Abstract
1. A comparison has been made of the effect of cooling, metabolic inhibitors and of ouabain on the electrogenic component of the sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres.
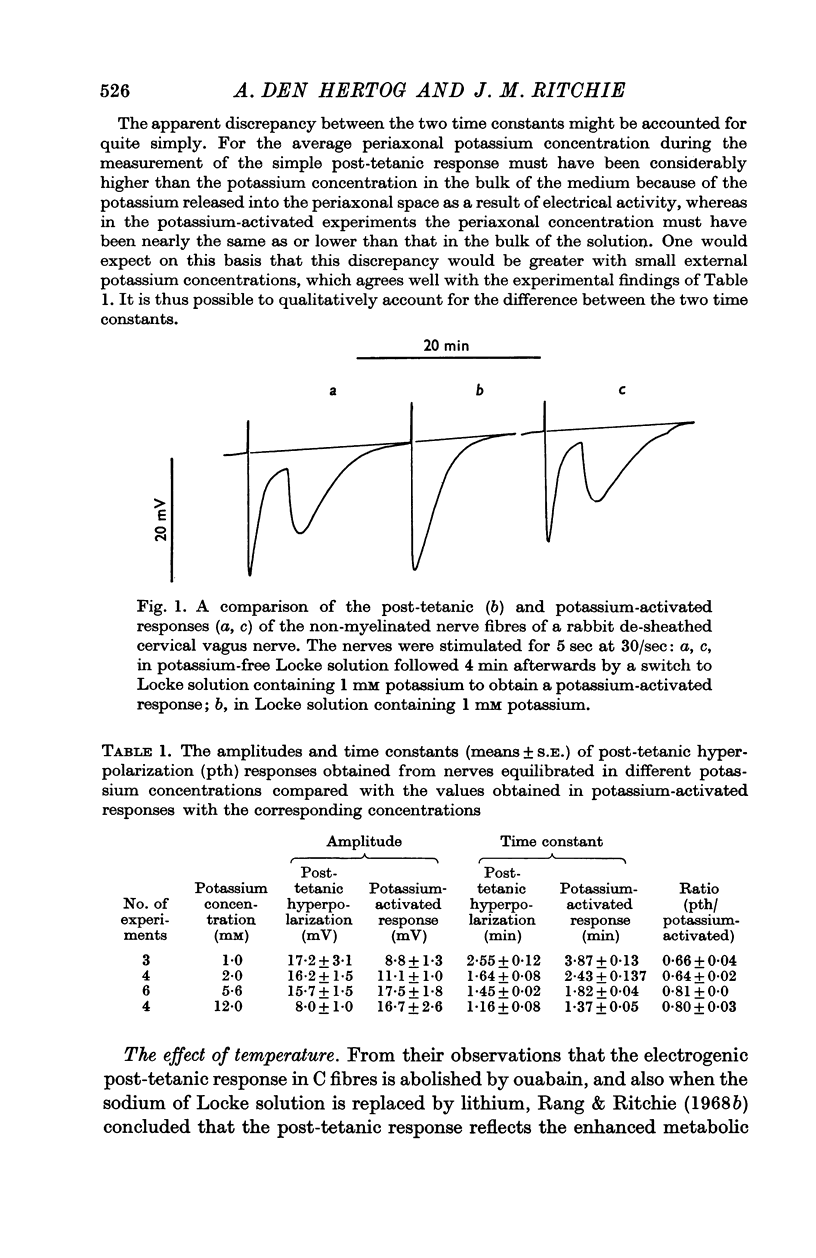
2. The hyperpolarization that occurs during the potassium-activated response that is obtained after a brief period of stimulation (5 sec, 30/sec) in potassium-free solution was taken as an index of the activity of the pump.
