Abstract
1. Isometric and isotonic contractions were recorded from cat flexor digitorum longus (FDL) and soleus muscles denervated for 28-35 days and compared with the responses of contralateral control muscles.
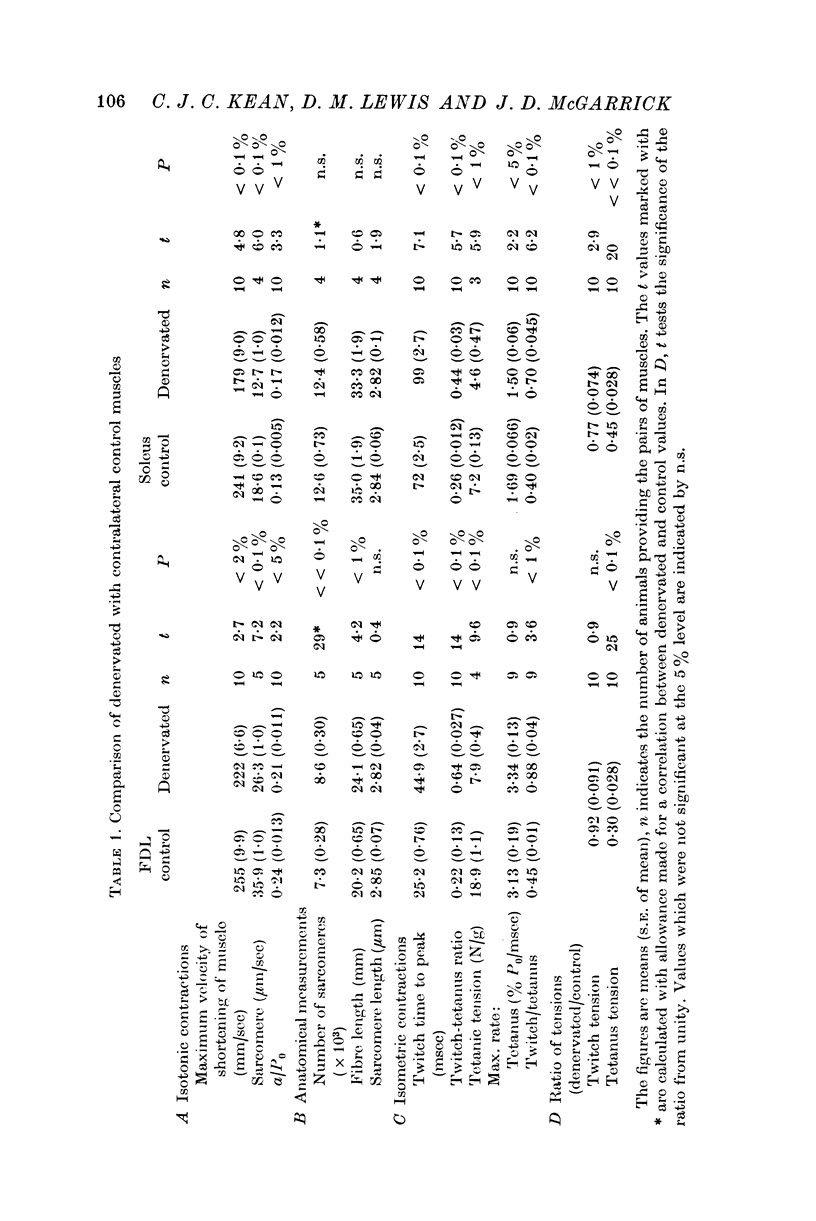
2. Isometric twitch time to peak was longer in the denervated muscles than in the controls. Tetanic tension was reduced whether expressed as absolute units, per gram or per unit area. Absolute twitch tensions were reduced less below the control values with a consequent increase of twitch-tetanus ratio. These results agree with earlier reports; but, in contrast, there was no reduction in the relative rate of rise of tension in the isometric tetanus of denervated compared with control FDL. The maximum rate of rise of tension in the twitch was only a little less than that in the fully fused tetanus in the denervated muscles.
