Abstract
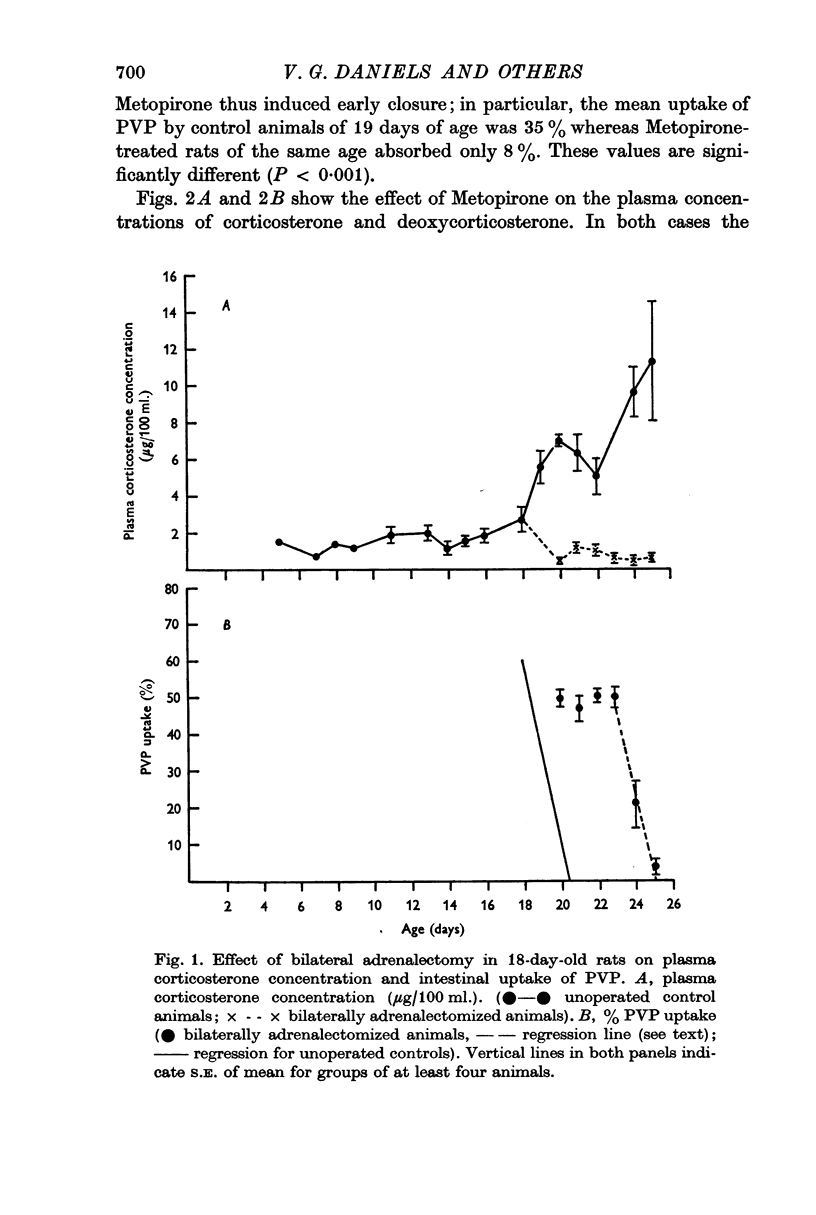
1. Bilateral adrenalectomy in 18-day-old rats resulted in an extension by approximately 4 days of the period during which the villous epithelial cells of the small intestine took up polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) of mean mol. wt. 160,000.
2. The eventual termination of PVP uptake (`closure') closely resembled normal closure in control animals: the time course of the decline in uptake and the histological changes indicated that more mature `PVP-impermeable' cells progressively ascended the villi.
