Abstract
1. Motor unit twitches were examined in cat flexor digitorum longus (fast twitch) and soleus (slow twitch) muscles. The time course of the effects of a standard tetanus on the peak twitch tension was plotted and the maximal potentiation or depression (the post-tetanic ratio) was measured.
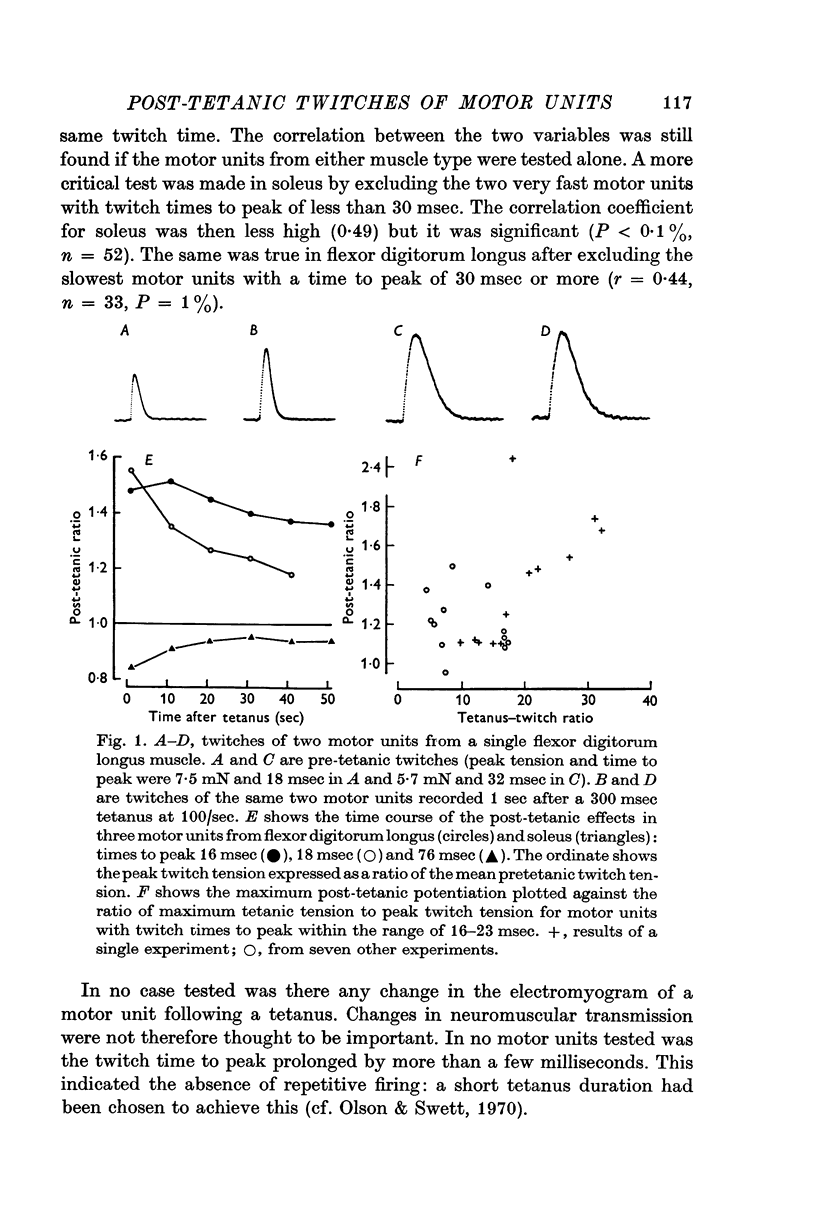
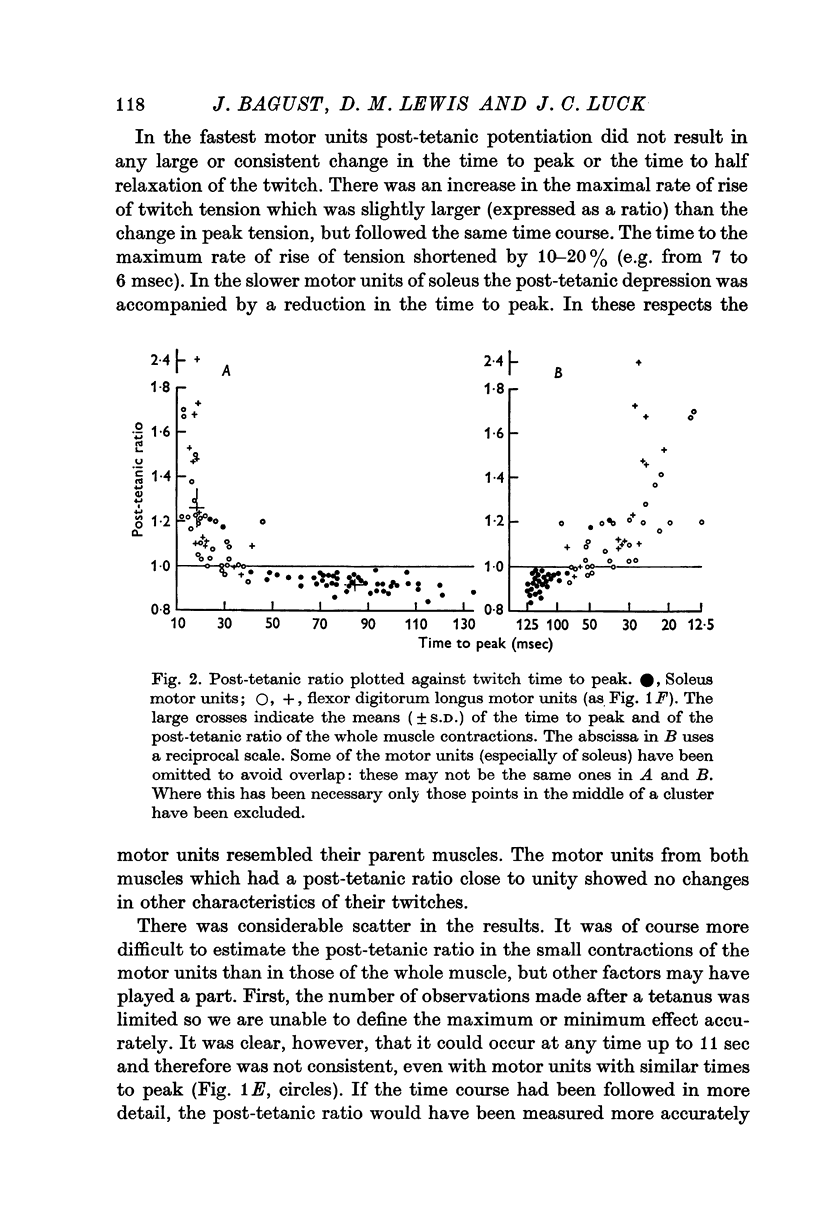
2. The post-tetanic ratio decreased continuously as the twitch time to peak of motor units increased; motor units from flexor digitorum longus and soleus could be described as a single population. The closest approximation to a linear relationship was found by plotting post-tetanic ratio against the reciprocal of time to peak.
3. The post-tetanic ratio was also related to the ratio of tetanic to twitch tension. The time of maximum potentiation or depression occurred between 1 and 11 sec, but this variable was unrelated to the time to peak or any other characteristic of the motor unit.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagust J., Knott S., Lewis D. M., Luck J. C., Westerman R. A. Isometric contractions of motor units in a fast twitch muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):87–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M., Luck J. C. Post-tetanic effects in cat motor units. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(1):26P–26P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., von Euler U. S. The after effects of a tetanus on mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1938 Jun 14;93(1):39–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly R., Gough W., Winegrad S. Characteristics of the isometric twitch of skeletal muscle immediately after a tetanus. A study of the influence of the distribution of calcium within the sarcoplasmic reticulum on the twitch. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jun;57(6):697–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M., Luck J. C., Knott S. A comparison of isometric contractions of the whole muscle with those of motor units in a fast-twitch muscle of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1972 Oct;37(1):68–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCPHEDRAN A. M., WUERKER R. B., HENNEMAN E. PROPERTIES OF MOTOR UNITS IN A HETEROGENEOUS PALE MUSCLE (M. GASTROCNEMIUS) OF THE CAT. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Jan;28:85–99. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCPHEDRAN A. M., WUERKER R. B., HENNEMAN E. PROPERTIES OF MOTOR UNITS IN A HOMOGENEOUS RED MUSCLE (SOLEUS) OF THE CAT. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Jan;28:71–84. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson C. B., Swett C. P., Jr Effect of prior activity on properties of different types of motor units. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):1–16. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Pope B. Chemical studies on light chains from cardiac and skeletal muscle myosins. Nature. 1971 Nov 12;234(5324):85–88. doi: 10.1038/234085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



