Abstract
1. Anionic conductance changes in Mauthner neurones of goldfish were measured during synaptically evoked inhibition and inhibition caused by iontophoretic application of the putative inhibitory transmitters glycine and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
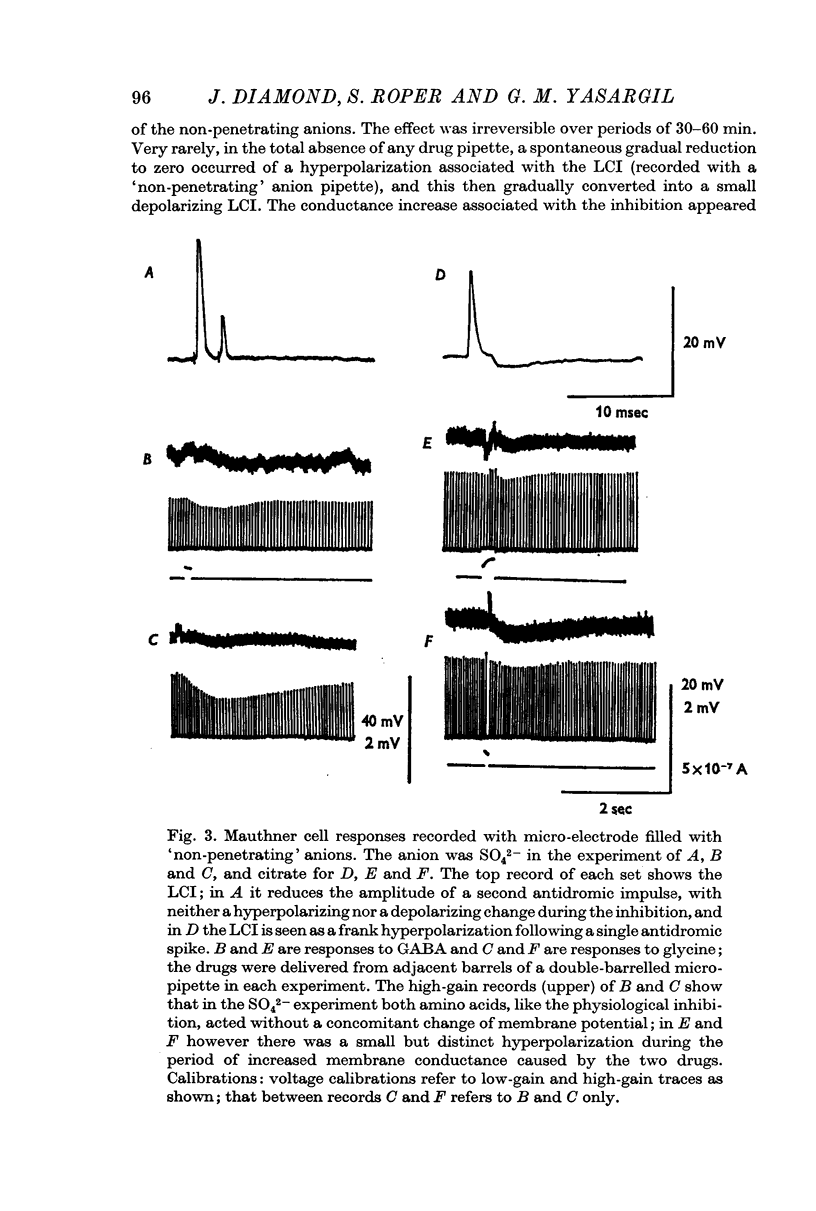
2. The effects of either amino acid were indistinguishable from those of the neural inhibitory transmitter(s). The membrane permeability during the neural or drug response was increased to Br-, Cl-, I-, SCN-, NO3-, ClO3-, and formate (HCOO-), but not to HCO3-, BrO3-, IO3-, SO4-, HPO4-, H2PO4-, acetate and citrate.
3. Strychnine was injected intramuscularly, iontophoretically, or applied topically to the exposed brain in order to compare quantitatively its ability to prevent inhibition evoked by synaptic activation and by pharmacological means. Inhibitions were measured by the increase in membrane conductance.
