Abstract
1 The characteristics of the group Ia synaptic input to triceps surae motoneurones have been examined in pentobarbitone-anaesthetized cats, using intracellular recording techniques. The mechanical properties of the muscle units innervated by the cells were determined and the motoneurone input resistance values were also measured.
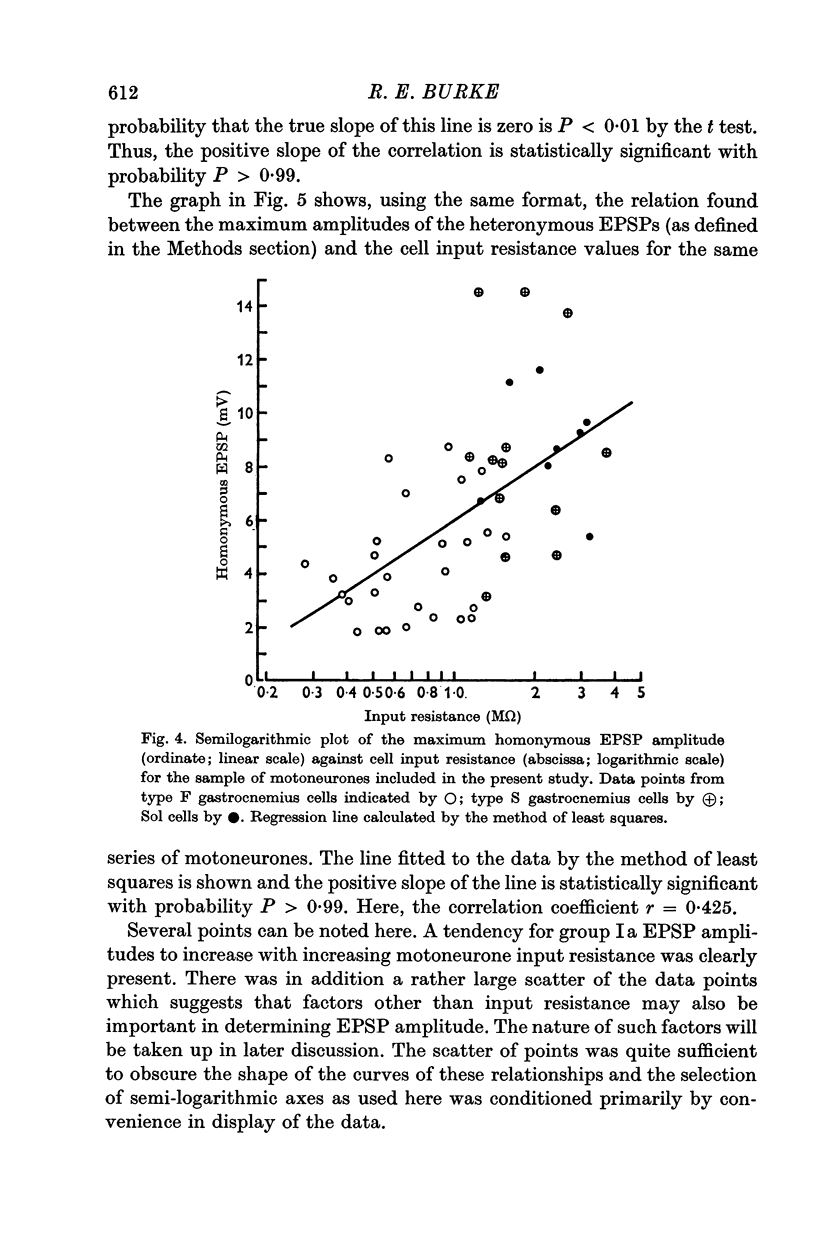
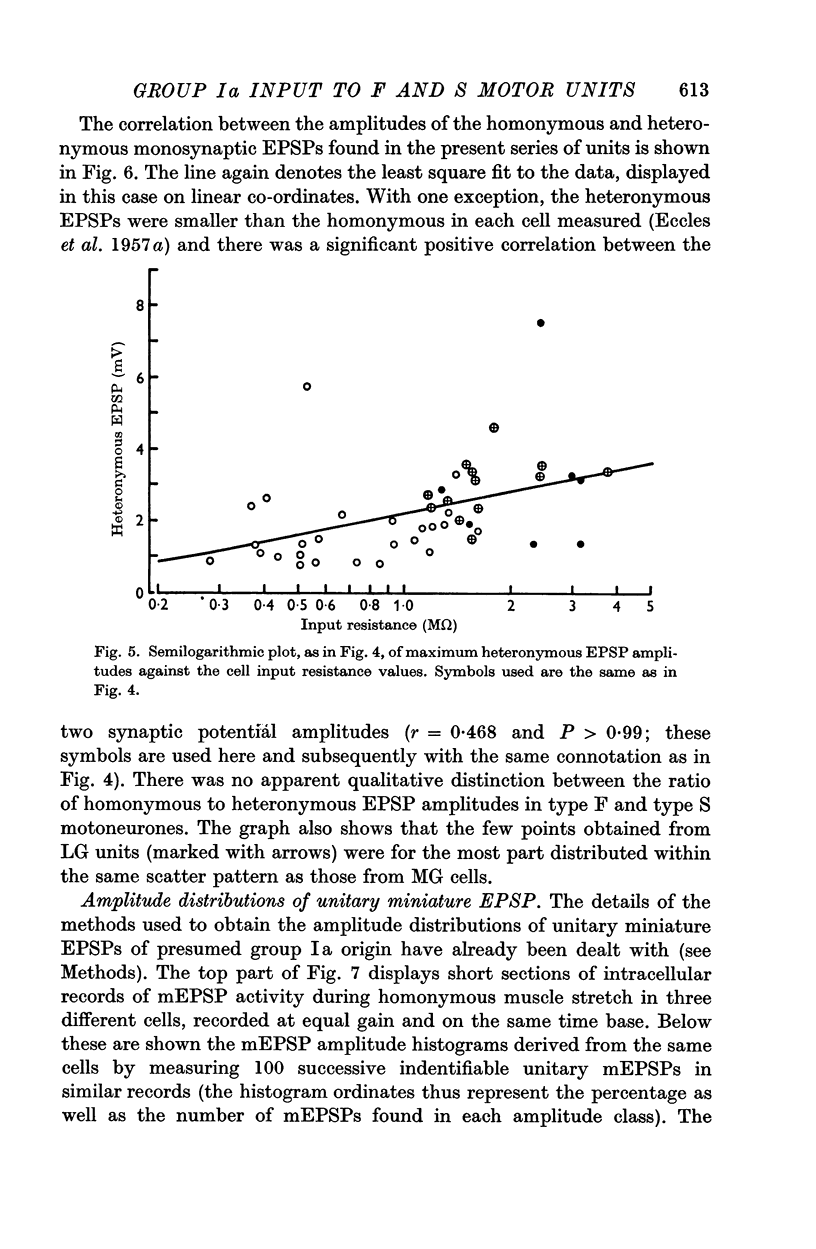
