Abstract
1. Ganglion cells of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum have been studied with intracellular micro-electrodes.
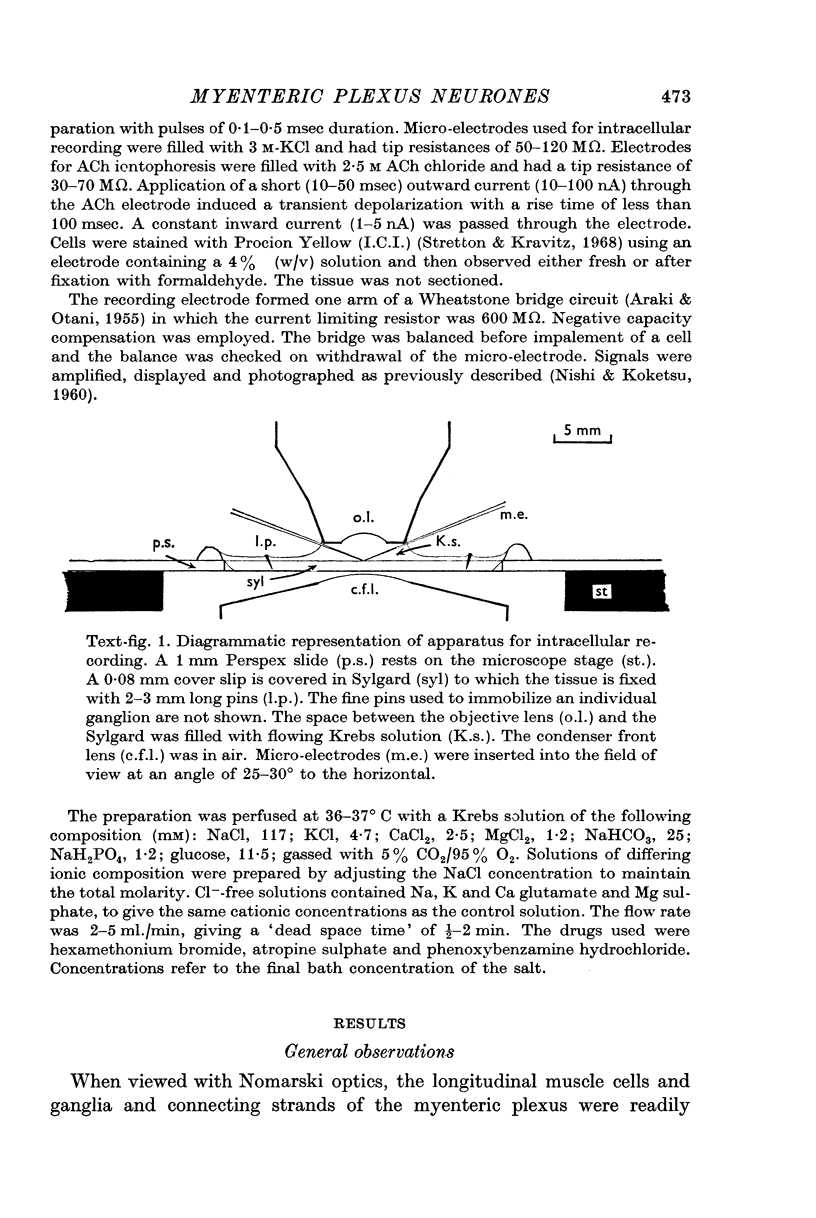
2. Three types of cell were distinguished. Type 1 cells had a high resistance (58 MΩ) and had properties similar to guinea-pig sympathetic ganglion cells. Type 2 cells were also excitable but had a lower resistance (21 MΩ) and showed accommodation to depolarizing current pulses. Type 3 cells were inexcitable.
