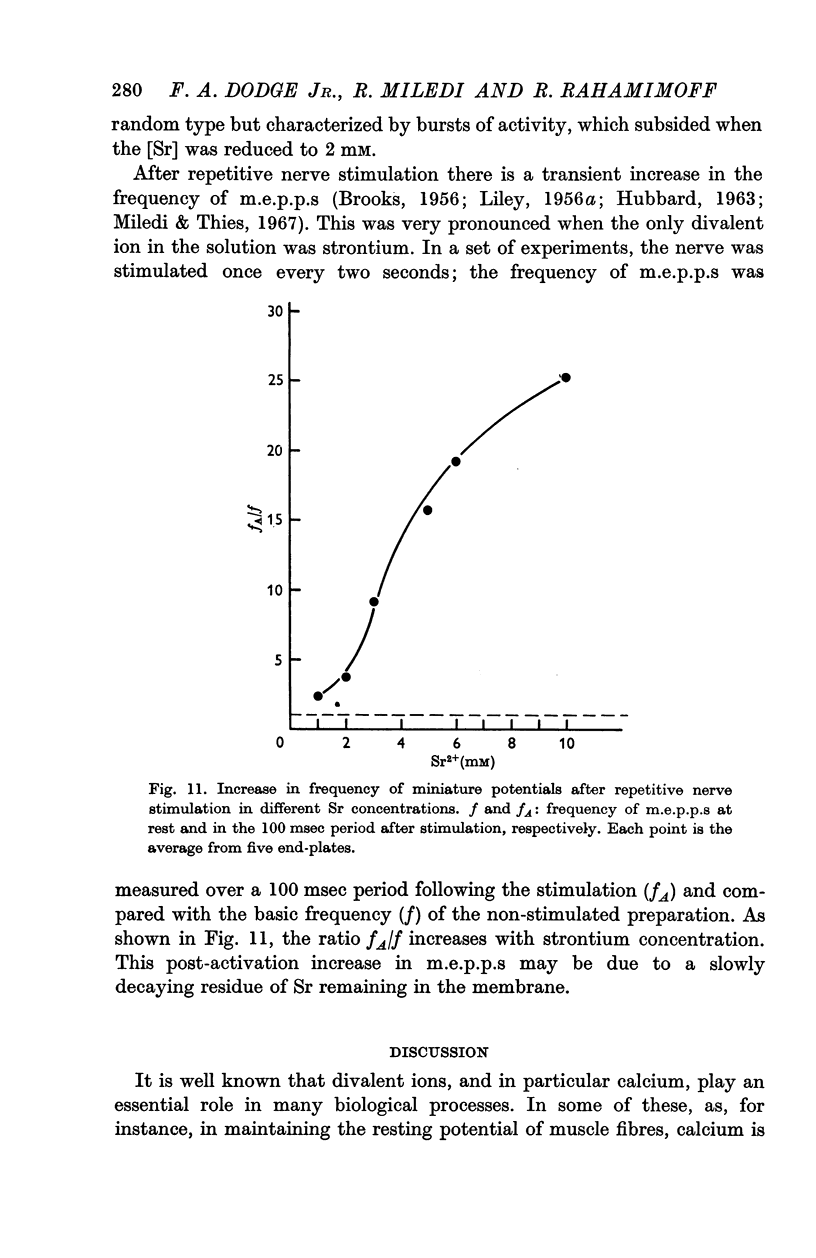
5. Neuromuscular transmission was blocked in some fibres when the concentration of strontium was raised beyond 10 mM. This junctional block was presumably due to a failure in the propagation of nerve impulses.
6. The post-stimulation increase in the frequency of miniature end-plate potentials, which is normally seen in calcium solutions, is also observed when calcium is substituted by strontium. The post-stimulation effect increases with the concentration of strontium.
7. It is concluded that strontium can substitute for calcium in the process of quantal release of transmitter. The physico-chemical mechanism of this substitution remains unknown.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACKMAN J. G., GINSBORG B. L., RAY C. On the quantal release of the transmitter at a sympathetic synapse. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:402–415. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. The end-plate potential in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):74–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKS V. B. An intracellular study of the action of repetitive nerve volleys and of botulinum toxin on miniature end-plate potentials. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):264–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beránek R., Vyskocil F. The action of tubocurarine and atropine on the normal and denervated rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(1):53–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., ENGBAEK L. The nature of the neuromuscular block produced by magnesium. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):370–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. THE EFFECTS OF ALKALINE EARTHS AND OTHER DIVALENT CATIONS ON ADRENAL MEDULLARY SECRETION. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:231–241. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C., Lorković H., Weber A. The effect of the replacement of calcium by strontium on excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Oct;186(2):295–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., GINSBORG B. L. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):516–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Hubbard J. I. Evidence for a Poisson distribution of miniature end-plate potentials and some implications. Nature. 1965 Oct 23;208(5008):395–396. doi: 10.1038/208395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., NAKA K. I. THE INITIATION OF SPIKE POTENTIAL IN BARNACLE MUSCLE FIBERS UNDER LOW INTRACELLULAR CA++. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:141–162. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I. REPETITIVE STIMULATION AT THE MAMMALIAN NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION, AND THE MOBILIZATION OF TRANSMITTER. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:641–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Jones S. F., Landau E. M. On the mechanism by which calcium and magnesium affect the spontaneous release of transmitter from mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):355–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENDEN D. J., REGER J. F. THE ROLE OF RESTING POTENTIAL CHANGES IN THE CONTRACTILE FAILURE OF FROG SARTORIUS MUSCLES DURING CALCIUM DEPRIVATION. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:889–901. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. A STUDY OF SPONTANEOUS MINIATURE POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:389–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. PROPAGATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY IN MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:453–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE MEASUREMENT OF SYNAPTIC DELAY, AND THE TIME COURSE OF ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:483–495. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. On the factors which determine the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):267–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Failure of neuromuscular propagation in rats. J Physiol. 1958 Mar 11;140(3):440–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Presynaptic failure of neuromuscular propagation in rats. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:1–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):656–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The timing of calcium action during neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):535–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The quantal components of the mammalian end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):571–587. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Slater C. R. The action of calcium on neuronal synapses in the squid. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):473–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Thies R. E. Post-tetanic increase in frequency of miniature end-plate potentials in calcium-free solutions. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):54P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mines G. R. On the replacement of calcium in certain neuro-muscular mechanisms by allied substances. J Physiol. 1911 Mar 29;42(3):251–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1911.sp001433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]