Abstract
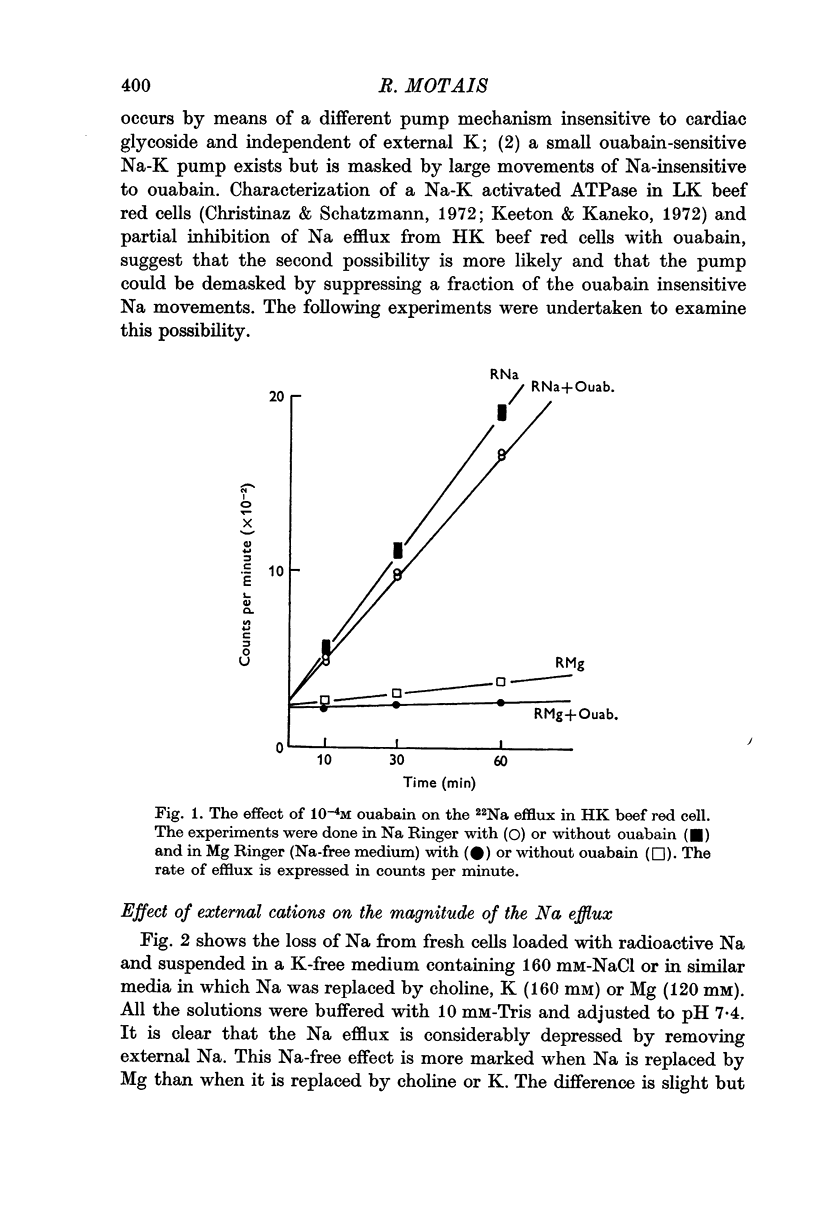
1. The relative importance of the Na efflux components in beef red cells has been evaluated. The component which is insensitive to ouabain, which does not require external K but depends on the presence of external Na, accounts for about 90% of the total Na efflux.
