Abstract
1. Single muscle fibres from frog semitendinosus were subjected to sudden changes in [K]o, while recording membrane potential.
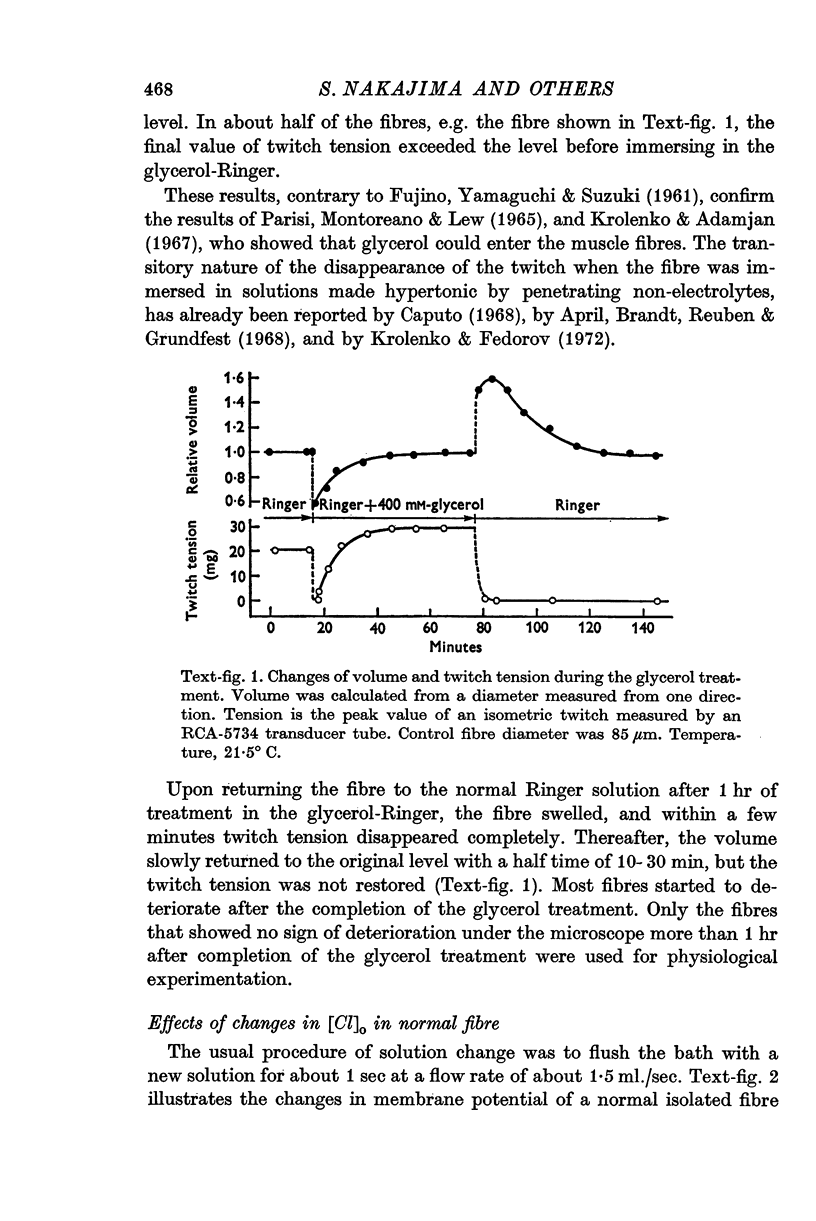
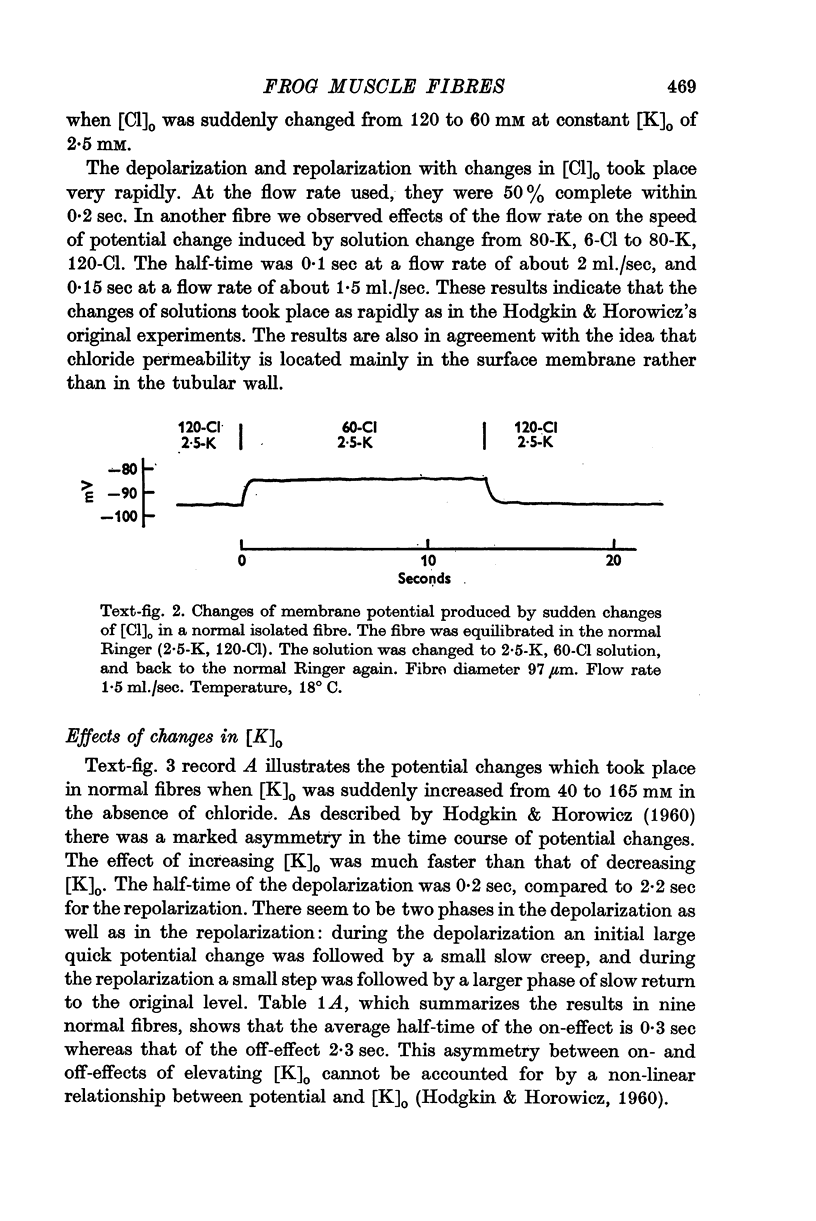
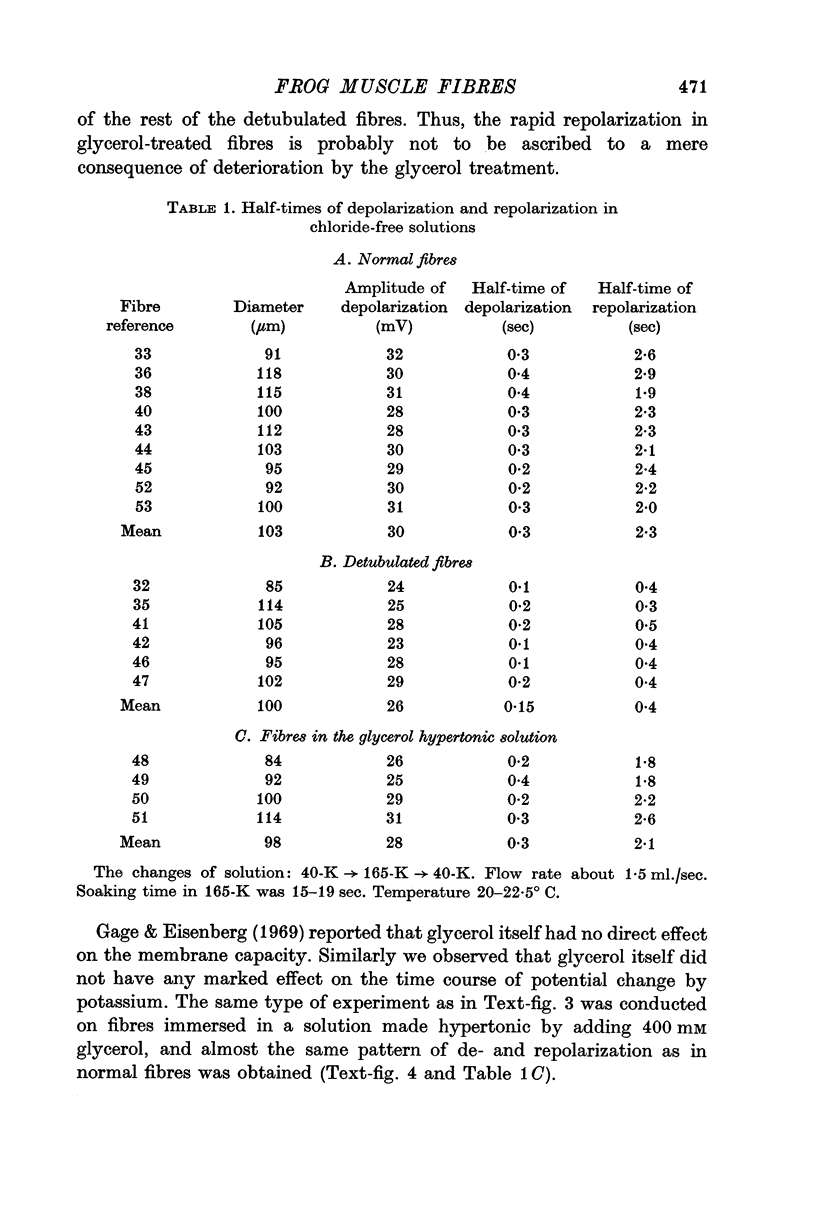
2. In agreement with Hodgkin & Horowicz (1960), a sudden increase in [K]o in normal fibres produced a rapid depolarization (half-time 0·3 sec), whereas a sudden decrease in [K]o produced a slower repolarization (half-time 2-3 sec).
