Abstract
The effects of eserine and D-tubocurarine on the axon and Schwann cell membrane potentials have been studied in the giant nerve fibre of the squid.
1. The addition of eserine at concentrations of up to 10-4 M to the external sea-water medium has no appreciable effects on either the Schwann cell electrical potential of unstimulated nerve fibres or on the resting and action potentials of the axon.
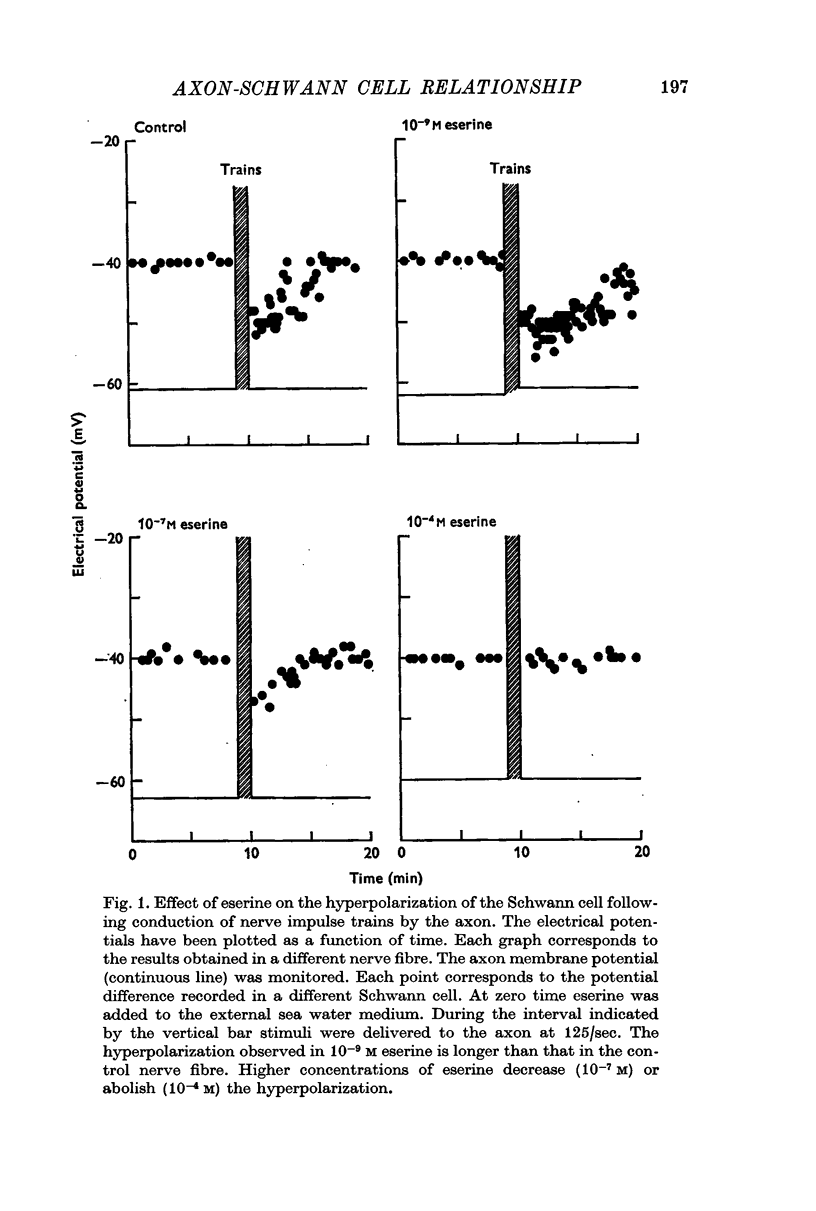
2. However, eserine at a concentration of 10-9 M prolongs the long-lasting Schwann cell hyperpolarizations which follow the conduction of impulse trains by the axon.
3. Higher concentrations of eserine (10-7, 10-4 M) decrease and block the long-lasting effects of nerve impulse train conduction.
4. D-tubocurarine at concentrations of up to 10-5 M has no appreciable effect on the resting and action potentials of the axon.