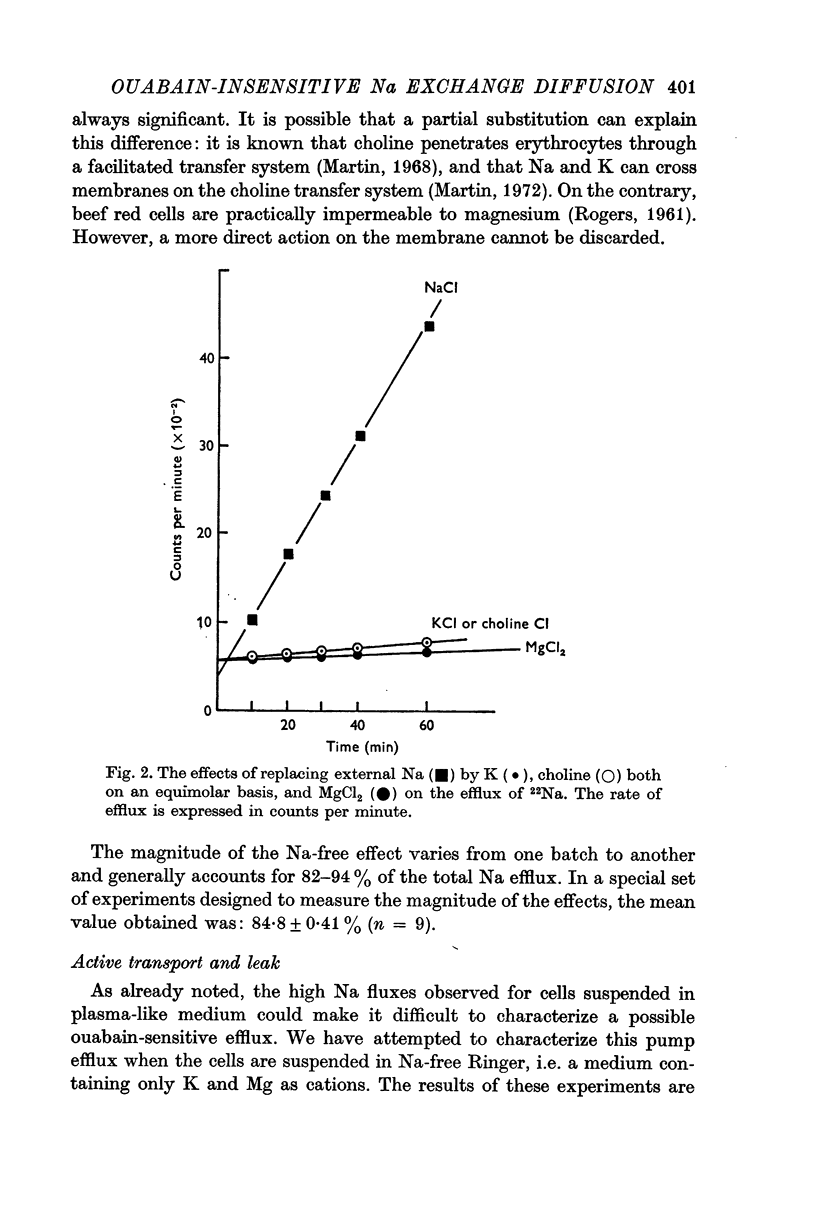
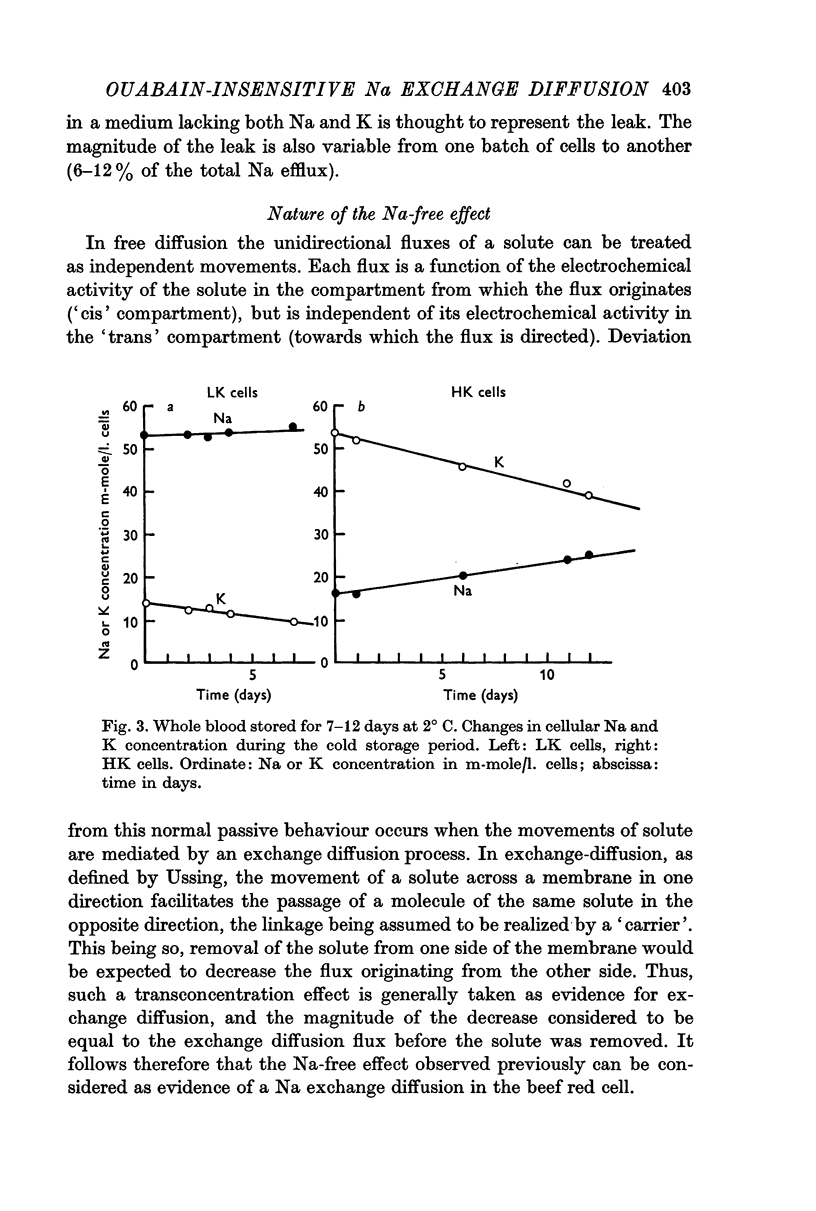
2. The experiments reported in this paper are consistent with the presence of an ouabain-insensitive Na+-Na+ exchange process accounting for this ouabain-insensitive external Na dependent efflux.
