Abstract
1. Rabbits, previously sensitized to egg albumen, were anaesthetized and then rendered anaphylactic by a further injection of egg albumen; total lung conductance of flow, lung compliance, breathing rate, tidal volume, end-tidal CO2%, systemic arterial and right atrial blood pressures and heart rate were measured. Before induction of anaphylaxis, some rabbits were vagotomized, some had their vagi cooled to block differential conduction, and others were paralysed and artificially ventilated to minimize secondary changes in afferent activity from the lungs and in blood gas tensions.
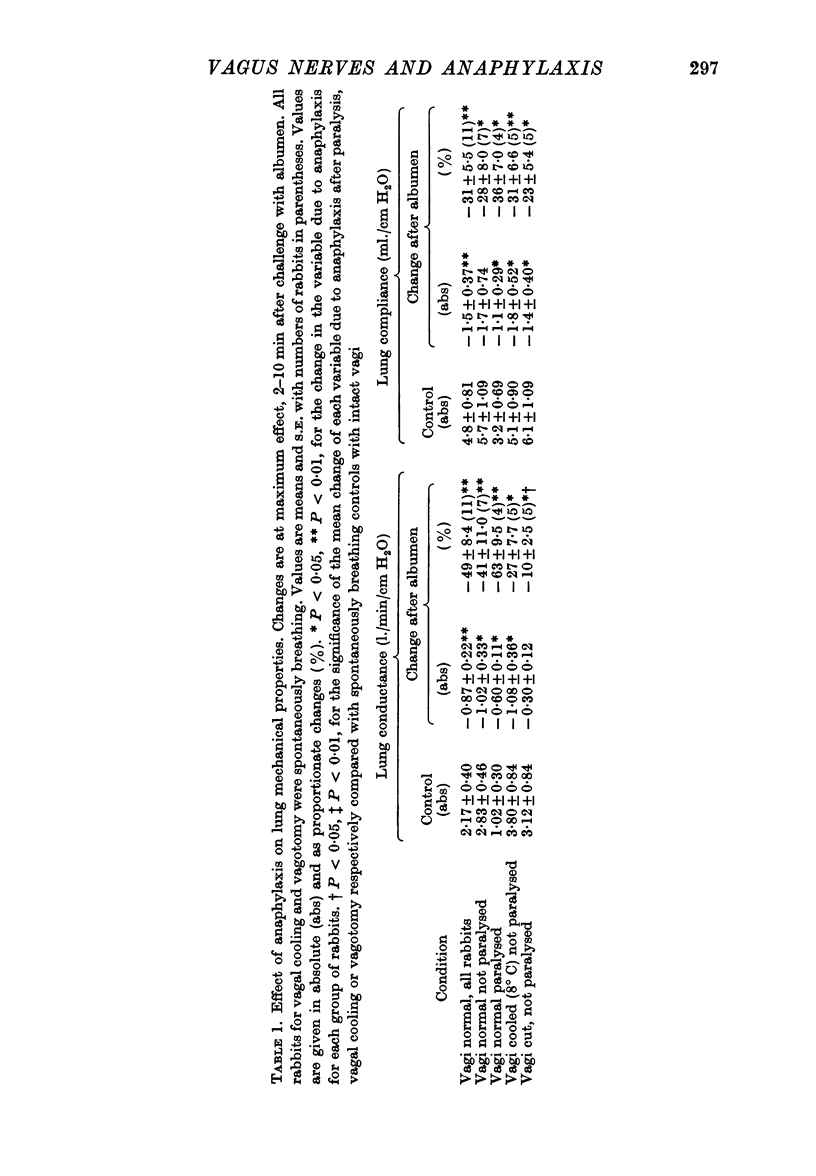
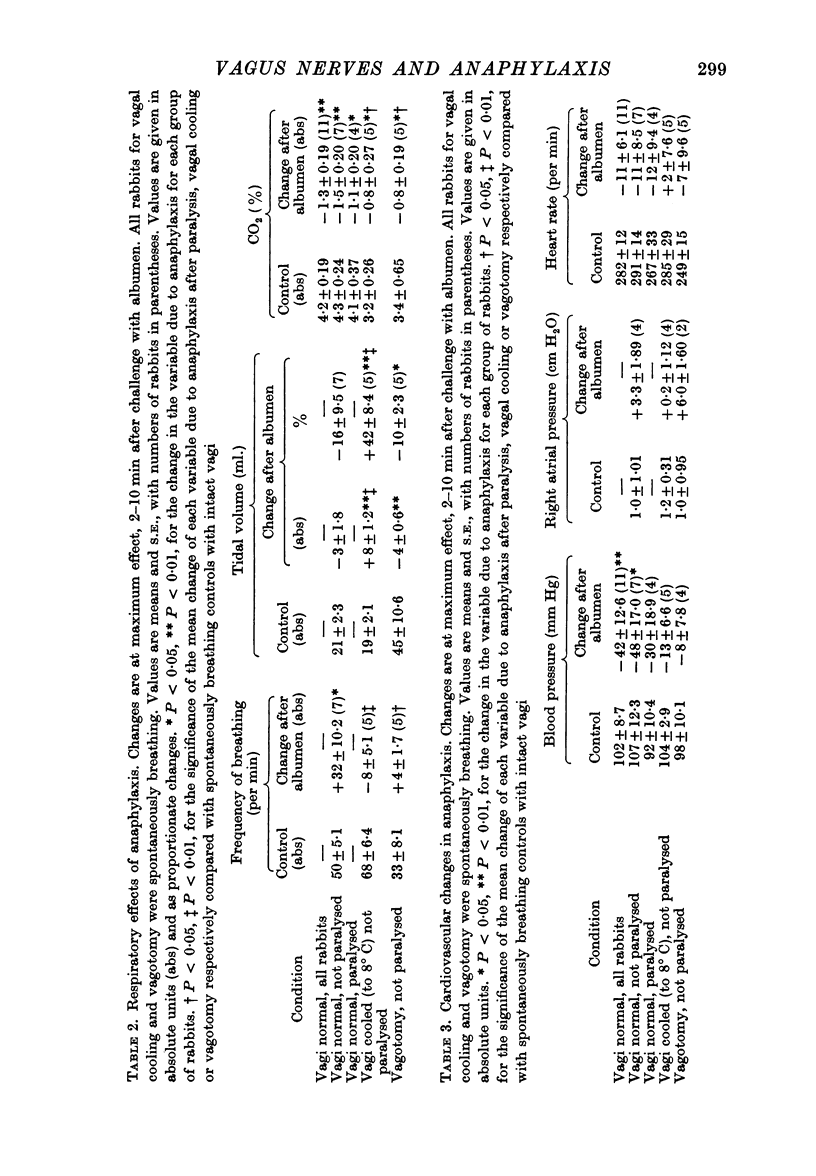
