Abstract
1. Acetylcholine produced end-plate current (e.p.c.) noise is shown to be the results of statistical fluctuations in the ionic conductance of voltage clamped end-plates of Rana pipiens.
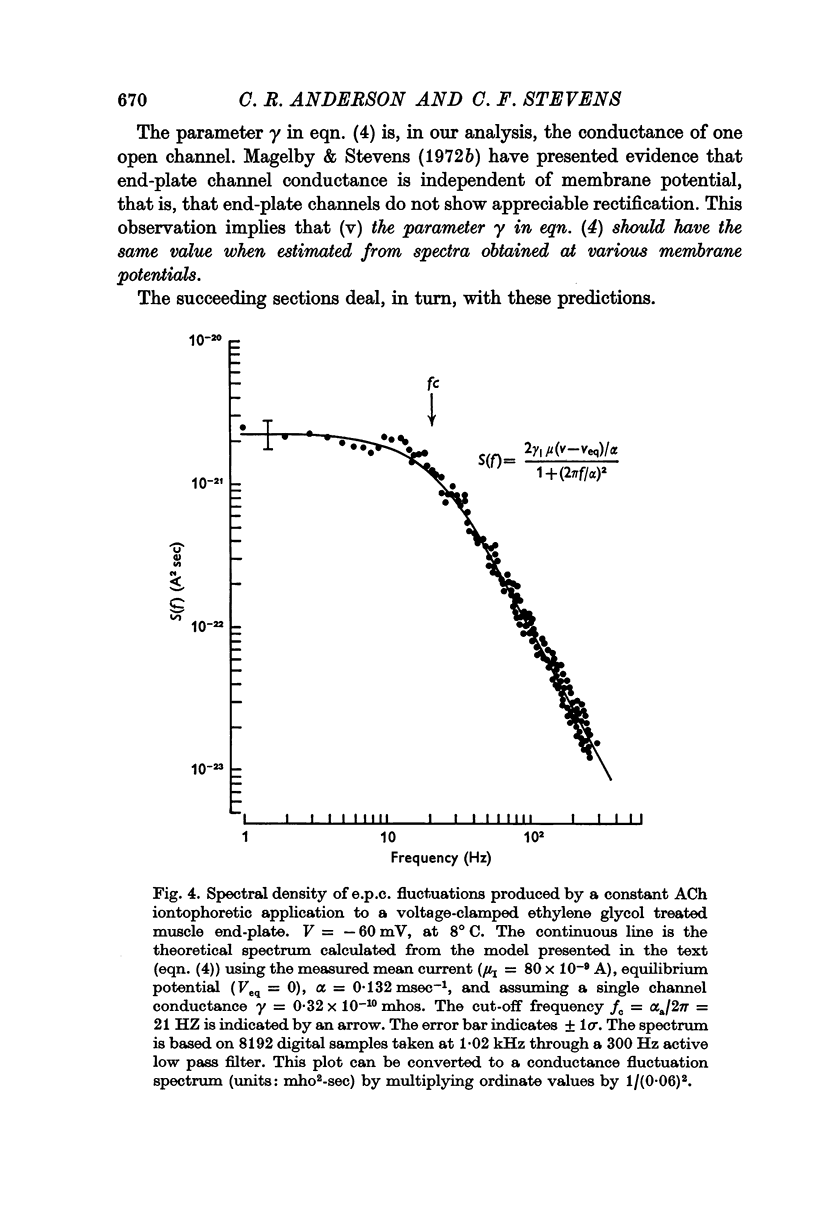
2. These e.p.c. fluctuations are characterized by their e.p.c. spectra which conform to a relation predicted from a simple model of end-plate channel gating behaviour.
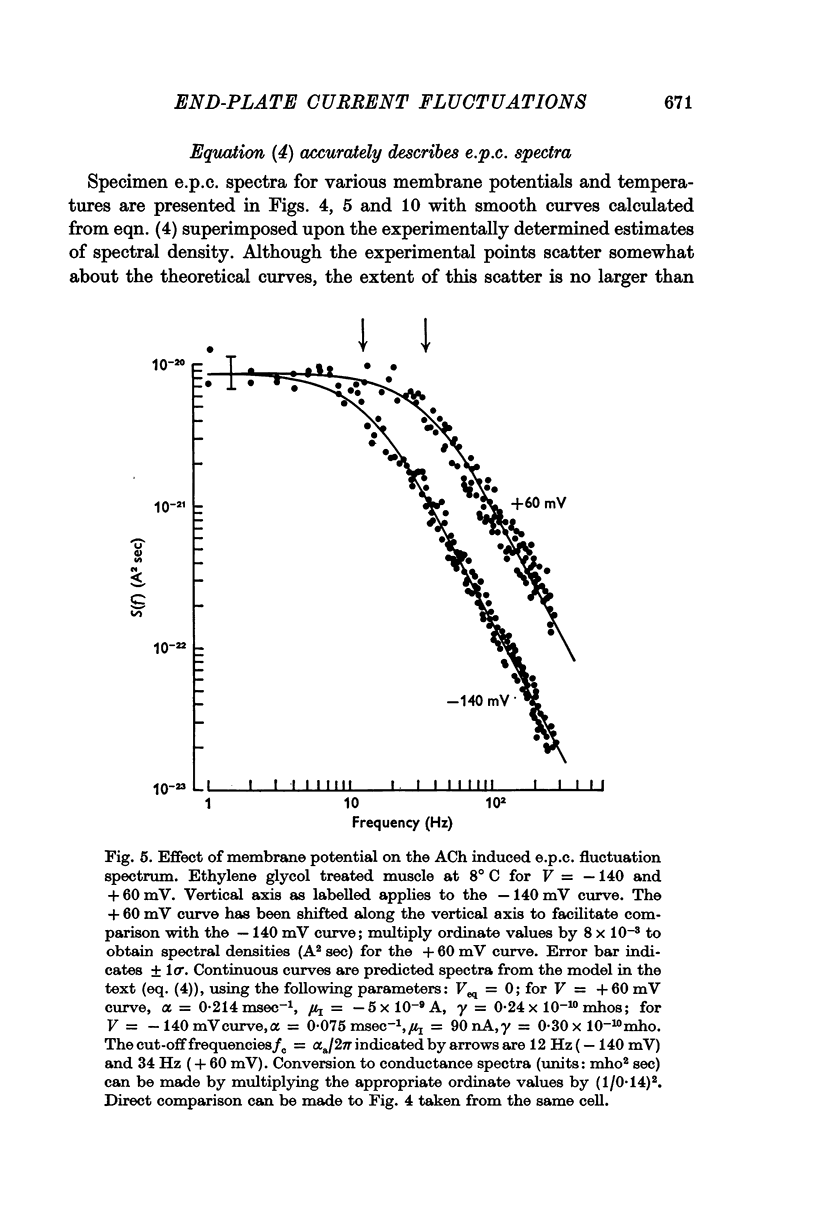
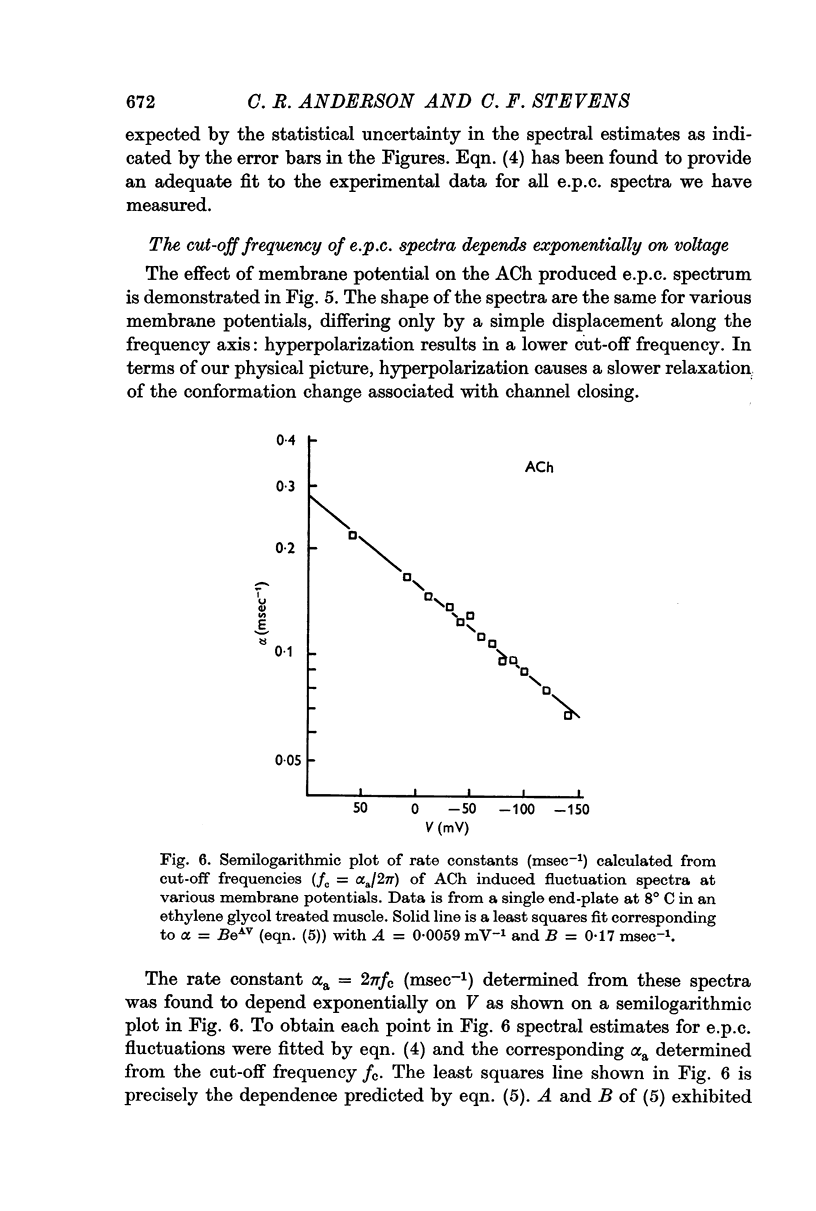
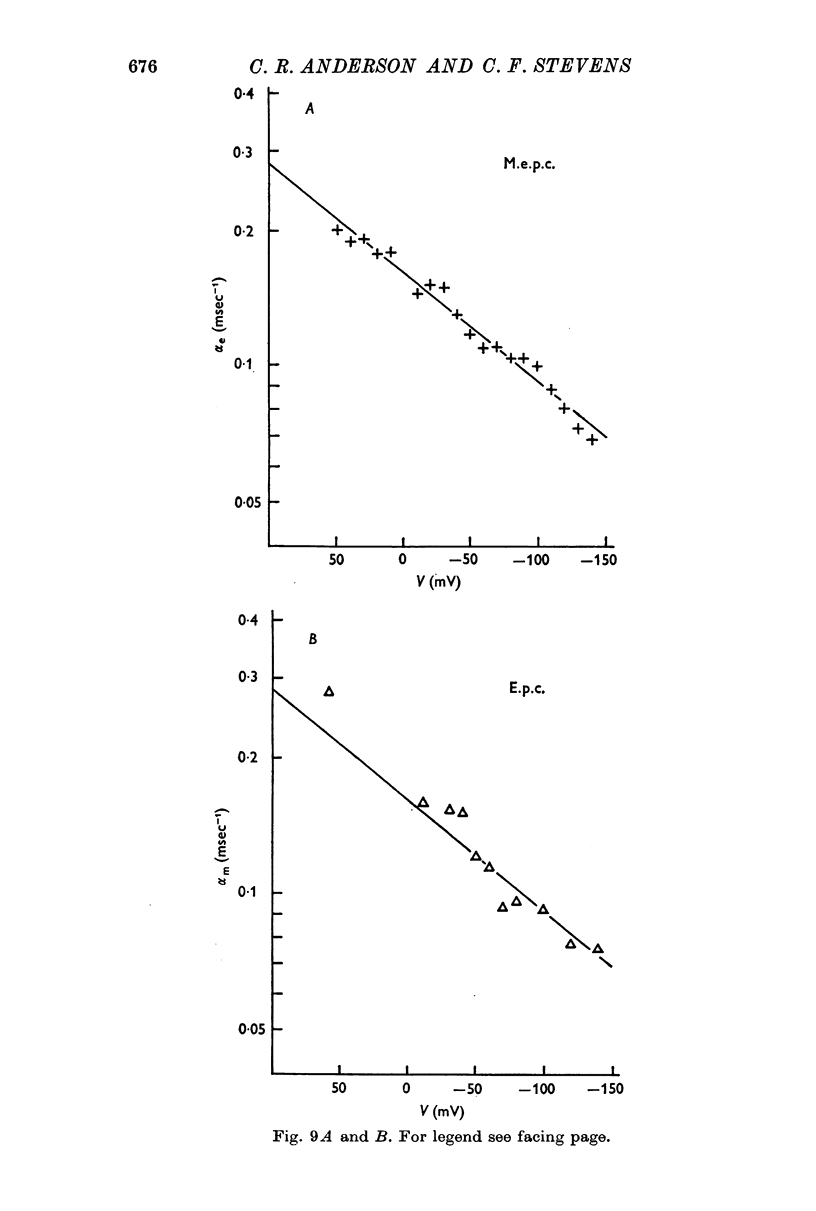
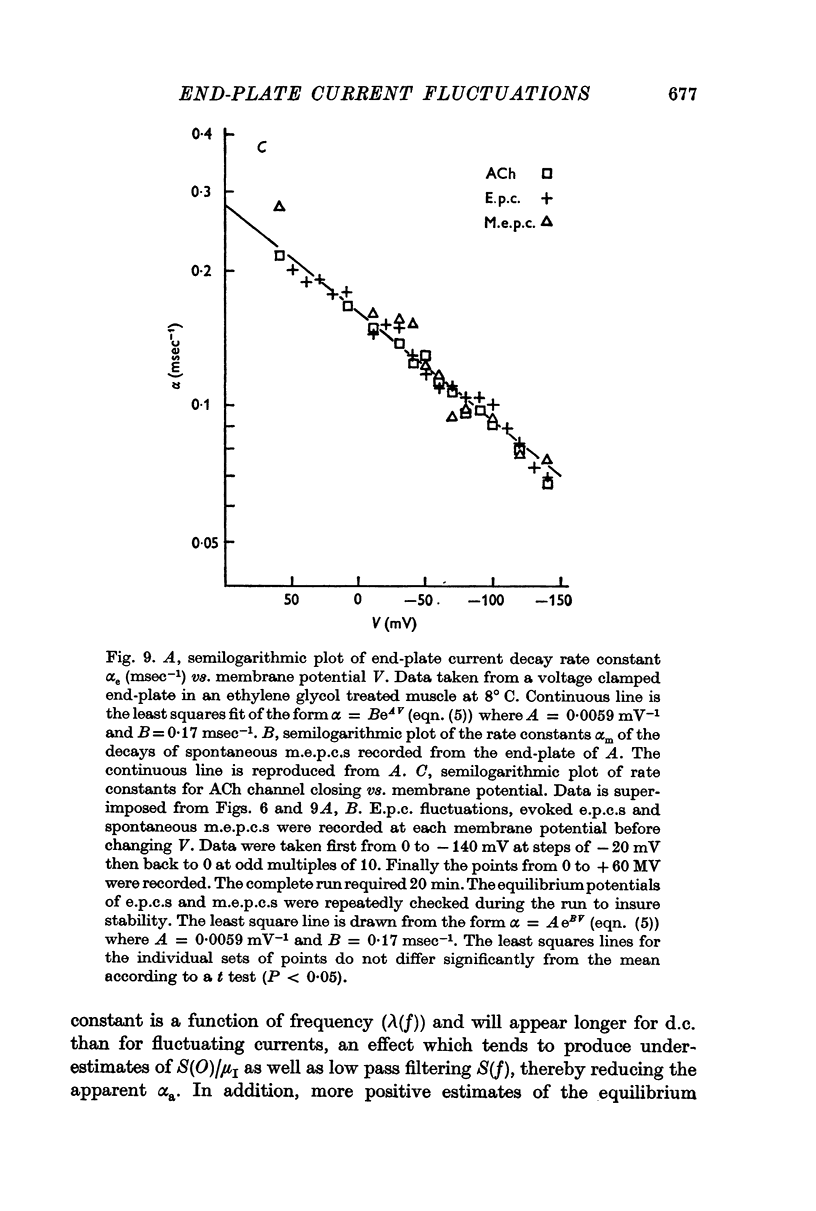
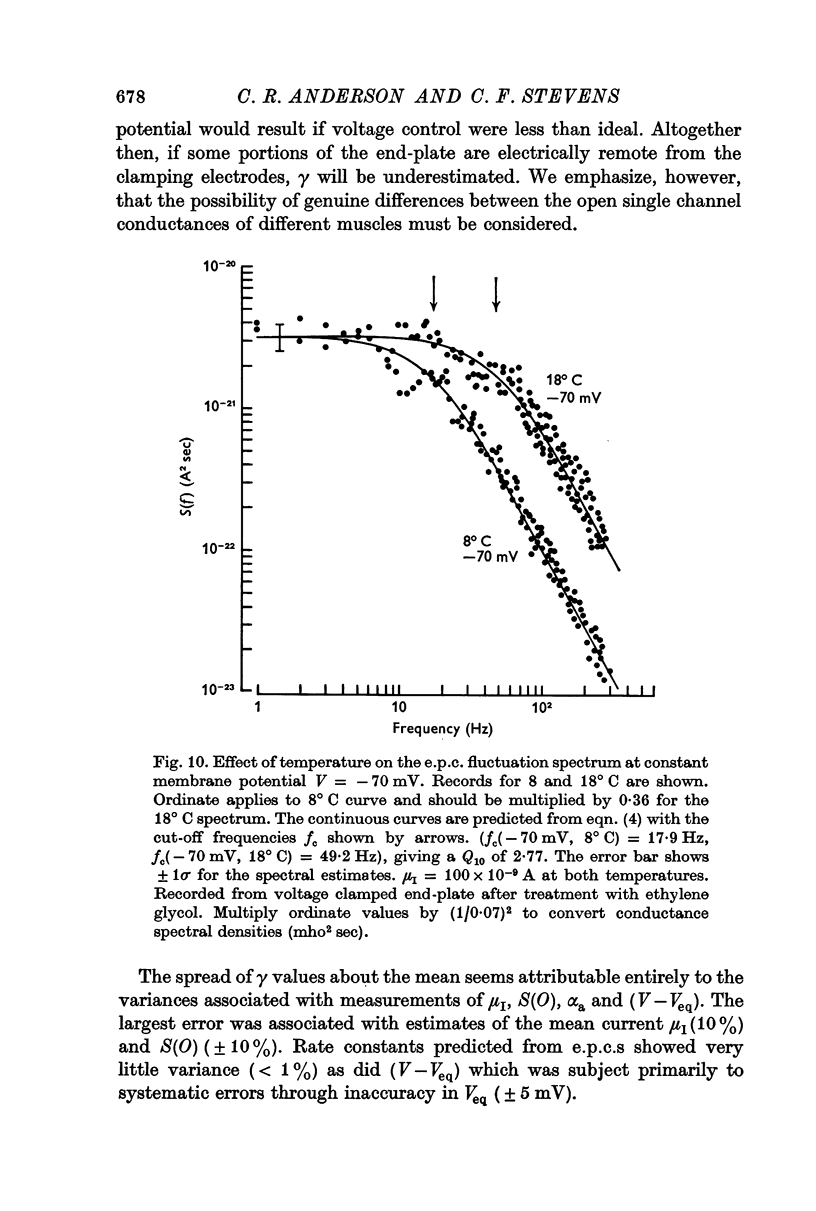
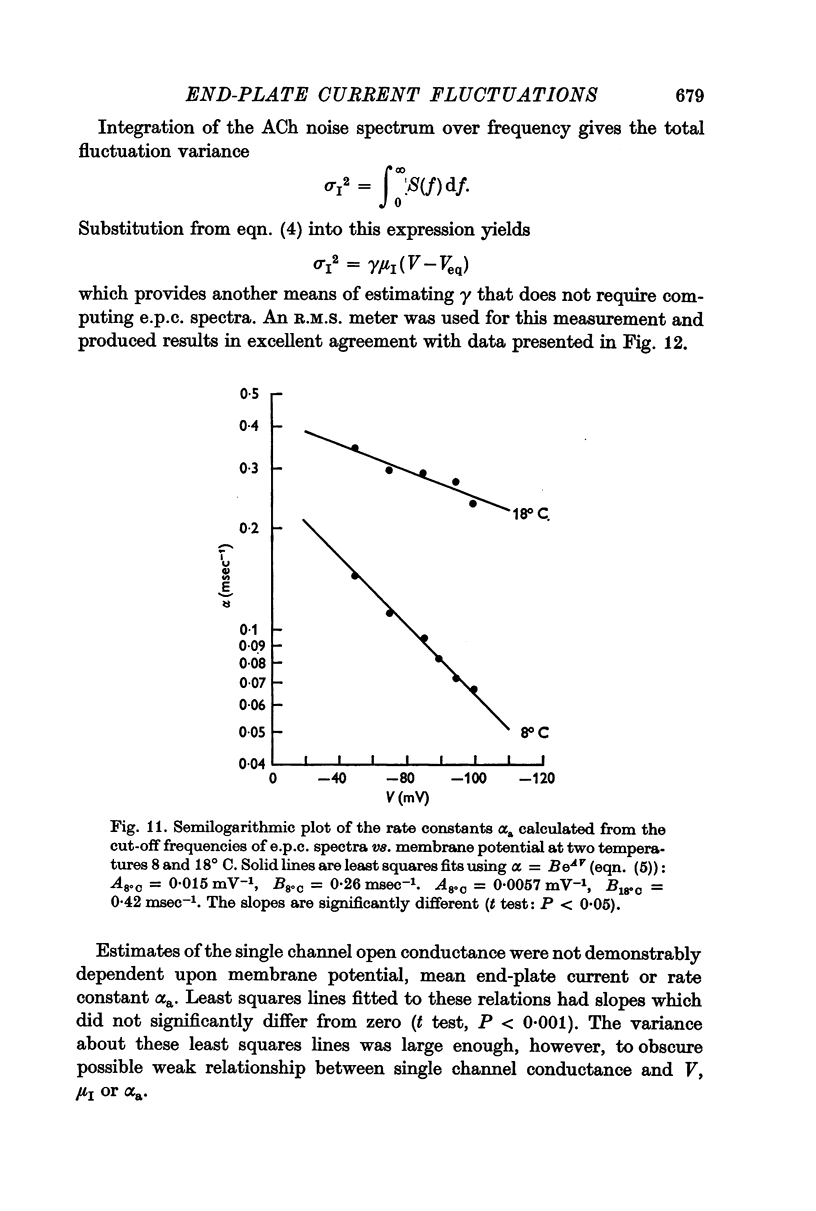
3. The rate constant of channel closing α is determined from e.p.c. spectra and is found to depend on membrane potential V according to the relation α = BeAV (B = 0·17 msec-1±0·04 S.E., A = 0·0058 mV-1±0·0009 S.E. at 8° C) and to vary with temperature T with a Q10 = 2·77, at -70 mV. A and B in this expression both vary with T and therefore produce a membrane potential dependent Q10 for α.
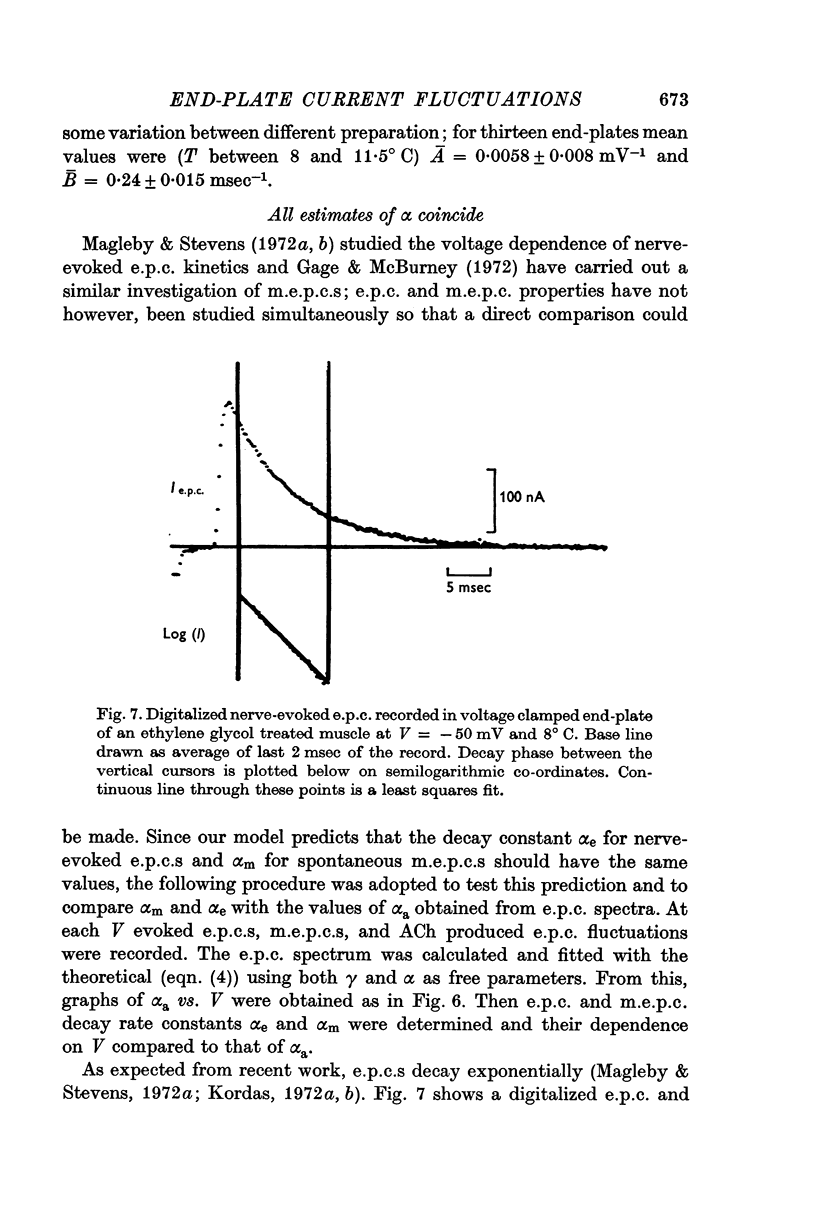
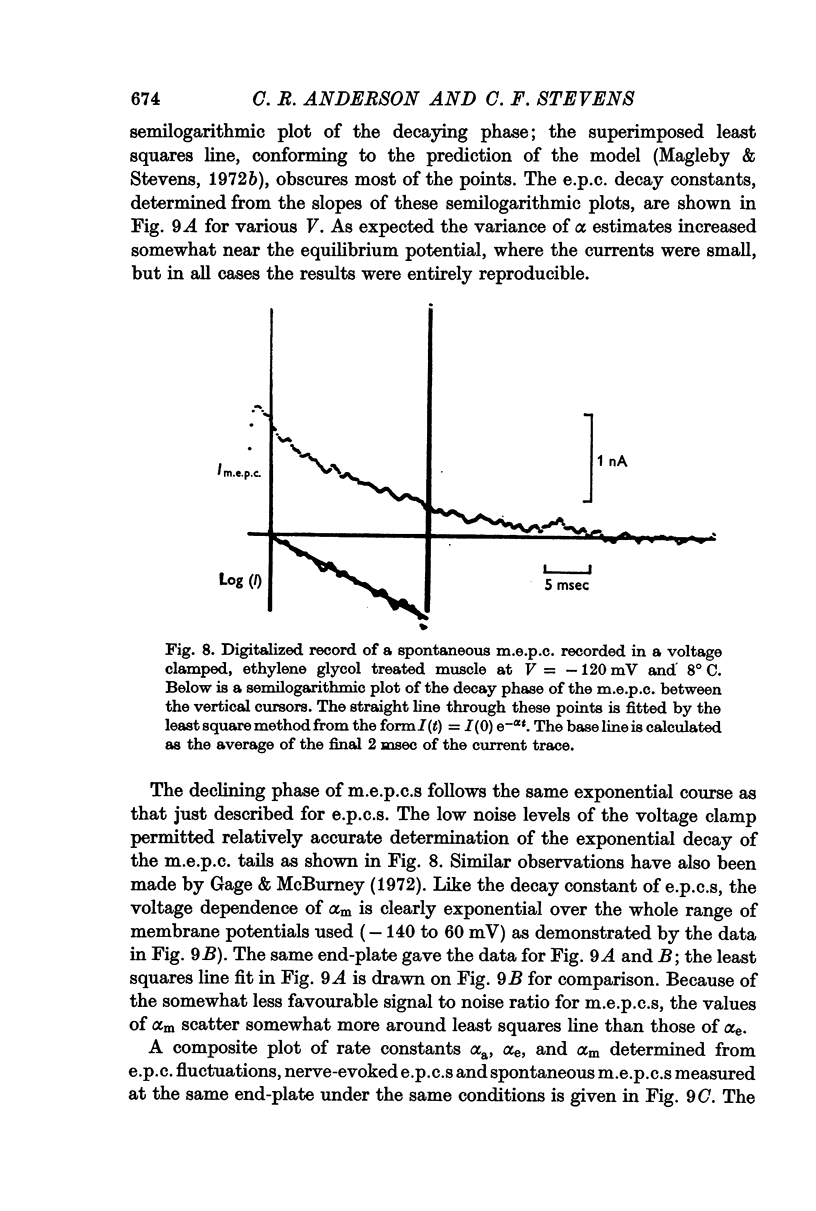
4. Nerve-evoked e.p.c.s and spontaneous miniature e.p.c.s decay exponentially in time with a rate constant which depends exponentially on V. The magnitude and voltage dependence of this decay constant is exactly that found from e.p.c. spectra for the channel closing rate α.
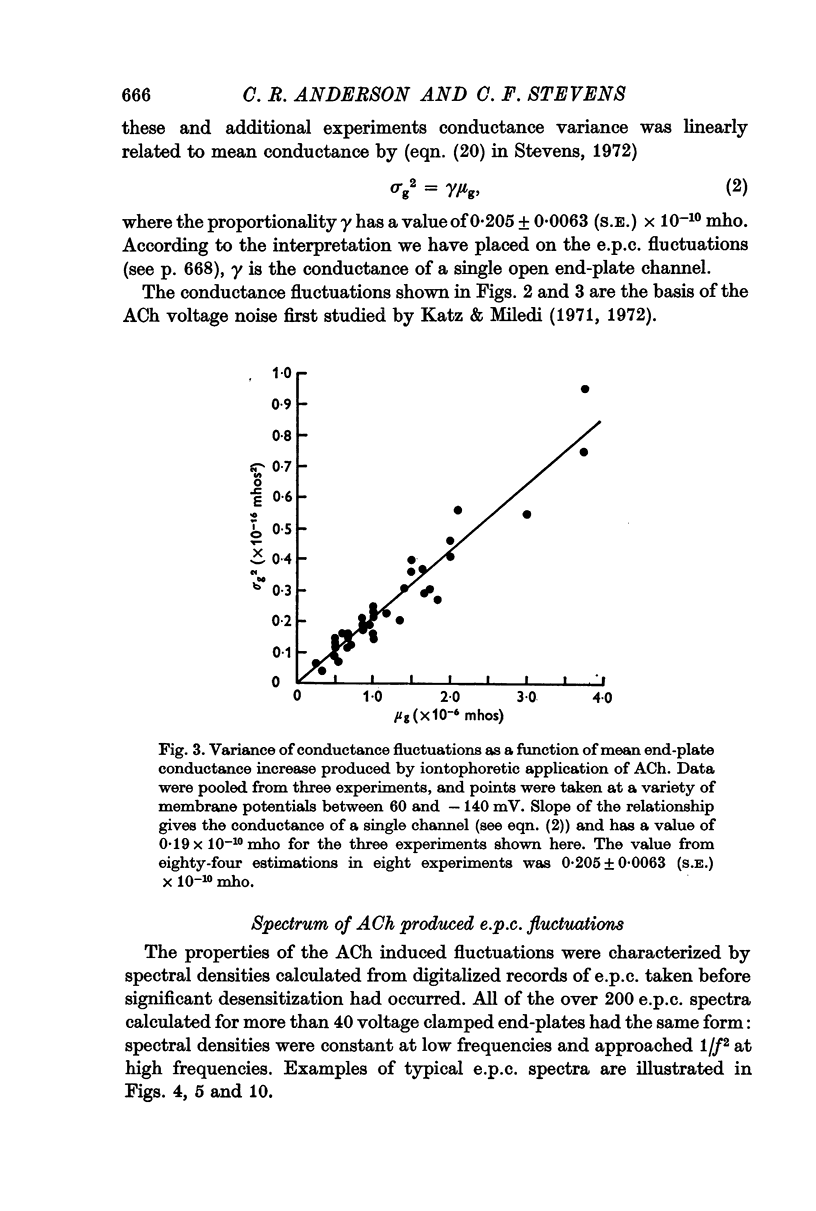
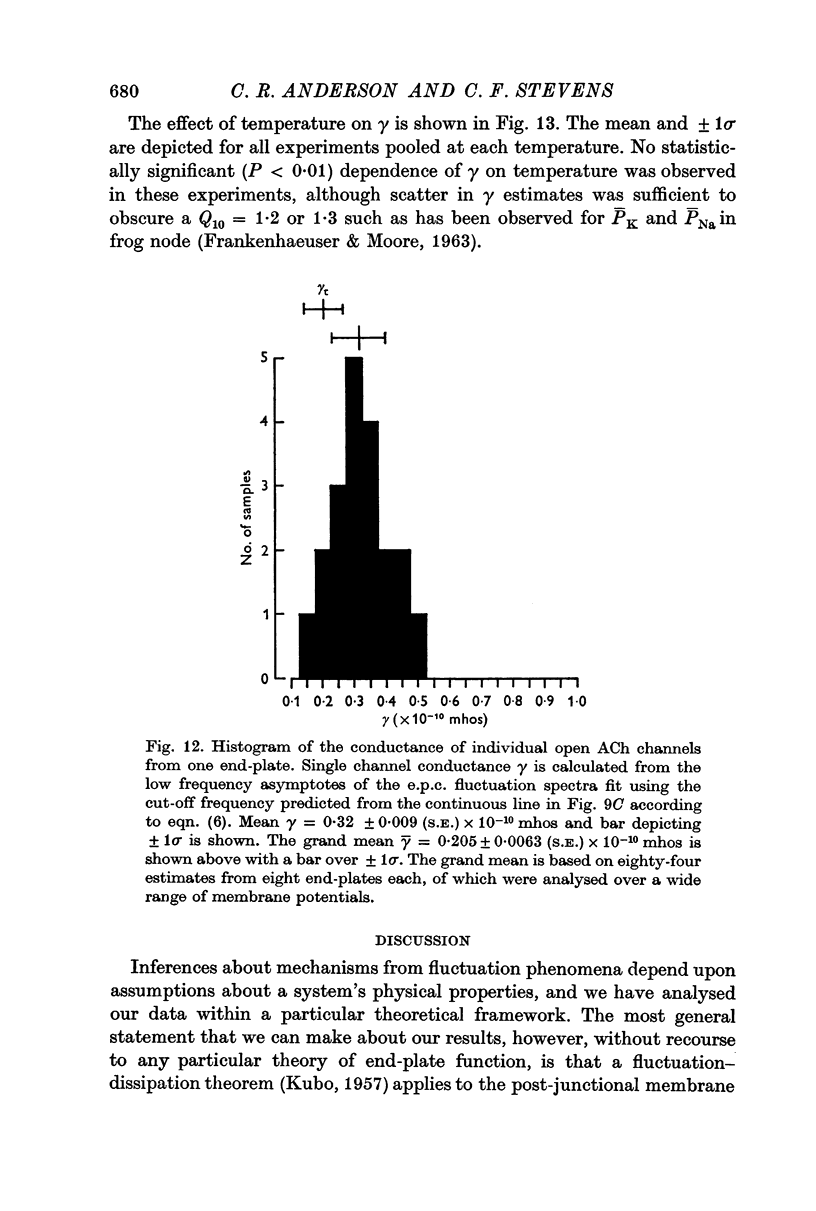
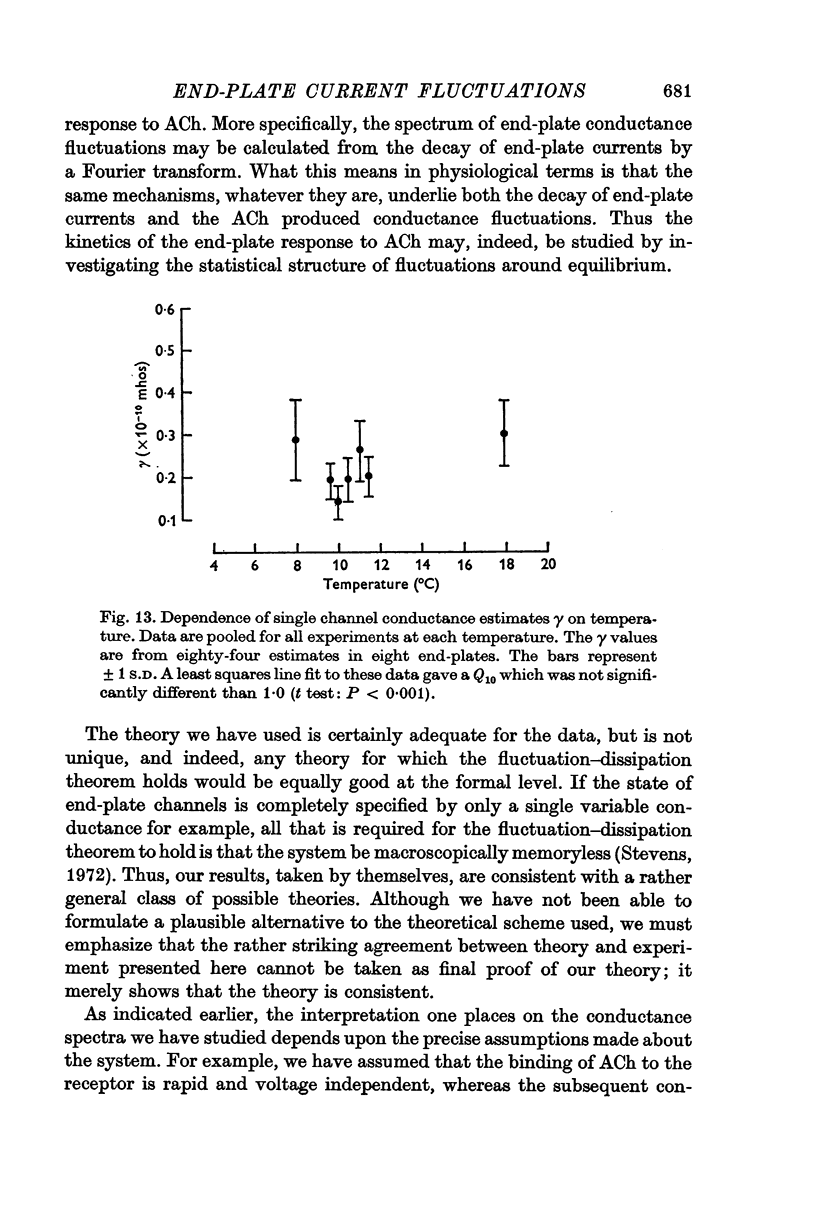
