Abstract
1. The size of the tonic stretch reflex of the soleus or gastrocnemius muscle of the decerebrate cat has been compared with the size of the reflex contraction elicited in the same muscle by high-frequency vibration applied to its tendon.
2. On the assumption that vibration preferentially excites the primary endings of the muscle spindles it may be used to estimate the relation between the reflex response and the frequency of the Ia input to the spinal cord. On this basis, the increase in tension evoked by increasing extension is too great to be explained by the increase in Ia input with extension previously found on single fibre recording in comparable preparations.
3. When vibration was superimposed on stretch reflexes elicited by different extensions, the size of the additional contraction elicited by the vibration remained approximately constant. If the stretch and vibration reflexes both depended entirely upon the Ia pathway, then occlusion between them would have been expected instead of the simple summation which was found.
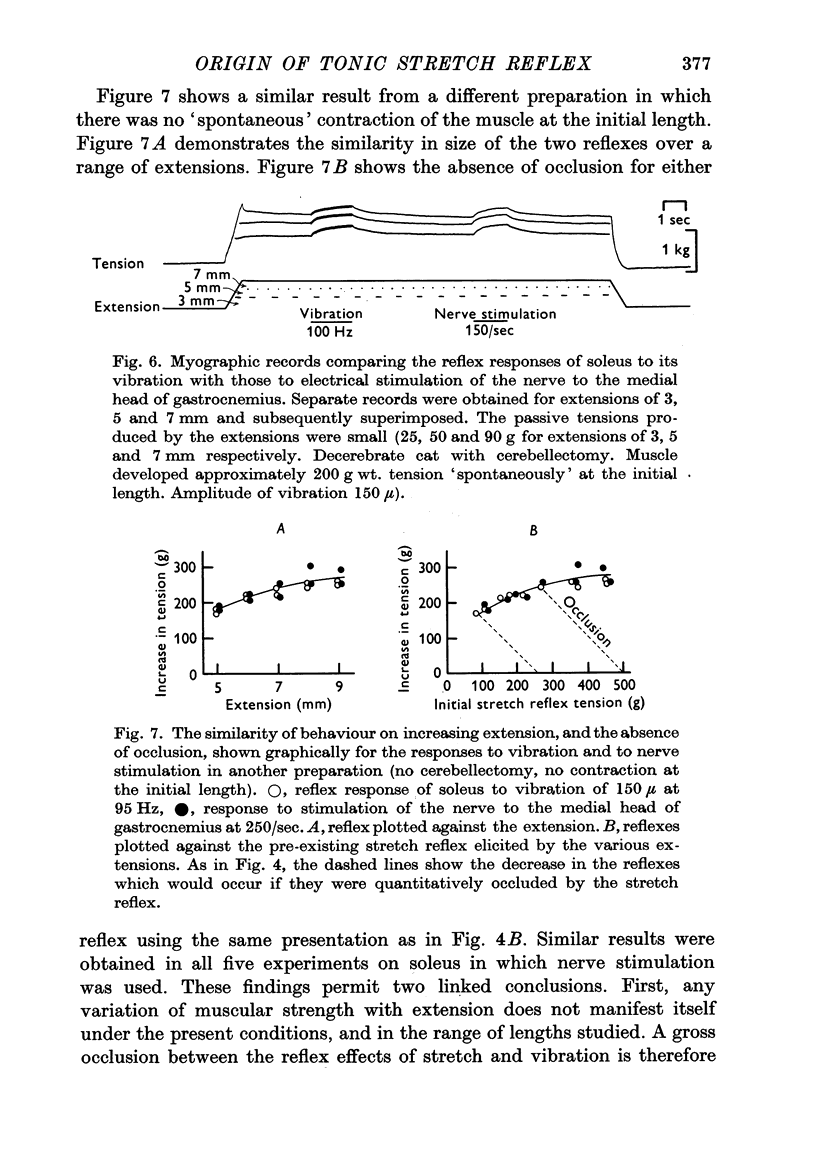
4. The absence of occlusion was not due to variation of the contractile strength of the muscle with its extension. This was shown by finding that the reflex contraction of soleus produced by stimulating the medial gastrocnemius nerve also remained the same size when elicited at different lengths of the muscle.
