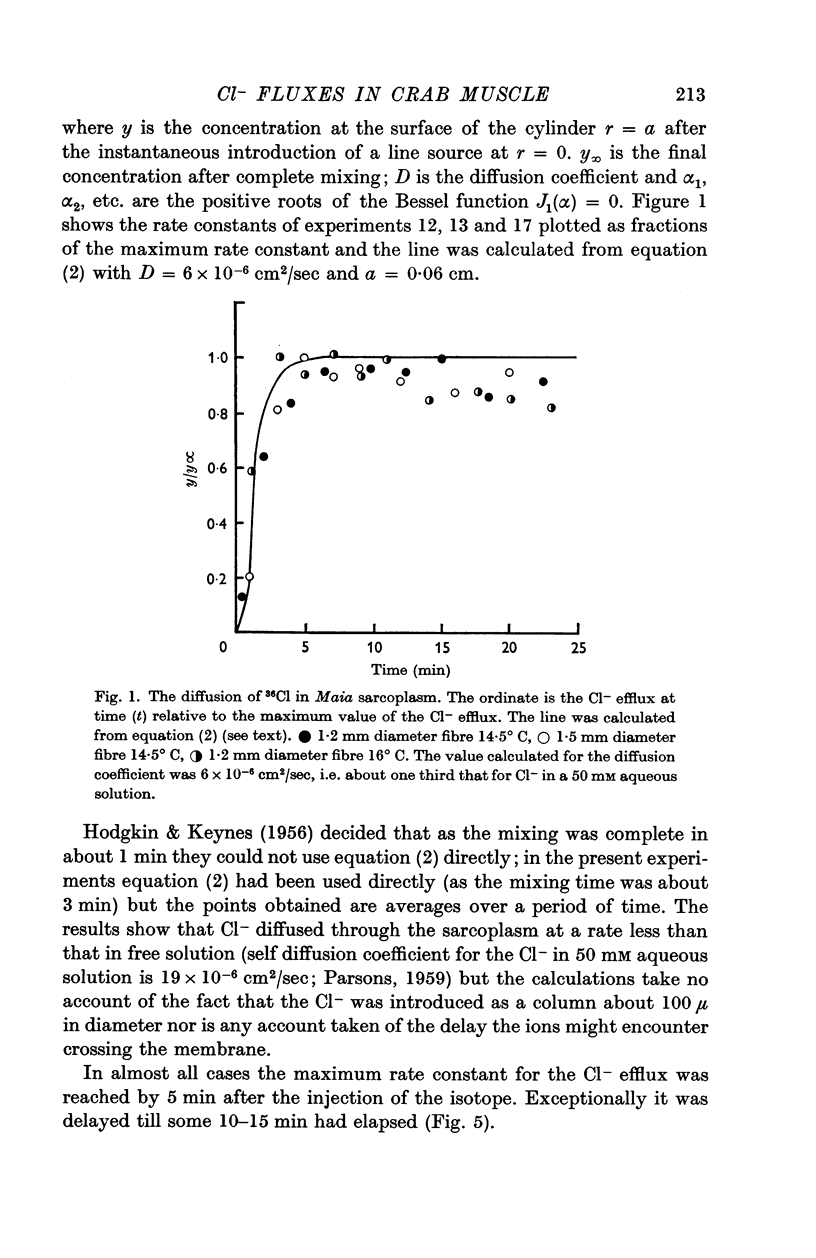
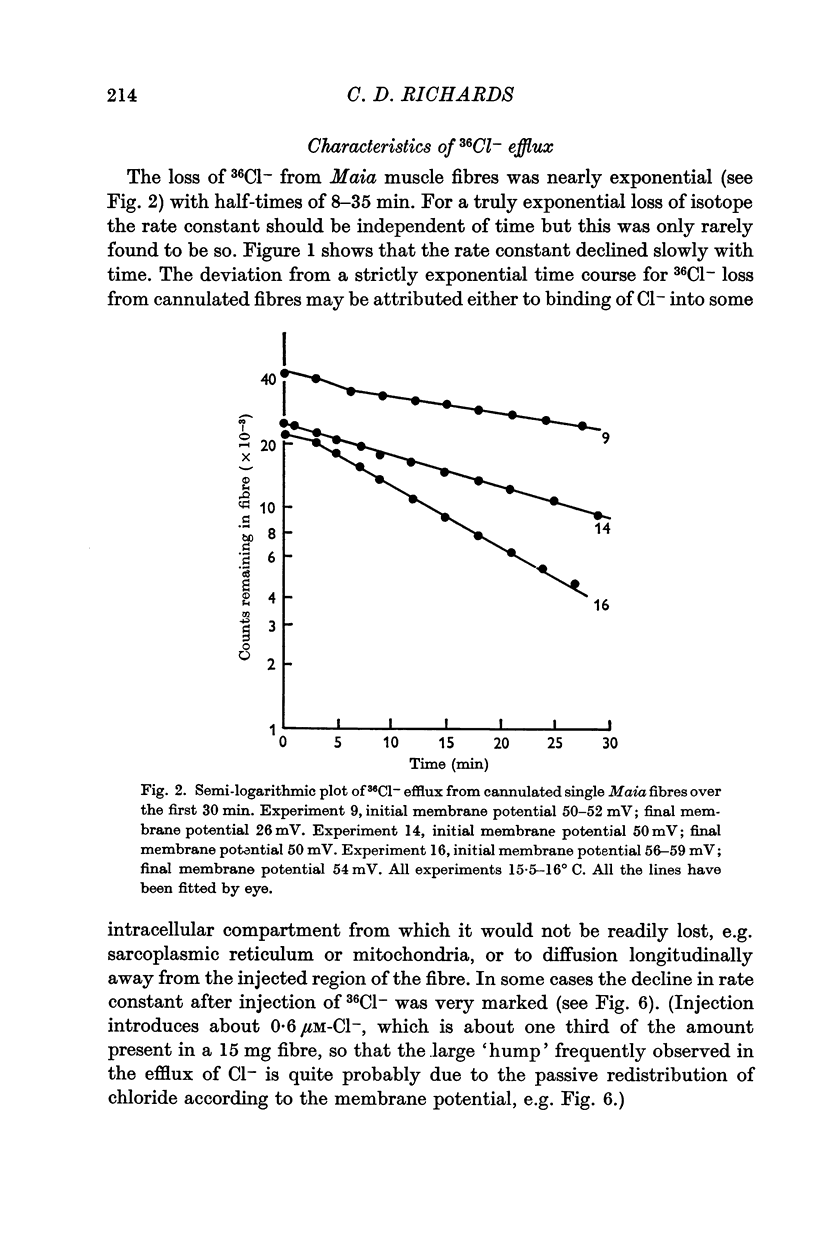
