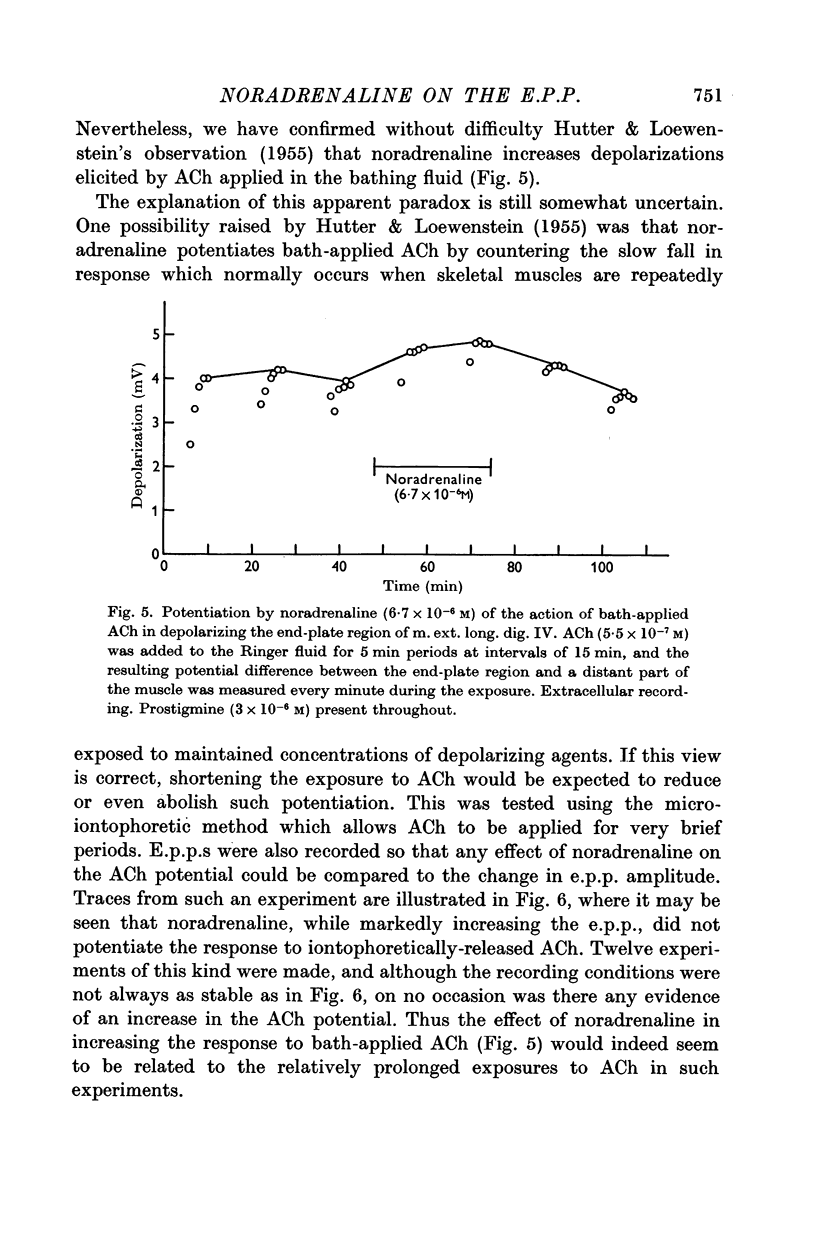
Abstract
1. The action of noradrenaline in increasing the amplitude of the end-plate potential (e.p.p.) has been studied in magnesium-blocked frog skeletal muscle.
