Abstract
1. Rats were treated twice daily for 7 days with neostigmine and the diaphragm was isolated for study of its acetylcholine content, release upon nerve stimulation and the number of receptors in the end-plate.
2. While the content of total acetylcholine was unchanged, the release of acetylcholine on stimulation with trains of 500 pulses at 100 Hz every 20 sec was reduced by about 50%. Five days after the end of neostigmine treatment the release of acetylcholine recovered to normal.
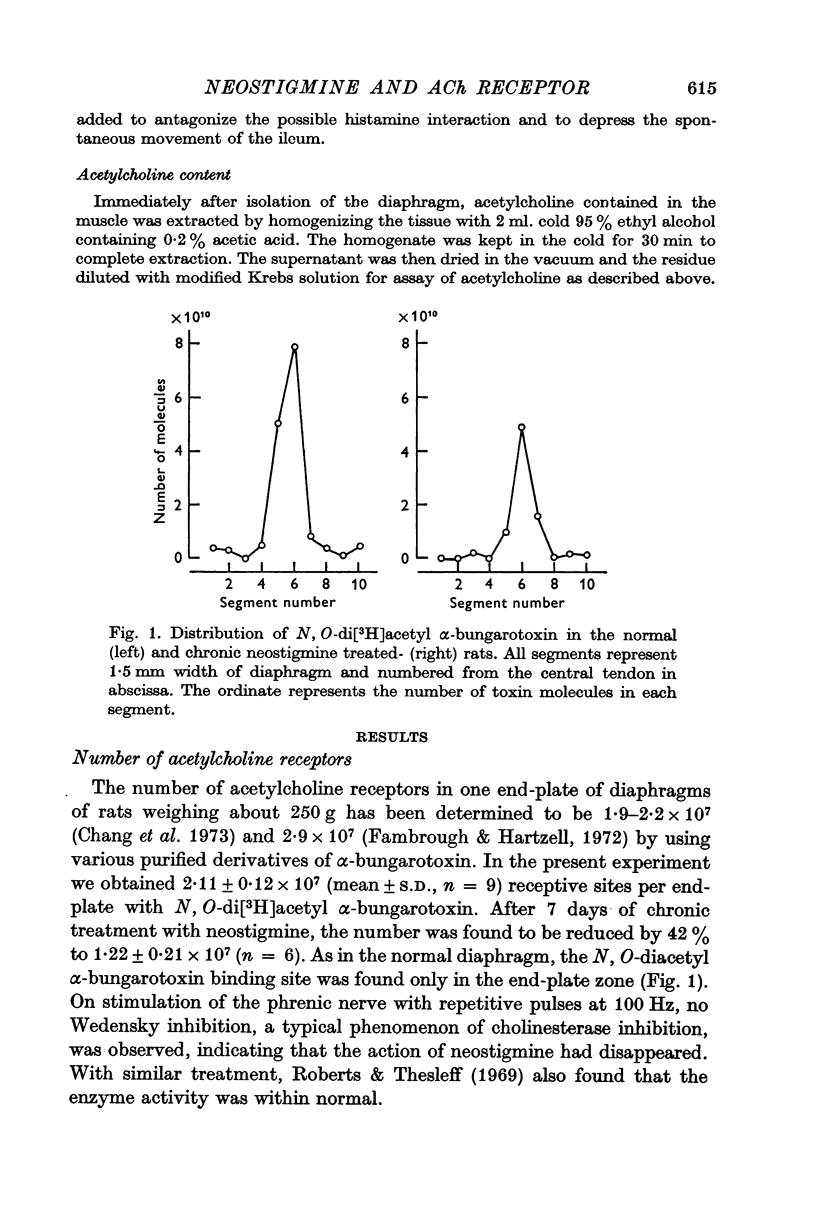
3. The total number of acetylcholine receptors in the end-plate as measured from the binding of N, O-di[3H]acetyl α-bungarotoxin was reduced from 2·1 × 107 to 1·2 × 107 per end-plate.
4. The above-mentioned changes are not due to acute pharmacological effects of neostigmine, nor to an immediate effect of cholinesterase inhibition but presumably due to chronic accumulation of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. A study of supersensitivity in denervated mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 23;147(1):178–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Wieckowski J., Chiu T. H. Cholinergic receptor molecules and cholinesterase molecules at mouse skeletal muscle junctions. Nature. 1971 Nov 26;234(5326):207–209. doi: 10.1038/234207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bit L. Z., Dawson M. J. The site and mechanism of the control of cholinergic sensitivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Dec;175(3):673–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L. Z., Hyslop K., Hyndman J. Antiparasympathomimetic effects of cholinesterase inhibitor treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Jul;157(1):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley G. A., Heading C. E. Tolerance to neostigmine. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):590P–591P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG C. C., LEE C. Y. ISOLATION OF NEUROTOXINS FROM THE VENOM OF BUNGARUS MULTICINCTUS AND THEIR MODES OF NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING ACTION. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963 Jul 1;144:241–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Chen T. F., Chuang S. T. N,O-di and N,N,O-tri ( 3 H) acetyl -bungarotoxins as specific labelling agents of cholinergic receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;47(1):147–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Hartzell H. C. Acetylcholine receptors: number and distribution at neuromuscular junctions in rat diaphragm. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L. "Trophic" influences of nerve on muscle. Physiol Rev. 1968 Oct;48(4):645–687. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. S. THE ORIGIN OF THE ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASED SPONTANEOUSLY FROM THE GUINEA-PIG ISOLATED ILEUM. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:555–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Motor units in the rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1958 Mar 11;140(3):427–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhillips J. J., Dar M. S. Resistance to the effect of carbachol on the cardiovascular system and on the isolated ileum of rats after subacute administration of an organophosphorus cholinesterase inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Jun;156(3):507–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhillips J. J. Subsensitivity of the rat ileum to cholinergic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Apr;166(2):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. V., Thesleff S. Acetylcholine release from motor-nerve endings in rats treated with neostigmine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969;6(3):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90186-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