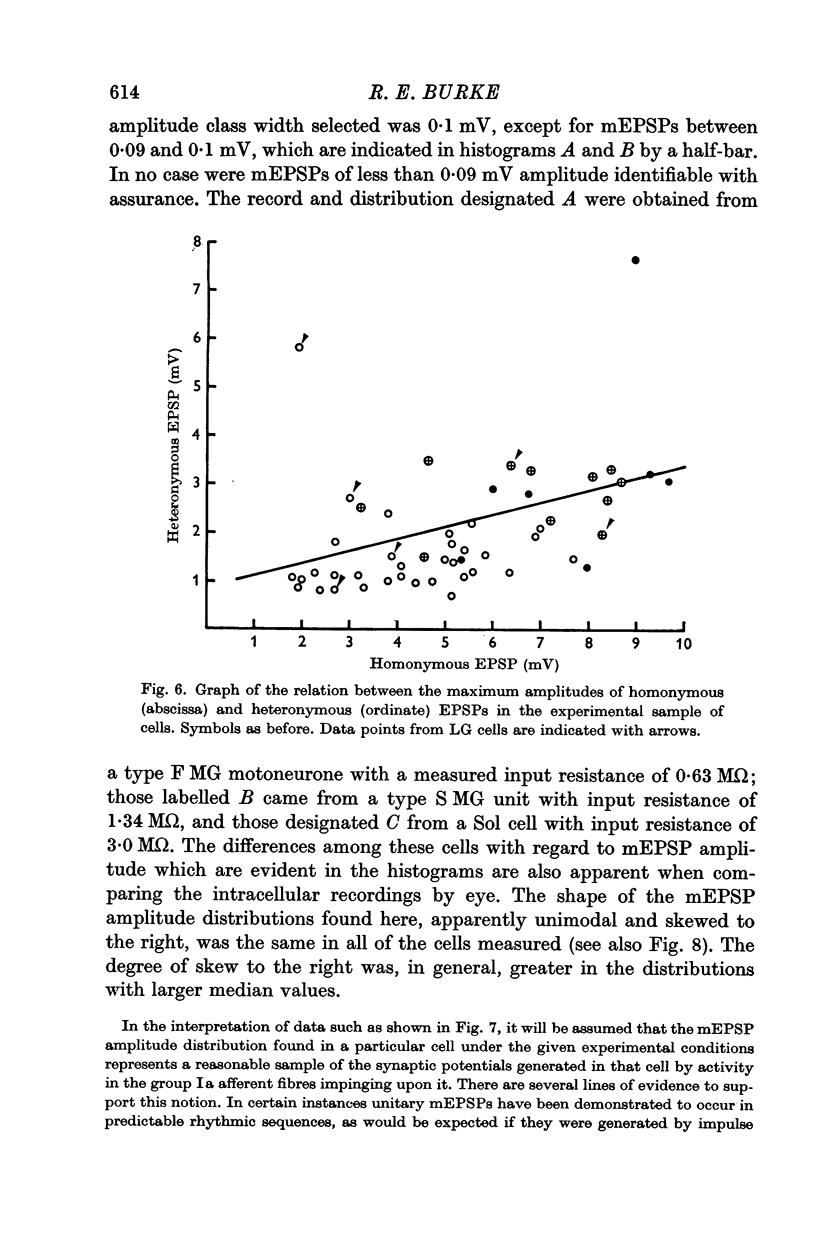
2. A significant positive correlation was found between the maximum amplitudes of homonymous composite (electrically evoked) monosynaptic excitatory post-synaptic potentials (EPSPs) and the motoneurone input resistance values across the entire population of units sampled. The same correlation in the case of heteronymous EPSPs was also significant although somewhat less strong.