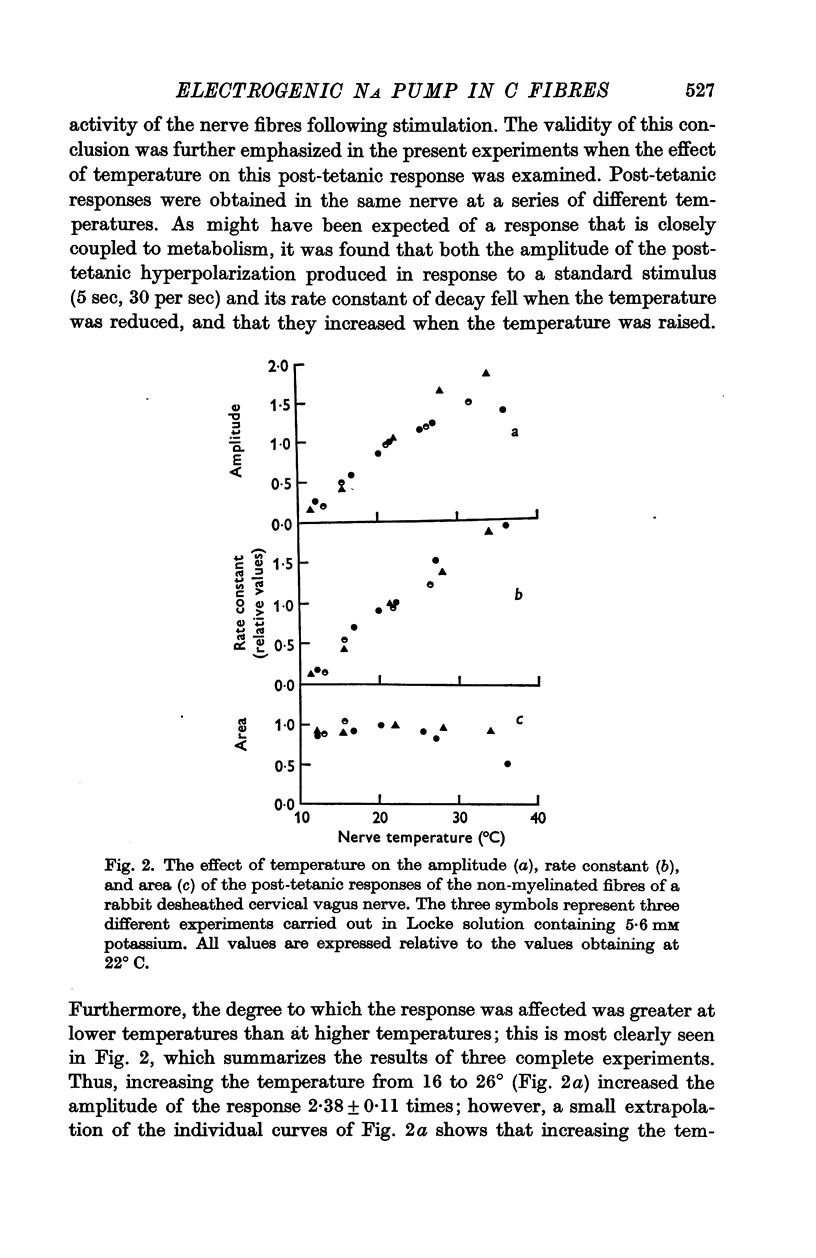
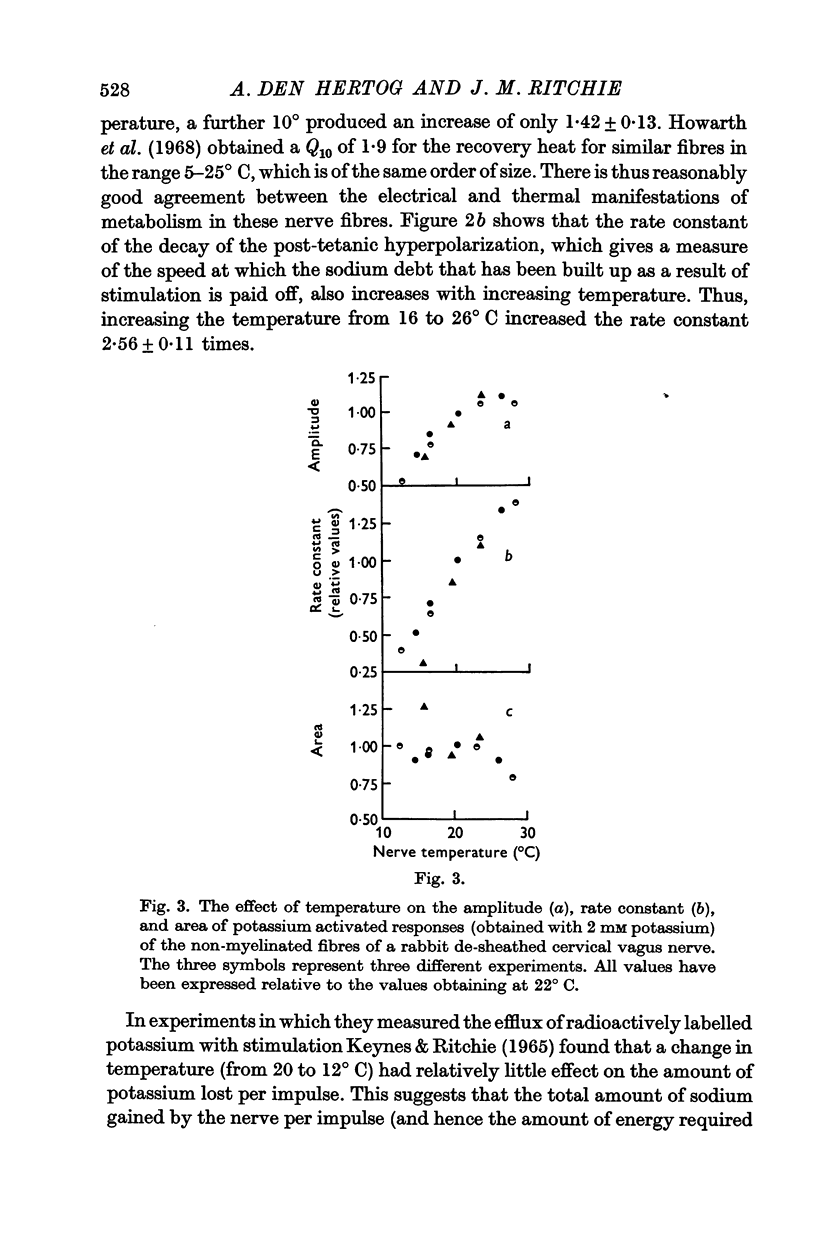
3. Cooling decreased the amplitude and rate constant of decay of the potassium-activated response. The area of the response, which reflects the total amount of sodium that is extruded after activity, remained constant.