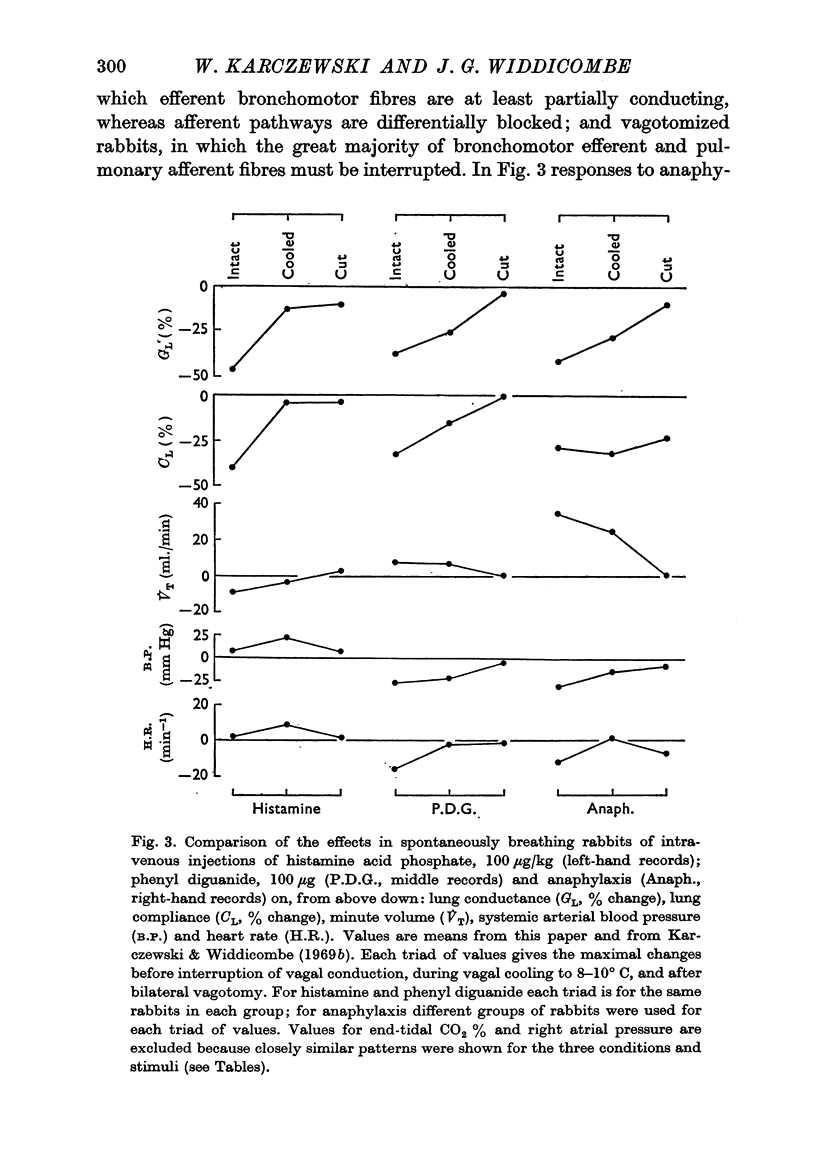
2. Lung conductance was reduced by anaphylaxis in spontaneously breathing and in artificially ventilated rabbits, and the effect was lessened by vagal cooling and greatly reduced by vagotomy; the hyperventilation of anaphylaxis took the form of an increase in tidal volume rather than in respiratory frequency during vagal cooling, and all changes in ventilation were abolished by vagotomy. These effects are therefore dependent on the integrity of vagal nervous pathways.
3. Lung compliance was reduced by anaphylaxis to a similar degree in all groups of rabbits; all groups showed similar falls in end-tidal CO2%. These effects are therefore not dependent on the integrity of vagal conduction.
4. Anaphylaxis reduced systemic arterial blood pressure, the response being smaller when the vagi were cooled or cut.
5. It is concluded that anaphylaxis has direct actions on the pulmonary vascular bed, the distal airways or the alveoli. However, the changes in breathing, blood pressure and large airway calibre are mainly dependent on vagal reflex activity. By analogy with responses to injections of histamine and phenyl diguanide (Karczewski & Widdicombe, 1969b) it is concluded that anaphylaxis stimulates lung deflation and irritant receptors which mediate much of the reflex responses.