5. The conductance γ of a single open end-plate channel has been estimated from e.p.c. spectra and is found not to be detectibly dependent on membrane potential, temperature and mean end-plate current. γ = 0·32±0·0045 (S.E.) × 10-10 mhos. Some variation in values for γ occurs from muscle to muscle.
6. It is concluded that the relaxation kinetics of open ACh sensitive ionic channels is the rate limiting step in the decay of synaptic current and that this channel closing has a single time constant. The relaxation rate is independent of how it is estimated (ACh produced e.p.c. fluctuations, e.p.c., m.e.p.c.), and is consistent with the hypothesis that individual ionic channels open rapidly to a specific conductance which remains constant for an exponentially distributed duration.
7. The voltage and temperature dependence of the channel closing rate constant agree with the predictions of a simple dipole-conformation change model.
Full text
PDF






















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chock P. B. Relaxation methods and enzymology. Biochimie. 1971;53(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Inward and delayed outward membrane currents in isolated neural somata under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):1–19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Gage P. W. Electrical properties of toad sartorius muscle fibres in summer and winter. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):619–641. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIGEN M., HAMMES G. G. ELEMENTARY STEPS IN ENZYME REACTIONS (AS STUDIED BY RELAXATION SPECTROMETRY). Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1963;25:1–38. doi: 10.1002/9780470122709.