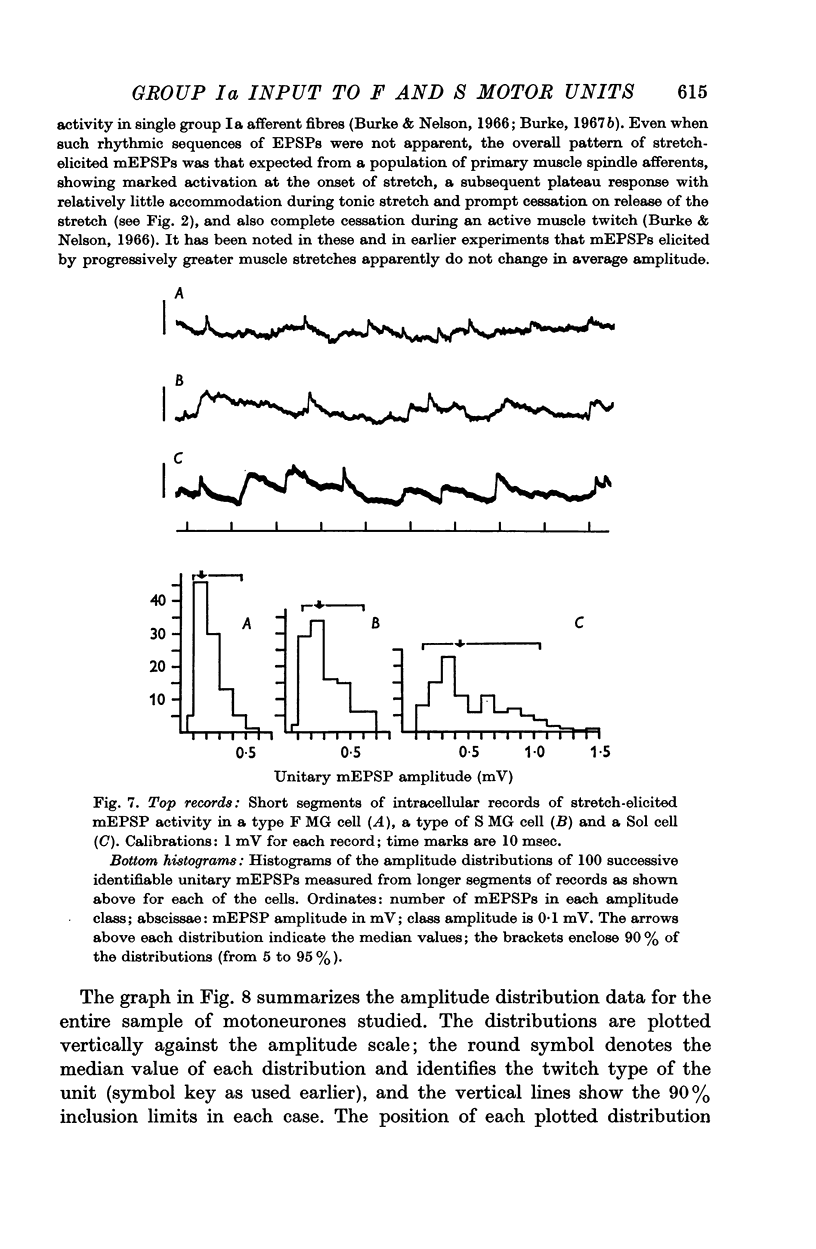
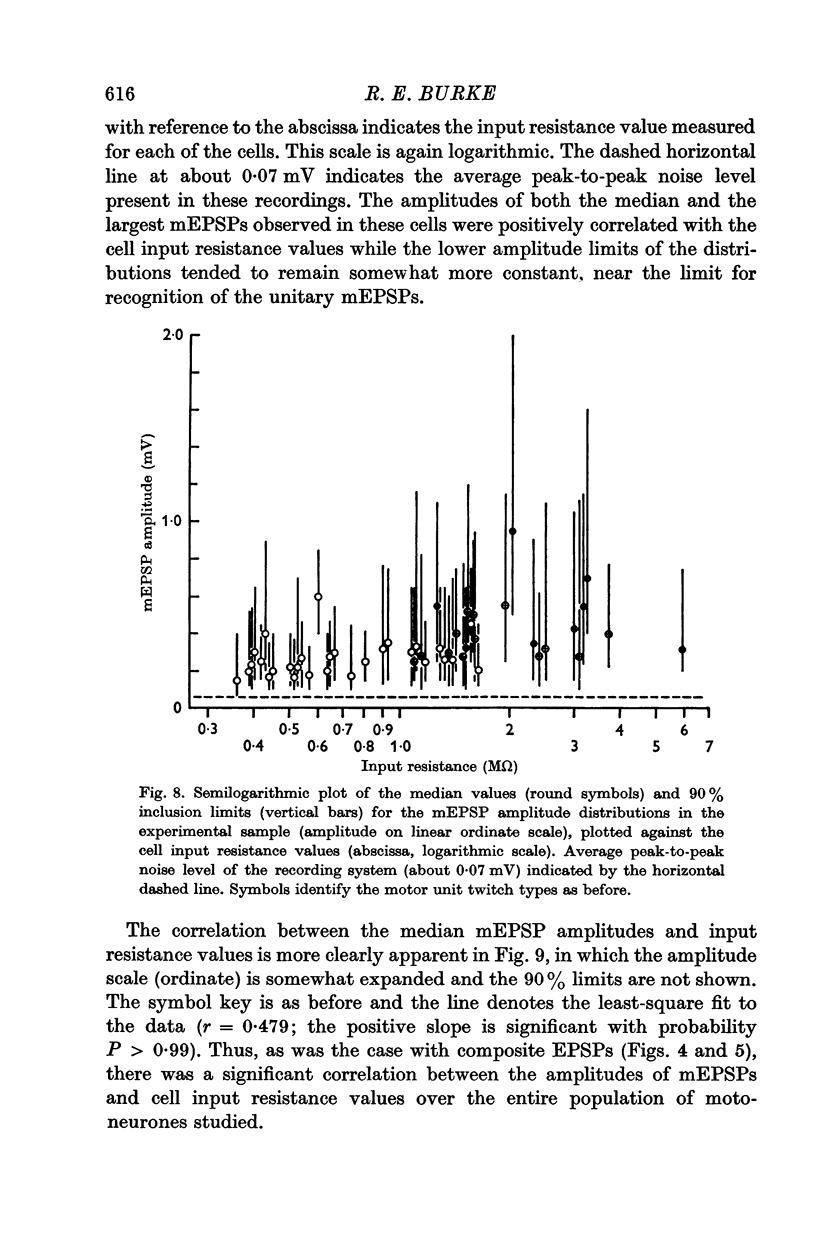
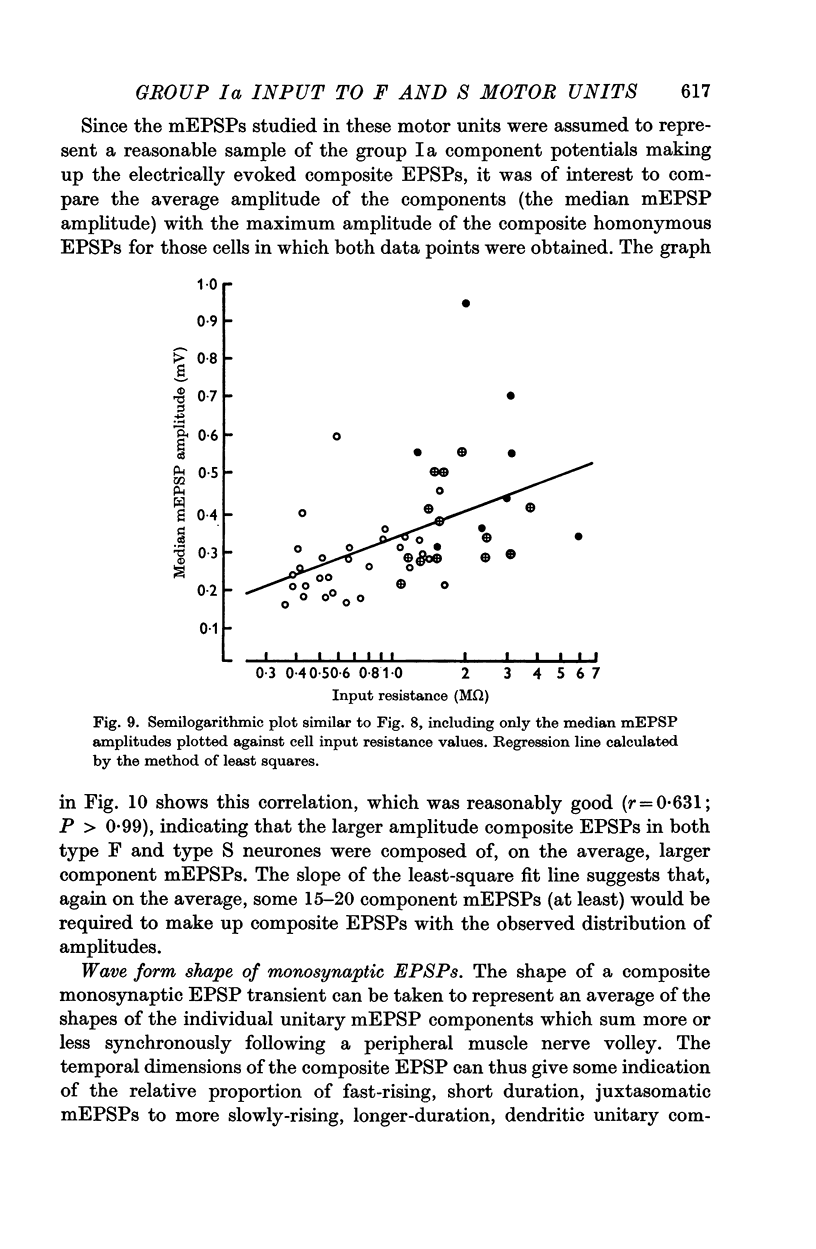
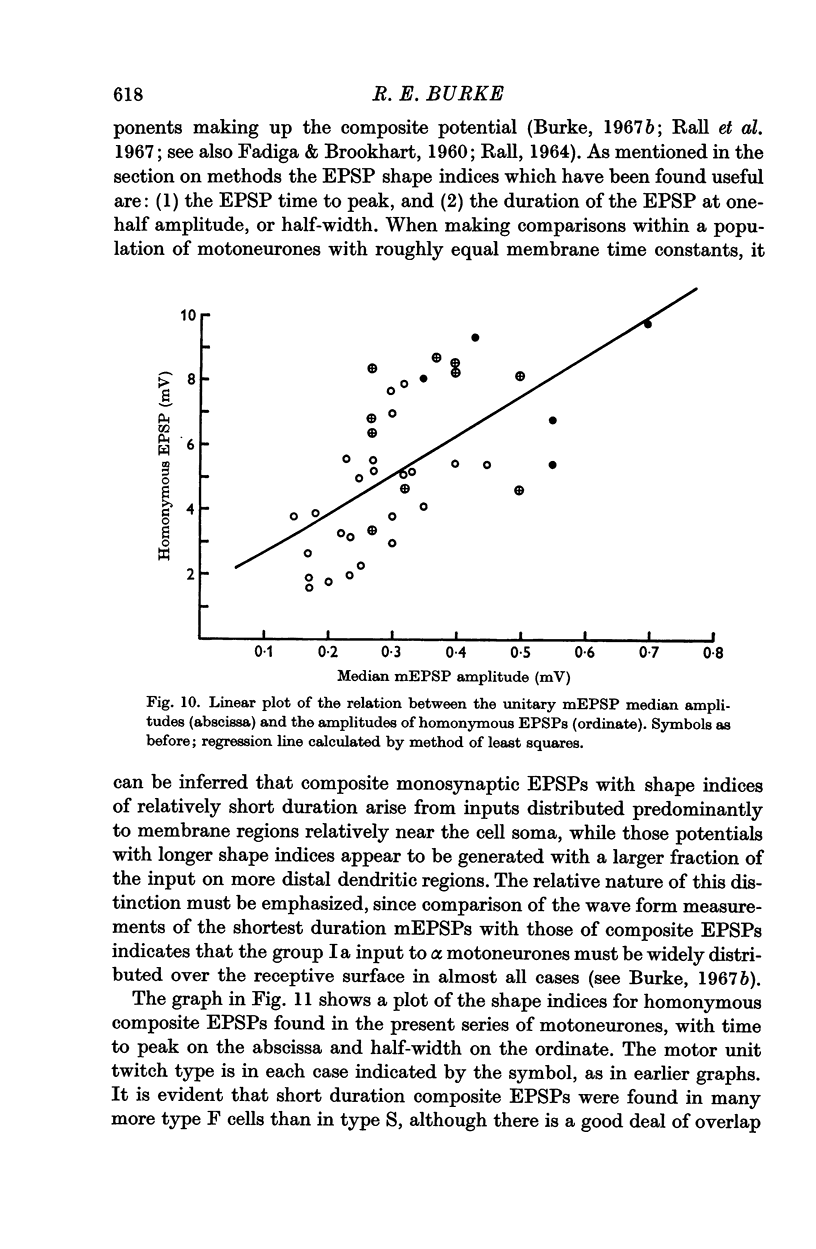
3. The distribution of the amplitudes of unitary miniature EPSPs (mEPSPs) of presumed group Ia origin, elicited by small static stretches of the homonymous muscles, were also studied. A significant positive