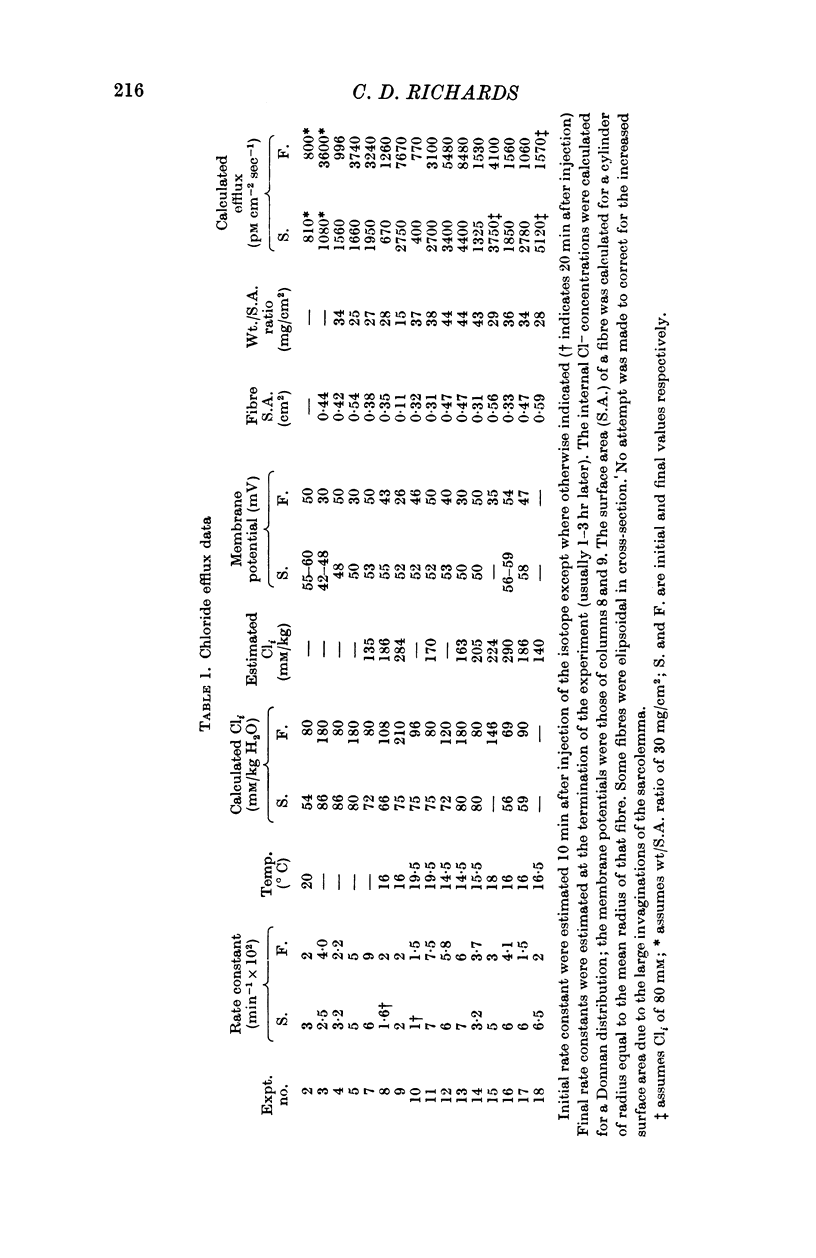
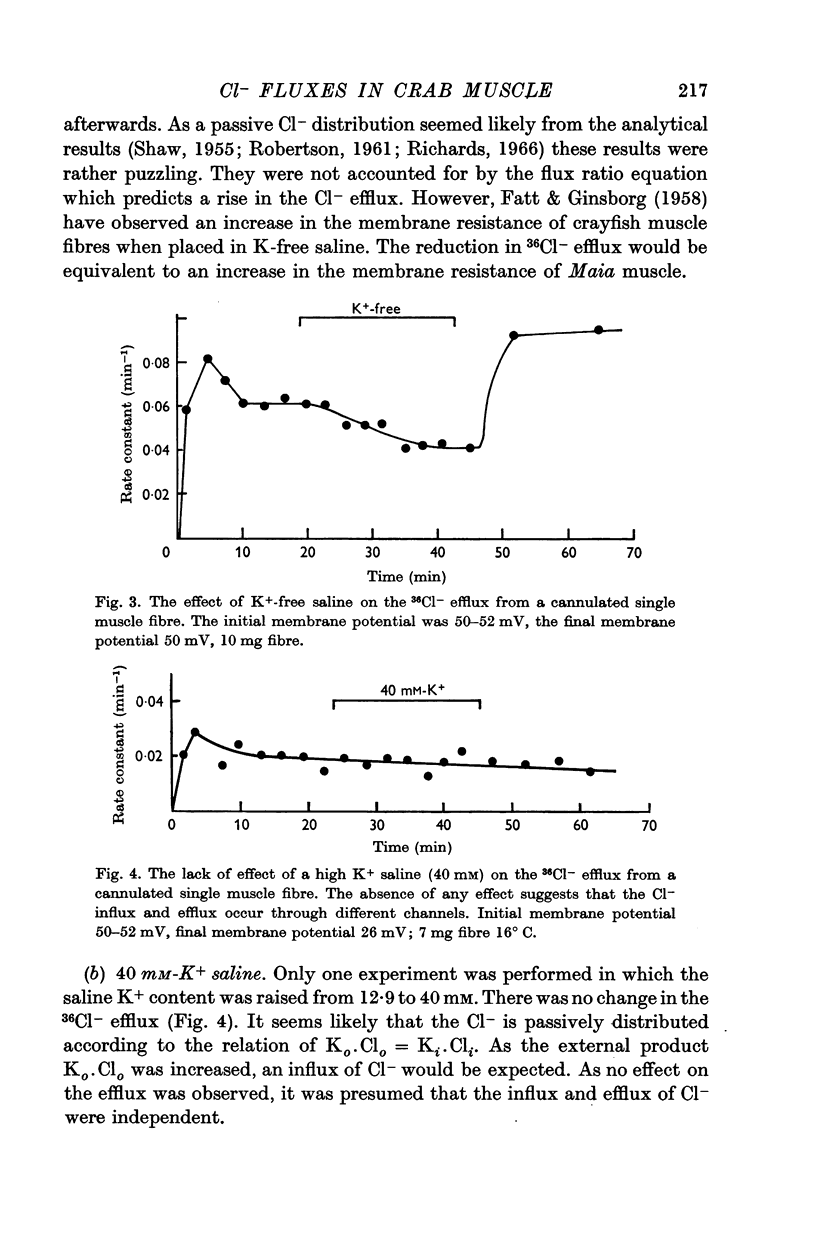
Abstract
1. Isotopic techniques were used to study the efflux of Cl- from single cannulated muscle fibres of the crab Maia squinado.