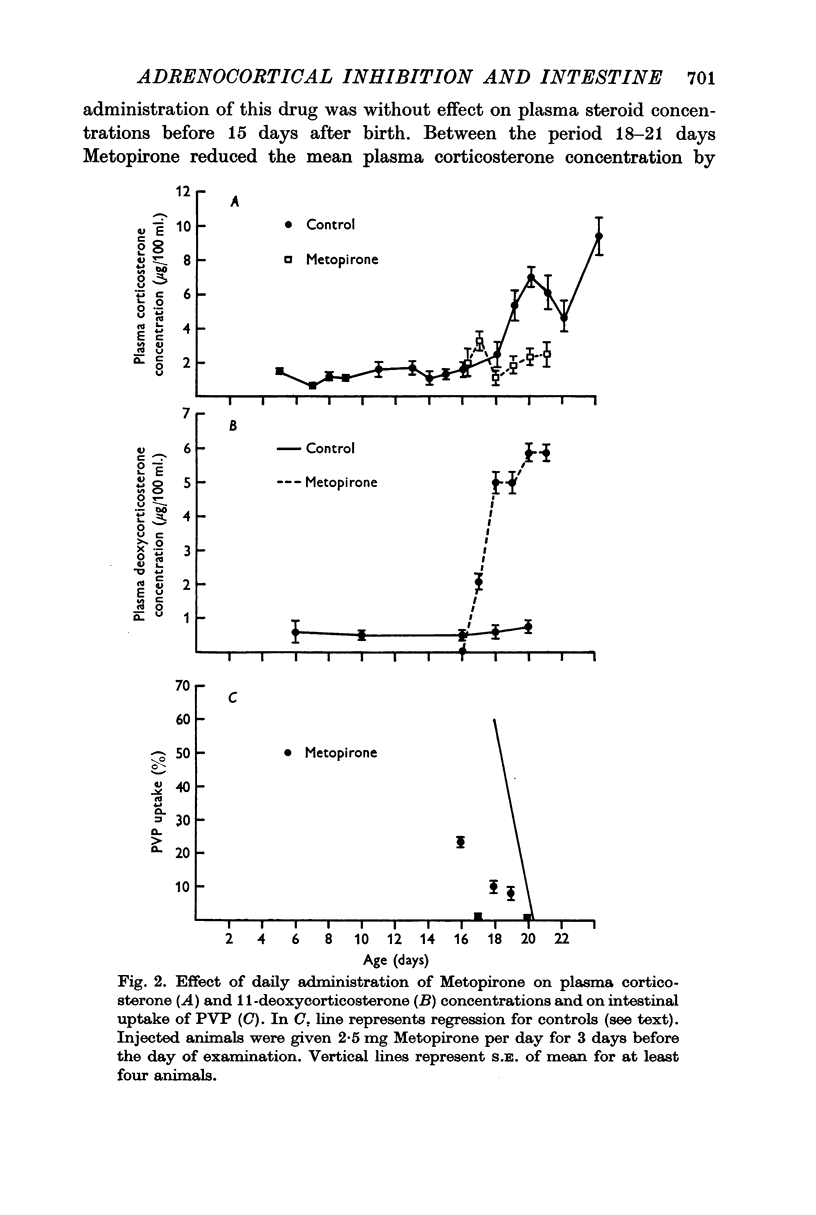
3. Injection of Metopirone was ineffective in animals 10 days after birth, but when injected after day 13 caused closure within 3 days.
4. Metopirone injection significantly reduced the plasma concentration of corticosterone and caused a marked rise in the plasma concentration of deoxycorticosterone.
