Abstract
1. The studies described herein involve the use of light scattering measurements to characterize the ultrastructural arrangement of the constituent collagen fibrils in rabbit corneal stromas.
2. Theoretical light scattering techniques for calculating the scattering to be expected from the structures revealed by electron micrographs are discussed, and comparison with the experimental light scattering tests the validity of these structures.
3. The wave-length dependence of light transmission and of angular light scattering from normal corneas is in agreement with the short range ordering of collagen fibrils depicted in electron micrographs.
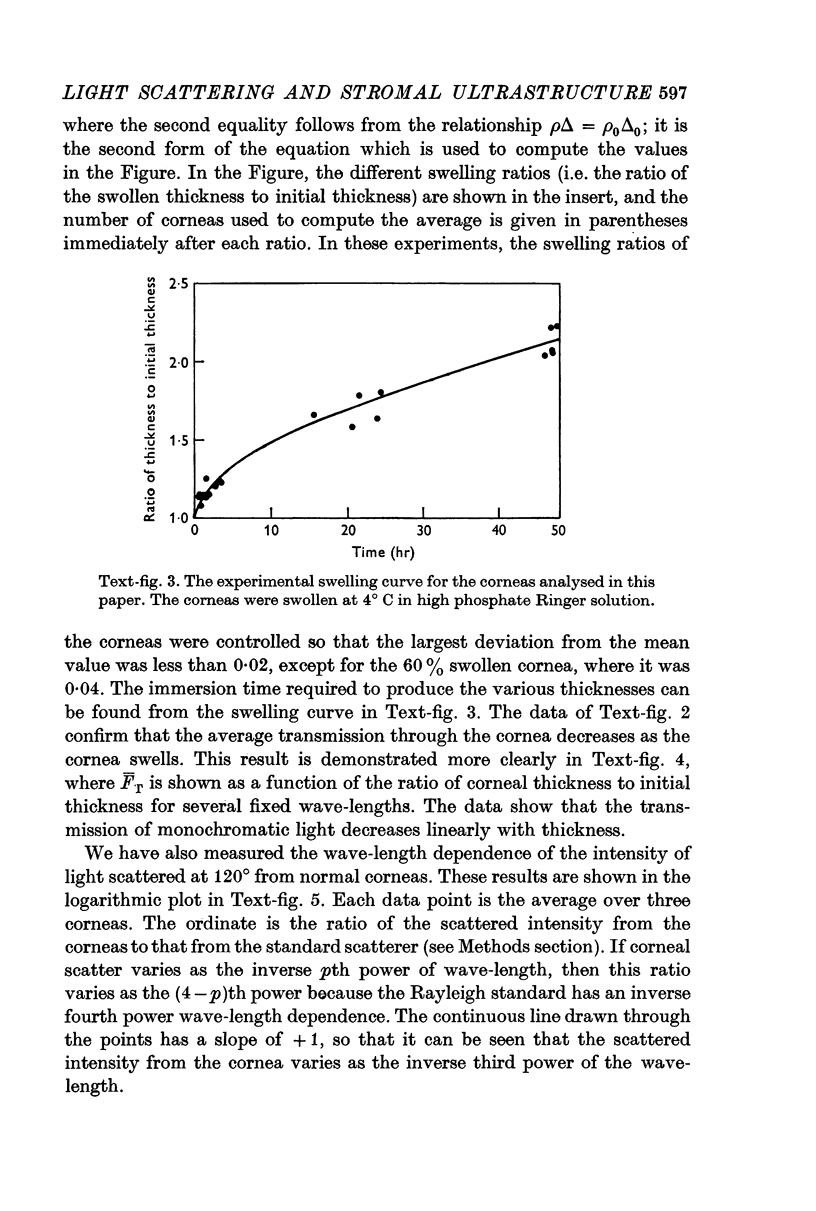
4. The transmission measurements on oedematous rabbit corneas indicate that transmission decreases linearly with the ratio of thickness to normal thickness.