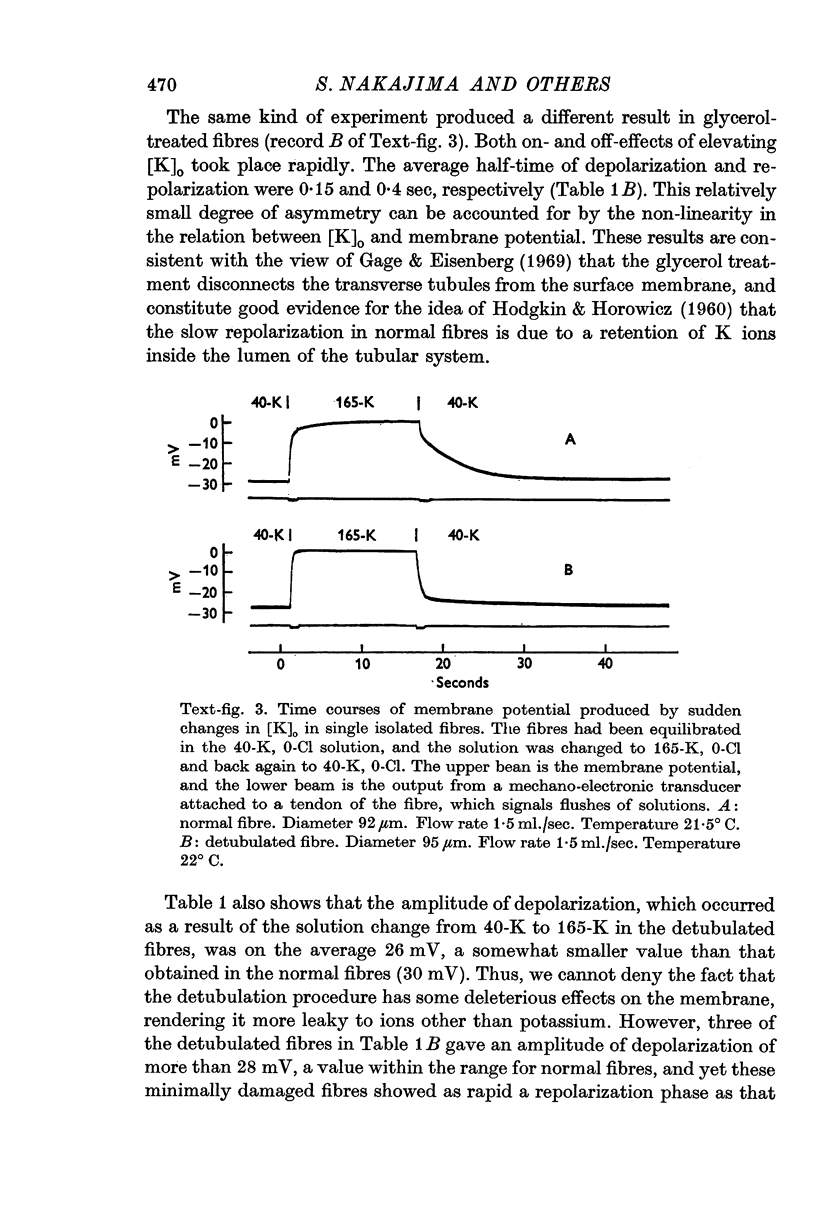
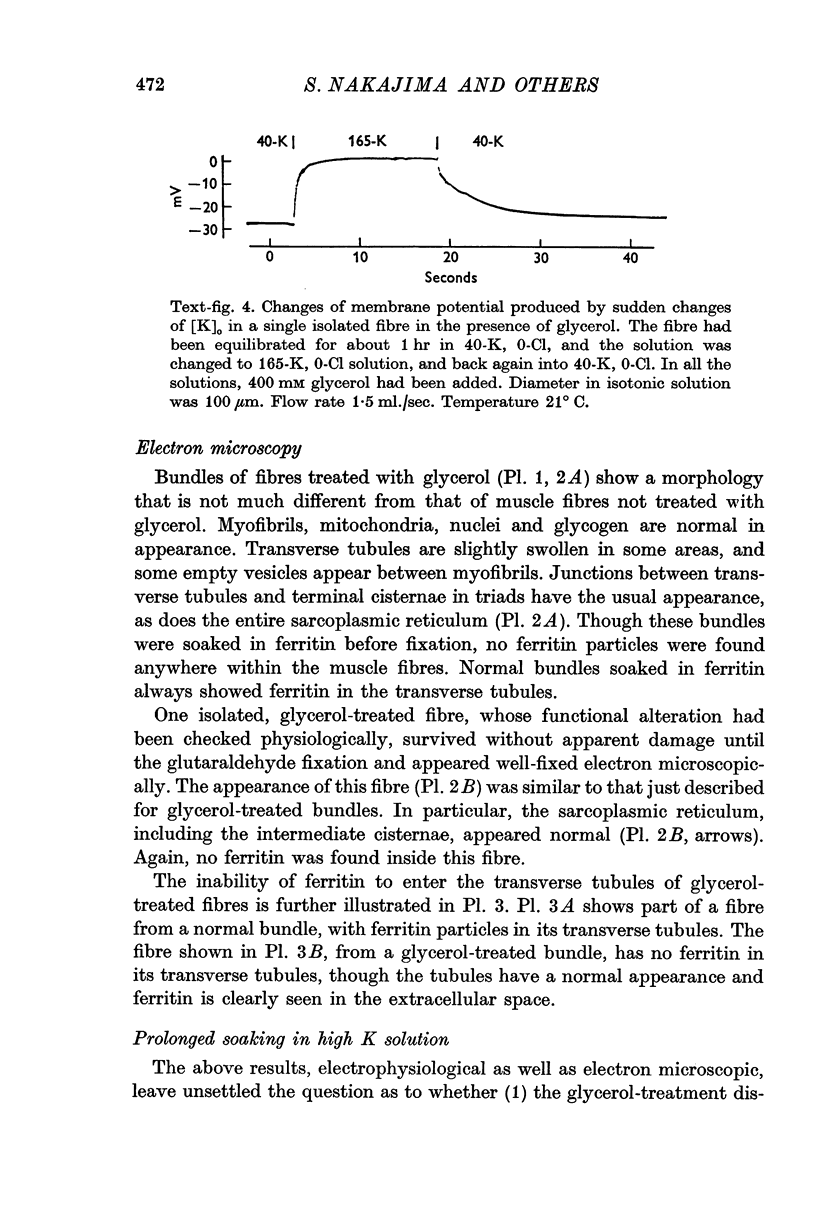
3. Fibres were subjected to `glycerol-treatment', a procedure which was supposed to produce a functional disconnexion of the T-system from the surface. In these glycerol-treated fibres both depolarization and repolarization induced by changes of [K]o took place rapidly.
4. The results suggest that the slowness of the repolarization in normal fibres is due to a retention of K ions inside the T-tubules.