correlation was found between the median amplitudes of the mEPSP distributions and the input resistance values in the motoneurones studied. Positive correlation was also observed between the amplitudes of the median mEPSPs and the maximum homonymous composite EPSPs in the cells for which both data points were available.
4. In each of these correlations, the synaptic potential amplitudes tended to be larger in the relatively high resistance type S (slow twitch muscle unit) motoneurones from both gastrocnemius and soleus motor pools, than in the lower resistance type F (fast twitch muscle unit) gastrocnemius cells.
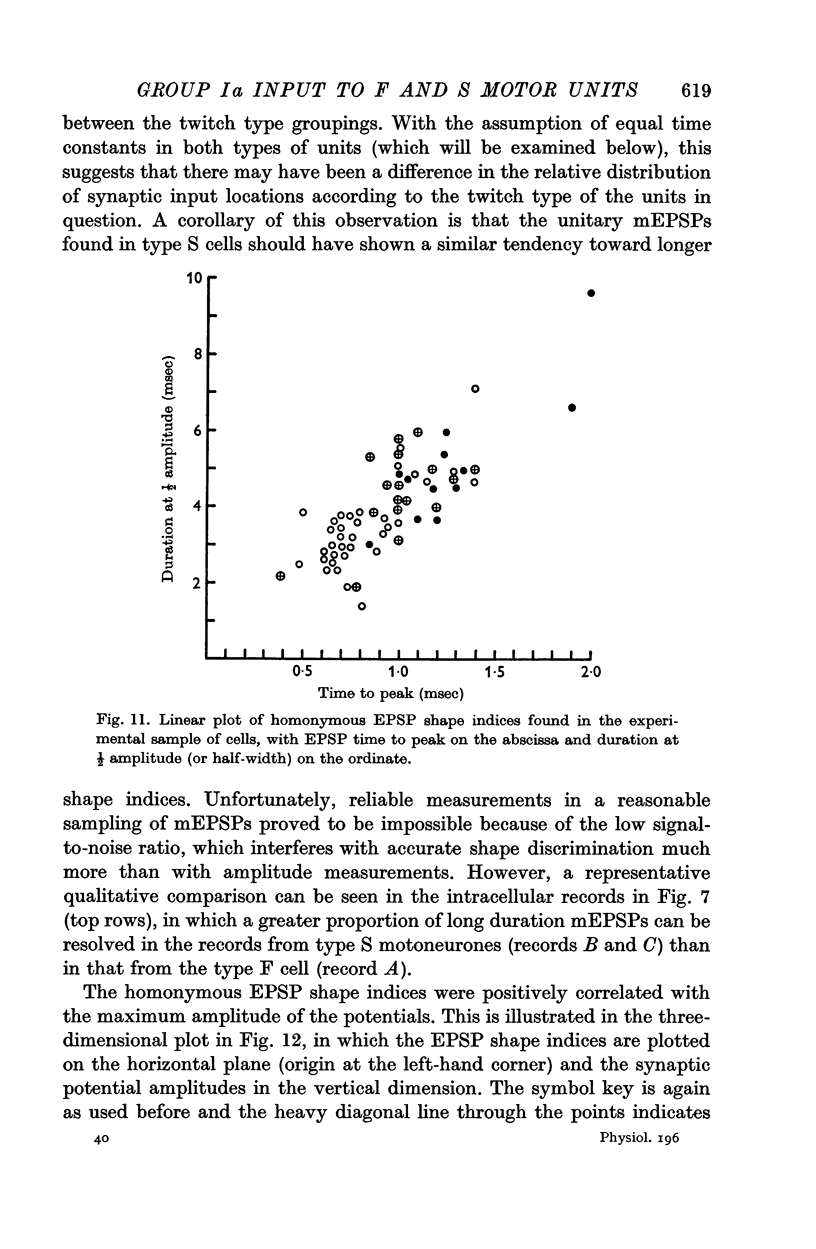
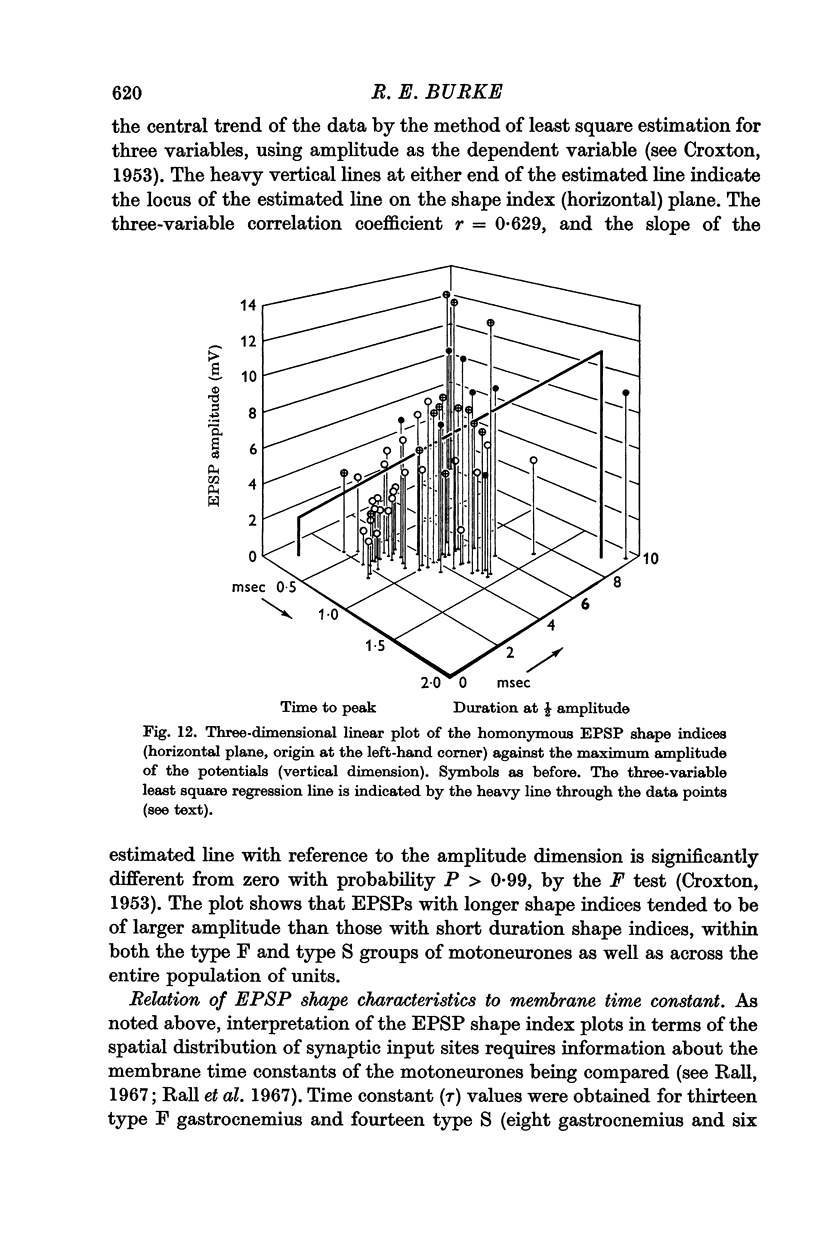
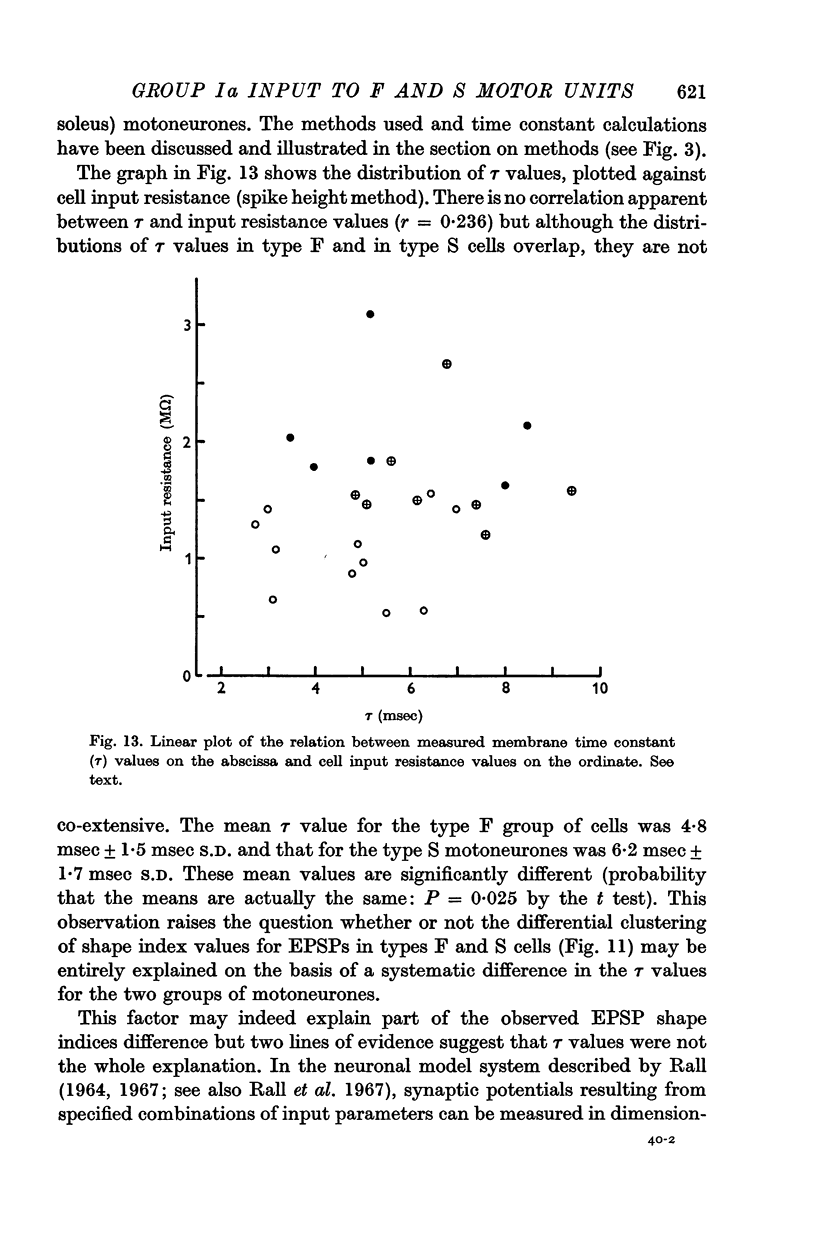