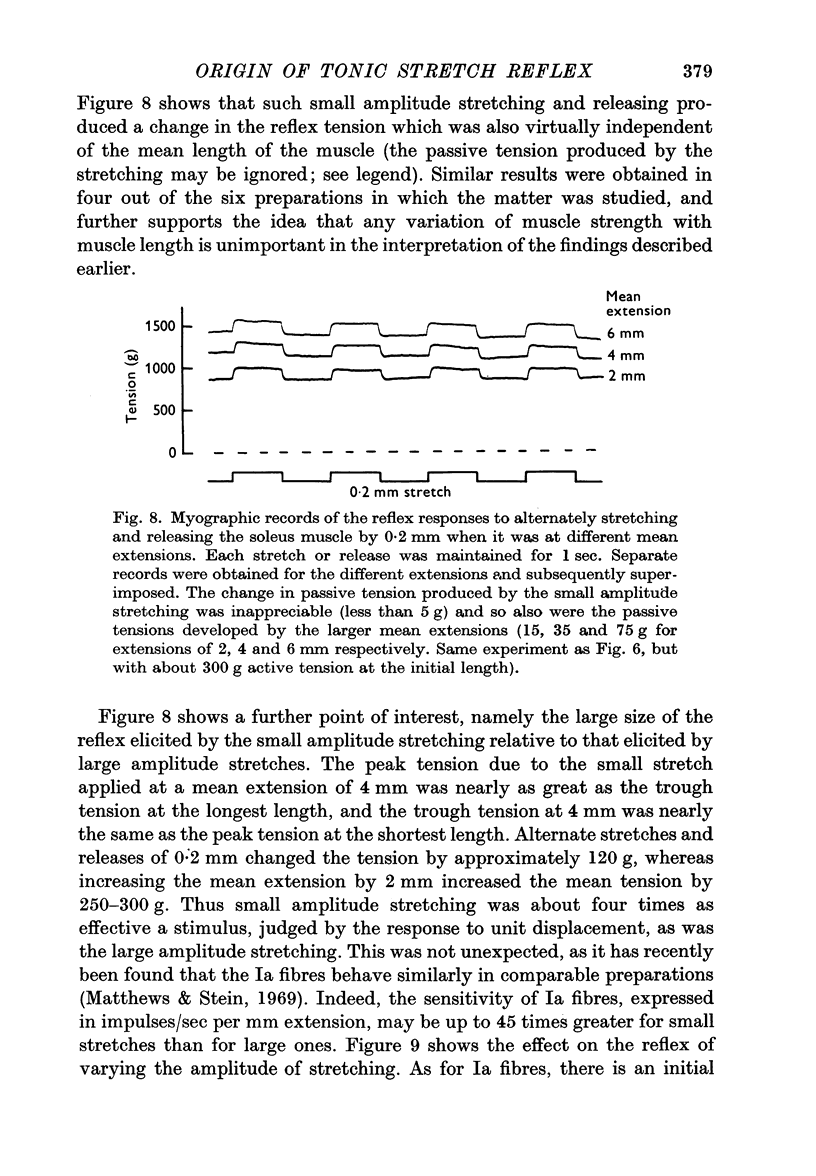
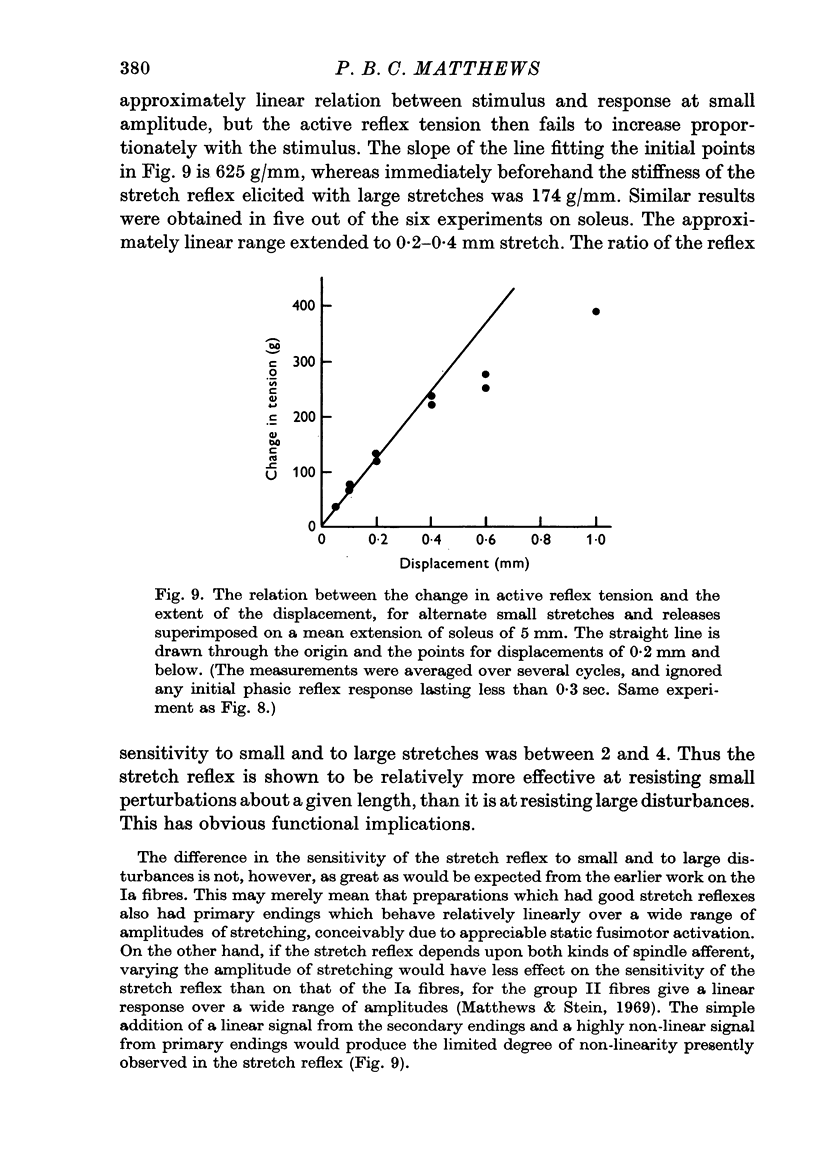
5. The reflex effects were studied of superimposing alternate stretches and releases of 0·2 mm, on extensions of several mm. The small stretches elicited responses which were larger than expected from the response to large stretches, and which were approximately the same size at different mean lengths of the muscle.
6. It is concluded that the tonic stretch reflex of the decerebrate cat cannot readily be explained solely by the increase in Ia discharge produced by stretching, as usually believed. Instead, it is suggested that the group II afferent fibres from the secondary endings of the muscle spindle also play an important part in its production.