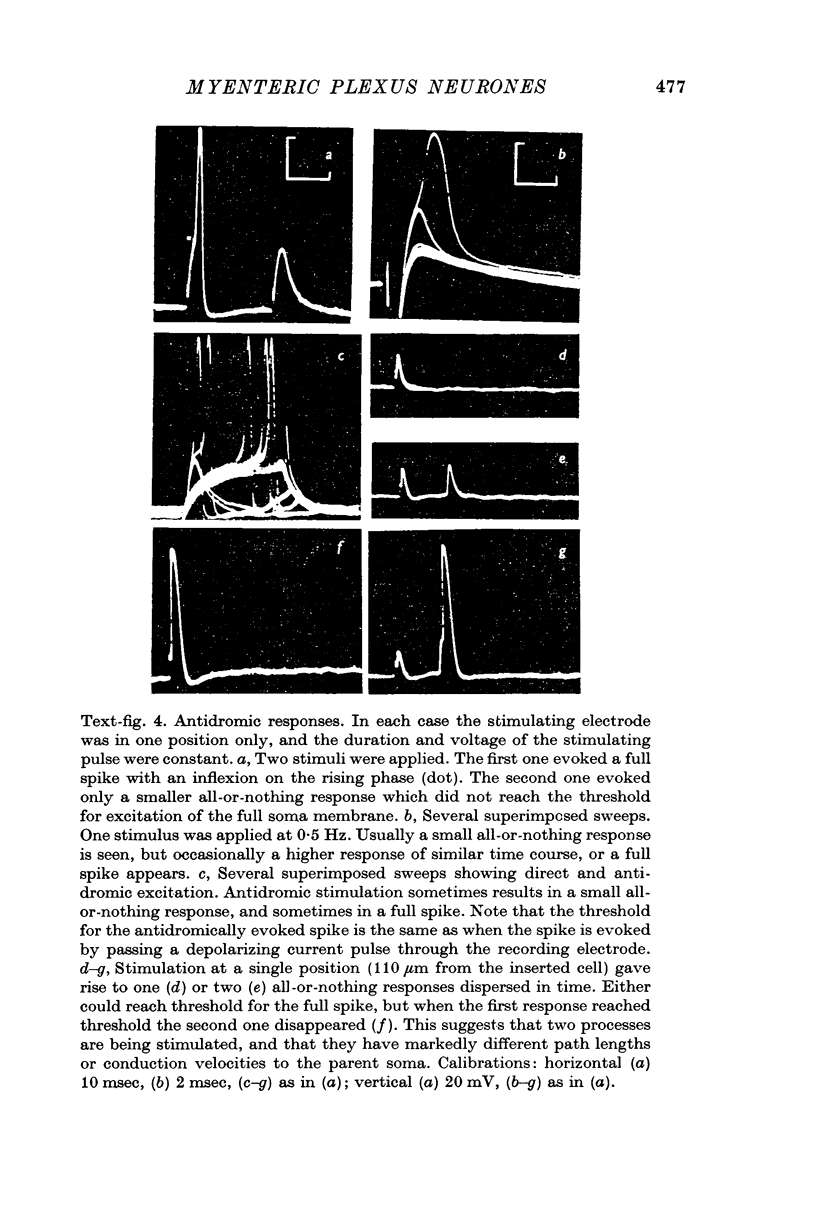
3. Point stimulation within 150 μm excited neurones either antidromically or orthodromically, sometimes both.
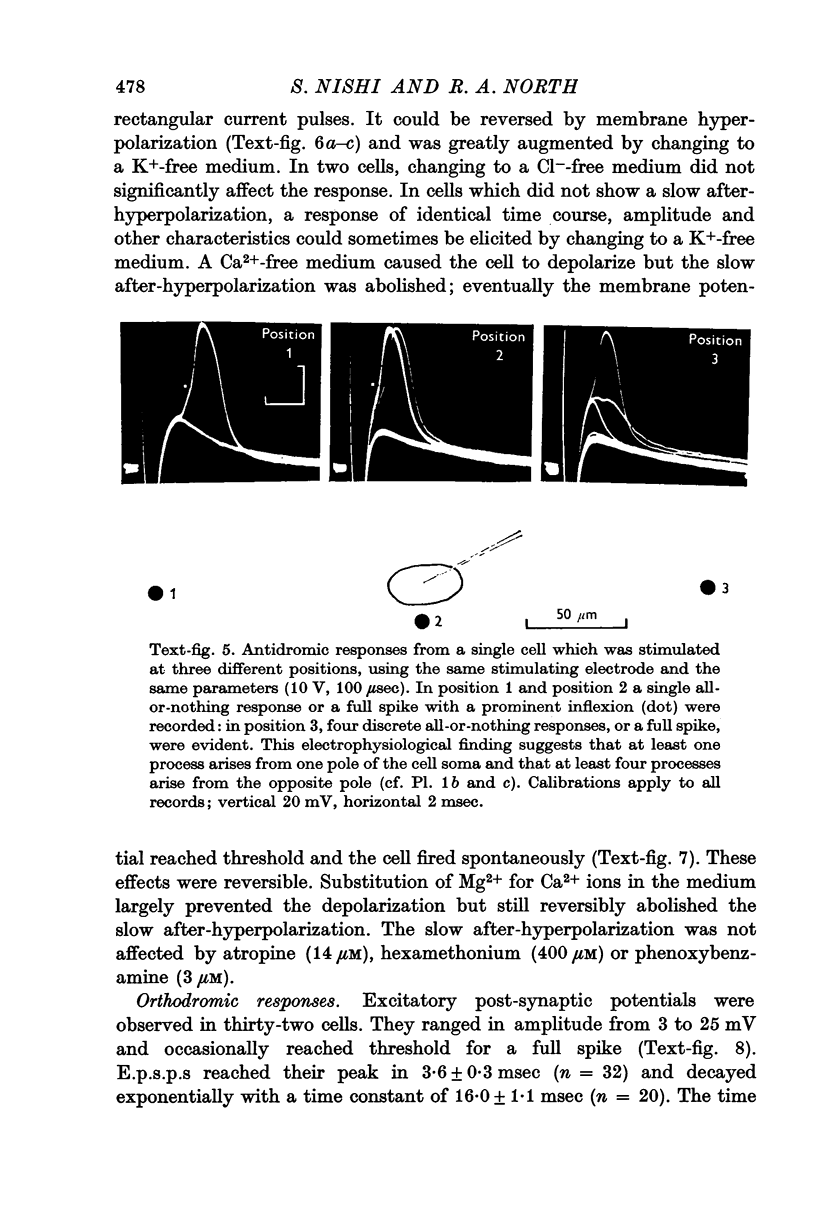
4. Antidromic responses had a small all-or-nothing component which was subthreshold for the soma spike. Two or more such components sometimes occurred, and were probably due to stimulation of two or more cell processes.