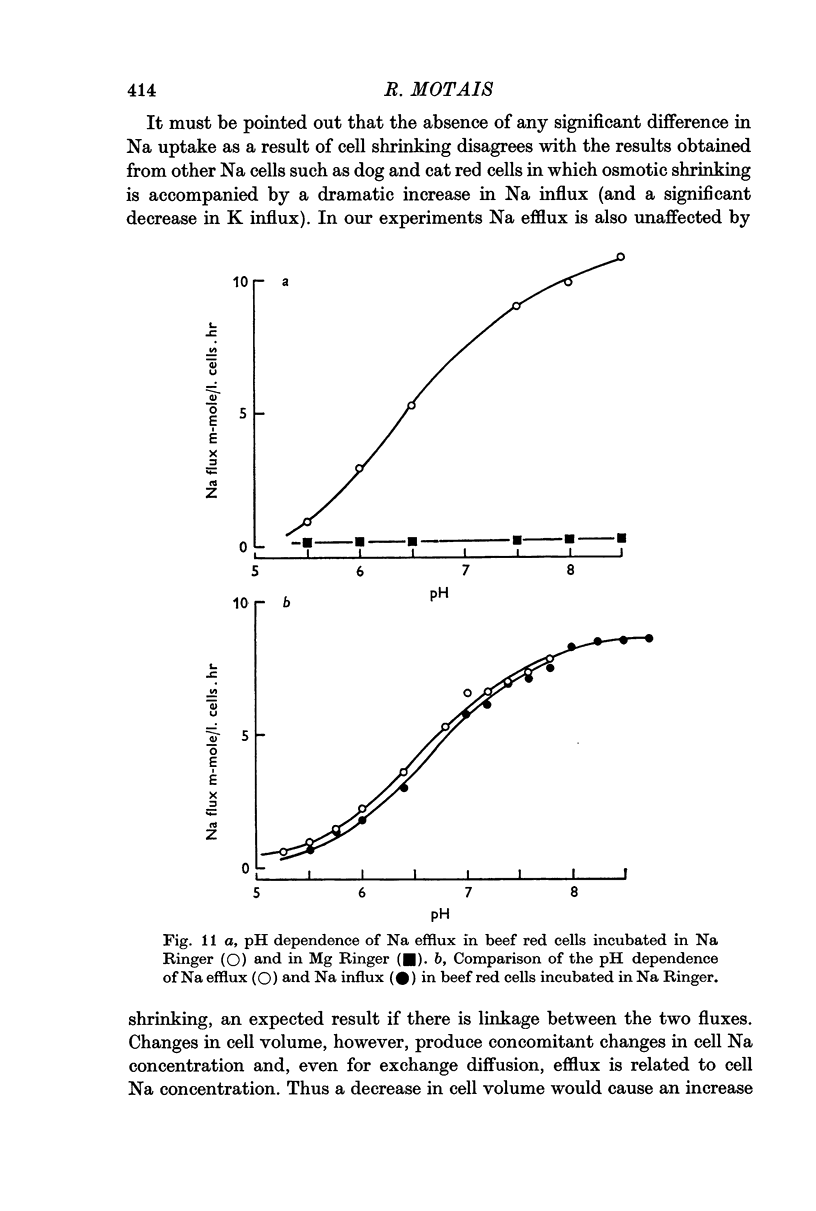
3. A strictly parallel behaviour of influx and efflux is observed when the pH is altered. The exchange diffusion process is inhibited over 90% by a decrease in pH from range pH 8·0-5·5.
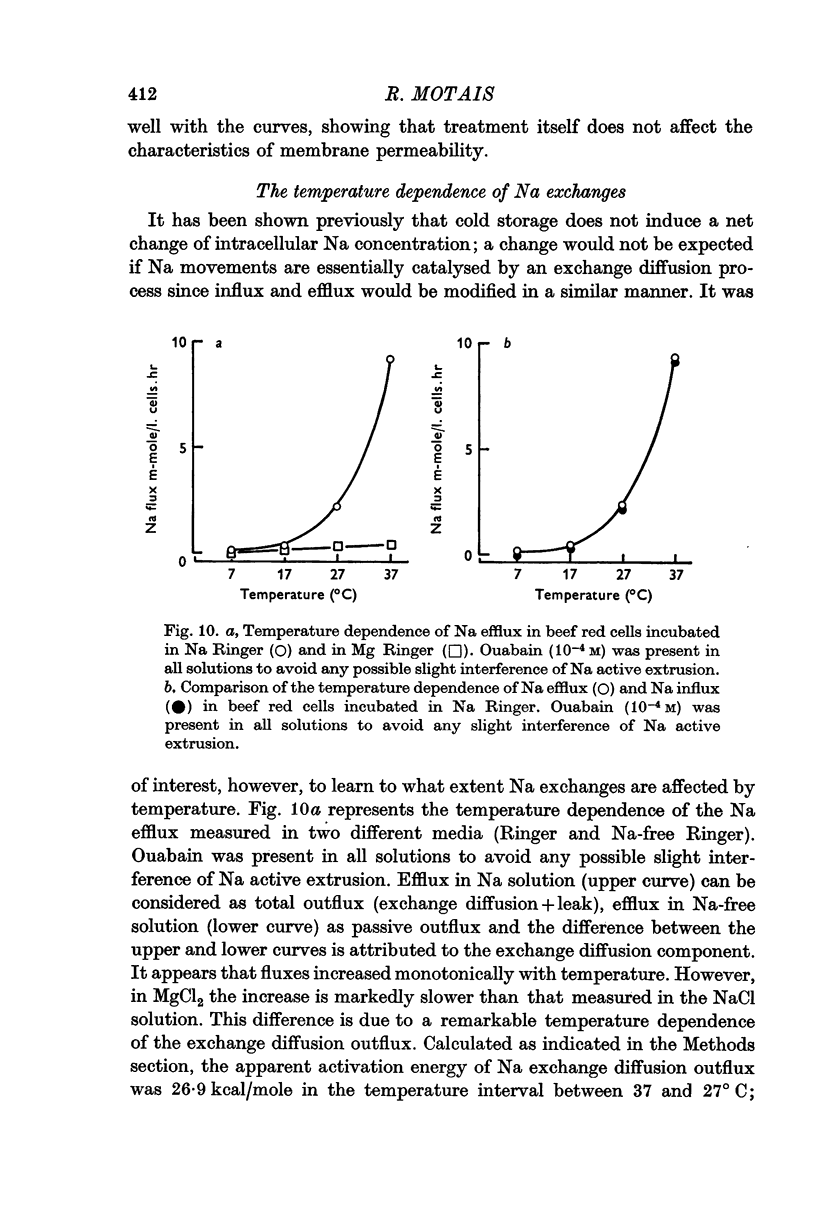
4. Both Na efflux and influx are markedly increased by raising the temperature from 27 to 37° C.
