Abstract
1. Illumination of the isolated outer segments of rod photoreceptors loaded with 42K or 86Rb reduces the efflux of these ions.
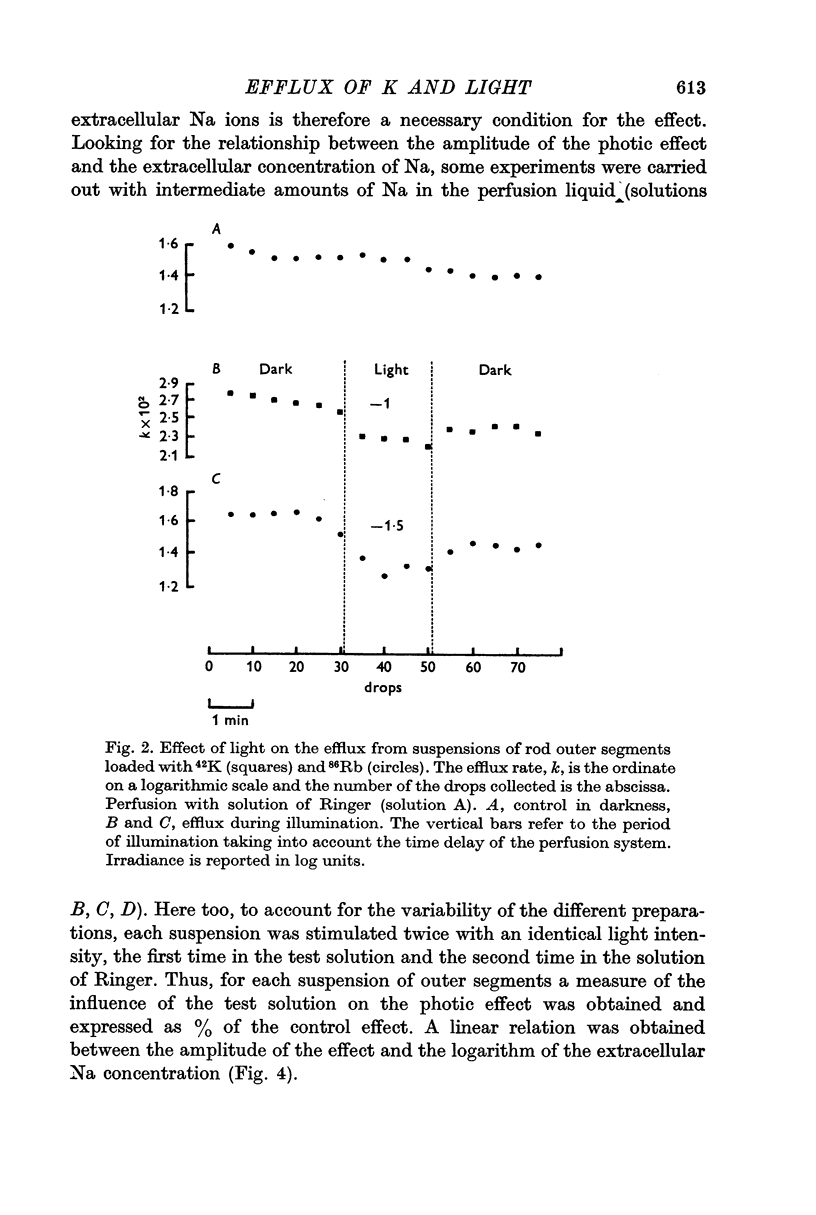
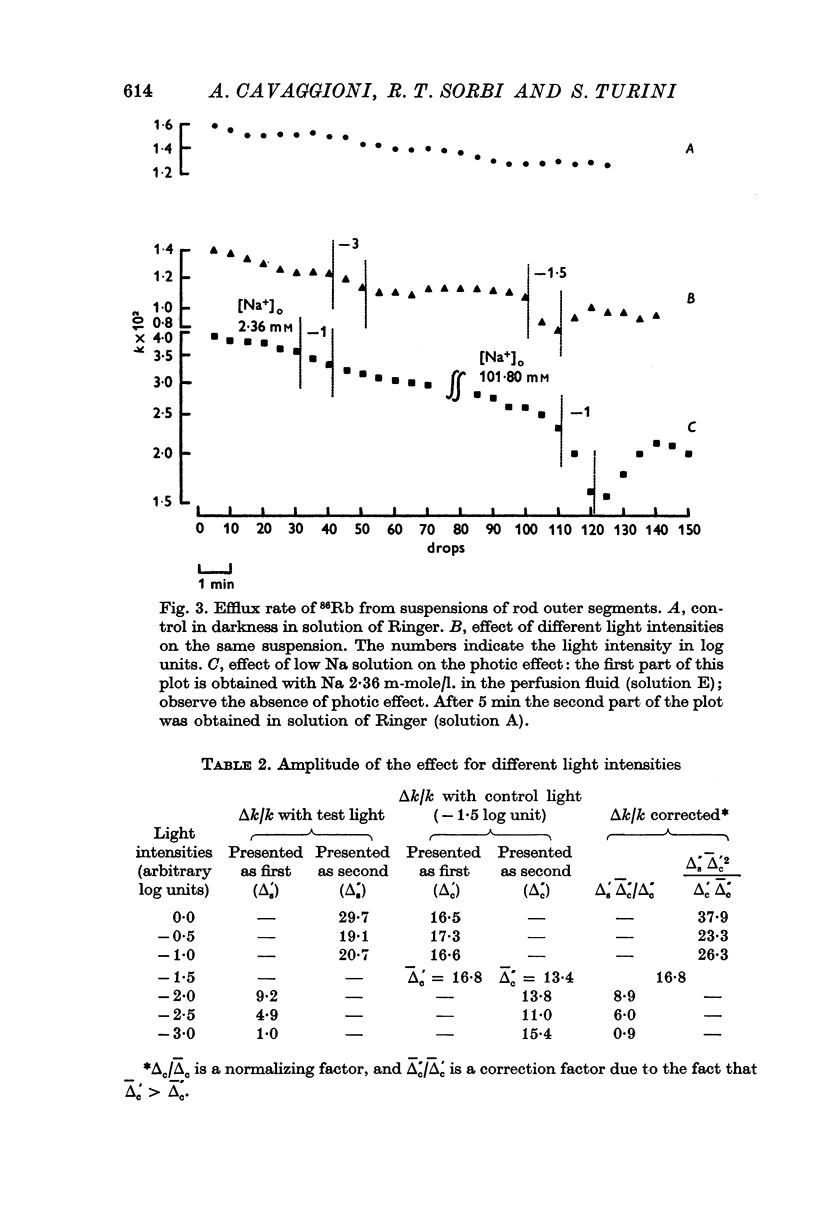
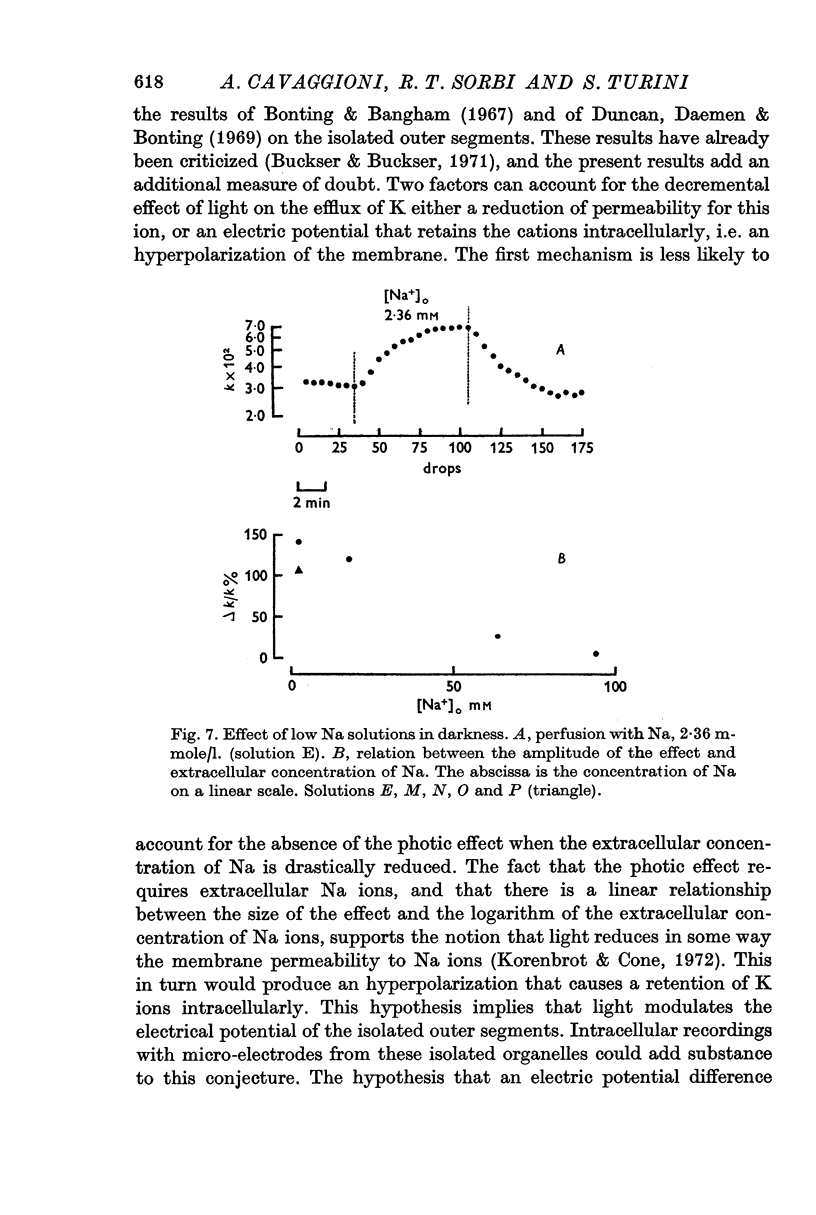
2. During the perfusion of the isolated rod outer segments with a solution containing only 2·36 mM-Na the effect of light is absent, and the amplitude of the photic effect is linearly related to the logarithm of the extracellular Na concentration.