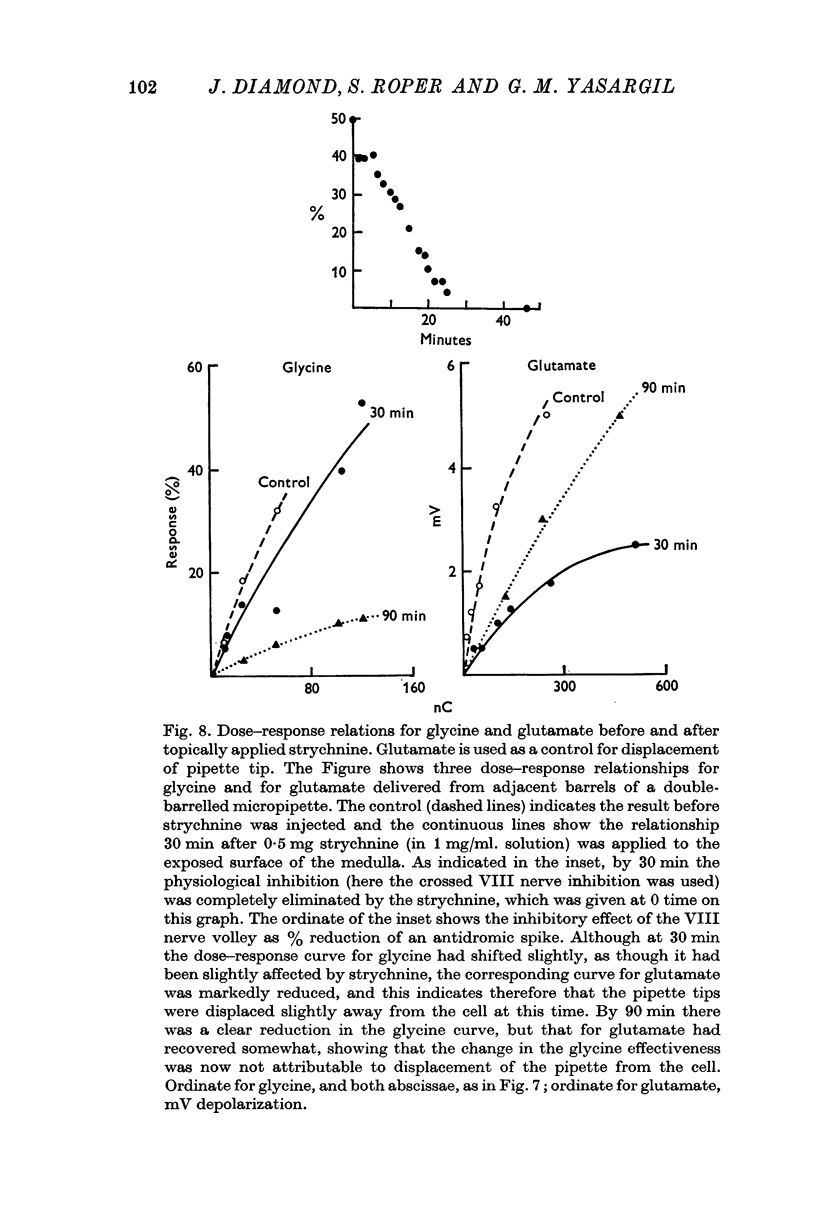
4. Strychnine, at concentrations just adequate to block completely the late collateral inhibition (LCI) and crossed VIII nerve inhibition, had little effect on the pharmacological inhibition caused by glycine, and sometimes there was no detectable effect at all. In one experiment even a local iontophoretic application of strychnine in a sufficient dose to diffuse over the cell and block the LCI almost completely, merely halved the effect of a small dose of glycine applied to the same localized region of the membrane.
5. Higher concentrations of strychnine than those necessary to block synaptically evoked inhibition would reduce the effect of glycine but not that of GABA. The evidence indicated that any apparent effect of strychnine upon GABA could be explained by displacement of the GABA-containing iontophoretic pipette.
6. The glycine-blocking action of iontophoretic pulses of strychnine was of relatively very slow onset and long duration compared to the effects of pulses of glycine and GABA.