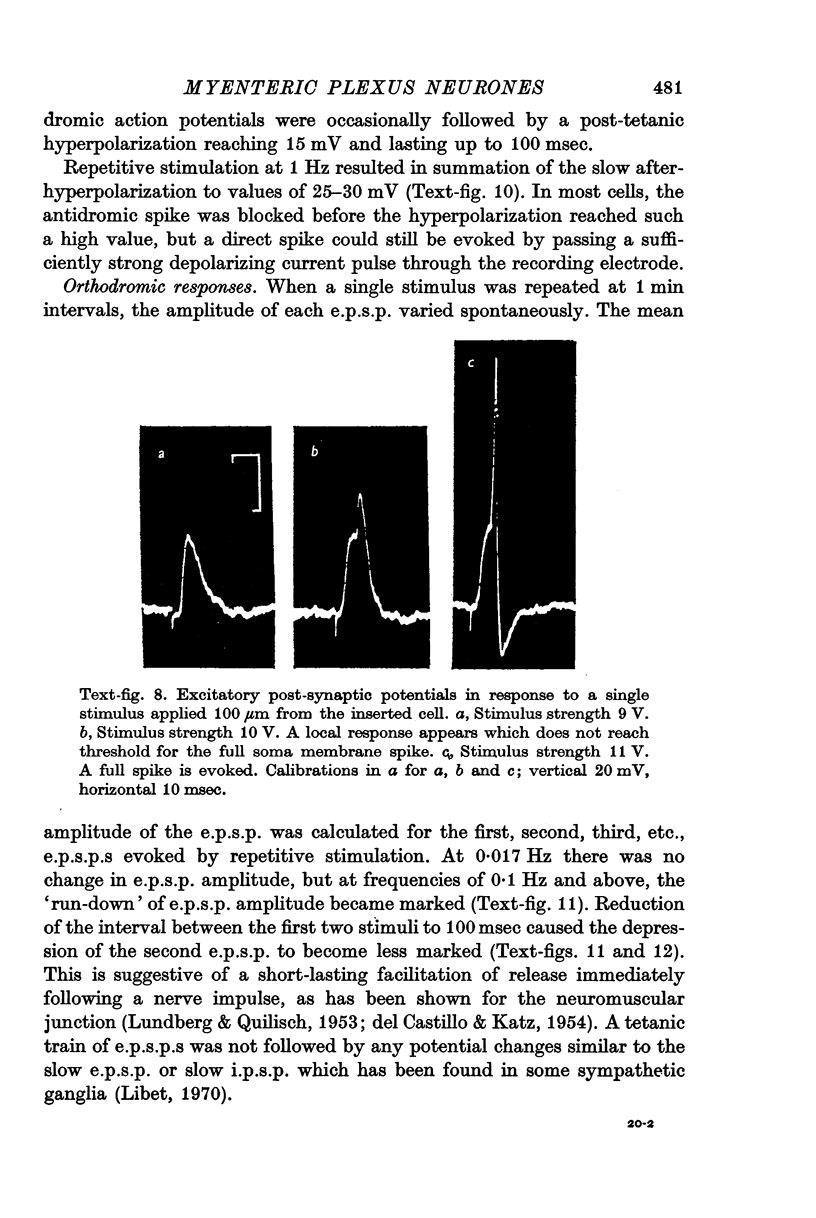
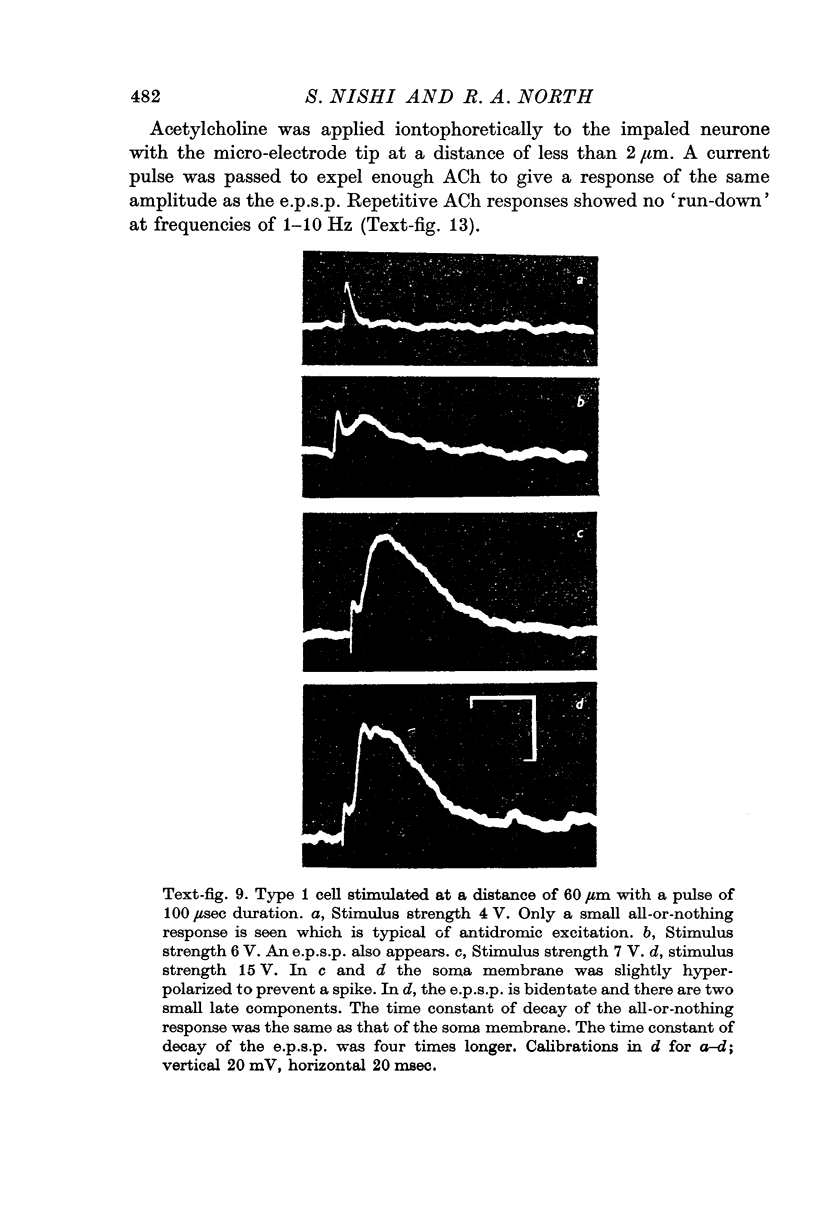
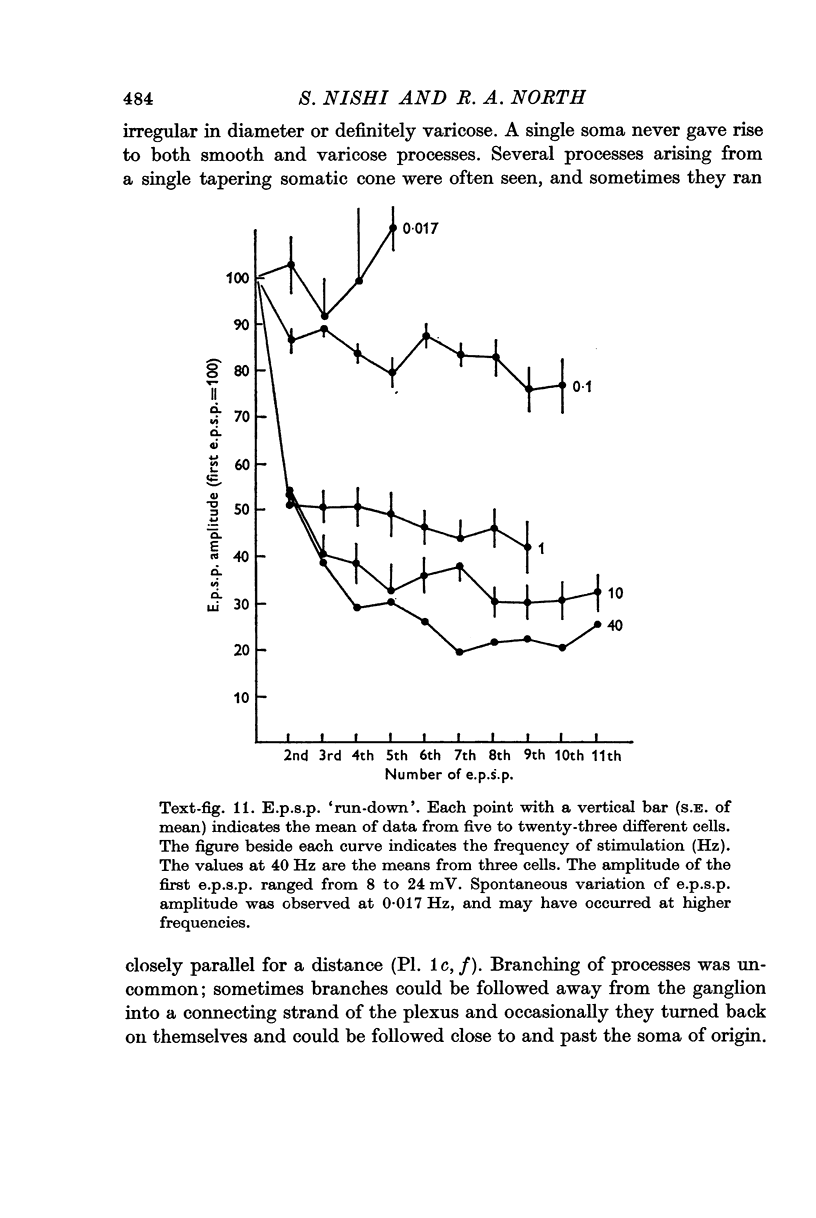