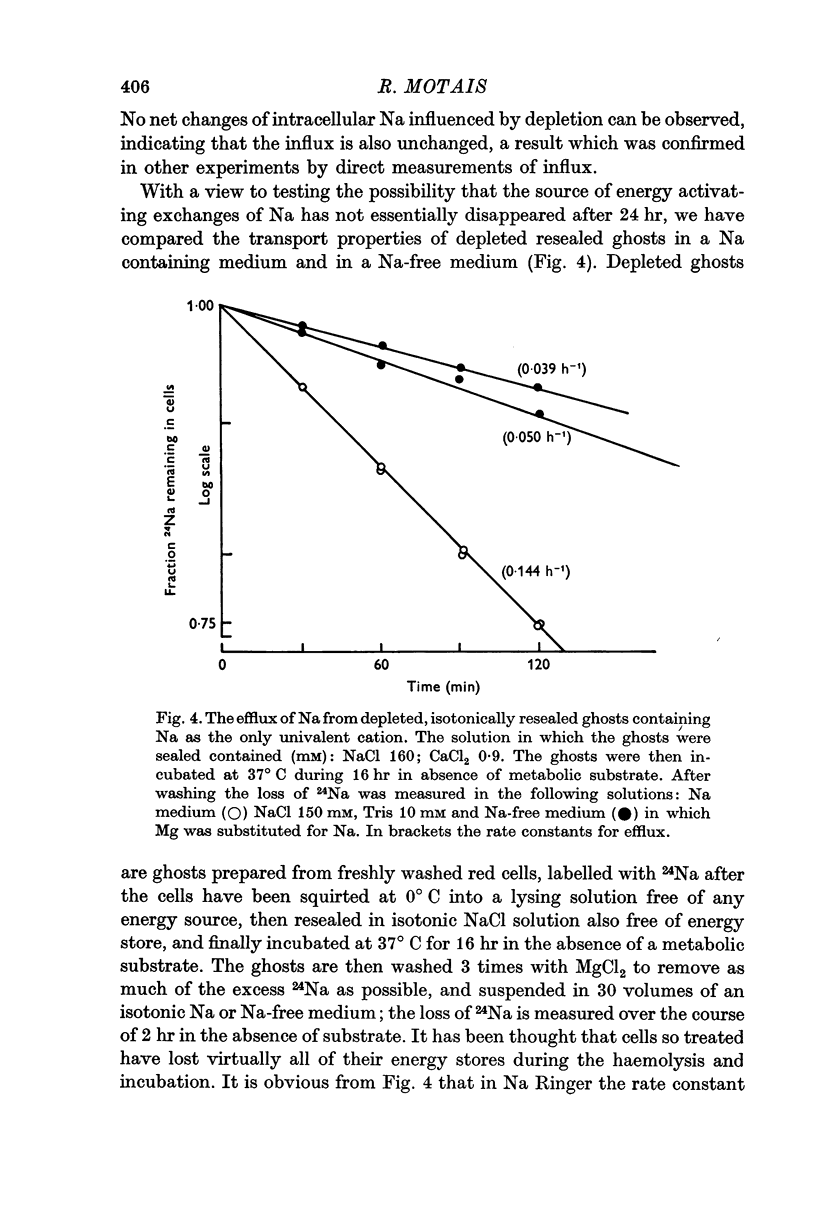
5. Energy depleted cells and fresh cells behave similarly in respect to Na movements. In depleted resealed ghosts, a large Na-dependent efflux occurs. No chemical energy and no special nucleotide is required for the Na+-Na+ exchanges.
