Abstract
Mammalian glial cells were identified and studied in the optic nerves of anaesthetized rats.
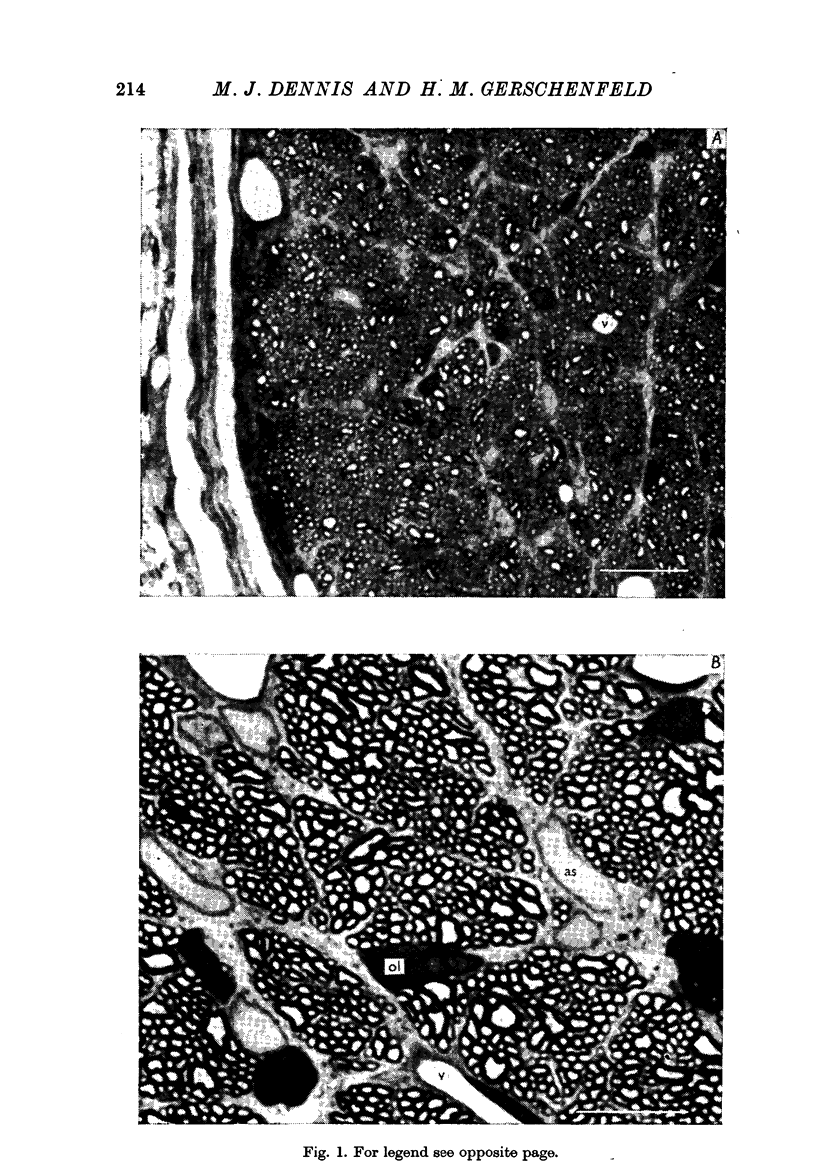
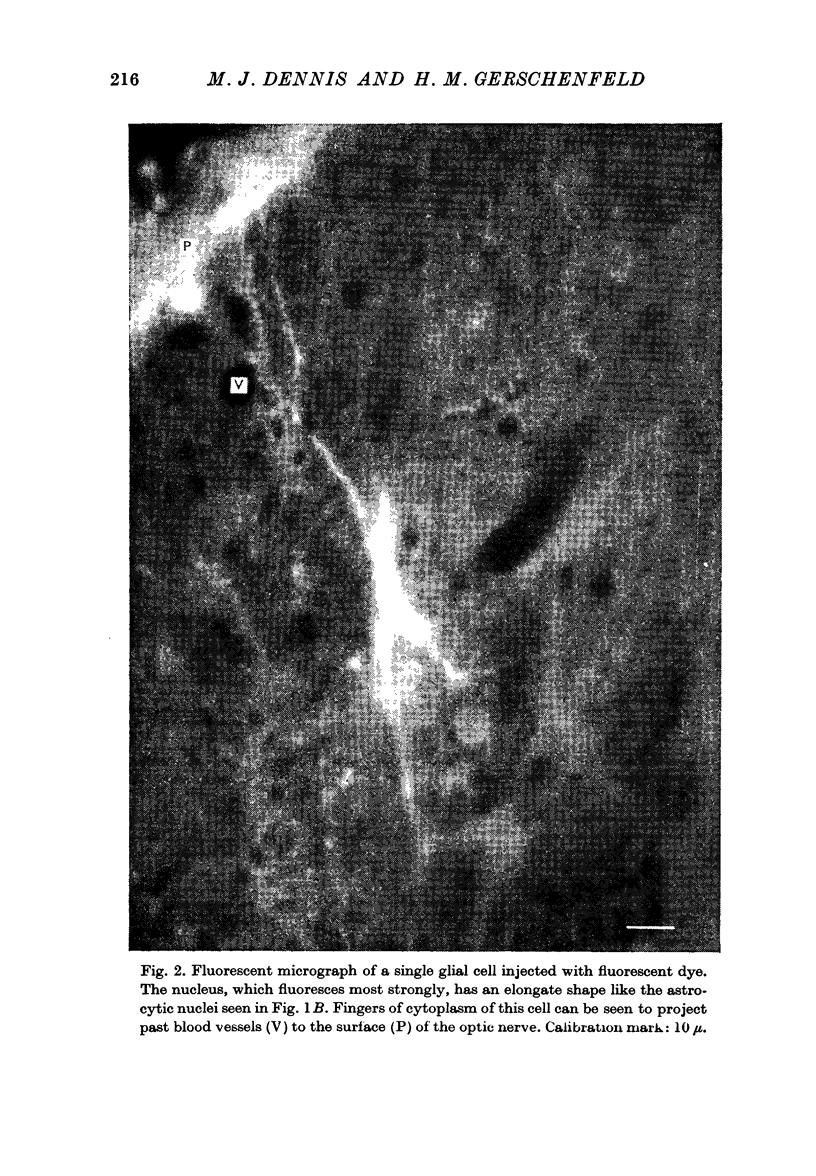
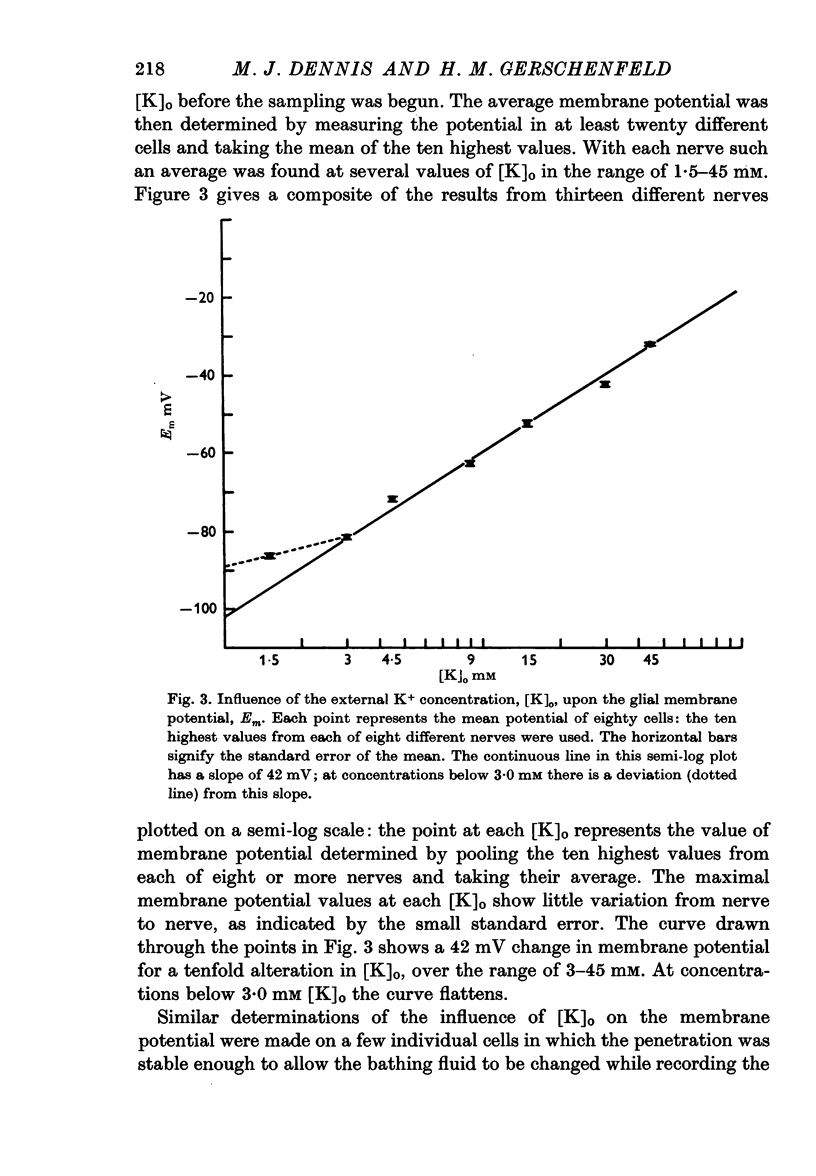
Cells with membrane potentials of 77-85 mV were located in the optic nerve with capillary micropipettes. These were shown to be neuroglia by iontophoretic injection of a fluorescent dye through the recording electrode, followed by histological verification of the location of the dye. No distinction was made between astroglia and oligodendroglia.