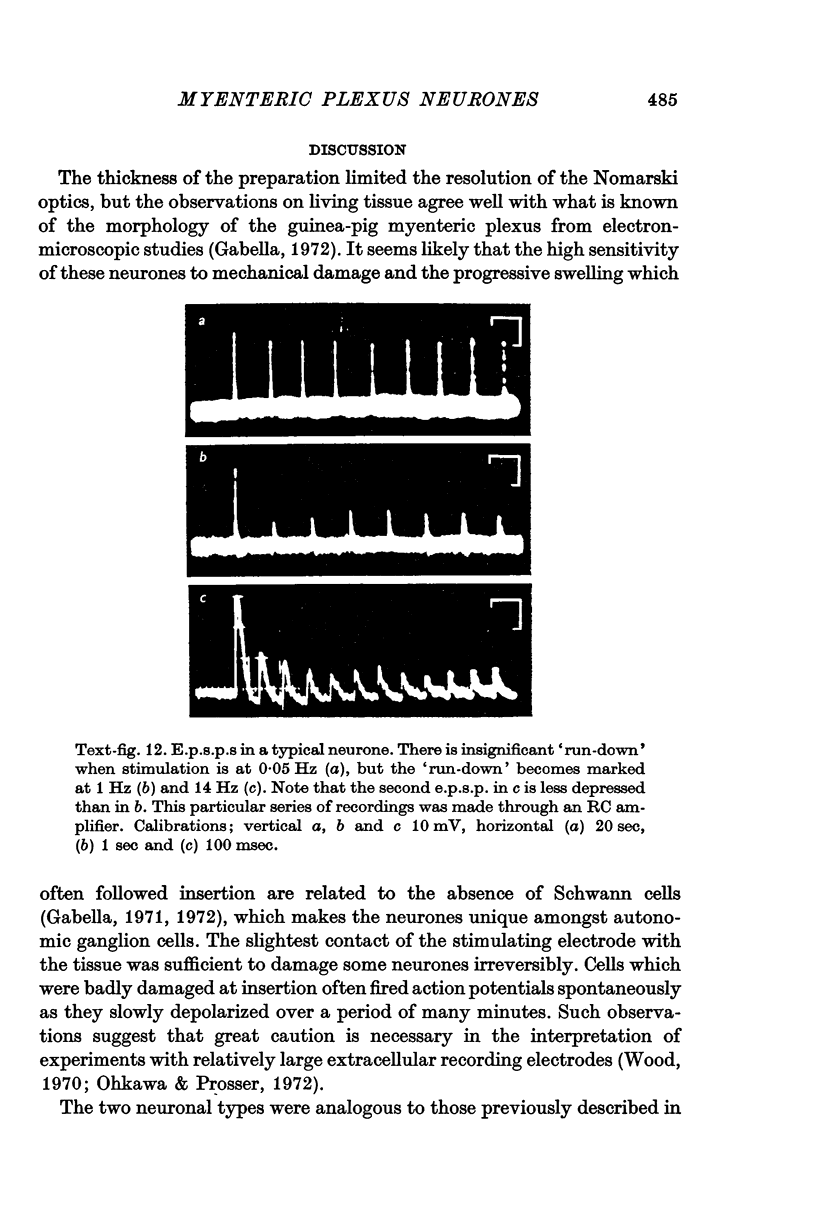
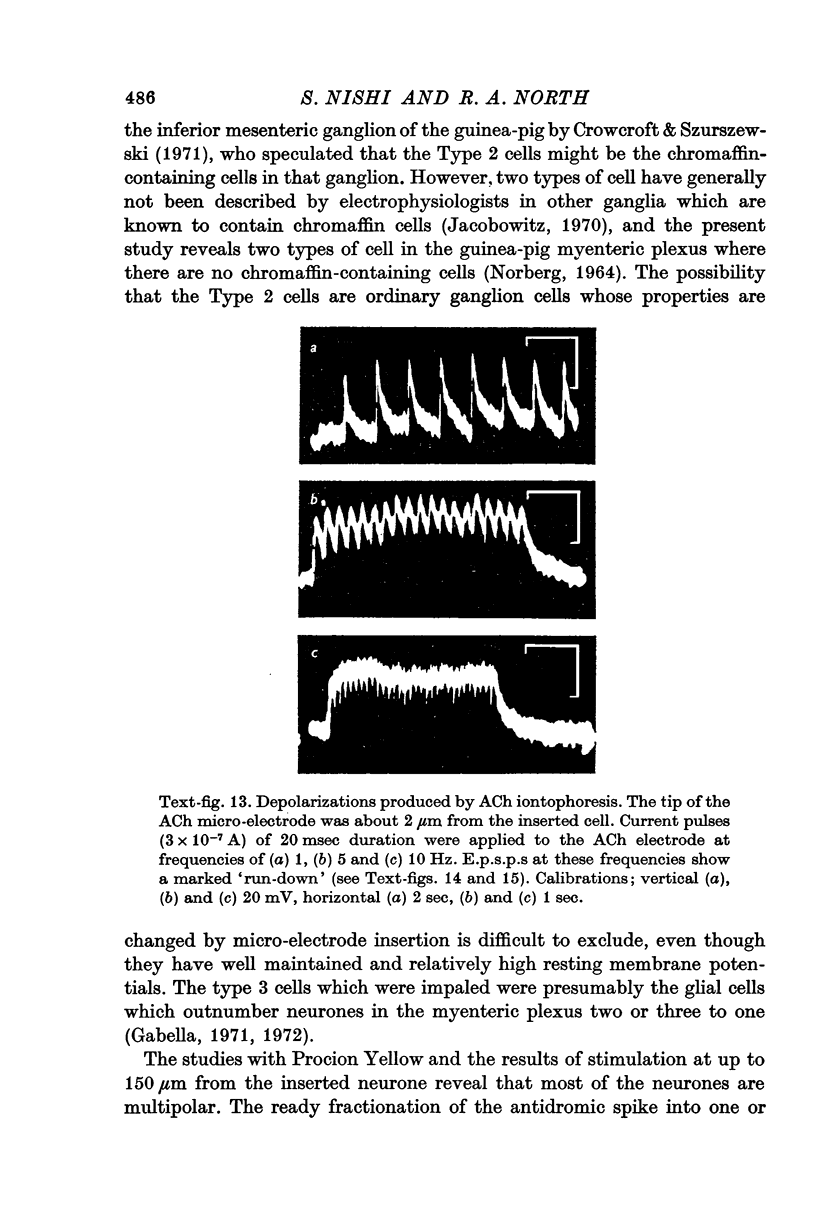
5. Excitatory post-synaptic potentials (e.p.s.p.s) were blocked by