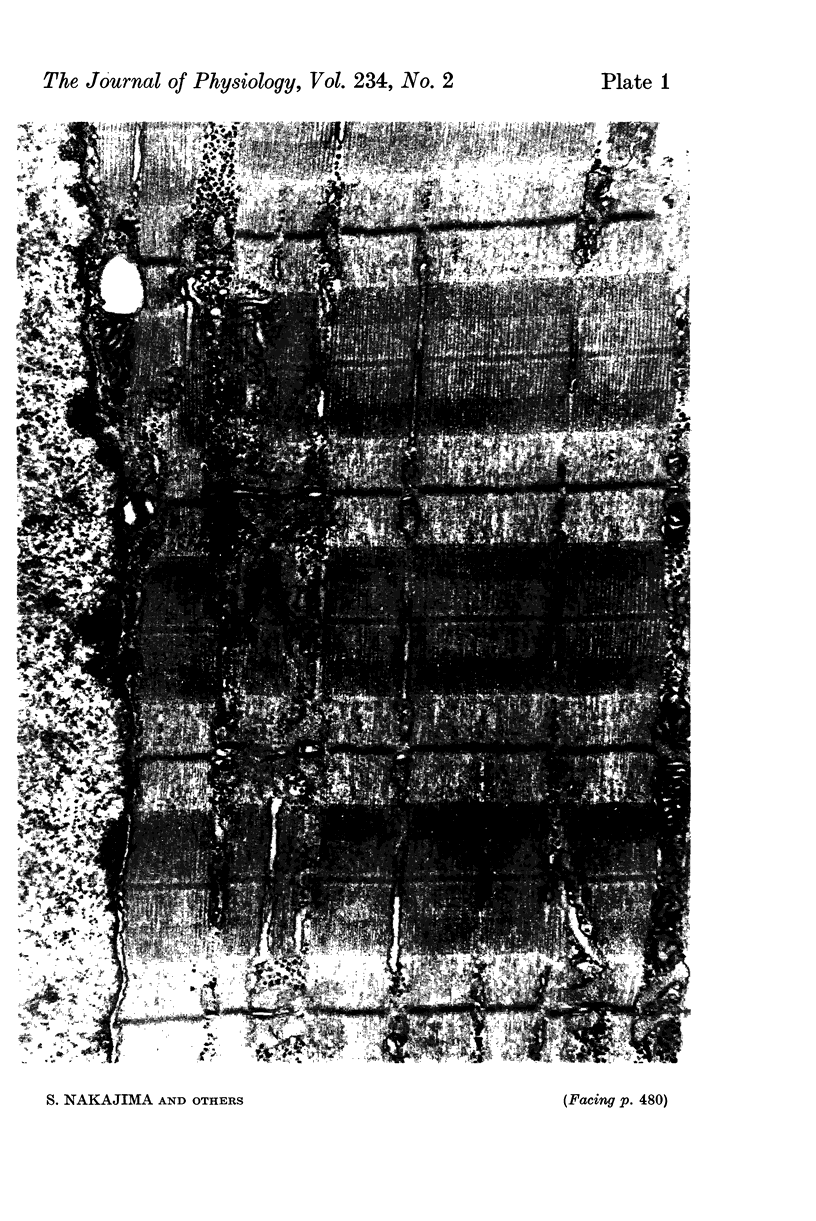
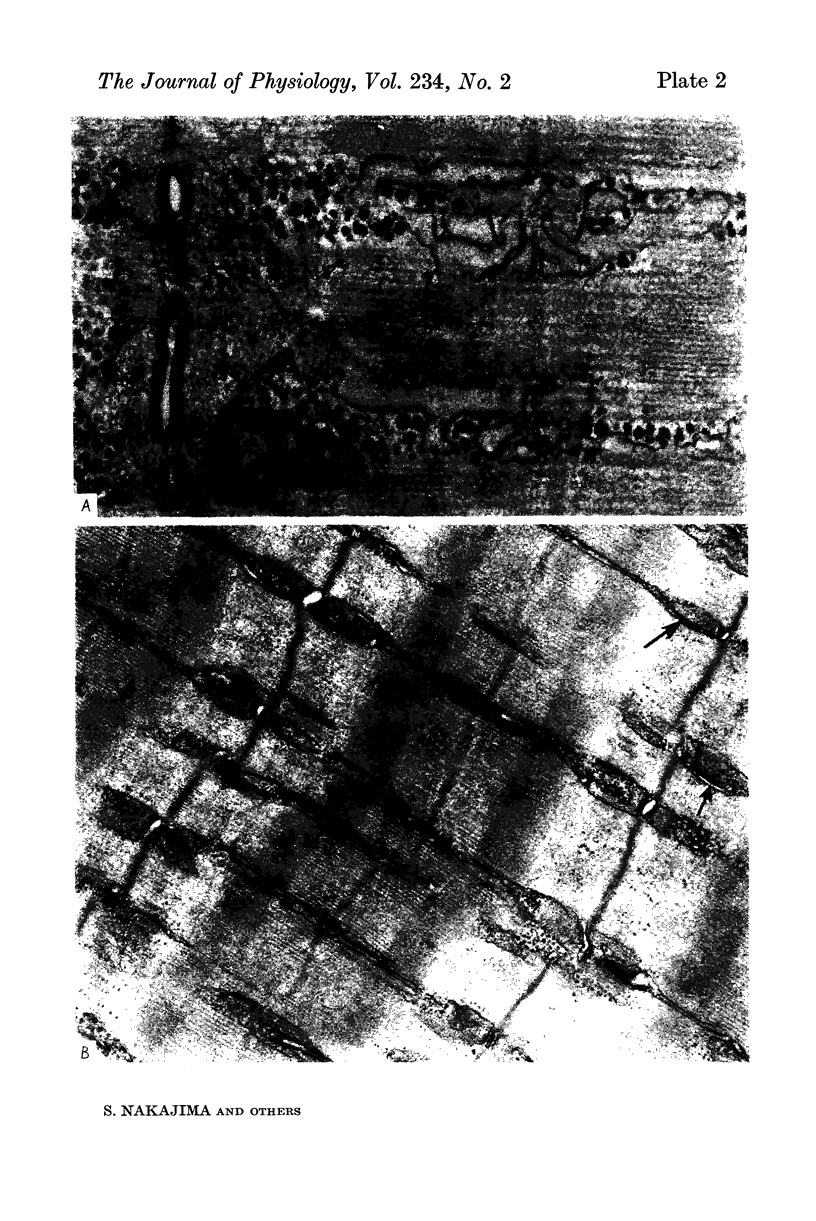
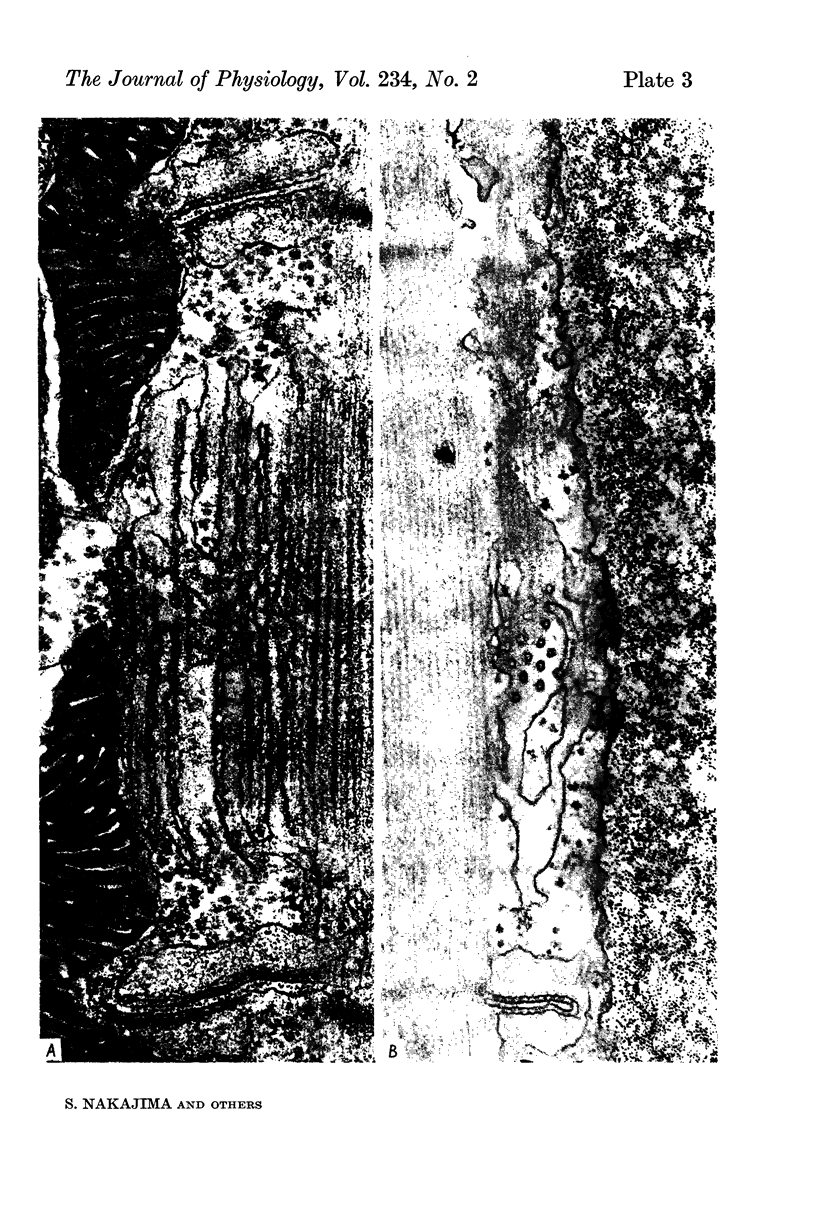
5. Electron microscopical observation of single fibres or bundles of fibres, which have been soaked in a Ringer containing ferritin, revealed that normal fibres contained ferritin particles in the T-system, while glycerol-treated fibres showed no ferritin. Except for the presence of some large vacuoles and some swelling of the T-system, glycerol-treated fibres appeared morphologically normal.