7. These findings can be interpreted as either (1) strychnine has a presynaptic action, preventing the release of inhibitory neurotransmitter, in addition to its less potent post-synaptic one in blocking pharmacological inhibition, or (2) strychnine acts entirely post-synaptically, but the physiological transmitter action differs from that of glycine and GABA in being considerably more sensitive to strychnine antagonism. In either case, the use of strychnine as evidence for the claim that glycine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter at the Mauthner cell is questionable.
Full text
PDF






















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASADA Y. EFFECTS OF INTRACELLULARLY INJECTED ANIONS ON THE MAUTHNER CELLS OF GOLDFISH. Jpn J Physiol. 1963 Dec 15;13:583–598. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.13.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aprison M. H., Werman R. The distribution of glycine in cat spinal cord and roots. Life Sci. 1965 Nov;4(21):2075–2083. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90325-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY K., EASTON D. M., ECCLES J. C. An investigation of primary or direct inhibition. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):474–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Crawford J. M. Central synaptic transmission--microelectrophoretic studies. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1969;9:209–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.09.040169.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A. A pharmacological study of the depression of spinal neurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00235443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A., Johnston I. H. The hyperpolarization of spinal motoneurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;5(3):235–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00238666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO L., KATZ B. A study of curare action with an electrical micromethod. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):339–356. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H., Werman R. The effects of strychnine on the inhibition of interneurons by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Mar;8(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Graham L. T., Jr, Shank R. P., Werman R., Aprison M. H. Changes in amino acid concentrations associated with loss of spinal interneurons. J Neurochem. 1967 Oct;14(10):1025–1031. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Huxley A. F. The activation and distribution of GABA and L-glutamate receptors on goldfish Mauthner neurones: an analysis of dendritic remote inhibition. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):669–723. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J., FURUKAWA T. Intracellular and extracellular responses of the several regions of the Mauthner cell of the goldfish. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Nov;25:732–771. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.6.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T., FUKAMI Y., ASADA Y. EFFECTS OF STRYCHNINE AND PROCAINE ON COLLATERAL INHIBITION OF THE MAUTHNER CELL OF GOLDFISH. Jpn J Physiol. 1964 Aug 15;14:386–399. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.14.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T., FURSHPAN E. J. Two inhibitory mechanisms in the Mauthner neurons of goldfish. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jan;26:140–176. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.1.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSMITH T. H. Rates of action of bath-applied drugs at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:368–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. T., Jr, Shank R. P., Werman R., Aprison M. H. Distribution of some synaptic transmitter suspects in cat spinal cord: glutamic acid, aspartic acid, gamma-aminobutyric acid, glycine and glutamine. J Neurochem. 1967 Apr;14(4):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. A STUDY OF SPONTANEOUS MINIATURE POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:389–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai N., Yamamoto C. Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on the potentials evoked in vitro in the superior colliculus. Experientia. 1967 Oct 15;23(10):822–823. doi: 10.1007/BF02146865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S., Krnjević K., Morris M. E., Yim G. K. Anionic permeability of cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(1):11–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00236105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. The action of glycine on cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00238328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinstry D. N., Koelle G. B. Inhibition of release of acetylcholine by strychnine and its implications regarding transmission by the olivo-cochlear bundle. Nature. 1967 Feb 4;213(5075):505–506. doi: 10.1038/213505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. J. The effect of convulsant drugs on coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):132–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01983.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata K., Takeda K., Shinozaki H. Further study on pharmacological properties of the cerebellar-induced inhibition of deiters neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1970 Nov 26;11(4):327–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00237907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The kinetics of action of acetylcholine antagonists in smooth muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Apr 19;164(996):488–510. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roper S., Diamond J., Yassargil G. M. Does strychnine block inhibition post-synaptically? Nature. 1969 Sep 13;223(5211):1168–1169. doi: 10.1038/2231168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi K., Takayanagi I. Effects of strychnine, derivatives of phenyl acetate and catecholamines on contraction and acetylcholine output from the cholinergic nerve ending of guinea pig ileum. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1966 Jun;16(2):211–216. doi: 10.1254/jjp.16.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H. Inhibitory of glycine on spinal neurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):81–95. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