hexamethonium (400 μM). They progressively declined in amplitude when elicited at frequencies of 0·05 Hz or more, and this is discussed in relation to studies on acetylcholine (ACh) output.
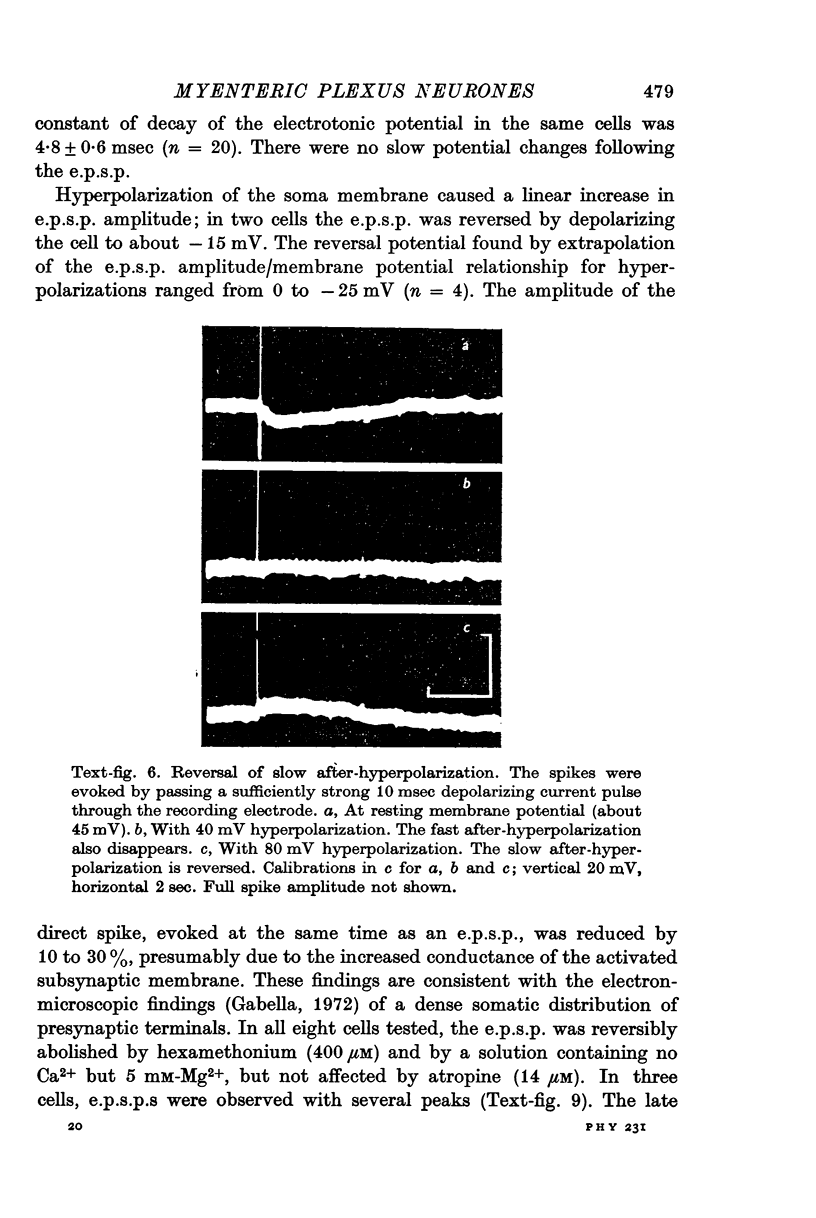
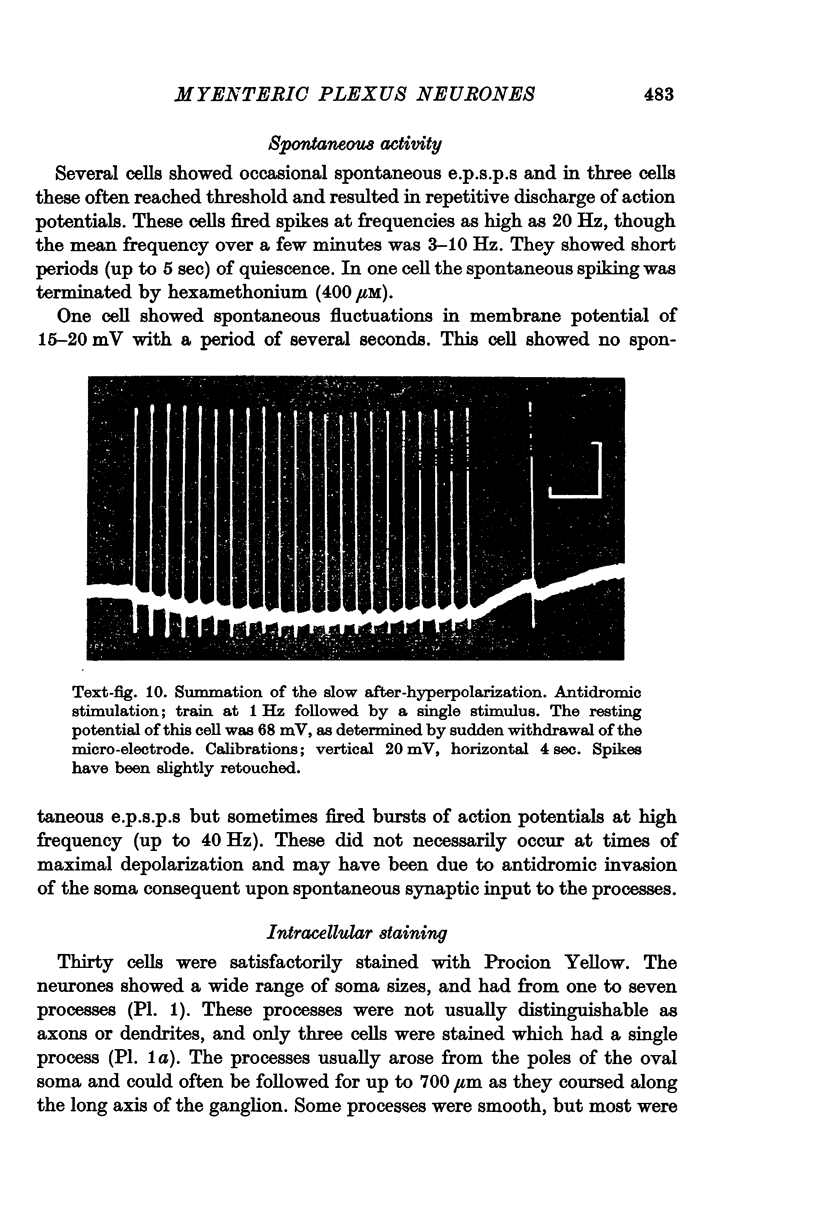
6. Many cells often showed a slow after-hyperpolarization following a direct or antidromic spike. Its mechanism and significance are discussed.
