Abstract
1. In tetanic contractions during which shortening has occurred the total heat produced is greater than in isometric controls.
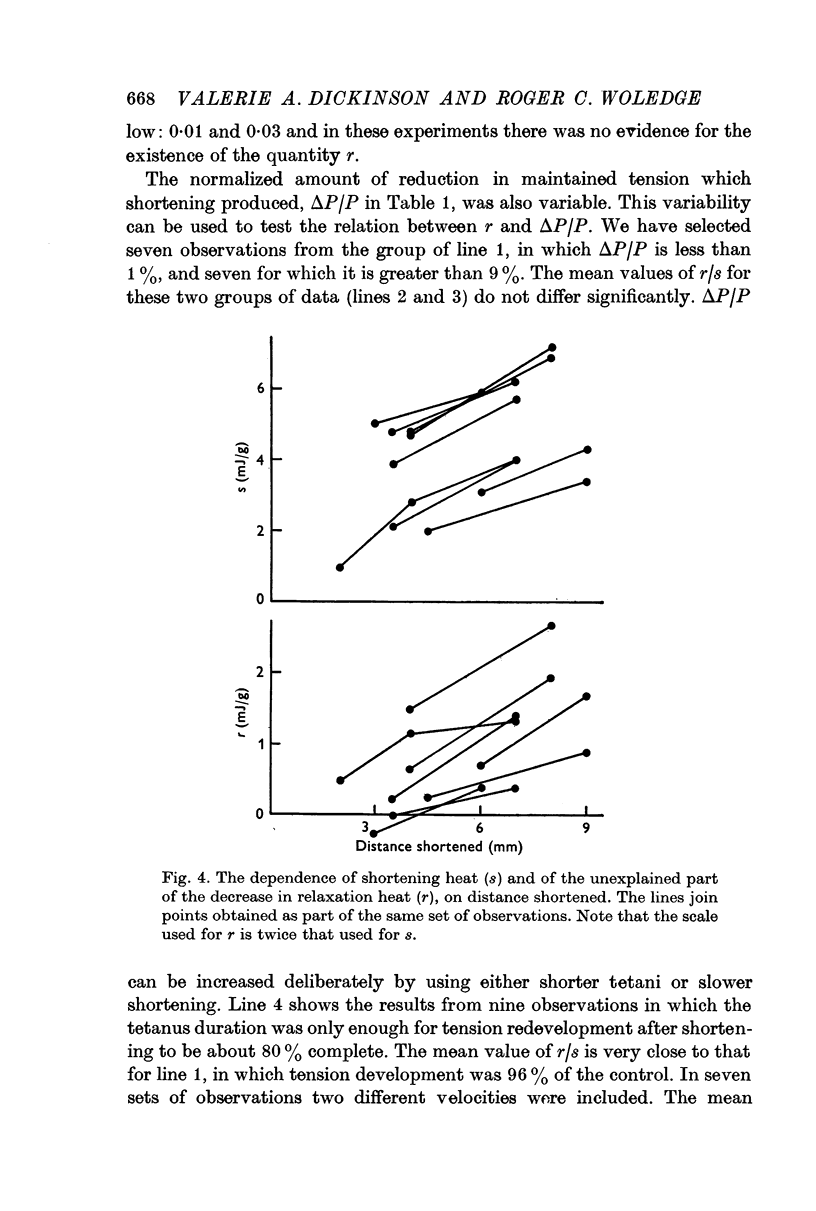
2. The amount of this excess, measured after relaxation, is less than the shortening heat measured before relaxation. In other words relaxation heat is less after contractions with shortening.
3. Only a small part of this reduction in relaxation heat can be explained by the reduced thermoelastic heat and work dissipation due to the lower tension maintained after shortening.
4. In the few experiments in which the full tension is redeveloped after shortening the relaxation heat is still reduced.
5. Decreases in the tension redeveloped after shortening, caused by using shorter tetani, or slower shortening, are not accompanied by decreases in the relaxation heat greater than can be accounted for by the assumed physical results of the lower tension.
6. It is suggested that the reduction in relaxation heat after shortening is due to the occurrence of a reaction in which the exothermic process causing the shortening heat is reversed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABBOTT B. C. The heat production associated with the maintenance of a prolonged contraction and the extra heat produced during large shortening. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):438–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert X., Lebacq J. The heat of shortening during the plateau of tetanic contraction and at the end of relaxation. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(1):181–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSON F. D., HARDY D. J., WILKIE D. R. Total energy production and phosphocreatine hydrolysis in the isotonic twitch. J Gen Physiol. 1963 May;46:851–882. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn W. O. A quantitative comparison between the energy liberated and the work performed by the isolated sartorius muscle of the frog. J Physiol. 1923 Dec 28;58(2-3):175–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1923.sp002115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn W. O. The relation between the work performed and the energy liberated in muscular contraction. J Physiol. 1924 May 23;58(6):373–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1924.sp002141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C., Kretzschmar K. M., Wilkie D. R., Woledge R. C. Chemical change and energy output during muscular contraction. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):163–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V., HOWARTH J. V. Alternating relaxation heat in muscle twitches. J Physiol. 1957 Dec 31;139(3):466–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. THE EFFECT OF LOAD ON THE HEAT OF SHORTENING OF MUSCLE. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:297–318. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. THE EFFECT OF TENSION IN PROLONGING THE ACTIVE STATE IN A TWITCH. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Mar 17;159:589–595. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. The heat produced by a muscle after the last shock of a tetanus. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:518–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V., WOLEDGE R. C. An examination of absolute values in myothermic measurements. J Physiol. 1962 Jul;162:311–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEWELL B. R., WILKIE D. R. An analysis of the mechanical components in frog's striated muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):515–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEWELL B. R., WILKIE D. R. The mechanical properties of relaxing muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;152:30–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell B. R., Kretzschmar M., Woledge R. C. Length and tension transducers. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):10P–12P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Larson R. E., Davies R. E. The chemical energetics of muscle contraction. I. Activation heat, heat of shortening and ATP utilization for activation-relaxation processes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Dec 23;174(1036):293–313. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLEDGE R. C. Heat production and energy liberation in the early part of a muscular contraction. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:211–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLEDGE R. C. The thermoelastic effect of change of tension in active muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:187–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