Full text
PDF





















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVORD E. C., Jr, FUORTES M. G. Reflex activity of extensor motor units following muscular afferent excitation. J Physiol. 1953 Nov 28;122(2):302–321. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anastasijević R., Todorović A. B., Vuco J. The differential reflex excitability of alpha motoneurons of decerebrate cats caused by vibration applied to the tendon of the gastrocnemius medialis muscle. Brain Res. 1968 Nov;11(2):336–346. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Bessou P., Laporte Y. Action of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres on secondary endings of cat's spindles. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):160–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSOU P., LAPORTE Y. Activation des fibres afférentes amyéliniques d'origine musculaire. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1958;152(11):1587–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIANCONI R., GRANIT R., REIS D. J. THE EFFECTS OF EXTENSOR MUSCLE SPINDLES AND TENDON ORGANS ON HOMONYMOUS MOTONEURONES IN RELATION TO GAMMA-BIAS AND CURARIZATION. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:331–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIANCONI R., van der MEULEN J. The response to vibration of the end organs of mammalian muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jan;26:177–190. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK L. G., ECCLES J. C., RALL W. Experimental investigations on the afferent fibres in muscle nerves. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1951 Oct 30;138(893):453–475. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1951.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN M. C., CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. OBSERVATIONS ON THE FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF THE TIBIALIS POSTERIOR MUSCLE OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:140–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., LEWIS D. M. THE RATE OF TENSION DEVELOPMENT IN ISOMETRIC TETANIC CONTRACTIONS OF MAMMALIAN FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 Feb;176:337–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Engberg I., Matthews P. B. The relative sensitivity to vibration of muscle receptors of the cat. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):773–800. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Lawrence D. G., Matthews P. B. Static fusimotor fibres and the position sensitivity of muscle spindle receptors. Brain Res. 1969 Jun;14(1):173–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Supraspinal control of interneurones mediating spinal reflexes. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:565–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDRED E., GRANIT R., MERTON P. A. Supraspinal control of the muscle spindles and its significance. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):498–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HENATSCH H. D. Gamma control of dynamic properties of muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Jul;19(4):356–366. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.4.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
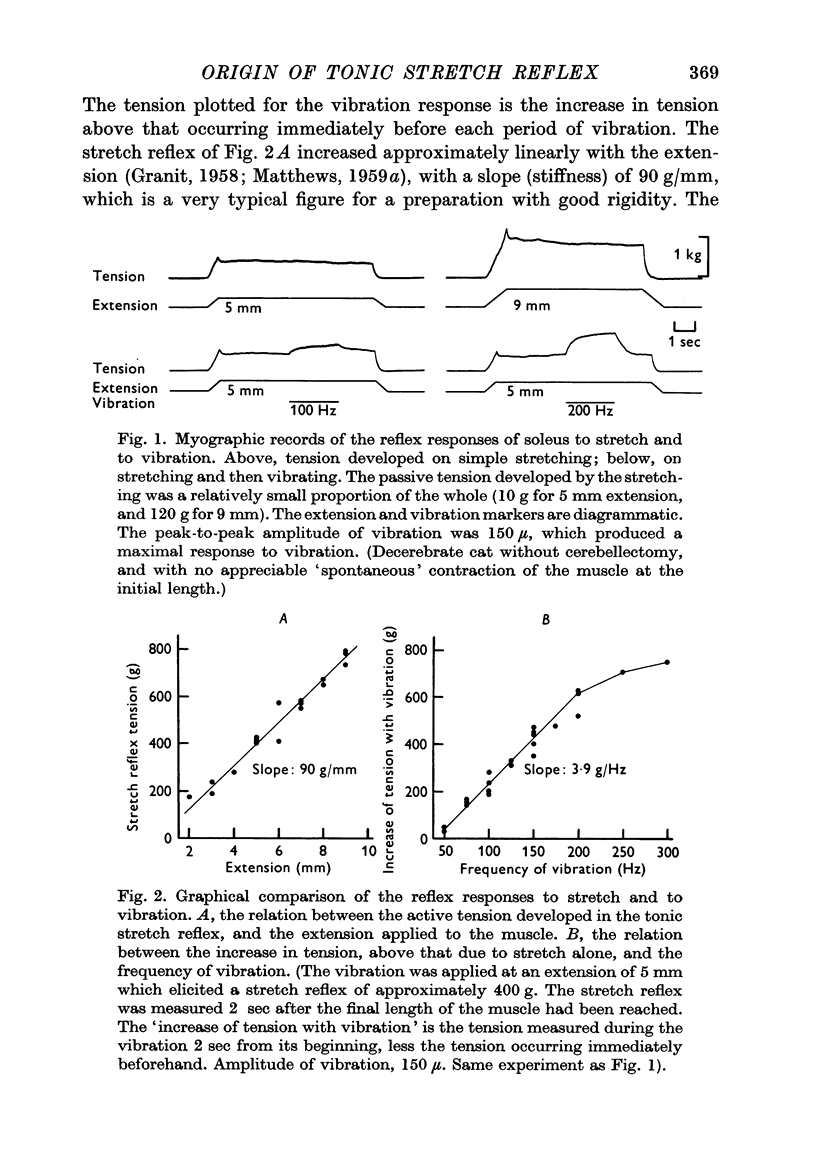
- GRANIT R. Neuromuscular interaction in postural tone of the cat's isometric soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):387–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R., Kellerth J. O., Szumski A. J. Intracellular autogenetic effects of muscular contration on extensor motoneurones. The silent period. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):484–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., PERL E. R. Spinal reflex mechanisms concerned with skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:538–579. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