7. Spontaneous e.p.s.p.s and spikes were occasionally seen.
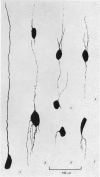
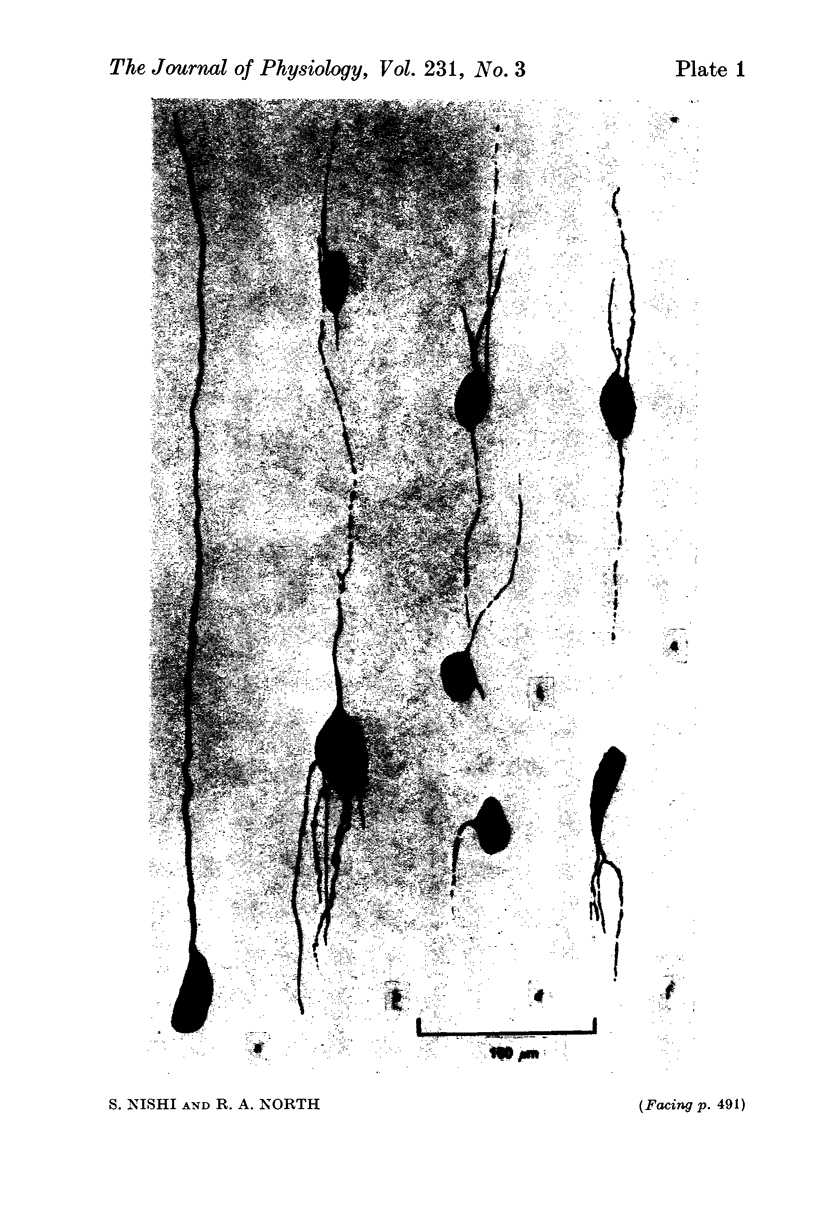
8. Intracellular injection of a fluorescent dye reveals that the neurones have one to seven processes, which usually arise from the poles of the oval soma.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., OTANI T. Response of single motoneurons to direct stimulation in toad's spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1955 Sep;18(5):472–485. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman J. G., Purves R. D. Intracellular recordings from ganglia of the thoracic sympathetic chain of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):173–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortoff A. Digestion: motility. Annu Rev Physiol. 1972;34:261–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.34.030172.001401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A. L., Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Mode of action of morphine-like drugs on autonomic neuro-effectors. Nature. 1968 Dec 7;220(5171):1040–1042. doi: 10.1038/2201040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Quastel D. M. A quantitative study of end-plate potentials in isolated human muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Jun;178(3):505–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabella G. Fine structure of the myenteric plexus in the guinea-pig ileum. J Anat. 1972 Jan;111(Pt 1):69–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Prosser C. L., Spence I. Some properties of the neurones of Auerbach's plexus. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):60P–61P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz D. Catecholamine fluorescence studies of adrenergic neurons and chromaffin cells in sympathetic ganglia. Fed Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;29(6):1929–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTERLITZ H. W., ROBINSON J. A. Reflex contractions of the longitudinal muscle coat of the isolated guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1959 May 19;146(2):369–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J. Impulse transmission in the myenteric plexus-longitudinal muscle preparation of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;43(1):74–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J. Spontaneous electrical activity and nerve-mediated inhibition in the innervated longitudinal muscle strip of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):126P–128P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J., Watt A. J. The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on inhibitory alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;39(2):398–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb12903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Waterfield A. A. The effect of the interval between electrical stimuli on the acetylcholine output of the myenteric plexus-longitudinal muscle preparation of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Sep;40(1):162P–163P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Lisiewicz A. Injections of calcium ions into spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):363–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., QUILISCH H. On the effect of calcium on presynaptic potentiation and depression at the neuro-muscular junction. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1953;111:121–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B. Generation of slow inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic potentials. Fed Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;29(6):1945–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J., Kuffler S. W. Visual identification of synaptic boutons on living ganglion cells and of varicosities in postganglionic axons in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):485–508. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHI S., KOKETSU K. Electrical properties and activities of single sympathetic neurons in frogs. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Feb;55:15–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030550104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORBERG K. A. ADRENERGIC INNERVATION OF THE INTESTINAL WALL STUDIED BY FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1964 Sep;3:379–382. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(64)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa H., Prosser C. L. Electrical activity in myenteric and submucous plexuses of cat intestine. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1412–1419. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perri V., Sacchi O., Caella C. Electrical properties and synaptic connections of the sympathetic neurons in the rat and guinea-pig superior cervical ganglion. Pflugers Arch. 1970;314(1):40–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00587045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton A. O., Kravitz E. A. Neuronal geometry: determination with a technique of intracellular dye injection. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):132–134. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D. Electrical activity from single neurons in Auerbach's plexus. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jul;219(1):159–169. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S. Aktionspotentiale der Ganglienzelle des Auerbachschen Plexus im Kaninchendünndarm. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;288(2):95–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]