Abstract
1. The positive dynamic current in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres was studied using `voltage clamp' technique. The major portion of this current was carried by Cl- ions.
2. A pre-step in membrane potential changed the response of this current to a subsequent depolarization in a way that is similar to the Na inactivation process described by Hodgkin & Huxley (1952a, b).
3. Recovery of this current after its activation could be described reasonably well by a single exponential process, and the time course of the recovery varied with membrane voltage.
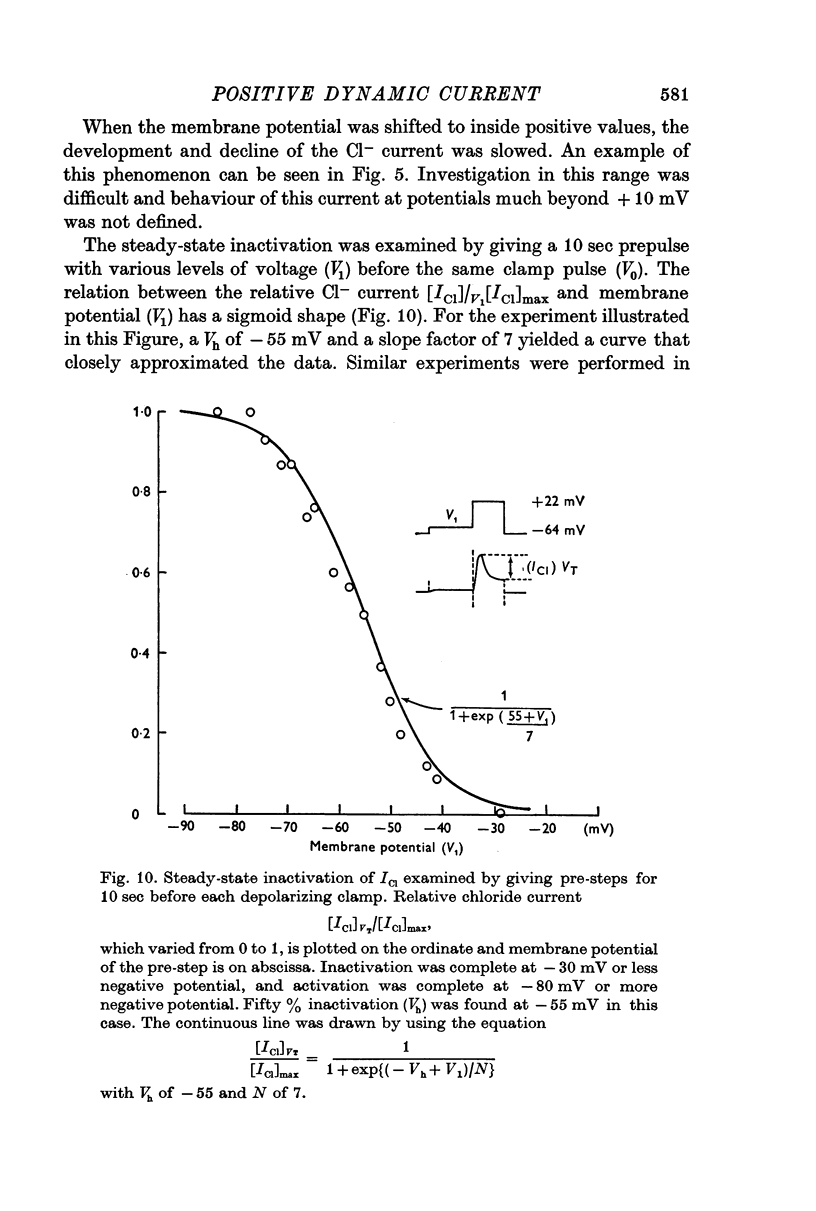
4. The relation of steady-state inactivation of the current to membrane voltage showed a sigmoid shape, varying from 100% at membrane potential of -30 mV to 0% at -80 mV. The membrane potential at 50% inactivation was -53 mV.
5. The Cl- current may play a role in the shape of the Purkinje fibre action potential, but exact definition depends on determining the voltage and time dependence of all the ionic currents that flow during the plateau.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DECK K. A., KERN R., TRAUTWEIN W. VOLTAGE CLAMP TECHNIQUE IN MAMMALIAN CARDIAC FIBRES. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1964 Jun 9;280:50–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00412615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DECK K. A., TRAUTWEIN W. IONIC CURRENTS IN CARDIAC EXCITATION. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1964 Jun 9;280:63–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00412616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Peper K., Rüdel R., Trautwein W. The dynamic chloride component of membrane current in Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;295(3):197–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01844100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozzard H. A. Membrane capacity of the cardiac Purkinje fibre. J Physiol. 1966 Jan;182(2):255–267. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAFFEY C. T., MULLINS L. J. Ion fluxes during the action potential in Chara. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 30;144(3):505–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons W. R., Fozzard H. A. Voltage dependence and time dependence of contraction in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. Circ Res. 1971 Apr;28(4):446–460. doi: 10.1161/01.res.28.4.446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWICZ P. THE EFFECTS OF ANIONS ON EXCITABLE CELLS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Jun;16:193–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausworth O., Noble D., Tsien R. W. The dependence of plateau currents in cardiac Purkinje fibres on the interval between action potentials. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):27–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Warner A. E. The pH sensitivity of the chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):403–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Warner A. E. The voltage dependence of the chloride conductance of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):275–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Lieberman M. Heart: excitation and contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1971;33:479–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.33.030171.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J. Efflux of chloride ions during the action potential of Nitella. Nature. 1962 Dec 8;196:986–987. doi: 10.1038/196986a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. Outward membrane currents activated in the plateau range of potentials in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):205–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peper K., Trautwein W. A membrane current related to the plateau of the action potential of Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1968;303(2):108–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00592629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Slow inactivation of currents in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(1):233–253. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitek M., Trautwein W. Slow inward current and action potential in cardiac Purkinje fibres. The effect of Mn plus,plus-ions. Pflugers Arch. 1971;323(3):204–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00586384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. E. Kinetic properties of the chloride conductance of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):291–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