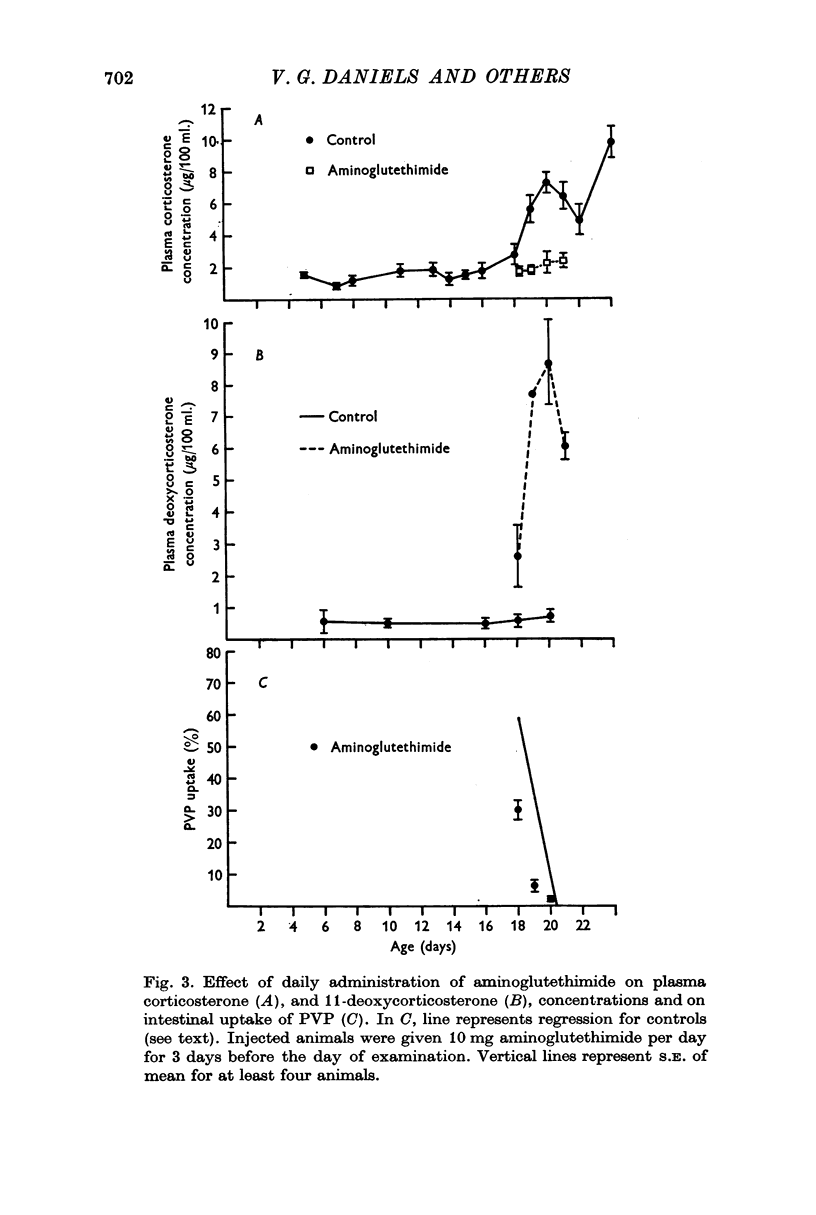
5. Aminoglutethimide injection also produced precocious closure and had an effect similar to Metopirone on the plasma concentrations of corticosterone and deoxycorticosterone.
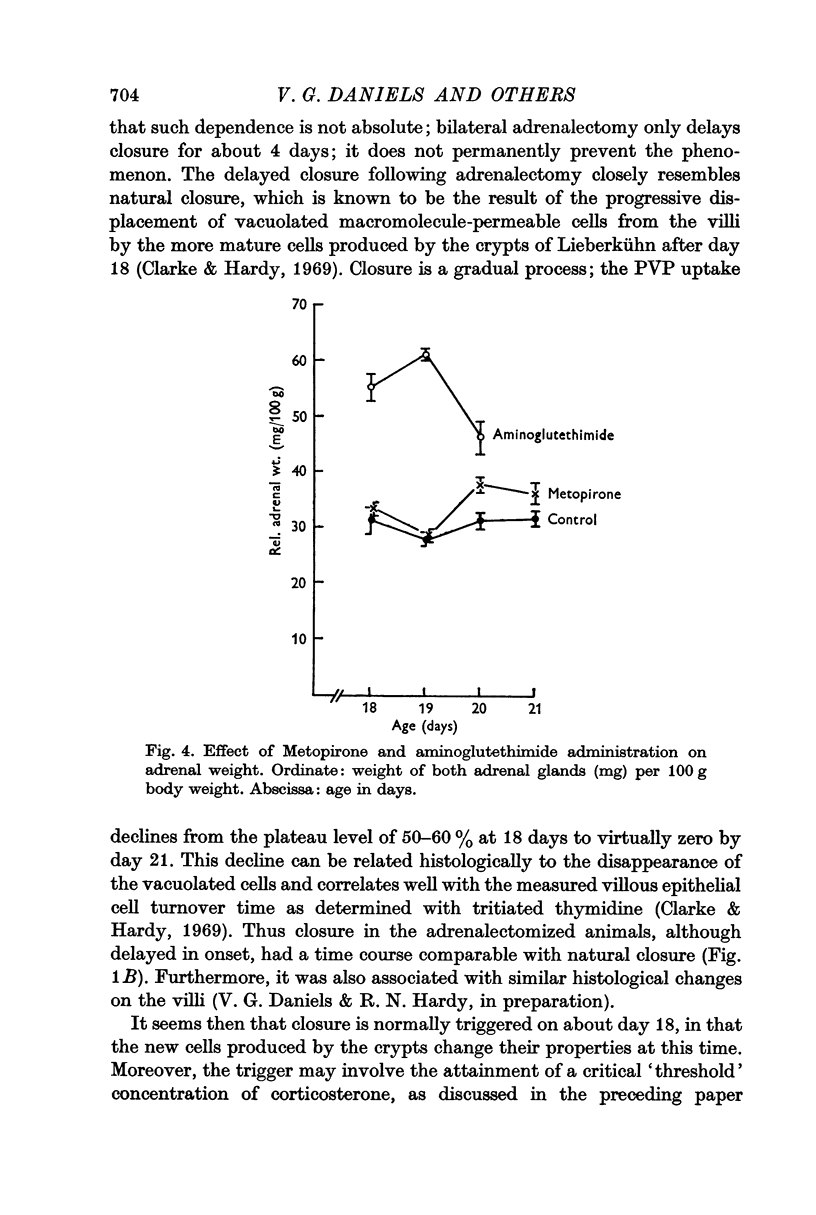
6. Injection of Metopirone or aminoglutethimide increased the relative adrenal weight compared with control animals. Aminoglutethimide was more effective and caused approximately a 100% increase in adrenal weight.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHART J. J., SHEPPARD H. Pharmacology and biochemistry of some amphenone analogues and other adrenal cortical inhibitors. J Med Pharm Chem. 1959 Oct;1:407–441. doi: 10.1021/jm50006a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK S. L., Jr The ingestion of proteins and colloidal materials by columnar absorptive cells of the small intestine in suckling rats and mice. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):41–50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. M., Hardy R. N. An analysis of the mechanism of cessation of uptake of macromolecular substances by the intestine of the young rat ('closure'). J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):127–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels V. G., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K. W., Nathanielsz P. W. Adrenocortical hormones and absorption of macromolecules by the small intestine of the young rat. J Endocrinol. 1972 Feb;52(2):405–406. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0520405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels V. G., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K. W., Nathanielsz P. W. The influence of exogenous steroids on macromolecule uptake by the small intestine of the new-born rat. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):681–695. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels V. G., Hardy R. N. The role of the adrenal gland in the control of intestinal absorption of macromolecules by the young rat. Experientia. 1972 Mar 15;28(3):272–273. doi: 10.1007/BF01928683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter R. N., Fishman L. M., Ney R. L., Liddle G. W. Inhibition of adrenal corticosteroid synthesis by aminoglutethimide: studies of the mechanism of action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Apr;27(4):473–480. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-4-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIDAY R. The effect of steroid hormones on the absorption of antibody by the young rat. J Endocrinol. 1959 Jan;18(1):56–66. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0180056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinowska K. W., Hardy R. N., Nathanielsz P. W. Neonatal adrenocortical function and its possible relation to the uptake of macromolecules by the small intestine of the guinea-pig and rabbit. J Endocrinol. 1972 Nov;55(2):397–404. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0550397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. E. "Sephadex" column chromatography as an adjunct to competitive protein binding assays of steroids. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 7;232(27):21–24. doi: 10.1038/newbio232021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. E. Some studies of the protein-binding of steroids and their application to the routine micro and ultramicro measurement of various steroids in body fluids by competitive protein-binding radioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jul;27(7):973–990. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-7-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