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein G., Lecar H., Nossal R. The nature of the negative resistance in bimolecular lipid membranes containing excitability-inducing material. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):119–133. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Howell J. N., Vaughan P. C. The maintenance of resting potentials in glycerol-treated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):95–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G., FATT P. LINEAR ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF STRIATED MUSCLE FIBRES OBSERVED WITH INTRACELLULAR ELECTRODES. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Apr 14;160:69–123. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MOORE L. E. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY CHANGES IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:431–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. M. Relaxation spectra of potassium channel noise from squid axon membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):876–879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Armstrong C. M. Miniature end-plate currents in voltage-clamped muscle fibre. Nature. 1968 Apr 27;218(5139):363–365. doi: 10.1038/218363b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. Capacitance of the surface and transverse tubular membrane of frog sartorius muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):265–278. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. G., Haydon D. A. The unit conductance channel of alamethicin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 17;255(3):1014–1018. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90415-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Discreteness of conductance change in bimolecular lipid membranes in the presence of certain antibiotics. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):451–453. doi: 10.1038/225451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Further observations on acetylcholine noise. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio232124b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Membrane noise produced by acetylcholine. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):962–963. doi: 10.1038/226962a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. The effect of membrane polarization on the time course of the end-plate current in frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):493–502. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Drug receptors and their function. Nature. 1971 May 14;231(5298):91–96. doi: 10.1038/231091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevcik C., Narahashi T. Electrical properties and excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle treated with ethylene glycol. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Aug;60(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenga E., Verveen A. A. Membrane noise and ion transport in the node of Ranvier. Biomembranes. 1972;3:473–482. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0961-1_32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