Full text
PDF

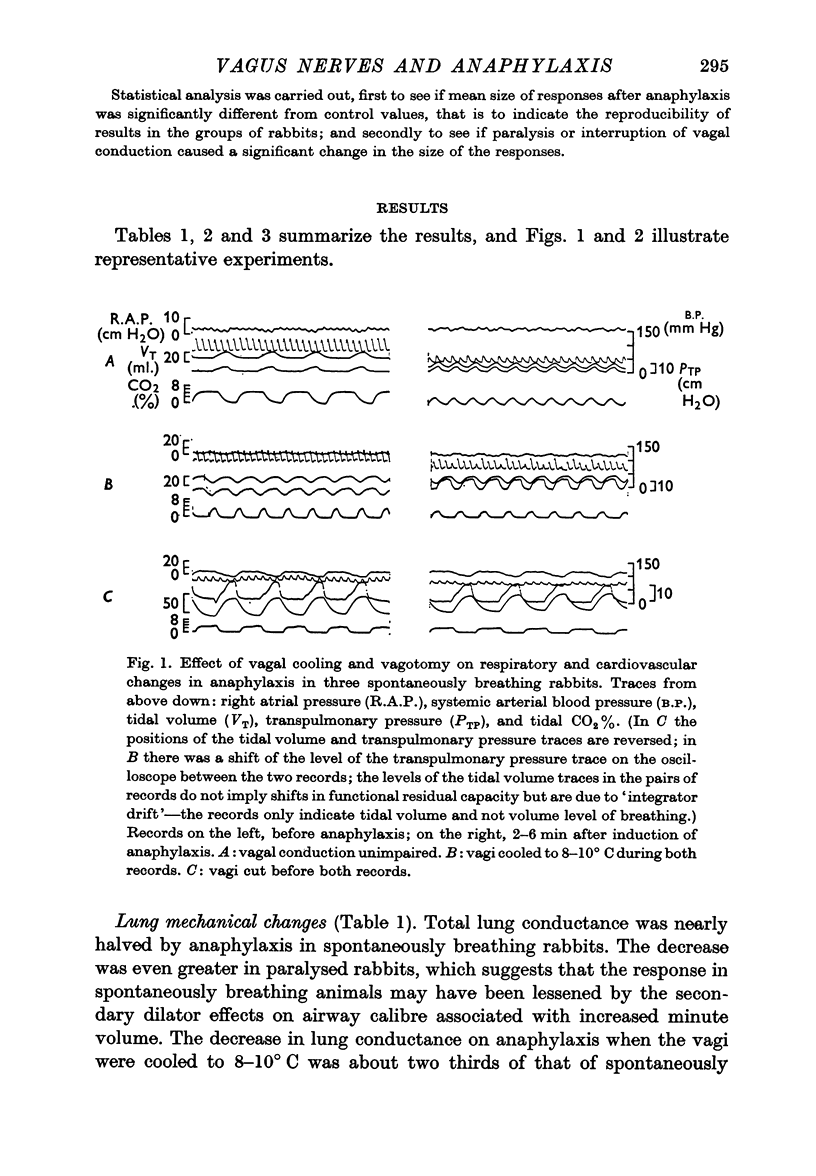
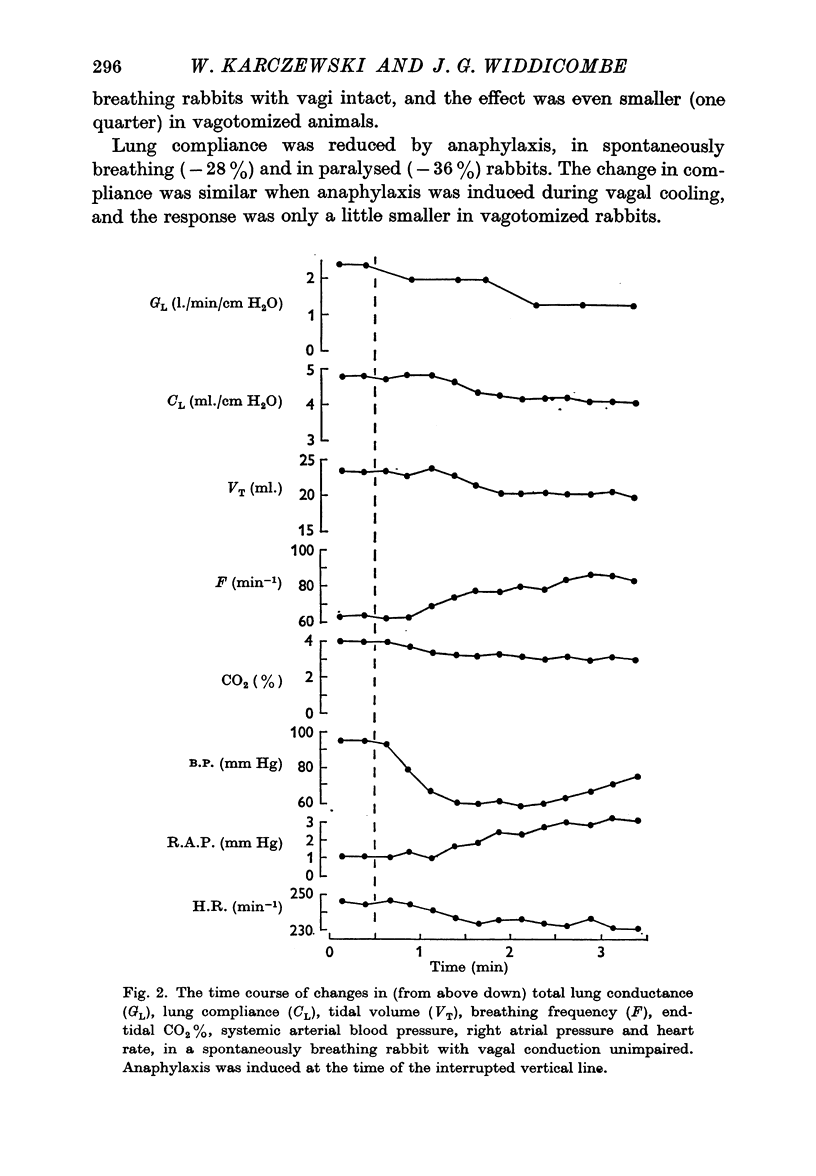





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERTY J. Versuche über den Anteil von Histamin am anaphylaktischen Asthma sowie Beobachtungen über Auslösung und Verhalten der Asthma- und Kreislaufsymptome anaphylaktischer Schockfragmente des Meerschweinchens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1959;14(3-4):162–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER H. O., HOLGATE J. A., SCHACHTER M., SHORLEY P. G. The bronchoconstrictor action of bradykinin in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1960 Jun;15:290–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1960.tb01247.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colebatch H. J., Olsen C. R., Nadel J. A. Effect of histamine, serotonin, and acetylcholine on the peripheral airways. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jan;21(1):217–226. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C., WIDDICOMBE J. G. Respiratory and cardiovascular reflexes from the heart and lungs. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):258–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeKock M. A., Nadel J. A., Zwi S., Colebatch H. J., Olsen C. R. New method for perfusing bronchial arteries: histamine bronchoconstriction and apnea. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jan;21(1):185–194. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankstein S. I., Sergeeva Z. N. Tonic activity of lung receptors in normal and pathological states. Nature. 1966 Jun 4;210(5040):1054–1055. doi: 10.1038/2101054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARCZEWSKI W. ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY OF THE VAGUS NERVE IN ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK INDUCED AFTER AN ELECTRIC STIMULATION OF THE BRAIN. Acta Allergol. 1964;19:236–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1962.tb03703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARCZEWSKI W. The electrical activity of the vagus nerve in anaphylactic shock. Acta Allergol. 1962;17:334–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1962.tb02960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski W., Widdicombe J. G. The effect of vagotomy, vagal cooling and efferent vagal stimulation on breathing and lung mechanics of rabbits. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):259–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski W., Widdicombe J. G. The role of the vagus nerves in the respiratory and circulatory responses to intravenous histamine and phenyl diguanide in rabbits. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):271–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECOMTE J. Les substances histamino-libératrices sont incapables de modifier le choc anaphylactique du lapin. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1956 Jun;64(3):302–308. doi: 10.3109/13813455609150217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEAD J. Mechanical properties of lungs. Physiol Rev. 1961 Apr;41:281–330. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1961.41.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONGAR J. L., SCHILD H. O. Cellular mechanisms in anaphylaxis. Physiol Rev. 1962 Apr;42:226–270. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1962.42.2.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. VAGAL AFFERENT FIBRES. Ergeb Physiol. 1963;52:74–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL B. A. Impulses in vagal afferent fibres from specific pulmonary deflation receptors: the response of these receptors to phenyl diguanide, potato starch, 5-hydroxytryptamine and nicotine, and their rôle in respiratory and cardiovascular reflexes. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1955 Apr;40(2):89–111. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1955.sp001116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVERINGHAUS J. W., STUPFEL M. Respiratory dead space increase following atropine in man, and atropine, vagal or ganglionic blockade and hypothermia in dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1955 Jul;8(1):81–87. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1955.8.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDICOMBE J. G. Regulation of tracheobronchial smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1963 Jan;43:1–37. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1963.43.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