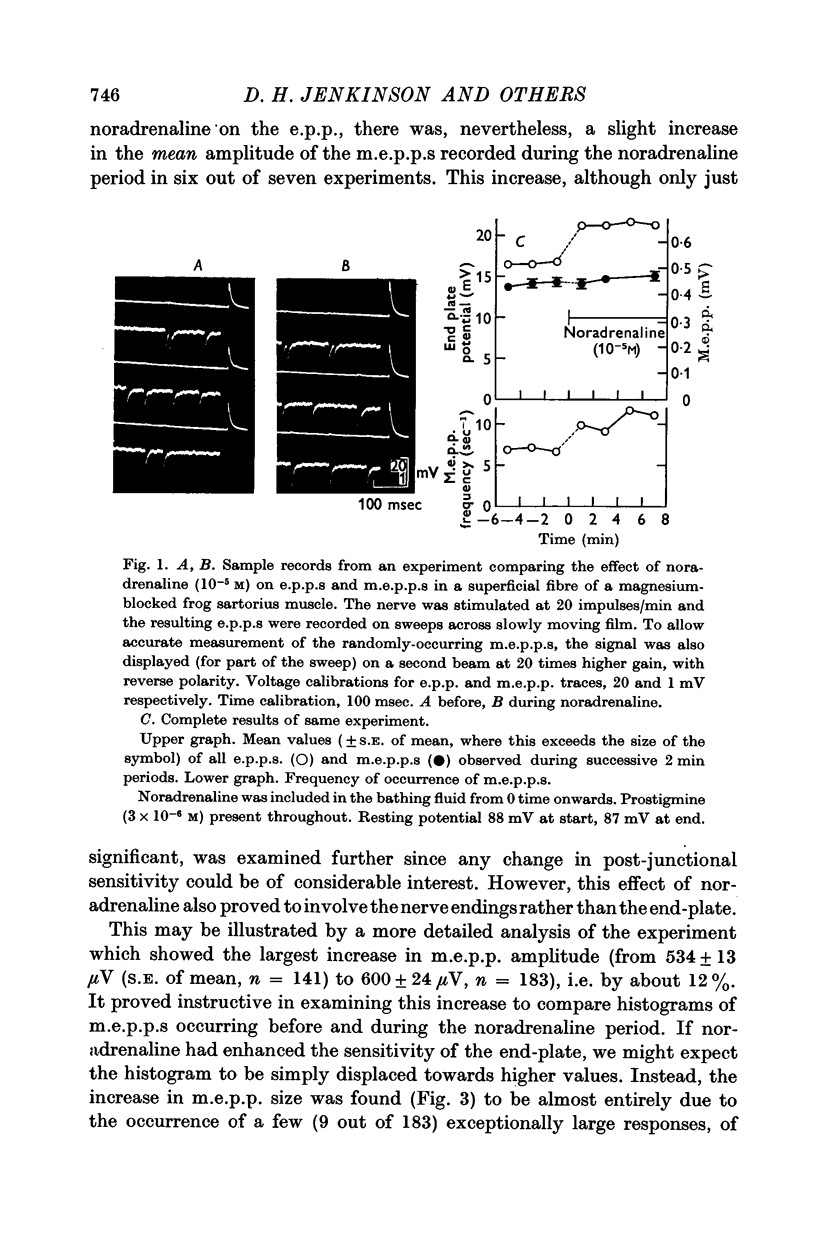
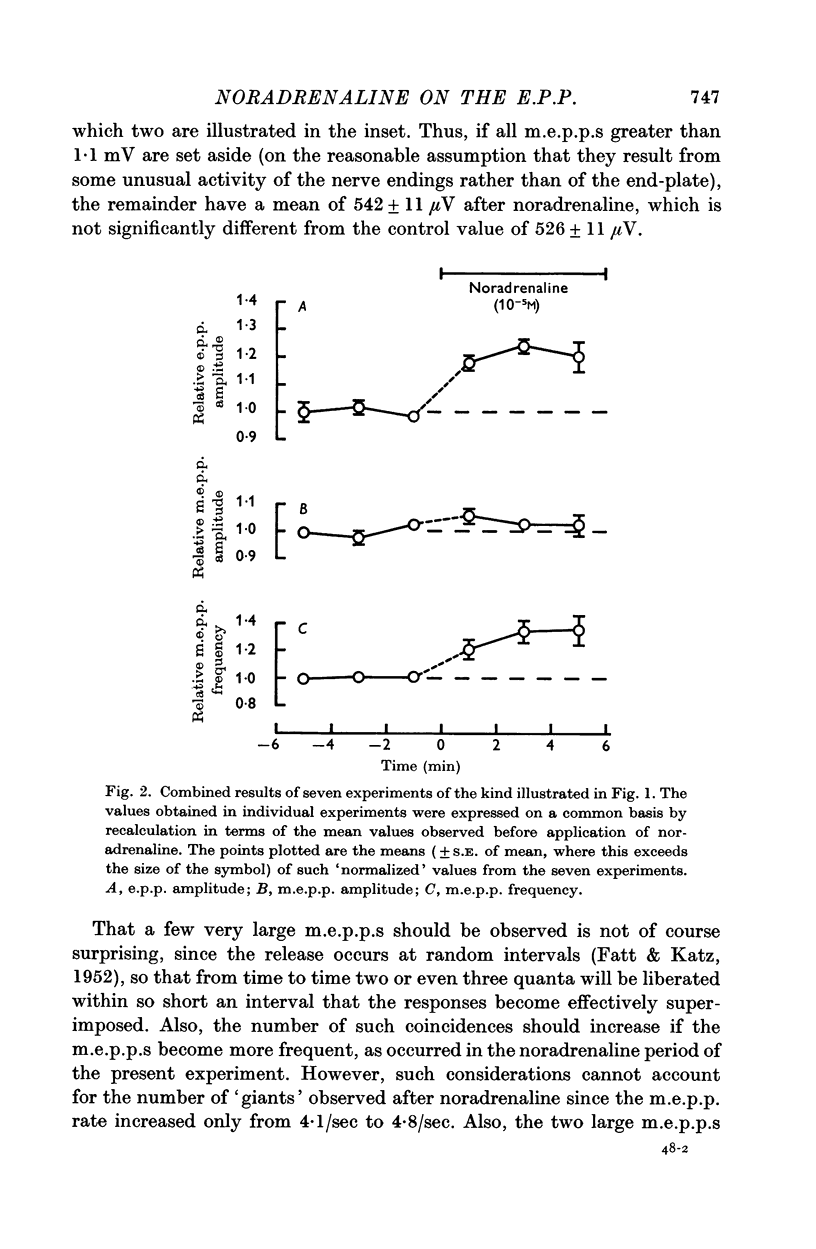
2. Noradrenaline (10-5 M) increased the e.p.p. by about 20% without causing any comparable change in the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potentials (m.e.p.p.s). It was concluded that noradrenaline acts by potentiating