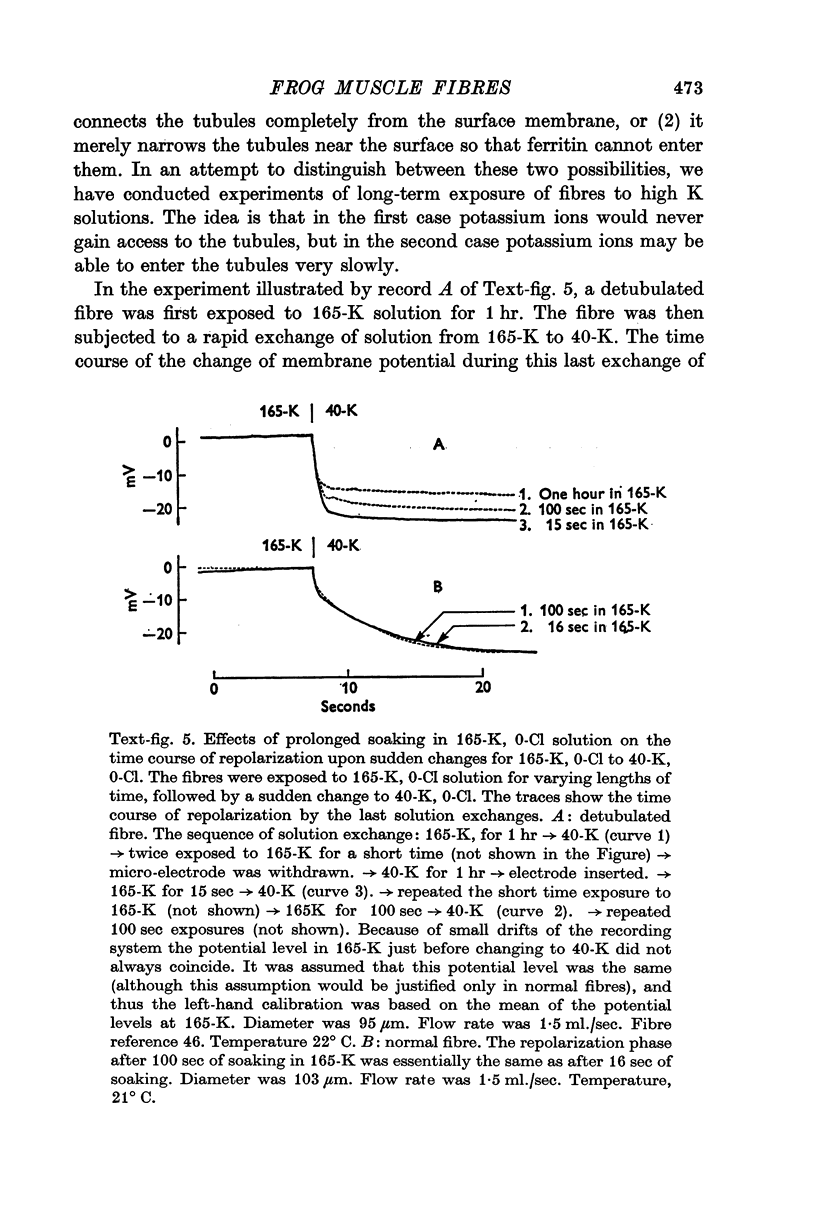
6. Prolonged soaking in a high potassium solution produced electrical effects suggesting that K ions can enter the tubules of treated fibres very slowly, in spite of their inaccessibility to ferritin.