Neuroglial cells gave no impulse activity. Their membrane potential was studied in isolated optic nerves by varying the ionic composition of the bathing fluid. The glial membrane potential depends predominantly on a transmembrane gradient of potassium ions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. J., Conway E. J. Potassium accumulation in muscle and associated changes. J Physiol. 1941 Aug 11;100(1):1–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge R. P. Glial cells and the central myelin sheath. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jan;48(1):197–251. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAAPANEN L., KOLMODIN G. M., SKOGLUND C. R. Membrane and action potentials of spinal interneurons in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 8;43(3-4):315–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILD W., TASAKI I. Morphological and physiological properties of neurons and glial cells in tissue culture. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Mar;25:277–304. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A., BRINLEY F. J., Jr Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. I. Sequential invasion and synaptic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:225–242. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., POTTER D. D. GLIA IN THE LEECH CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: PHYSIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND NEURON-GLIA RELATIONSHIP. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Mar;27:290–320. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karahashi Y., Goldring S. Intracellular potentials from "idle" cells in cerebral cortex of cat. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1966 Jun;20(6):600–607. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(66)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S., Krnjević K., Yim G. K. Unresponsive cells in cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1967 Dec;6(4):767–769. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(67)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Schwartz S. Some properties of unresponsive cells in the cerebral cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(4):306–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00237557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Nicholls J. G., Orkand R. K. Physiological properties of glial cells in the central nervous system of amphibia. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Jul;29(4):768–787. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.4.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Nicholls J. G. The physiology of neuroglial cells. Ergeb Physiol. 1966;57:1–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON P. G., ERULKAR S. D. SYNAPTIC MECHANISMS OF EXCITATION AND INHIBITION IN THE CENTRAL AUDITORY PATHWAY. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Nov;26:908–923. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLLS J. G., KUFFLER S. W. EXTRACELLULAR SPACE AS A PATHWAY FOR EXCHANGE BETWEEN BLOOD AND NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF THE LEECH: IONIC COMPOSITION OF GLIAL CELLS AND NEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:645–671. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS A. Plasma membrane contacts in the central nervous system. J Anat. 1962 Apr;96:237–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G. Intracellular records from Betz cells in the cat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1956 Jan;41(1):58–69. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1956.sp001163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed D. J., Withrow C. D., Woodbury D. M. Electrolyte and acid-base parameters of rat cerebrospinal fluid. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(3):212–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00235585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segundo J. P., Takenaka T., Encabo H. Electrophysiology of bulbar reticular neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1194–1220. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton A. O., Kravitz E. A. Neuronal geometry: determination with a technique of intracellular dye injection. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):132–134. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. E., Peters A. Electron microscopy of the early postnatal development of fibrous astrocytes. Am J Anat. 1967 Jul;121(1):131–152. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas J., Villegas R., Giménez M. Nature of the Schwann cell electrical potential. Effects of the external ionic concentrations and a cardiac glycoside. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jan;51(1):47–64. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardell W. M. Electrical and pharmacological properties of mammalian neuroglial cells in tissue-culture. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Sep 13;165(1000):326–361. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]