Abstract
1. Micro-injections of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) into the anterior hypothalamus of the rabbit produced fever which was nearly immediate in onset. The prostaglandin sensitive region appears to be identical to that described as being fever sensitive to leucocytic pyrogen.
2. Micro-injections of PGE1 into the posterior hypothalamus and midbrain reticular formation of the rabbit did not produce fever.
3. The febrile response to PGE1 injected into the anterior hypothalamus was dose dependent over a range of 20-1000 ng.
4. Ambient temperature influenced the thermoregulatory mechanism by which PGE1 fever evolved. In the cold, PGE1 fever was due to increased heat production while during heat exposure both evaporative and dry heat losses were reduced without significant changes in heat production. Vasoconstriction, confined mainly to the ears, was effective in producing fever in standard room environments (24-25° C) along with a small increase in heat production.
5. The preoptic anterior hypothalamic area retained its thermosensitivity during PGE1 fever; heating this area attenuated, while cooling augmented the fever.
6. The results support the view that PGE1 is a mediator of pyrogen induced fever.
Full text
PDF




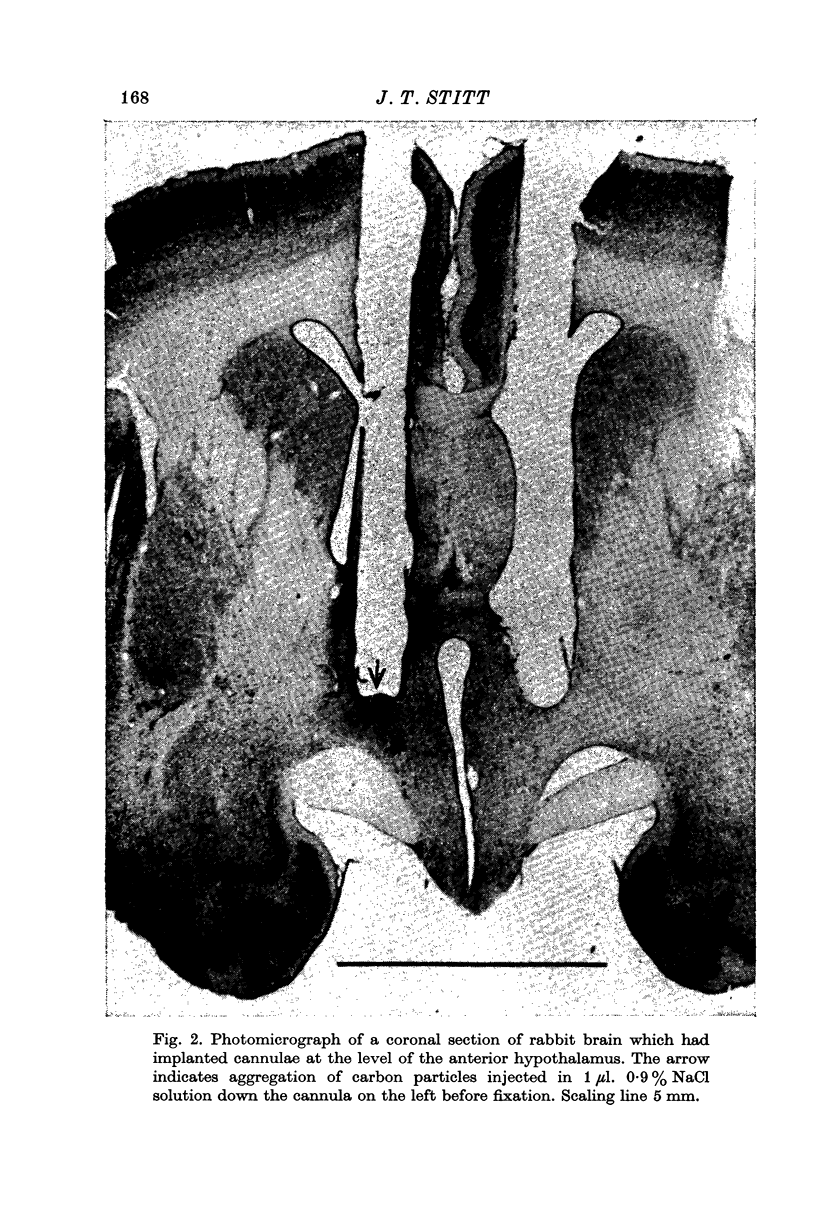
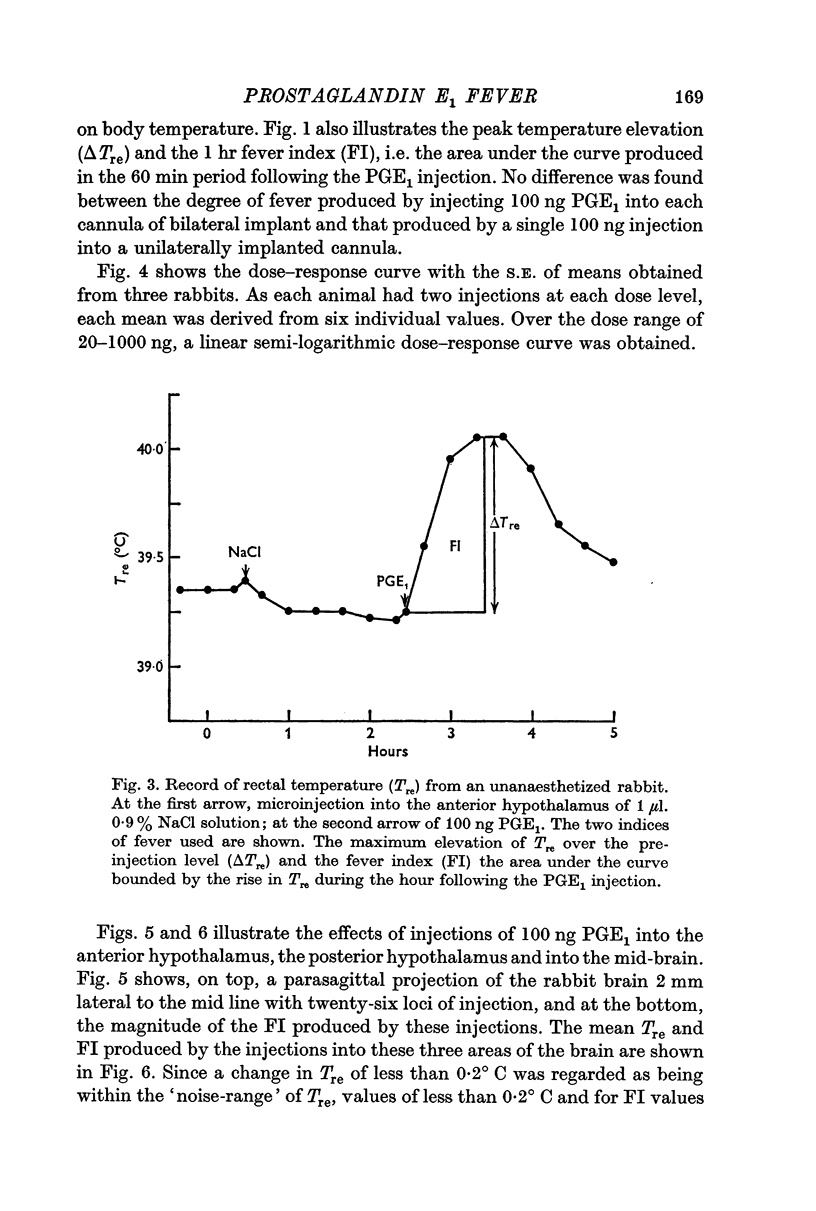










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN H. T., HAMMEL H. T., HARDY J. D. Modifications of the febrile response to pyrogen by hypothalamic heating and cooling in the unanesthetized dog. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Nov-Dec;53:247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. E., Cranston W. I., Honour A. J. Observations on the site & mode of action of pyrogens in the rabbit brain. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):325–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edinger H. M., Eisenman J. S. Thermosensitive neurons in tuberal and posterior hypothalamus of cats. Am J Physiol. 1970 Oct;219(4):1098–1103. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.4.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Myers R. D. Appearance of 5-hydroxytryptamine and an unidentified pharmacologically active lipid acid in effluent from perfused cerebral ventricles. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):837–855. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Fever produced by prostaglandin E1. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(3):547–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Saxena P. N. Further studies on prostaglandin E 1 fever in cats. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):739–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez R. R., Kluger M. J., Hardy J. D. Partitional calorimetry of the New Zealand white rabbit at temperatures 5-35 degrees C. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Nov;31(5):728–734. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.5.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guieu J. D., Hardy J. D. Effects of preoptic and spinal cord temperature in control of thermal polypnea. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Apr;28(4):540–542. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.4.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMEL H. T., HARDY J. D., FUSCO M. M. Thermoregulatory responses to hypothalamic cooling in unanesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1960 Mar;198:481–486. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEMINGWAY A., FORGRAVE P., BIRZIS L. Shivering suppression by hypothalamic stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Jul;17(4):375–386. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.4.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. L. A hypothalamic region responsive to localized injection of pyrogens. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):586–602. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. A possible role for prostaglandin E1 as a modulator for temperature regulation in the central nervous system of the cat. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):76P–77P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T., Hardy J. D. Unit responses in the rabbit's brain stem to changes in brain and cutaneous temperature. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Dec;27(6):848–857. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.27.6.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmes E. D., Park C. R. The regulation of body temperature during fever. Arch Environ Health. 1965 Dec;11(6):749–759. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1965.10664295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendorff C., Mooney J. J. Central nervous system sites of action of a purified leucocyte pyrogen. Am J Physiol. 1971 Mar;220(3):597–603. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.3.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER C. H., EVERETT J. W., GREEN J. D. The rabbit diencephalon in stereotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Dec;101(3):801–824. doi: 10.1002/cne.901010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T., Hardy J. D. Thermoregulation in the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). J Appl Physiol. 1971 Jul;31(1):48–54. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



