Abstract
Following trains of impulses, sensory neurones in the C.N.S. of the leech show a prolonged hyperpolarization, which lasts for seconds or minutes. In the present investigation the mechanisms that underly this hyperpolarization have been studied by recording intracellularly. Two factors have been found to be responsible. One is the activity of an electrogenic pump (see Baylor & Nicholls, 1969b); the other is a long-lasting change in K conductance.
1. Additional evidence that an electrogenic pump contributes to a slow after-hyperpolarization of leech sensory neurones is provided by the effects of injecting Na intracellularly. This leads to an increase in membrane potential that is blocked by the cardiac glycoside strophanthidin. Furthermore, after a train of impulses, reducing the K concentration in the external fluid characteristically reduces the hyperpolarizing action of the pump.
2. The hyperpolarization following impulses is associated with a reduction of the cell membrane resistance that can persist for several minutes.
3. Several lines of evidence suggest that the reduction in input resistance during the hyperpolarization is mainly due to an increased permeability to K. Thus, when the K concentration in Ringer fluid is reduced, the peak amplitude of the hyperpolarization following a train becomes larger. Furthermore, the conductance dependent part of the after-hyperpolarization has a reversal potential close to the equilibrium potential for K (EK). Substitution of Cl by SO4 has little effect either on the after-hyperpolarization or on the conductance change following a train.
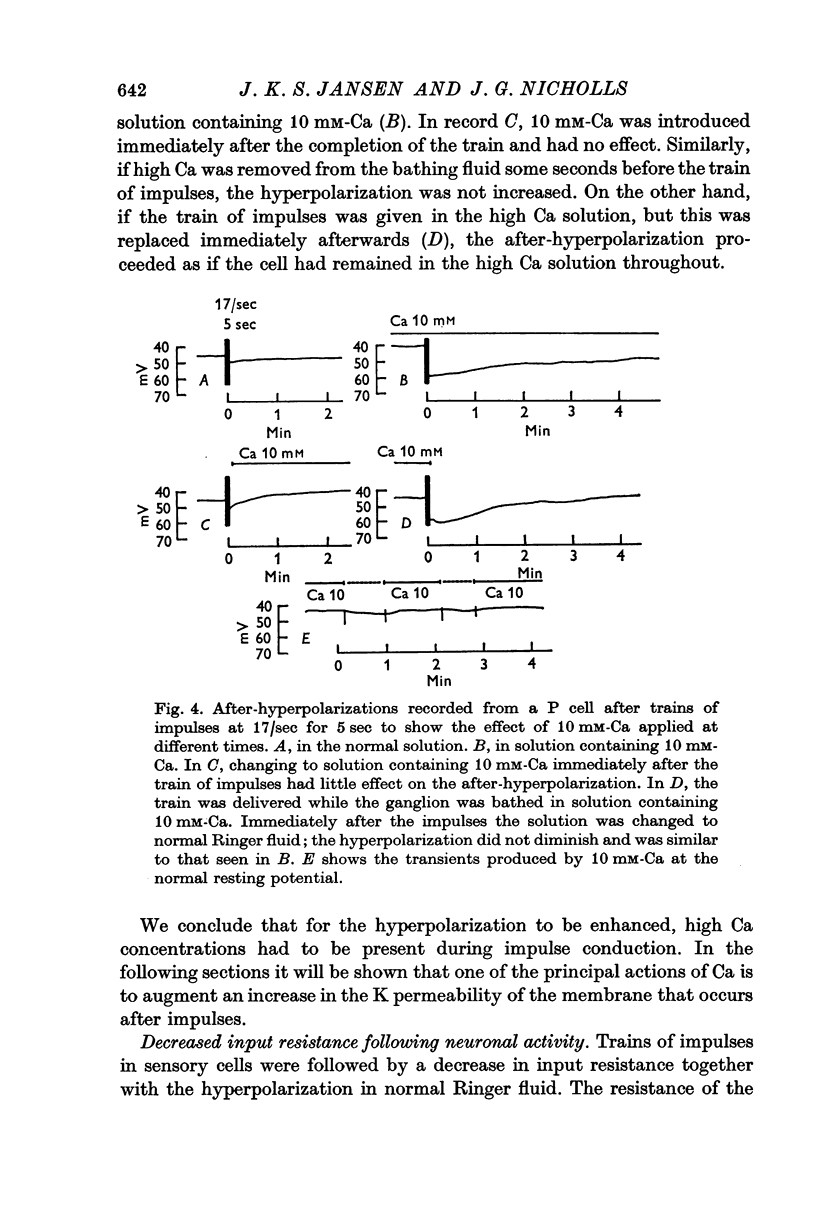
4. Increased external Ca concentrations lead to a marked increase in the hyperpolarization that follows impulse activity. The enhanced hyperpolarization in high Ca is associated with a corresponding reduction in input resistance. The amplitude and duration of the hyperpolarization following a brief train of impulses can be increased by a factor of 5 or more in Ringer fluid containing 10 mM-Ca instead of the usual 1·8 mM. The hyperpolarization and resistance changes still occur in solutions containing 20 mM-Mg.
5. To augment the hyperpolarization the increased concentration of Ca must be present during the train of impulses.
6. The relative contributions of the K conductance increase and of the electrogenic pump for generating the hyperpolarization after impulse activity are different in the three types of sensory cell responding to touch, pressure and noxious stimulation.
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L., Steinhardt R. A. The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):431–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Keynes R. D., Manil J., Shaw T. I., Steinhardt R. A. The ouabain-sensitive fluxes of sodium and potassium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):459–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nicholls J. G. After-effects of nerve impulses on signalling in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):571–589. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nicholls J. G. Changes in extracellular potassium concentration produced by neuronal activity in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):555–569. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nicholls J. G. Chemical and electrical synaptic connexions between cutaneous mechanoreceptor neurones in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):591–609. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodwick M. S., Junge D. Post-stimulus hyperpolarization and slow potassium conductance increase in Aplysia giant neurone. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):549–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. C. Factors governing movement and distribution of inorganic ions in nerve and muscle. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jan;48(1):1–64. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Prediction of repetitive firing behaviour from voltage clamp data on an isolated neurone soma. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):31–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geduldig D., Junge D. Sodium and calcium components of action potentials in the Aplysia giant neurone. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):347–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):583–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERKUT G. A., THOMAS R. C. AN ELECTROGENIC SODIUM PUMP IN SNAIL NERVE CELLS. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Jan;14:167–183. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., POTTER D. D. GLIA IN THE LEECH CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: PHYSIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND NEURON-GLIA RELATIONSHIP. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Mar;27:290–320. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Intracellular calcium injection causes increased potassium conductance in Aplysia nerve cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Jun 1;42(2):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLLS J. G., KUFFLER S. W. EXTRACELLULAR SPACE AS A PATHWAY FOR EXCHANGE BETWEEN BLOOD AND NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF THE LEECH: IONIC COMPOSITION OF GLIAL CELLS AND NEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:645–671. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Takahashi K. Post-tetanic hyperpolarization and electrogenic Na pump in stretch receptor neurone of crayfish. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(1):105–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J. G., Baylor D. A. Specific modalities and receptive fields of sensory neurons in CNS of the leech. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Sep;31(5):740–756. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.5.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J. G., Purves D. Monosynaptic chemical and electrical connexions between sensory and motor cells in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):647–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. On the electrogenic sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its activation by various external cations. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):183–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart A. E. Physiological and morphological properties of motoneurones in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):627–646. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Intracellular sodium activity and the sodium pump in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):55–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Measurement of current produced by the sodium pump in a snail neurone. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):23P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Membrane current and intracellular sodium changes in a snail neurone during extrusion of injected sodium. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):495–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