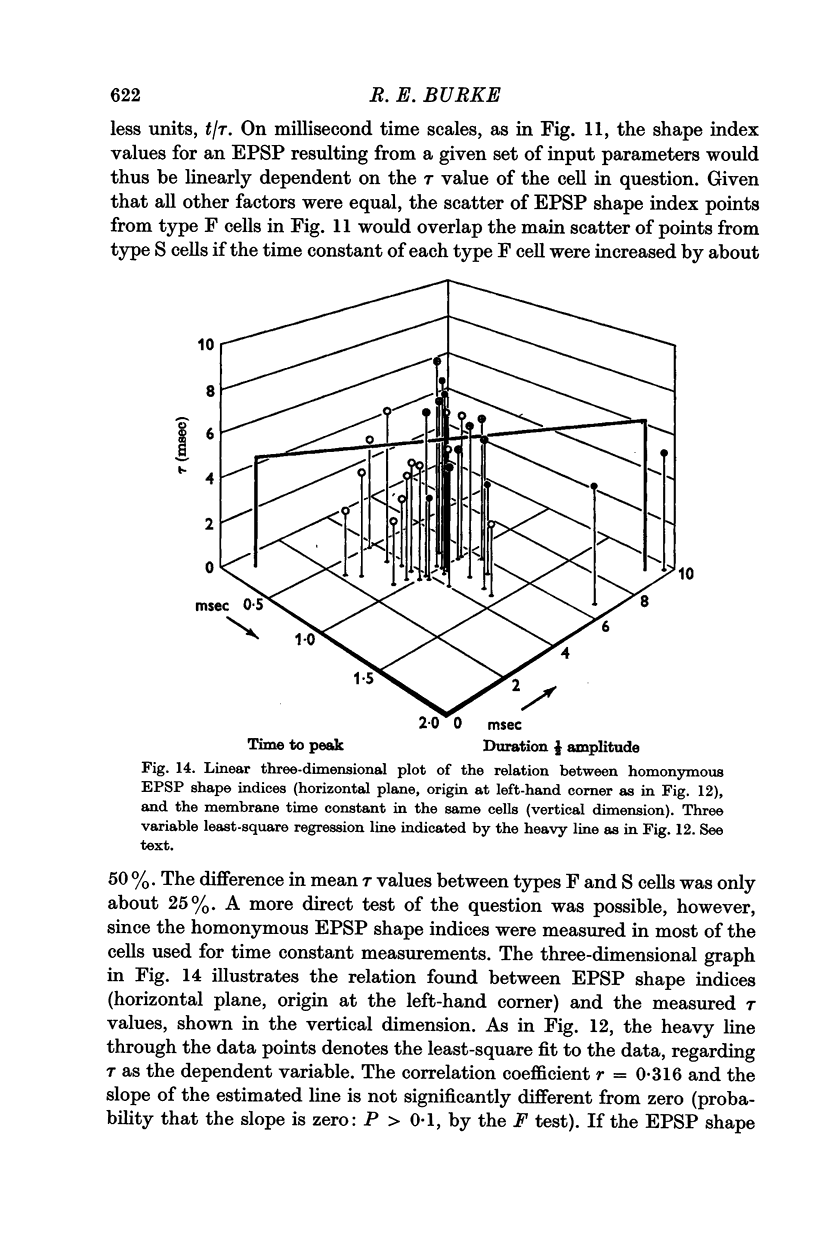
5. Examination of the shape of the homonymous monosynaptic EPSP wave forms in different motoneurones showed that these tended to be significantly longer in duration in type S cells than in type F. This difference could not be entirely accounted for by the relatively small difference in mean time constant values found in types F and S cells.
6. The results suggest that the density of group Ia synaptic terminals tends to be higher on type S motoneurones than on the type F cells. Further, cells receiving a relatively high density of group Ia input apparently tend to have a greater proportion of this input distributed to distal membrane regions than is the case in motoneurones receiving a relatively low input density.
