Abstract
1. Blood volume was measured with carbon monoxide on six hill-walkers before and immediately after a 28-mile walk on two occasions. The subjects had free access to food and fluid.
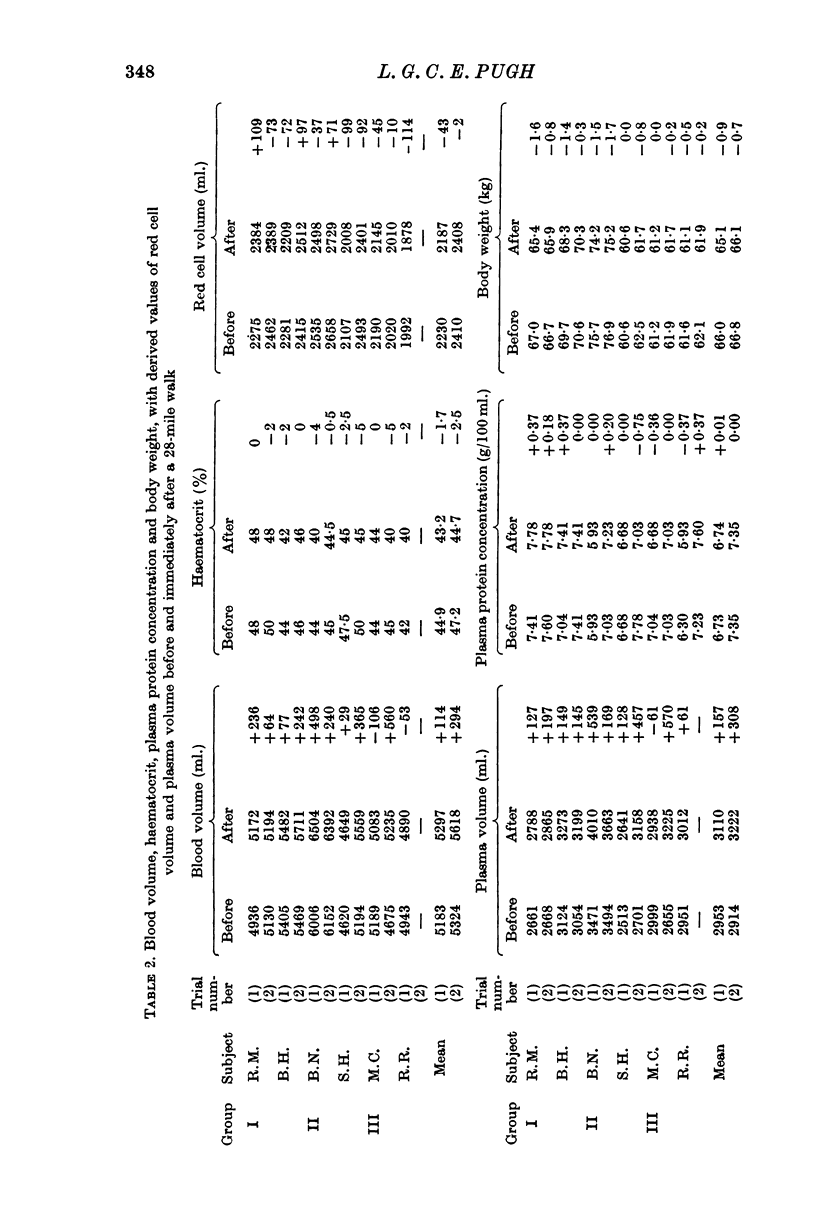
2. Blood volume increased and haematocrit fell significantly on both occasions compared with the control observations. The mean increase of blood volume was 204 ml. or 3·9% (P < 0·01) and the mean reduction of haematocrit was 2·1% (P < 0·02). Plasma volume calculated from these results increased by 233 ml. or 7·3%. There was no significant change in red cell volume or plasma protein concentration.
3. These changes are the opposite of those taking place in short-term exercise and suggest that in the absence of dehydration a compensatory adjustment of blood volume takes place during exercise of many hours duration.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRAND P. O., SALTIN B. PLASMA AND RED CELL VOLUME AFTER PROLONGED SEVERE EXERCISE. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Sep;19:829–832. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.5.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUER O. H., HENRY J. P. Circulatory basis of fluid volume control. Physiol Rev. 1963 Jul;43:423–481. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1963.43.3.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGERSEN M. I., RAWSON R. A. Blood volume. Physiol Rev. 1959 Apr;39(2):307–342. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider N. L., Meneely G. R. THE EFFECT OF EXERCISE ON THE VOLUME OF THE BLOOD. J Clin Invest. 1940 Jul;19(4):627–634. doi: 10.1172/JCI101165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUGH L. G. BLOOD VOLUME AND HAEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION AT ALTITUDES ABOVE 18,000 FT. (5500 M). J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:344–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTIN B., STENBERG J. CIRCULATORY RESPONSE TO PROLONGED SEVERE EXERCISE. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Sep;19:833–838. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UEHLINGER A., BUEHLMANN A. [Behavior of the blood volume during short-term physical exercise; determinations with Cr51 and I-131 albumin]. Cardiologia. 1961;38:357–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