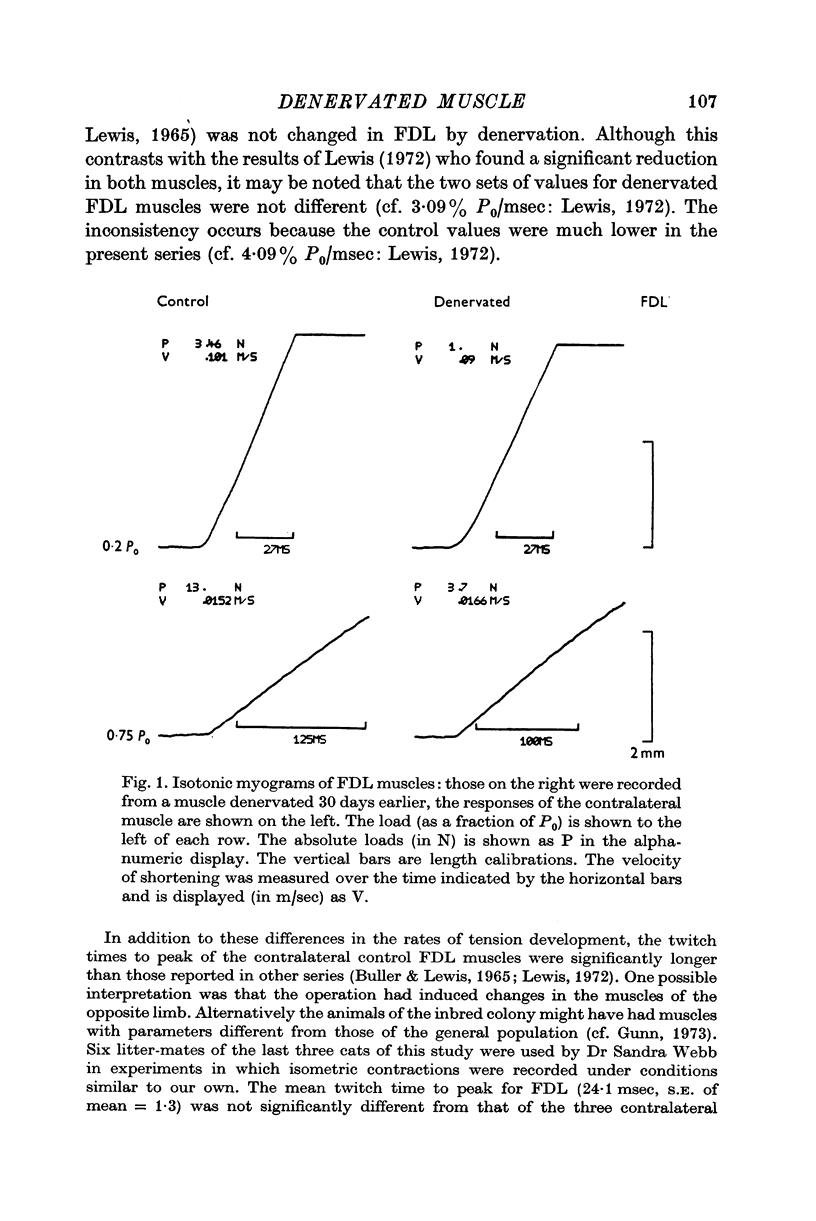
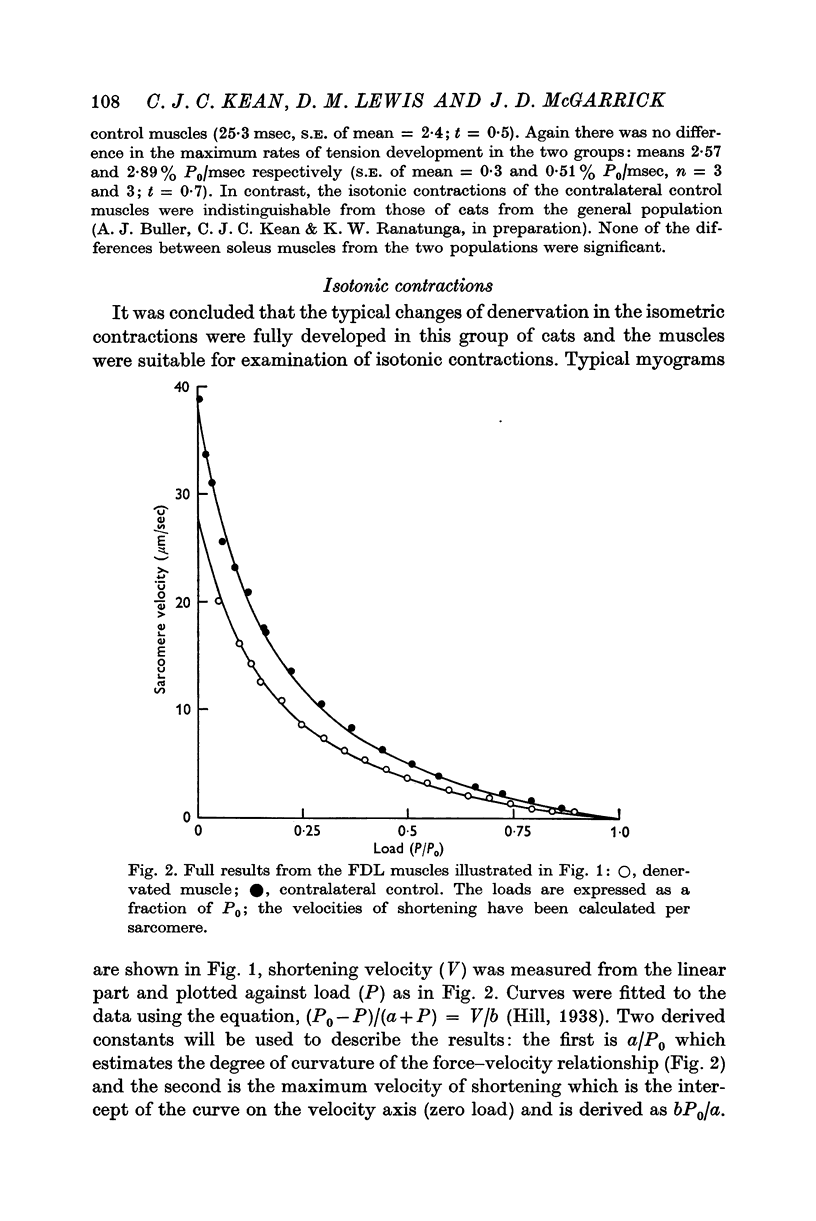
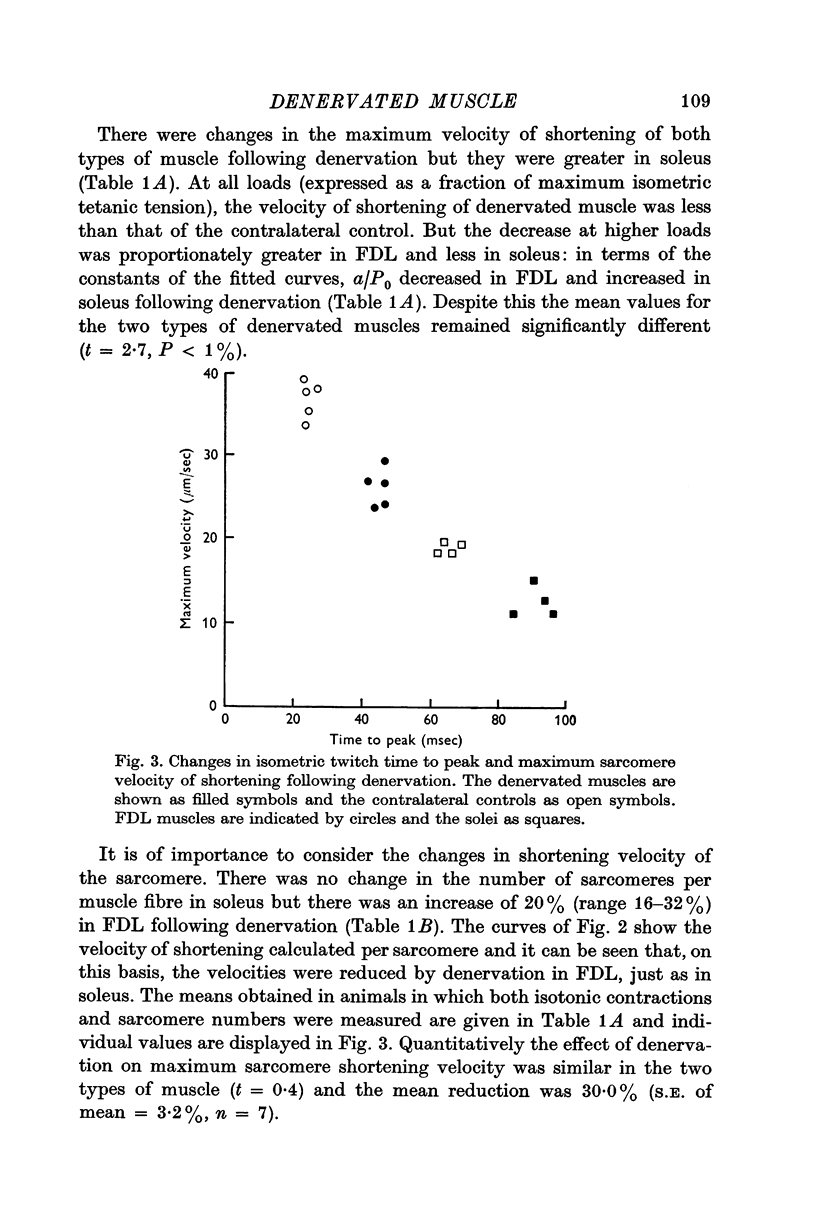
3. Whole muscle shortening velocity was reduced in the denervated soleus with no change in the number of sarcomeres per fibre. There was a smaller change in FDL muscles. This was the result of an increase in the number of sarcomeres per fibre which followed denervation in FDL, compensating for a decreased velocity of shortening of the sarcomere. Maximum sarcomere shortening velocity was reduced by 30% relative to control values in both muscles.
4. Measurements were made of the isometric contractions resulting from pairs of stimuli in an attempt to assess the period of maximal activation in the twitch. Maximum summation occurred when the second stimulus was given close to the time of the peak of the twitch in the denervated muscles.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley C. C., Ridgway E. B. On the relationships between membrane potential, calcium transient and tension in single barnacle muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):105–130. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., LEWIS D. M. THE RATE OF TENSION DEVELOPMENT IN ISOMETRIC TETANIC CONTRACTIONS OF MAMMALIAN FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 Feb;176:337–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall D. L., Buller A. J., Kean C. J. A displacement transducer for measuring muscle shortening. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(2):11P–11P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOSE R. DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLES OF THE RAT DURING DEVELOPMENT. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:74–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Mechanical properties of the cross-bridges of frog striated muscle. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218 (Suppl):59P–60P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M. The effect of denervation on the mechanical and electrical responses of fast and slow mammalian twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):51–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streter F. A., Gergely J., Salmons S., Romanul F. Synthesis by fast muscle of myosin light chains characteristic of slow muscle in response to long-term stimulation. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 3;241(105):17–19. doi: 10.1038/newbio241017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabary J. C., Tabary C., Tardieu C., Tardieu G., Goldspink G. Physiological and structural changes in the cat's soleus muscle due to immobilization at different lengths by plaster casts. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):231–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Pope B. Chemical studies on light chains from cardiac and skeletal muscle myosins. Nature. 1971 Nov 12;234(5324):85–88. doi: 10.1038/234085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Amood W. S., Buller A. J., Pope R. Long-term stimulation of cat fast-twitch skeletal muscle. Nature. 1973 Jul 27;244(5413):225–227. doi: 10.1038/244225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Amood W. S., Pope R. A comparison of the structural features of muscle fibres from a fast- and a slow-twitch muscle of the pelvic limb of the cat. J Anat. 1972 Oct;113(Pt 1):49–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