the release of acetylcholine by the nerve impulse, rather than by increasing the sensitivity of the end-plate.
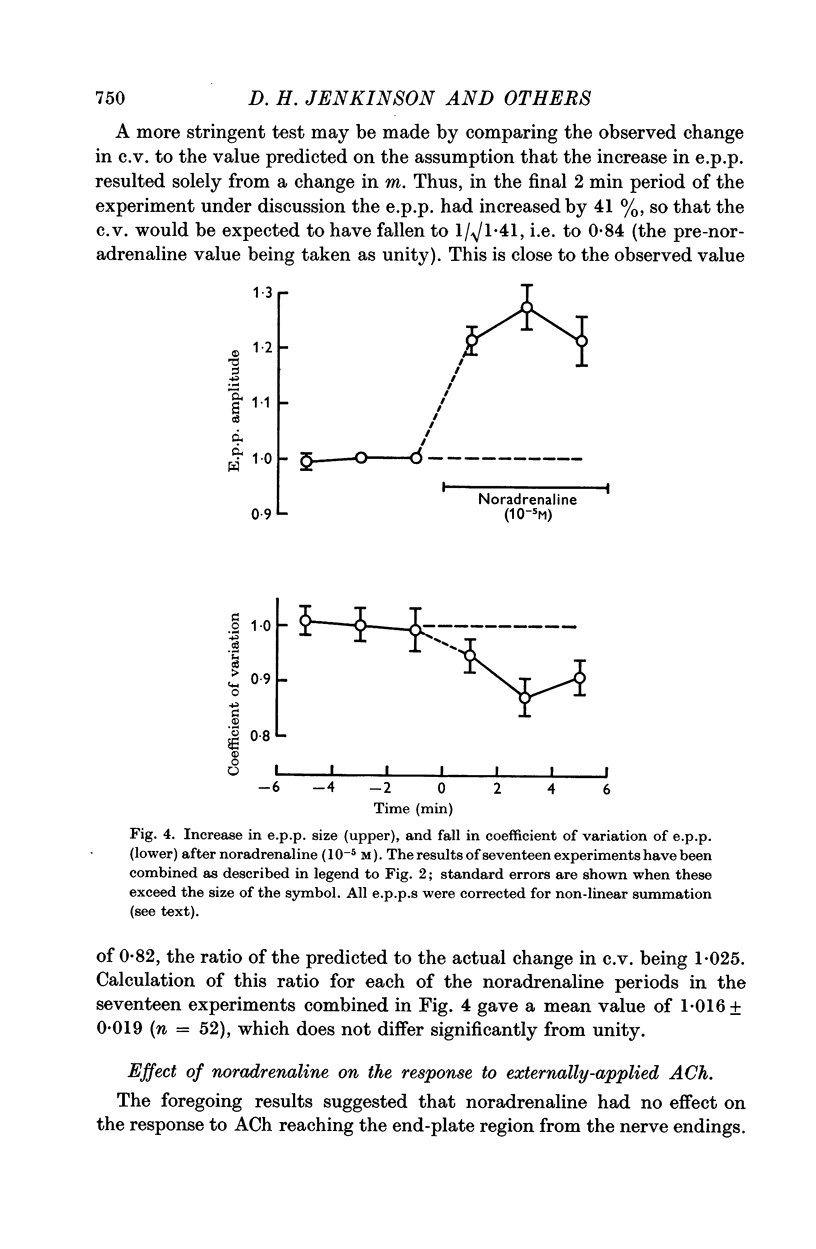
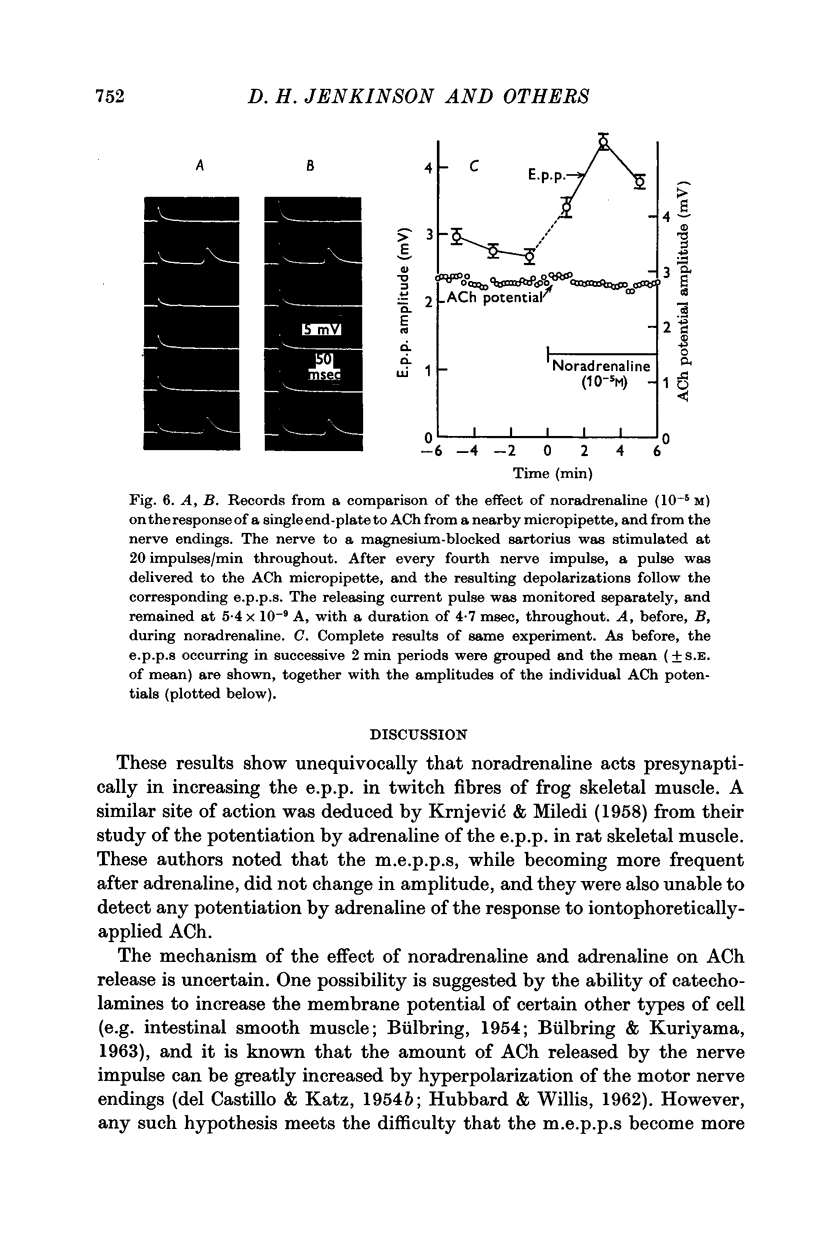
3. In support of this, it was found that the increase in e.p.p. amplitude was associated with a reduction in the variability of successive e.p.p.s, as is to be expected if the quantal content of the e.p.p. became larger. Further, noradrenaline was without effect on the response to iontophoretically-applied acetylcholine, although it potentiated depolarizations elicited by acetylcholine applied for much longer periods in the bathing fluid.