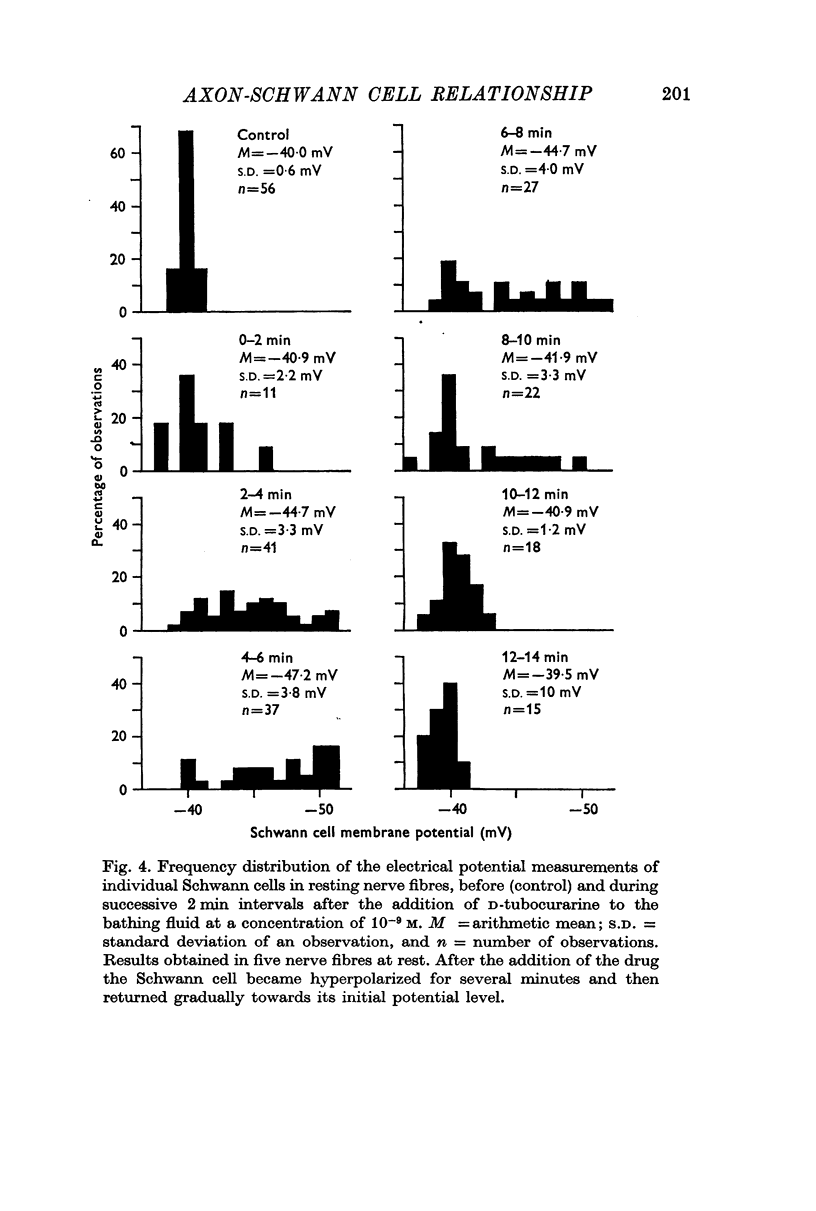
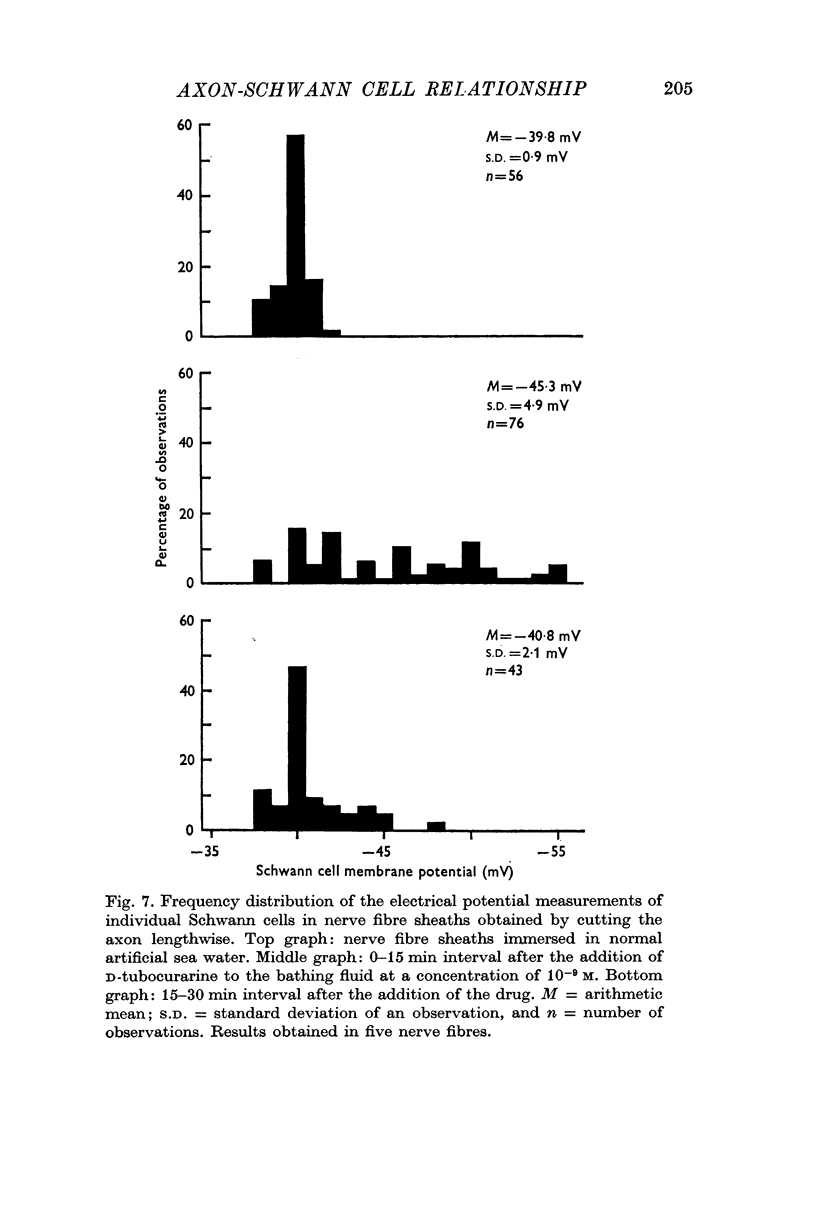
5. However, D-tubocurarine at a concentration of 10-9 M blocks completely the hyperpolarizing effects of nerve impulse trains on the Schwann cell electrical potential.
6. In addition to its blocking action, D-tubocurarine induces transient hyperpolarizations in the Schwann cells of unstimulated nerve fibres both in intact fibres and in slitted preparations.
7. These findings suggest that a cholinergic system, which may be located at the axon-Schwann cell boundary, is involved in the genesis of the long-lasting Schwann cell hyperpolarization caused by the conduction of nerve impulse trains by the axon.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brzin M., Dettbarn W. D., Rosenberg P., Nachmansohn D. Cholinesterase activity per unit surface area of conducting membranes. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):353–364. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. Responses of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo marmorata to salts and curarizing drugs. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Sep;2(5):369–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DETTBARN W. D., DAVIS F. A. Effects of acetylcholine on axonal conduction of lobster nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 21;66:397–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. Electrically evoked release of acetylcholine from Schwann cells at denervated motor end-plates. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):79P–81P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRENPREIS S. ACETYLCHOLINE AND NERVE ACTIVITY. Nature. 1964 Feb 29;201:887–893. doi: 10.1038/201887a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The antagonism between tubocurarine and substances which depolarize the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M., ARMETT C. J. The role of acetylcholine in conduction in mammalian nonmyelinated nerve fibers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Feb;139:201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini M. T., Dipolo R., Villegas R. Adenosine triphosphatase activity in the membranes of the squid nerve fiber. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):176–183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLEGAS R., VILLEGAS L., GIMENEZ M., VILLEGAS G. M. Schwann cell and axon electrical potential differences. Squid nerve structure and excitable membrane location. J Gen Physiol. 1963 May;46:1047–1064. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.5.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas J. Axon-Schwann cell interaction in the squid nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):275–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