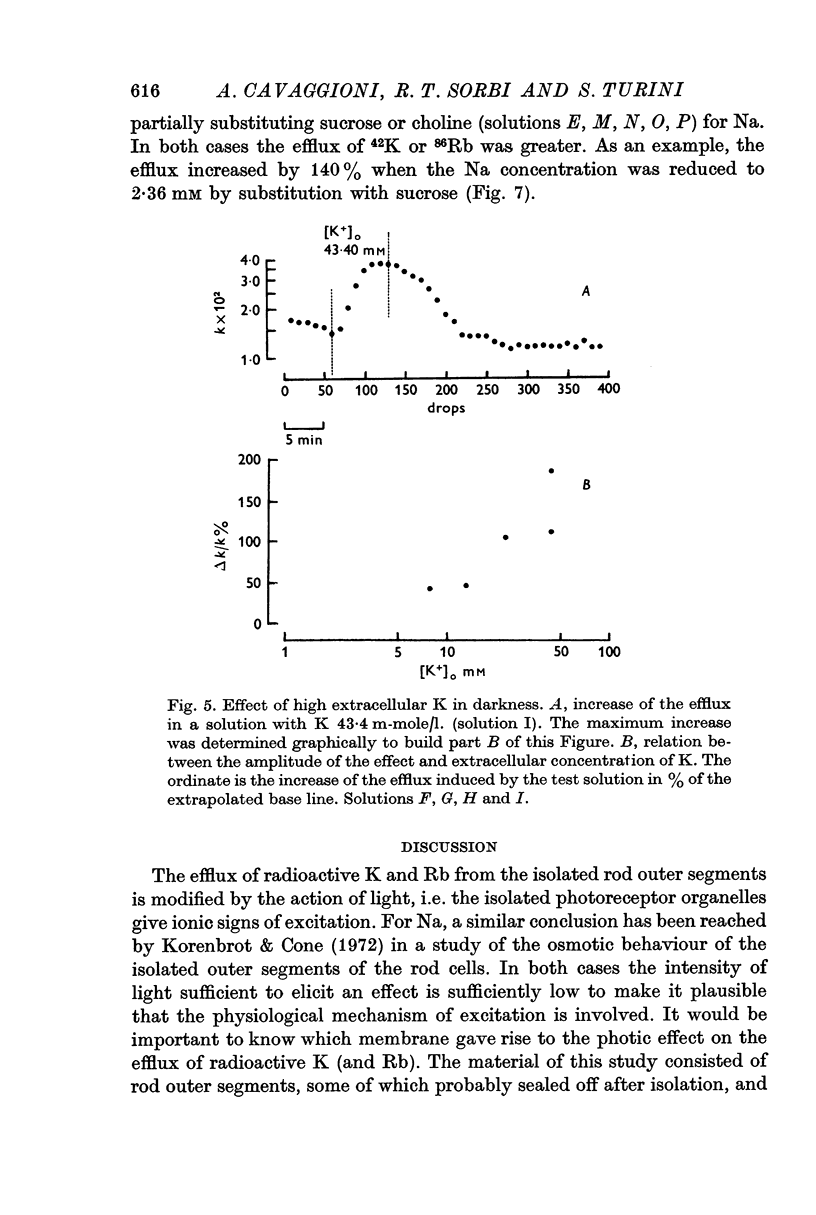
3. In darkness, raising the concentration of K in the fluid of perfusion gives an increase of the efflux of 86Rb and increasing the extracellular concentration of Ca yields a retention. The efflux of 86Rb and 42K is greater in darkness when sucrose or choline substitute for Na.
4. It is suggested that in darkness the isolated outer segments are permeable both to Na and to K. Light appears to decrease the permeability for Na ions. There is no evidence that the permeability for K ions is modified by light.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonting S. L., Bangham A. D. On the biochemical mechanism of the visual process. Exp Eye Res. 1967 Oct;6(4):400–413. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(67)80015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckser S., Buckser C. Sodium leakage in cattle rod outer segments. Exp Eye Res. 1971 Jul;12(1):138–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(71)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaggioni A., Sorbi R. T., Turini S. Efflux of potassium from the isolated frog retina: a study of the photic effect. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):427–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervetto L. Influence of sodium, potassium and chloride ions on the intracellular responses of turtle photoreceptors. Nature. 1973 Feb 9;241(5389):401–403. doi: 10.1038/241401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Penn R. D., Yoshikami S. Dark current and photocurrent in retinal rods. Biophys J. 1970 May;10(5):380–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86308-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenbrot J. I., Cone R. A. Dark ionic flux and the effects of light in isolated rod outer segments. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jul;60(1):20–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorbi R. T., Cavaggioni A. Illumination of the isolated frog retina and efflux of tracer potassium and rubidium. Vision Res. 1971 Sep;11(9):985–993. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