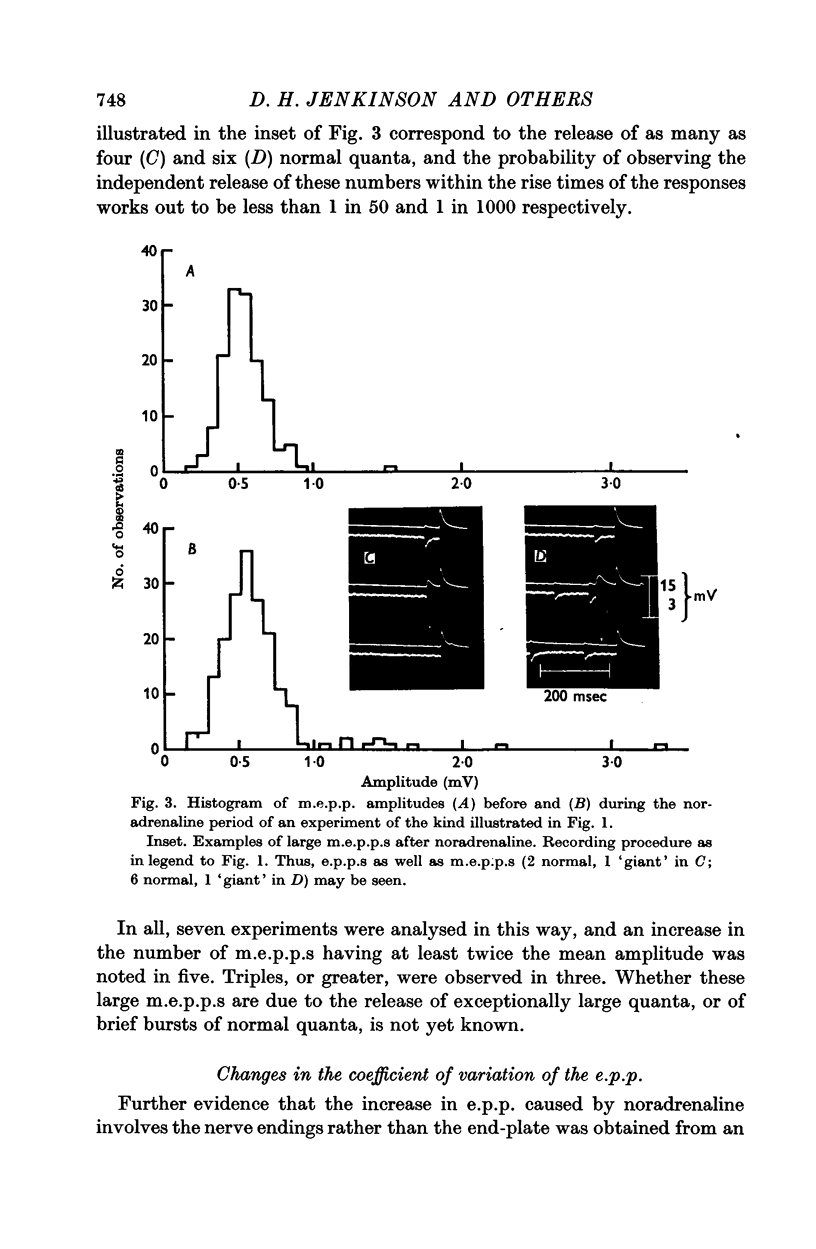
4. Noradrenaline increased the frequency of occurrence of m.e.p.p.s, and unusually large m.e.p.p.s. were occasionally observed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACKMAN J. G., GINSBORG B. L., RAY C. On the quantal release of the transmitter at a sympathetic synapse. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:402–415. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWMAN W. C., GOLDBERG A. A., RAPER C. A comparison between the effects of a tetanus and the effects of sympathomimetic amines on fast- and slow-contracting mammalian muscles. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Dec;19:464–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E., KURIYAMA H. Effects of changes in ionic environment on the action of acetylcholine and adrenaline on the smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:59–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E. Membrane potentials of smooth muscle fibres of the taenia coli of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1954 Aug 27;125(2):302–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman W. C., Raper C. Adrenotropic receptors in skeletal muscle. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Feb 10;139(3):741–753. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb41241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman W. C., Raper C. Effects of sympathomimetic amines on neuromuscular transmission. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Aug;27(2):313–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Changes in end-plate activity produced by presynaptic polarization. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):586–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. On the localization of acetylcholine receptors. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):157–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P. The electromotive action of acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):408–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I., WILLIS W. D. Hyperpolarization of mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163:115–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., LOEWENSTEIN W. R. Nature of neuromuscular facilitation by sympathetic stimulation in the frog. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):559–571. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The antagonism between tubocurarine and substances which depolarize the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Some effects produced by adrenaline upon neuromuscular propagation in rats. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 30;141(2):291–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):656–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. Spontaneous release of transmitter substance in multiquantal units. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):595–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKA M., NONOMURA Y. The action of phenolic substances on motor nerve endings. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Apr;140:41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