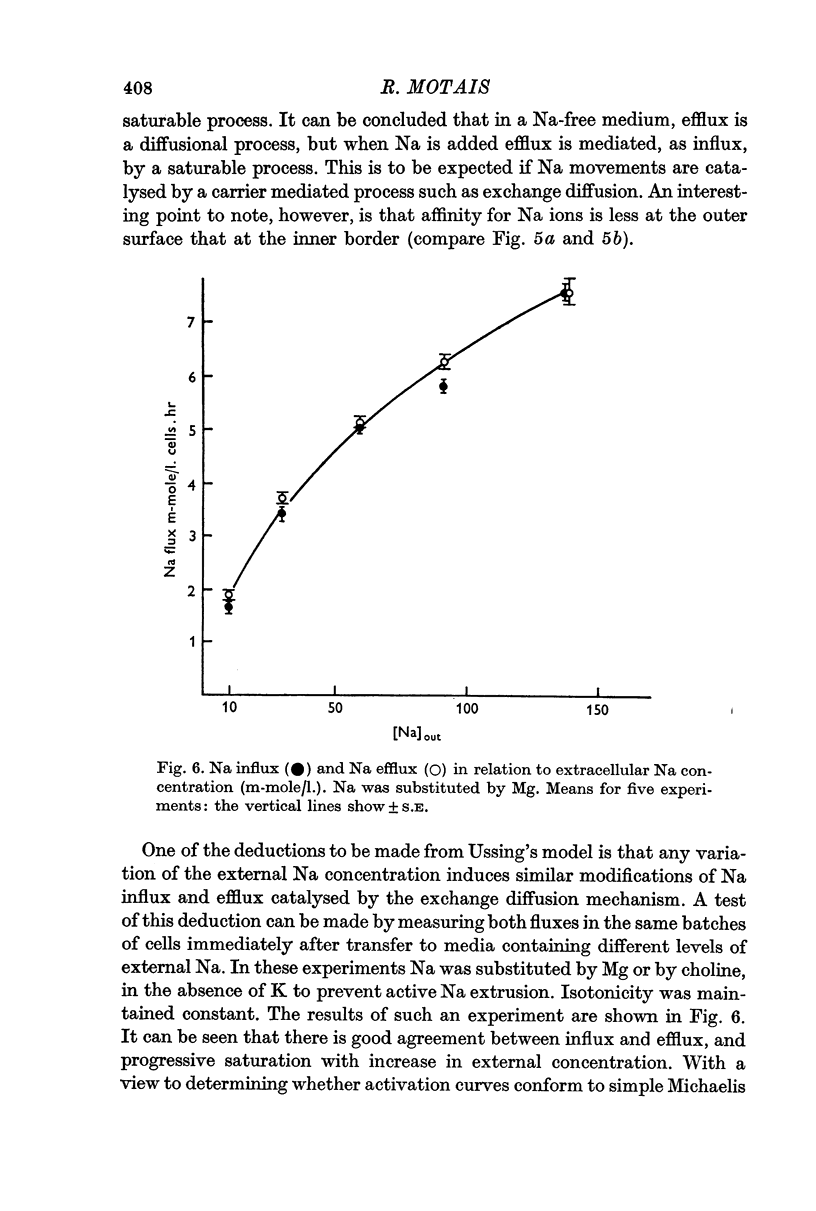
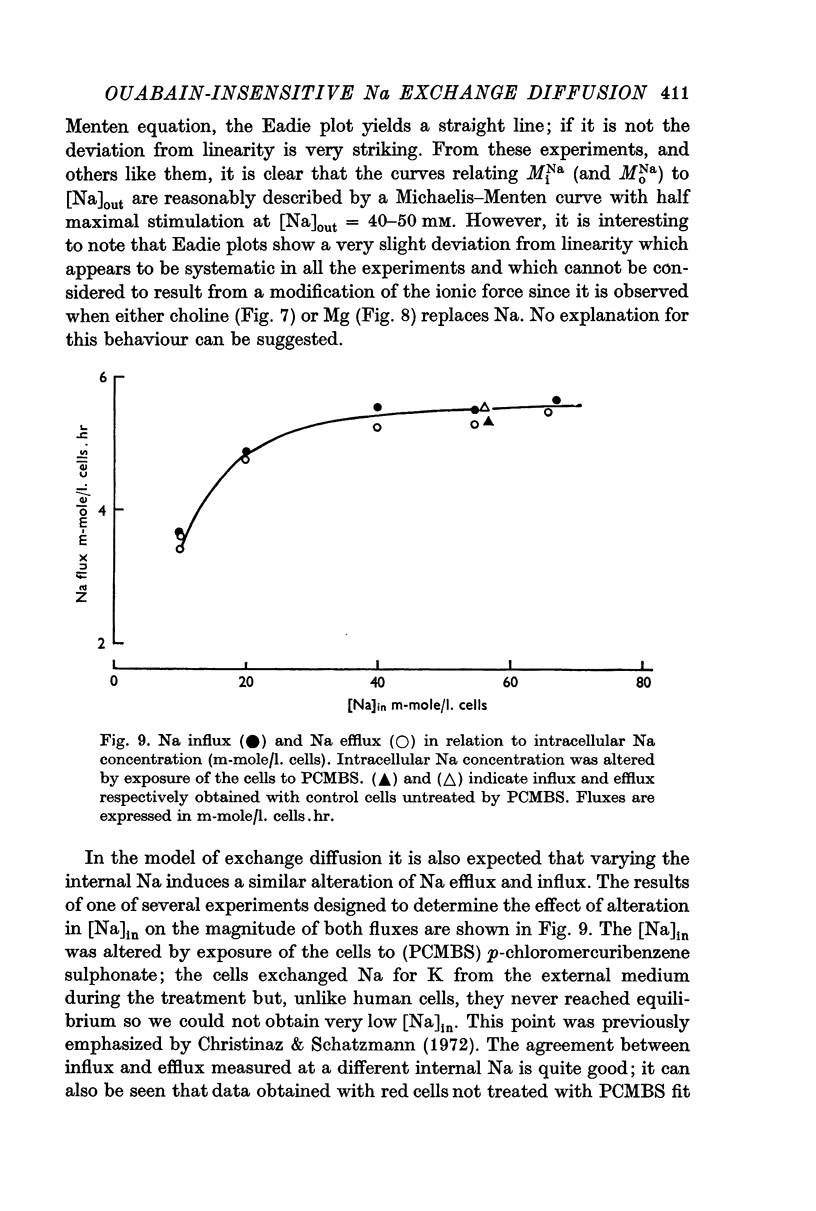
6. When the external or internal Na concentrations are changed, a parallel behaviour of influx and efflux is observed.