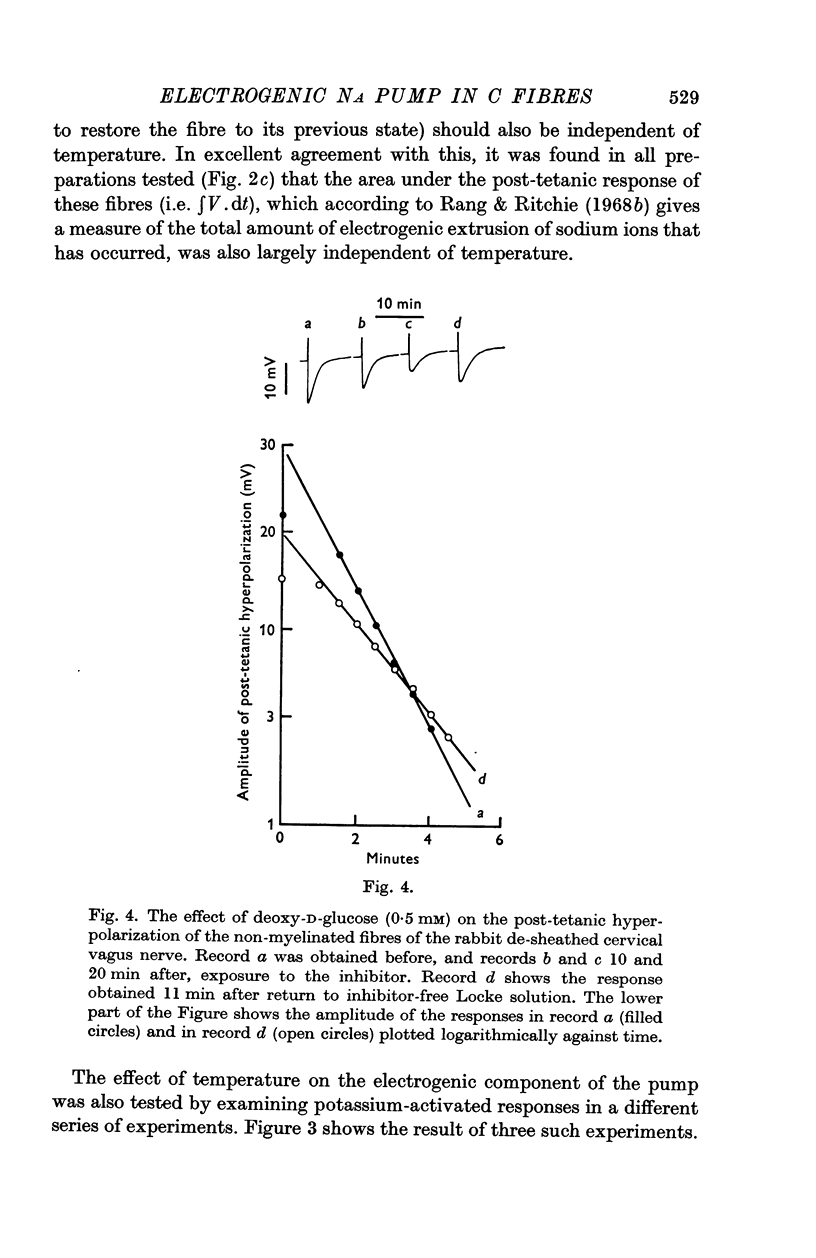
4. Exposure to the metabolic inhibitors deoxy-D-glucose and cyanide also decreased the amplitude and rate constant of the response; as with cooling, the area remained relatively constant.
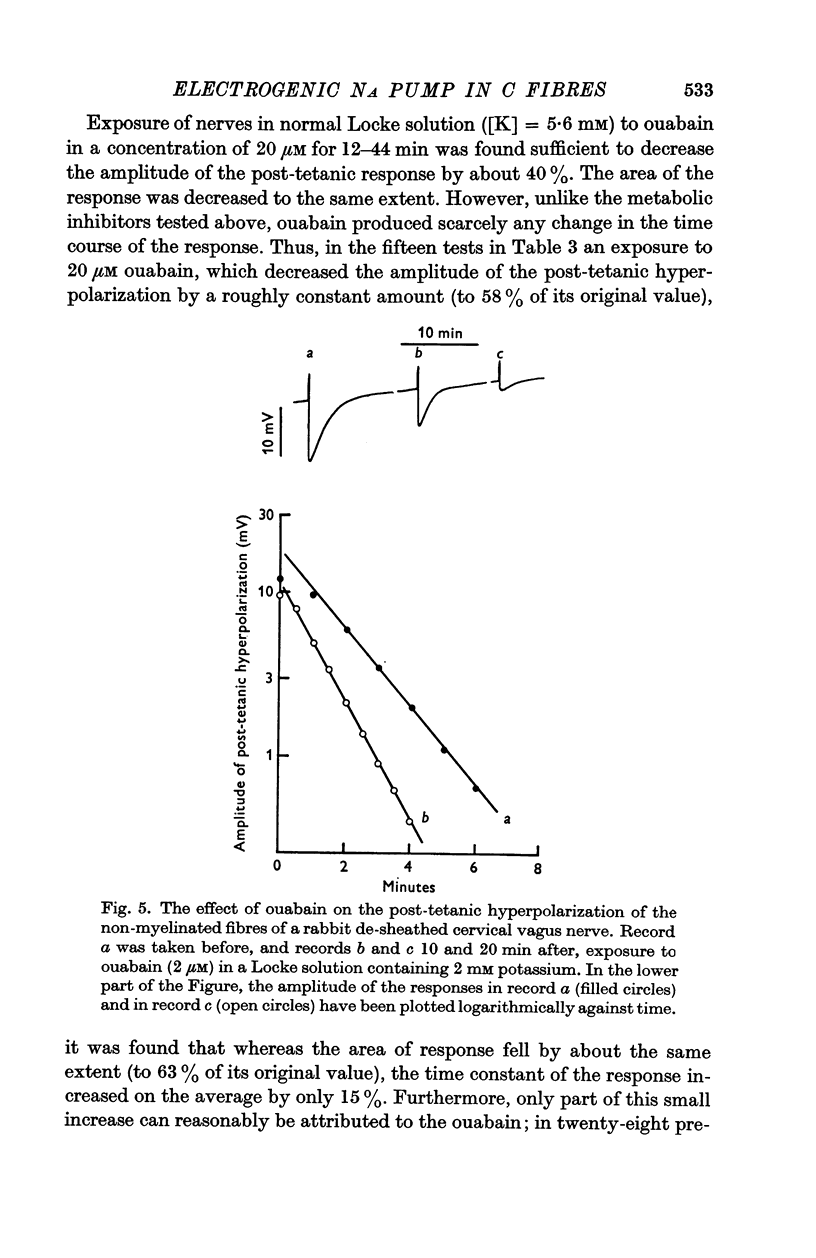
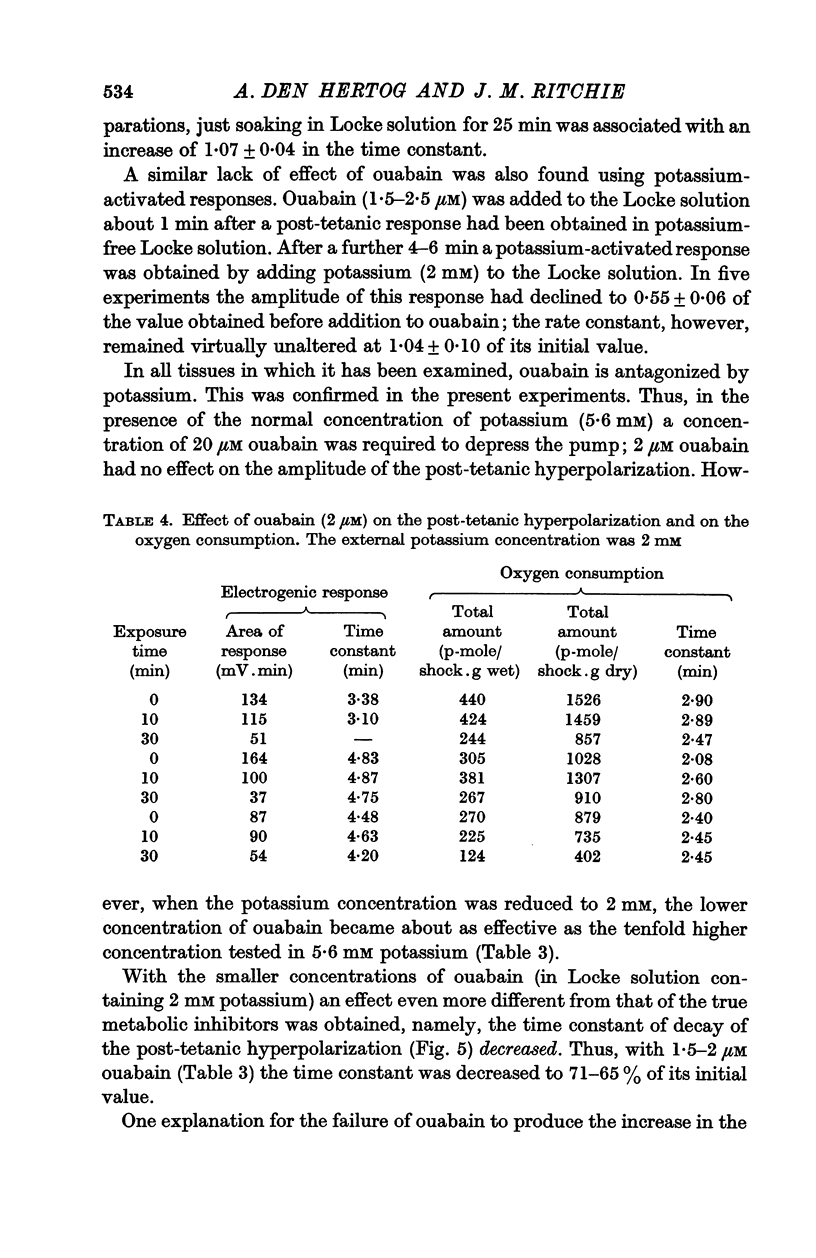
5. Ouabain, however, reduced the amplitude without reducing the rate constant, which was even sometimes increased with small concentrations of ouabain. The area of the response always decreased therefore.
6. The effects applying metabolic inhibitors are thus similar to those obtained on cooling, but differ from those of ouabain.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMETT C. J., RITCHIE J. M. The action of acetylcholine and some related substances on conduction in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1961 Feb;155:372–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMETT C. J., RITCHIE J. M. The action of acetylcholine on conduction in mammalian non-myelinated fibres and its prevention by an anticholinesterase. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;152:141–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Manil J. The rates of action of K+ and ouabain on the sodium pump in squid axons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 1;150(2):328–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. Sodium fluxes in internally dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Aug;52(2):181–211. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Hertog A., Ritchie J. M. The effect of some quanternary ammonium compounds and local anaesthetics on the electrogenic component of the sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969 May;6(2):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth J. V., Keynes R. D., Ritchie J. M. The origin of the initial heat associated with a single impulse in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):745–793. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Ritchie J. M. The movements of labelled ions in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1965 Jul;179(2):333–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M., STRAUB R. W. The hyperpolarization which follows activity in mammalian non-medullated fibres. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):80–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. On the electrogenic sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its activation by various external cations. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):183–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. The dependence on external cations of the oxygen consumption of mammalian non-myelinated fibres at rest and during activity. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):163–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. The ionic content of mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its alteration as a result of electrical activity. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):223–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. ENZYMATIC BASIS FOR ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF NA+ AND K+ ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jul;45:596–617. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAMPFLI R. A new method for measuring membrane potentials with external electrodes. Experientia. 1954 Dec 15;10(12):508–509. doi: 10.1007/BF02166189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUB R. W. Sucrose-gap apparatus for studying the resting and action potential in mammalian non-medullated fibres. J Physiol. 1957 Jan 23;135(1):2–4P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUTTLE R. S., WITT P. N., FARAH A. Therapeutic and toxic effects of ouabain on K ion fluxes in rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Jul;137:24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog A., Greengard P., Ritchie J. M. On the metabolic basis of nervous activity. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):511–521. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