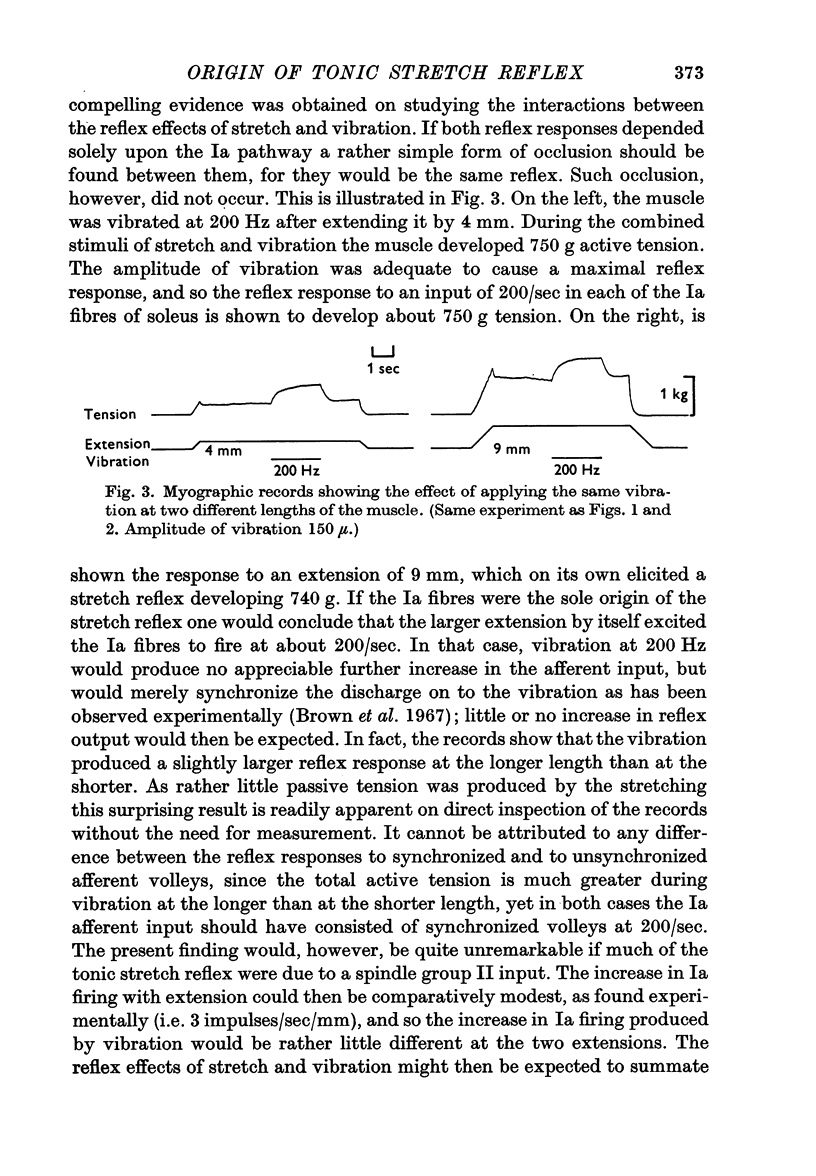
- HUNT C. C. Relation of function to diameter in afferent fibers of muscle nerves. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Sep 20;38(1):117–131. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J., Henneman E. Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):466–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSEN J. K., RUDJORD T. ON THE SILENT PERIOD AND GOLGI TENDON ORGANS OF THE SOLEUS MUSCLE OF THE CAT. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Dec;62:364–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb10435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M., PERL E. R. Alteration of spinal reflexes by interaction with suprasegmental and dorsal root activity. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:103–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
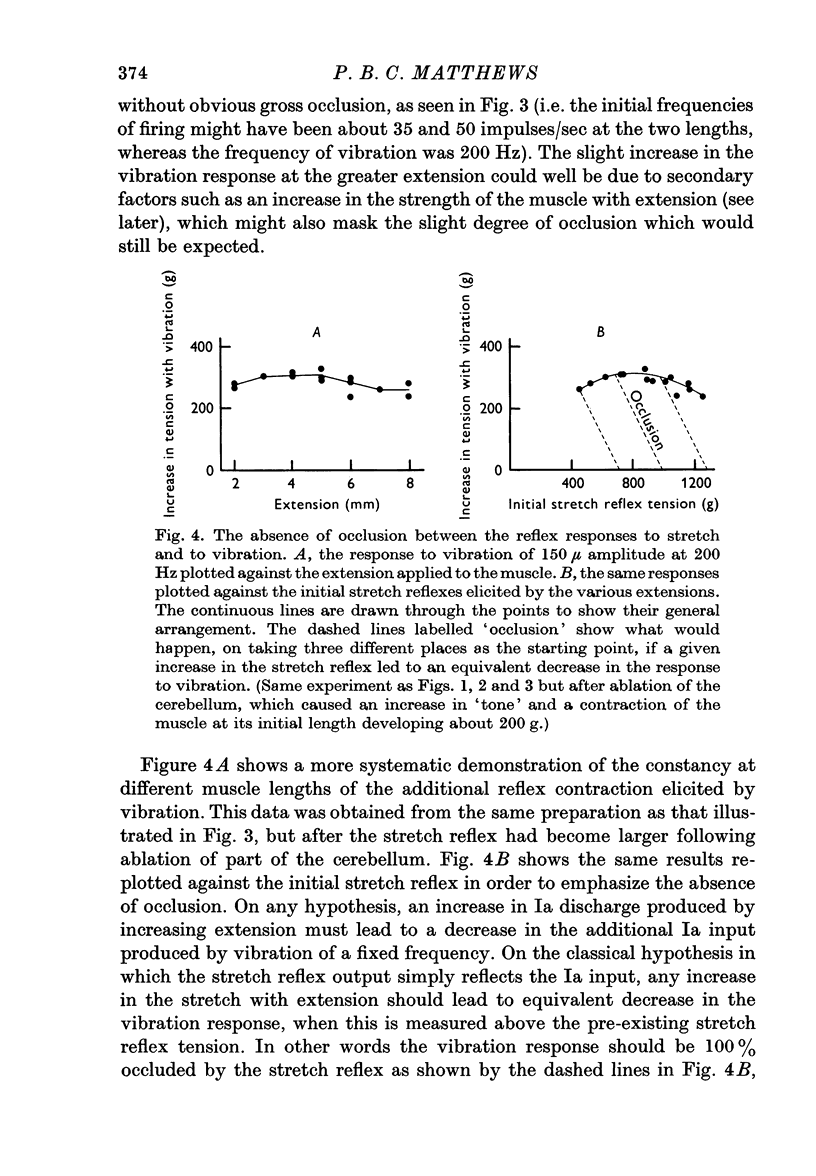
- MARK R. F. TONIC STRETCH REFLEXES IN THE CALF MUSCLES OF NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS. Nature. 1963 Jul 6;199:50–52. doi: 10.1038/199050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS P. B. MUSCLE SPINDLES AND THEIR MOTOR CONTROL. Physiol Rev. 1964 Apr;44:219–288. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1964.44.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS P. B., RUSHWORTH G. The selective effect of proCaine on the stretch reflex and tendon jerk of soleus muscle when applied to its nerve. J Physiol. 1957 Feb 15;135(2):245–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS P. B. The effect of the local application of procaine on the stretch reflex of the soleus muscle of the cat decerebrated by anaemia. J Physiol. 1958 Mar 11;140(3):408–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
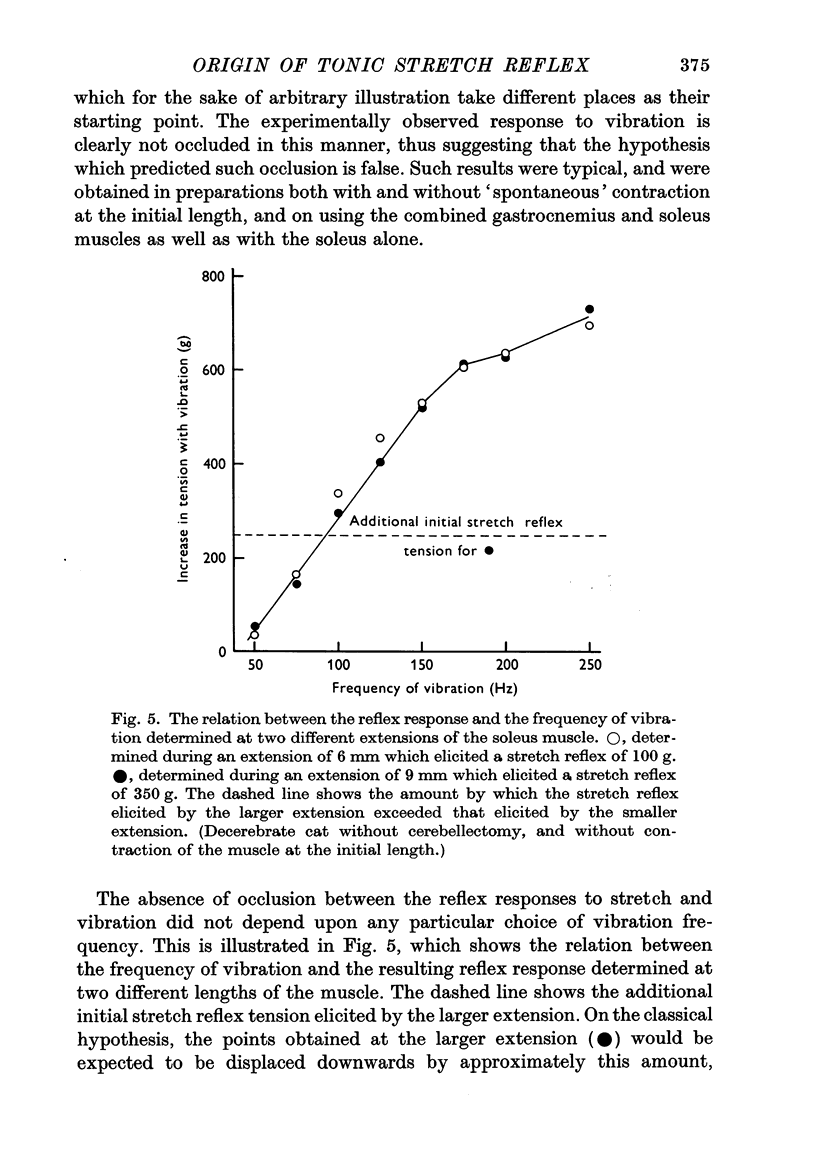
- Mark R. F., Coquery J. M., Paillard J. Autogenetic reflex effects of slow or steady stretch of the calf muscles in man. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(2):130–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00239167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. B. A study of certain factors influencing the stretch reflex of the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147(3):547–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. B., Stein R. B. The sensitivity of muscle spindle afferents to small sinusoidal changes of length. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):723–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. B. The dependence of tension upon extension in the stretch reflex of the soleus muscle of the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147(3):521–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. B. The reflex excitation of the soleus muscle of the decerebrate cat caused by vibbration applied to its tendon. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):450–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. Functional analysis of group III afferent fibres of mammalian muscles. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:250–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppele R. E., Terzuolo C. A. Myotatic reflex: its input-output relation. Science. 1968 Feb 16;159(3816):743–745. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3816.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rack P. M., Westbury D. R. The effects of length and stimulus rate on tension in the isometric cat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):443–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington C. S., Sowton S. C. Observations on reflex responses to single break-shocks. J Physiol. 1915 Jul 5;49(5):331–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1915.sp001713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