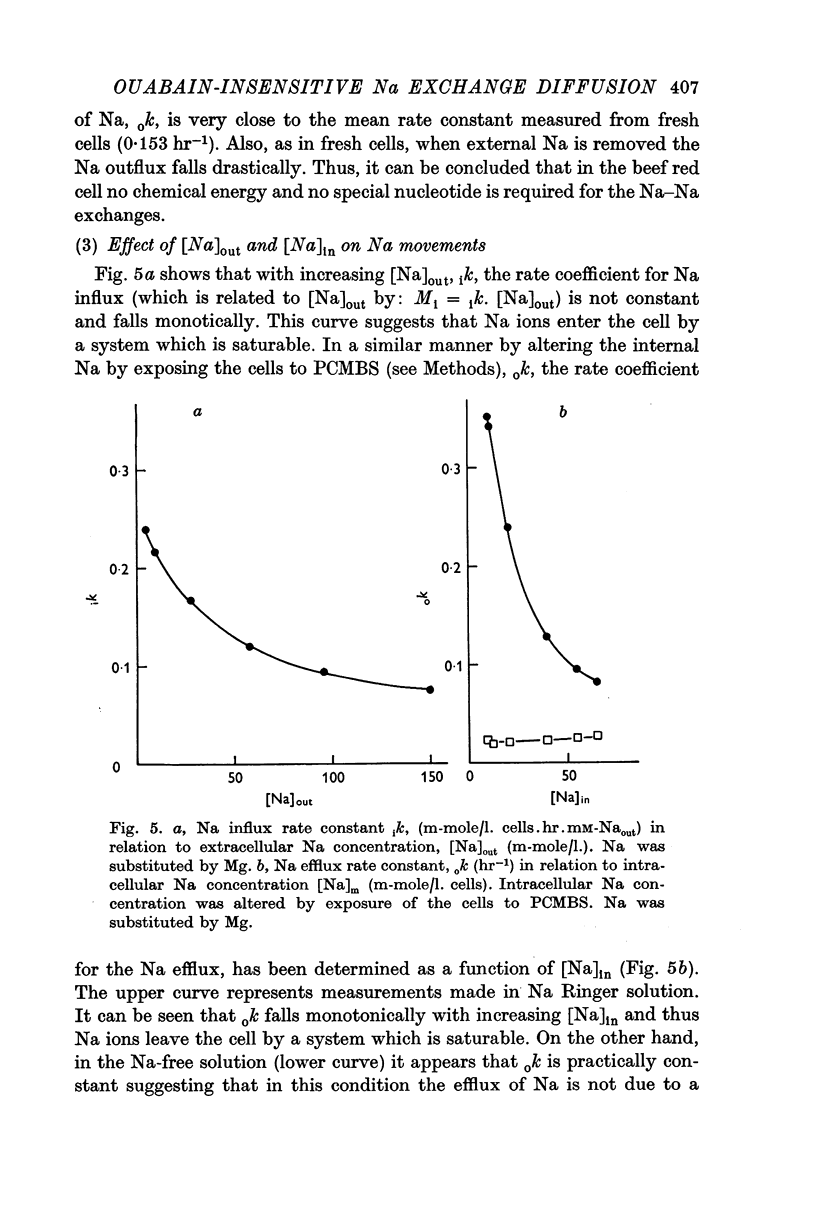
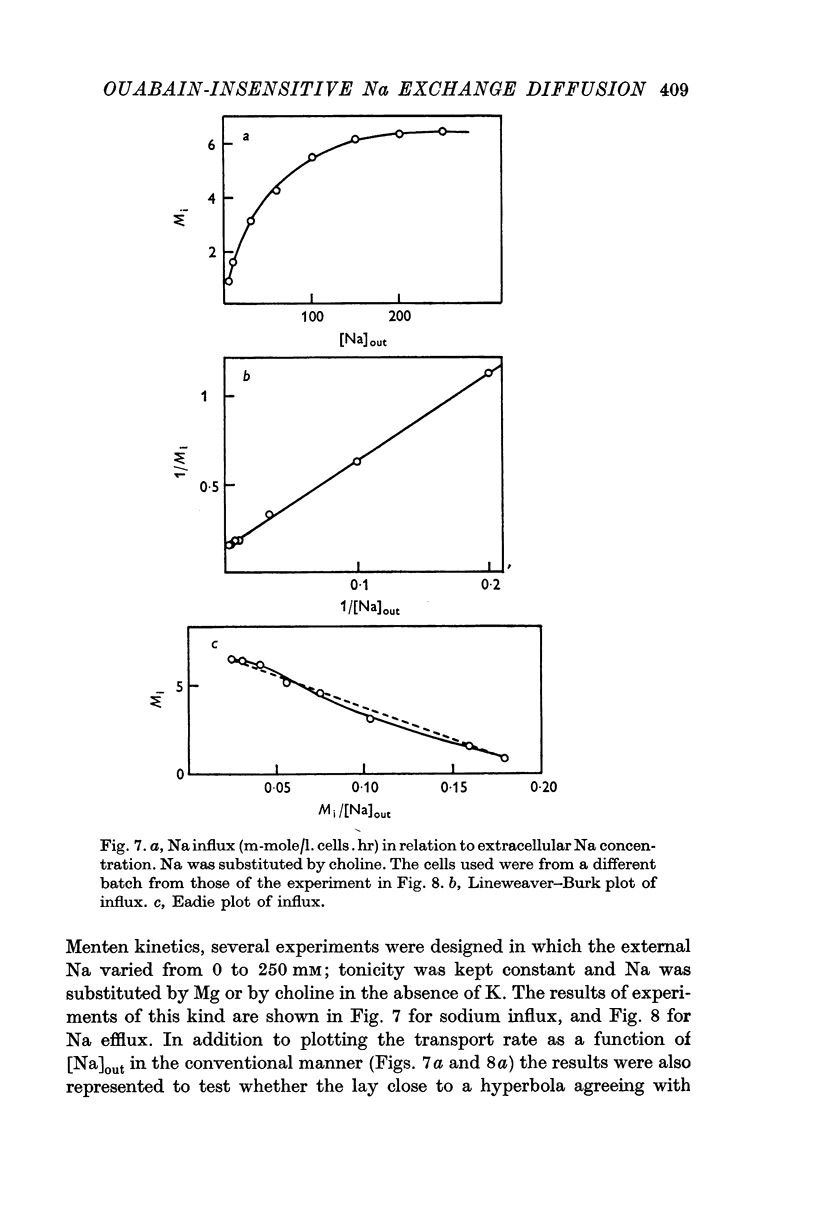
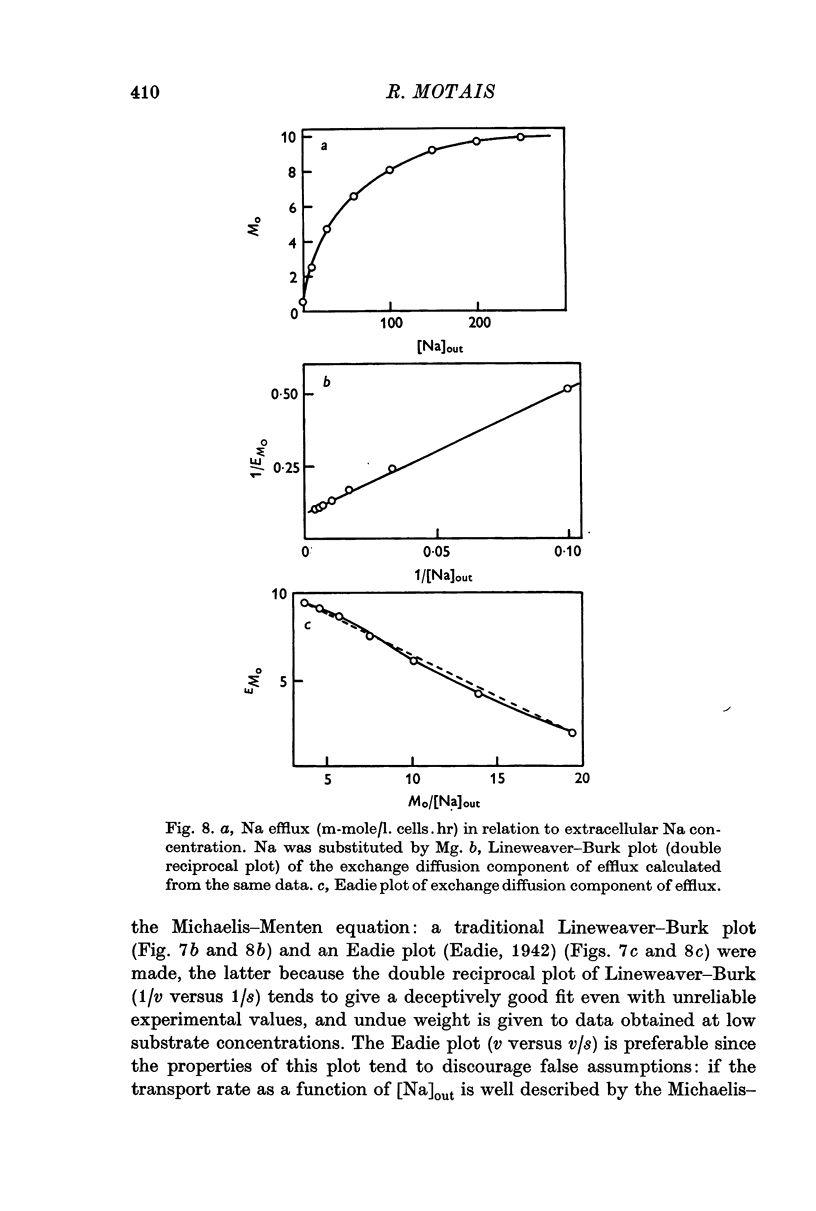
7. The relation between the magnitude of the exchange diffusion flux and the external or internal Na concentration fits quite well the Michaelis—Menten equation suggesting that only one Na+ reacts with the transport mechanism. The affinity for Na is lower however at the outer surface than at the inner border of the membrane.