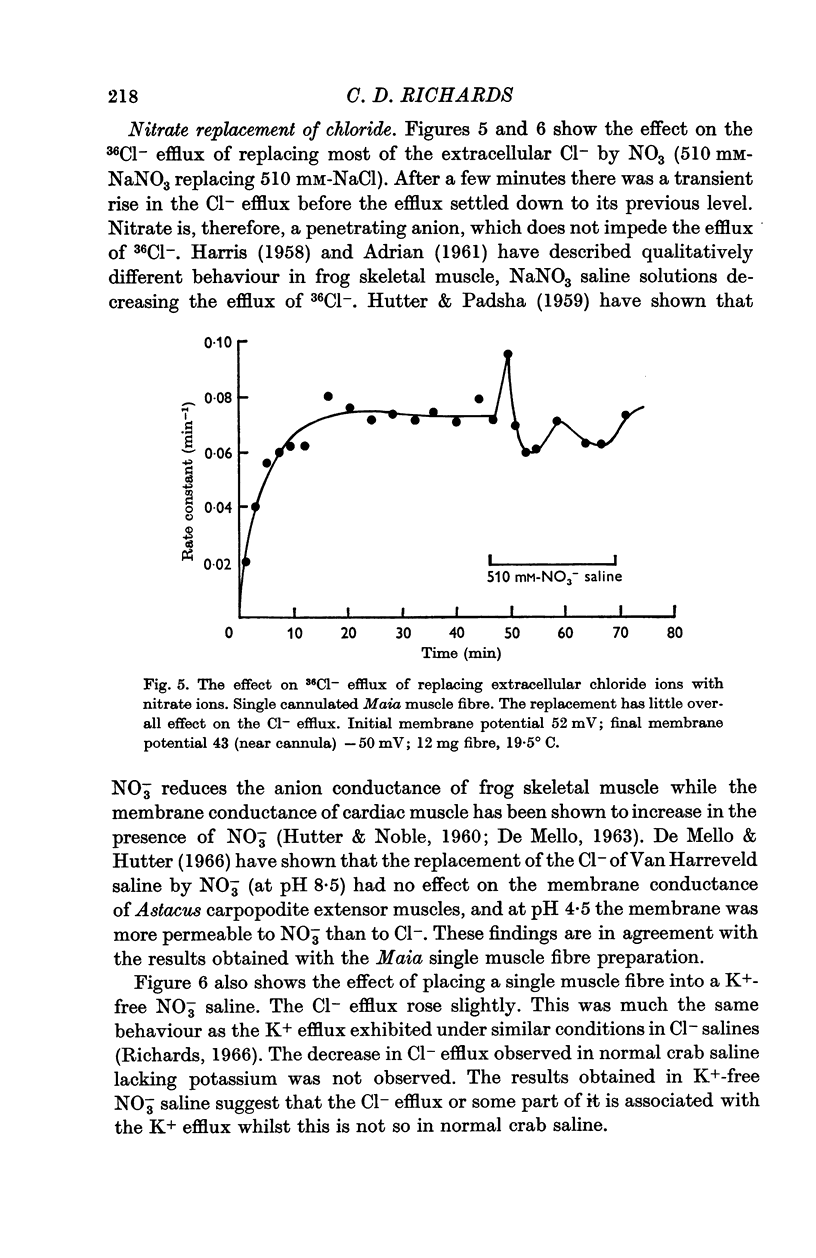
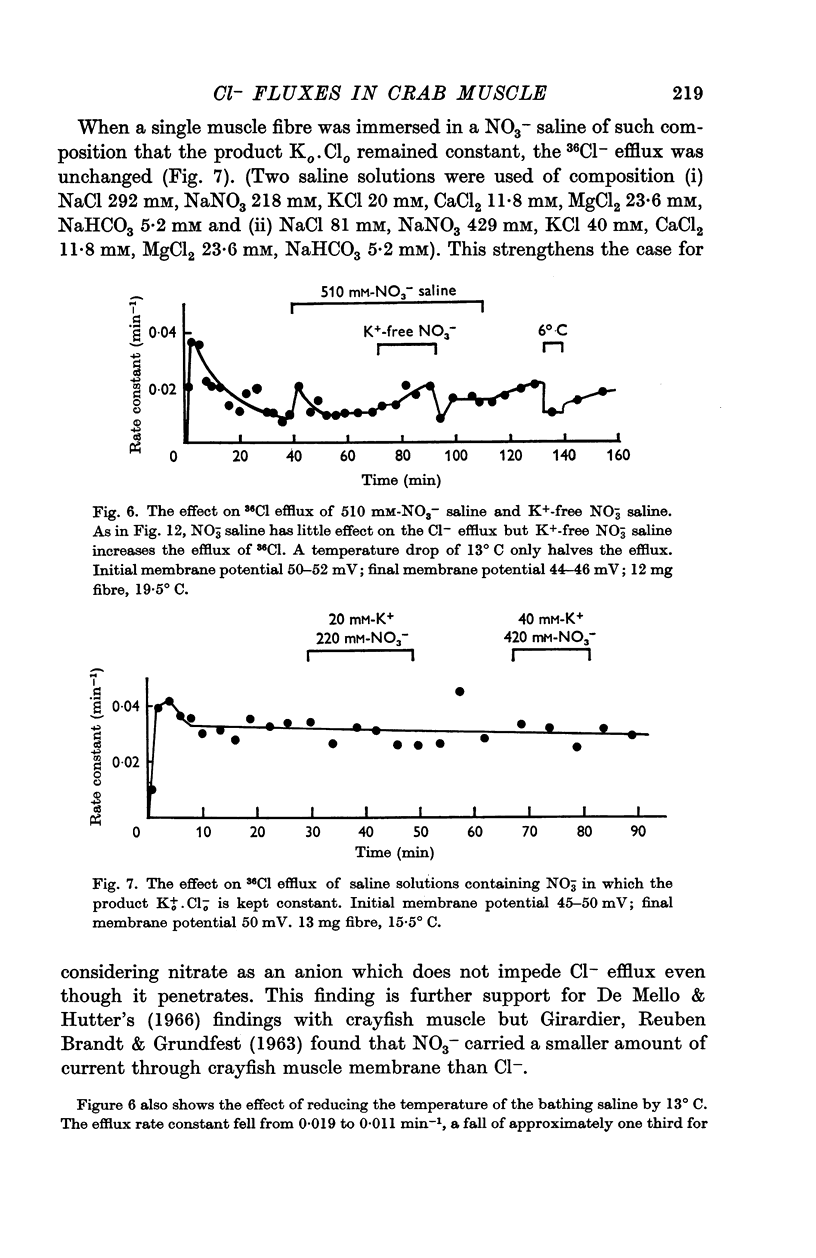
2. The efflux of 36Cl- was found to be exponential with steady rate constants ranging from 0·01 to 0·07 min-1. The steady efflux was ca. 1000-2000 pM cm-2 sec-1. The efflux was slightly depressed by K+-free saline and was unaffected by 40 mM-K+ saline and NO3- saline. The influx and efflux of Cl- were presumed independent.
3. The membrane conductance calculated from 36Cl- flux data was consistent with that determined by the method of electrotonic spread for other marine crustacean muscle fibres. Cl- accounted for most of the membrane conductance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. Internal chloride concentration and chloride efflux of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1961 May;156:623–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINLEY F. J., Jr SODIUM, POTASSIUM, AND CHLORIDE CONCENTRATIONS AND FLUXES IN THE ISOLATED GIANT AXON OF HOMARUS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Jul;28:742–772. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.4.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALDWELL P. C., KEYNES R. D. The permeability of the squid giant axon to radioactive potassium and chloride ions. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:177–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALDWELL P. C., WALSTER G. STUDIES ON THE MICRO-INJECTION OF VARIOUS SUBSTANCES INTO CRAB MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:353–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMELLO W. C. ROLE OF CHLORIDE IONS IN CARDIAC ACTION AND PACEMAKER POTENTIALS. Am J Physiol. 1963 Sep;205:567–575. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.3.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., GINSBORG B. L. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):516–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. The electrical properties of crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):171–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARDIER L., REUBEN J. P., BRANDT P. W., GRUNDFEST H. EVIDENCE FOR ANION-PERMSELECTIVE MEMBRANE IN CRAYFISH MUSCLE FIBERS AND ITS POSSIBLE ROLE IN EXCITATION-CONTRACTION COUPLING. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Sep;47:189–214. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J. Anion interaction in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 30;141(2):351–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Experiments on the injection of substances into squid giant axons by means of a microsyringe. J Physiol. 1956 Mar 28;131(3):592–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., NOBLE D. The chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:89–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., PADSHA S. M. Effect of nitrate and other anions on the membrane resistance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Apr 23;146(1):117–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C., Cocking E. C. High-efficiency liquid-scintillation counting of 14C-labelled material in aqueous solution and determination of specific activity of labelled proteins. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):626–633. doi: 10.1042/bj0960626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. CHLORIDE IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:690–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic fluxes in frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):359–382. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic movements during nervous activity. J Physiol. 1951 Jun;114(1-2):119–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