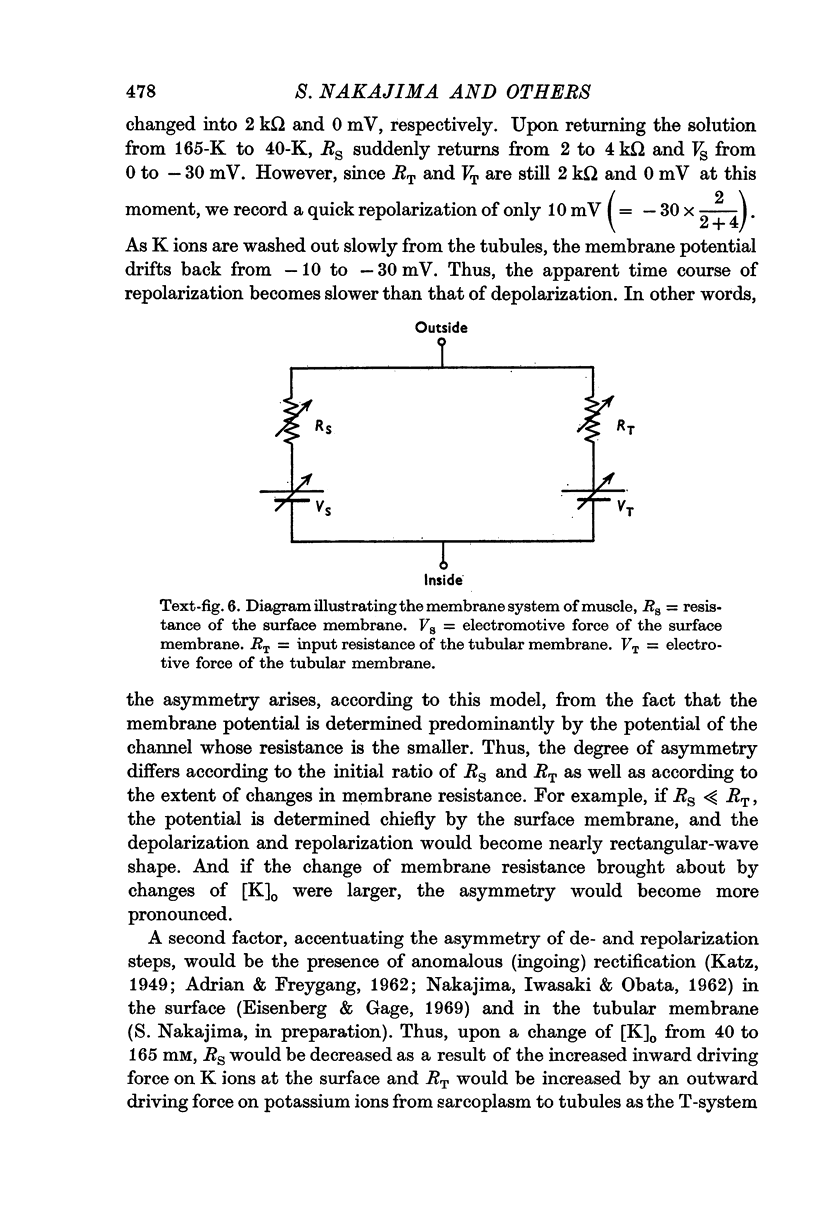
7. The main effect of glycerol-treatment does not seem to be a total disconnexion of the T-system from the fibre surface, but rather constriction of the T-tubules near their openings to the exterior.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- April E., Brandt P. W., Reuben J. P., Grundfest H. Muscle contraction: the effect of ionic strength. Nature. 1968 Oct 12;220(5163):182–184. doi: 10.1038/220182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C. Volume and twitch tension changes in single muscle fibers in hypertonic solutions. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):793–809. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg B., Eisenberg R. S. Selective disruption of the sarcotubular system in frog sartorius muscle. A quantitative study with exogenous peroxidase as a marker. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):451–467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Gage P. W. Ionic conductances of the surface and transverse tubular membranes of frog sartorius fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):279–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJINO M., YAMAGUCHI T., SUZUKI K. 'Glycerol effect' and the mechanism linking excitation of the plasma membrane with contraction. Nature. 1961 Dec 23;192:1159–1161. doi: 10.1038/1921159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. Capacitance of the surface and transverse tubular membrane of frog sartorius muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):265–278. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The effect of sudden changes in ionic concentrations on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:370–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. Analysis of the membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):121–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. The effect of diameter on the electrical constants of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):105–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolenko S. A., Adamian S. Ia. Pronitsaemost' myshechnykh volokon dlia neélektrolitov. Tsitologiia. 1967 Feb;9(2):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolenko S. A. Changes in the T-system of muscle fibres under the influence of influx and efflux of glycerol. Nature. 1969 Mar 8;221(5184):966–968. doi: 10.1038/221966a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolenko S. A., Fedorov V. V. Recovery of osometric twitches after glycerol removal. Experientia. 1972 Apr 15;28(4):424–425. doi: 10.1007/BF02008317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAJIMA S., IWASAKI S., OBATA K. Delayed rectification and anomalous rectification in frog's skeletal muscle membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Sep;46:97–115. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Nakajima Y., Peachey L. D. Speed of repolarization and morphology of glycerol-treated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):115P–116P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D., Schild R. F. The distribution of the T-system along the sarcomeres of frog and toad sartorius muscles. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):249–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules of the frog's sartorius. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):209–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]