8. The relation between this exchange process, the ouabain-insensitive Na-Na exchanges found in human red cell, and Ussing's model of exchange diffusion is discussed.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britton H. G. Exchange diffusion. Nature. 1970 Feb 21;225(5234):746–747. doi: 10.1038/225746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christinaz P., Schatzmann H. J. High potassium and low potassium erythrocytes in cattle. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):391–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURBIN R. P., KITAHARA S., STAHLMANN K., HEINZ E. EXCHANGE DIFFUSION OF CHLORIDE IN FROG GASTRIC MUCOSA. Am J Physiol. 1964 Dec;207:1177–1180. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.6.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J. The effects of transport inhibitors on sodium outflux and influx in red blood cells: evidence for exchange diffusion. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1804–1814. doi: 10.1172/JCI106398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. V. Electrolyte concentrations in red blood cells of British breeds of sheep. Nature. 1954 Nov 13;174(4437):931–932. doi: 10.1038/174931a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The behaviour of the sodium pump in red cells in the absence of external potassium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):159–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The stoicheiometry of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):217–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Rega A. F. Cation loading of red blood cells. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):459–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Hoffman J. F. Nucleotide requirements for sodium-sodium exchange catalysed by the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. F., Kregenow F. M. The characterization of new energy dependent cation transport processes in red blood cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):566–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton K. S., Kaneko J. J. Characterization of adenosine triphosphatase in erythrocyte membranes of the cow. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):30–35. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubowitz H. Exchange diffusion in human red blood cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):153–156. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubowitz H., Whittam R. Ion movements in human red cells independent of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1969 May;202(1):111–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. Concentrative accumulation of choline by human erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Apr;51(4):497–516. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. Extracellular cations and the movement of choline across the erythrocyte membrane. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleger K., Rummel W., Seifen E. Sodium and potassium permeability of red blood cells in dependence of the pH. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;295(3):255–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01844105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poznansky M., Solomon A. K. Effect of cell volume on potassium transport in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS T. A. The exchange of radioactive magnesium in erythrocytes of several species. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1961 Apr;57:119–121. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030570209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettori O., Lenoir J. P. Ouabain-insensitive active socium transport in erythrocytes: effect of external cation. Am J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(4):880–884. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.4.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romualdez A., Sha'afi R. I., Lange Y., Solomon A. K. Cation transport in dog red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jul;60(1):46–57. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPPARD C. W., MARTIN W. R., BEYL G. Cation exchange between cells and plasma of mammalian blood. II. Sodium and potassium exchange in the sheep, dog, cow, and man and the effect of varying the plasma potassium concentration. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Mar 20;34(4):411–429. doi: 10.1085/jgp.34.4.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORENSON A. L., KIRSCHNER L. B., BARKER J. Sodium fluxes in the erythrocytes of swine, ox, and dog. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jul;45:1031–1047. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.6.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Ouabain-insensitive sodium movements in the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Mar;57(3):259–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Sodium movements in the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Sep;56(3):322–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'afi R. I., Hajjar J. J. Sodium movement in high sodium feline red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jun;57(6):684–696. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.6.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSTESON D. C. Active transport, genetics, and cellular evolution. Fed Proc. 1963 Jan-Feb;22:19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSTESON D. C., HOFFMAN J. F. Regulation of cell volume by active cation transport in high and low potassium sheep red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Sep;44:169–194. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Breemen D., Van Breemen C. Calcium exchange diffusion in a porous phospholipid ion-exchange membrane. Nature. 1969 Aug 30;223(5209):898–900. doi: 10.1038/223898a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R. Potassium movements and ATP in human red cells. J Physiol. 1958 Mar 11;140(3):479–497. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