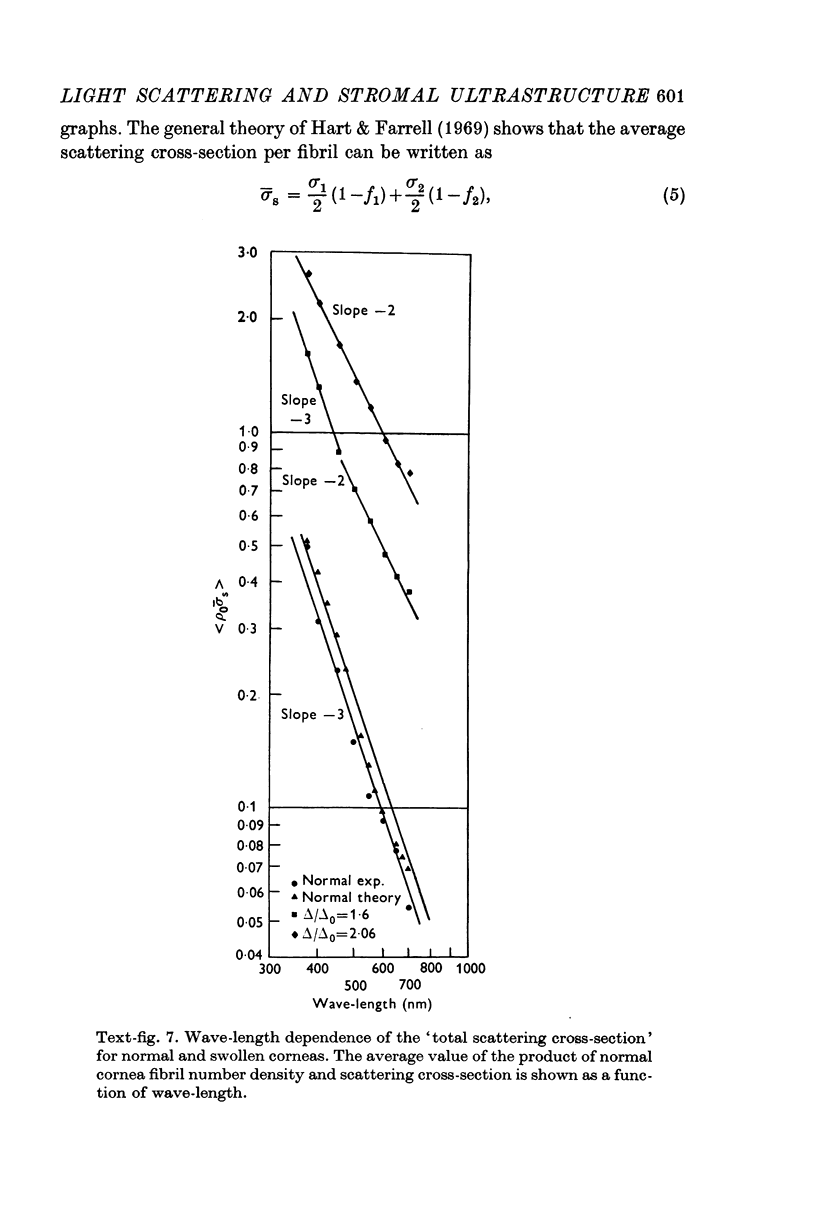
5. The wave-length dependence of transmission through cold swollen corneas indicates that the increased scattering is caused by large inhomogeneities in the ultrastructure. Electron micrographs do, indeed, reveal the presence of such inhomogeneities in the form of large regions completely devoid of fibrils.
Full text
PDF
























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COULOMBRE A. J., COULMBRE J. L. Corneal development. II. Transparency changes during rapid hydration. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Nov;46(5 Pt 2):276–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. L., Farrell R. A., Hart R. W., Langham M. E. The transparency of the mammalian cornea. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):601–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuk T. The wavelength dependence of scattered light intensity in rabbit corneas. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1971 Mar;18(2):92–96. doi: 10.1109/tbme.1971.4502808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUERRY D., 3rd, HAM W. T., Jr, RUFFIN R. S., SCHMIDT F. H., TILLER C. O., WIESINGER H., WILLIAMS R. C. The transmission of light; through the ocular media of the rabbit eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 1956 Dec;42(6):907–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. N., Benedek G. B., Dohlman C. H., Kravitt B. Structural alterations affecting transparency in swollen human corneas. Invest Ophthalmol. 1968 Oct;7(5):501–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. N., Benedek G. B. The relationship between morphology and transparency in the nonswelling corneal stroma of the shark. Invest Ophthalmol. 1967 Dec;6(6):574–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. W., Farrell R. A. Light scattering in the cornea. J Opt Soc Am. 1969 Jun;59(6):766–774. doi: 10.1364/josa.59.000766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIKKAWA Y. Light scattering studies of the rabbit cornea. Jpn J Physiol. 1960 Jun 29;10:292–302. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.10.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURICE D. M., GIARDINI A. A. A simple optical apparatus for measuring the corneal thickness, and the average thickness of the human cornea. Br J Ophthalmol. 1951 Mar;35(3):169–177. doi: 10.1136/bjo.35.3.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURICE D. M. The structure and transparency of the cornea. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 30;136(2):263–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurice D. M. The transparency of the corneal stroma. Vision Res. 1970 Jan;10(1):107–108. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(70)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGILVIE J. C. Ultraviolet radiation and vision. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1953 Dec;50(6):748–763. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1953.00920030759011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