Full text
PDF


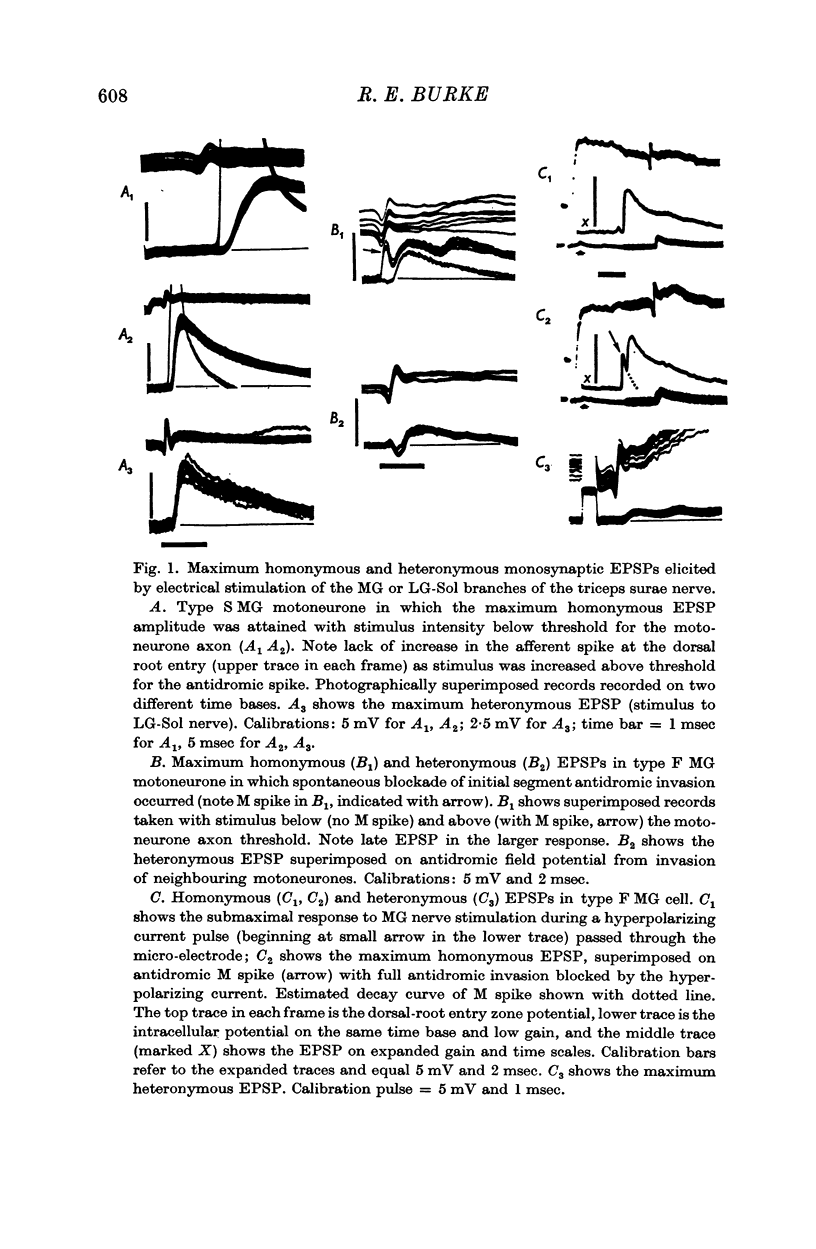

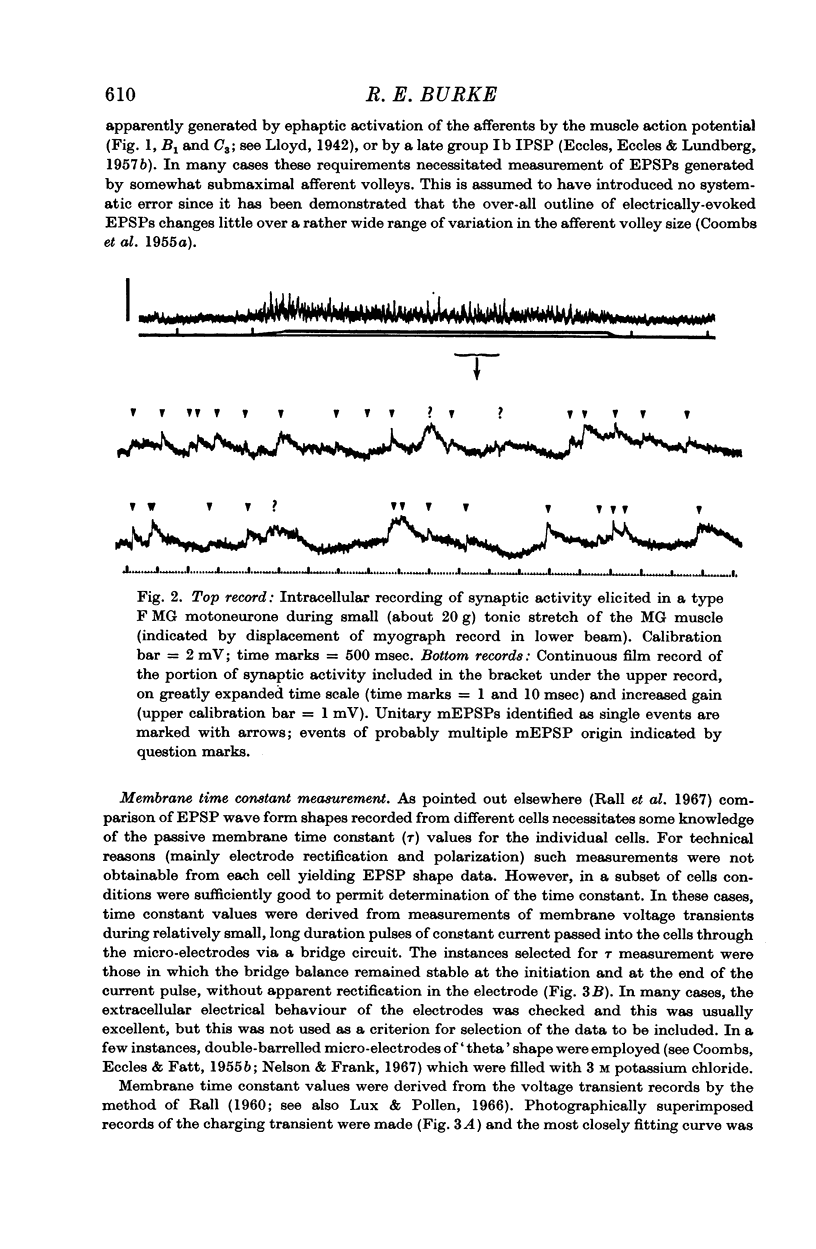
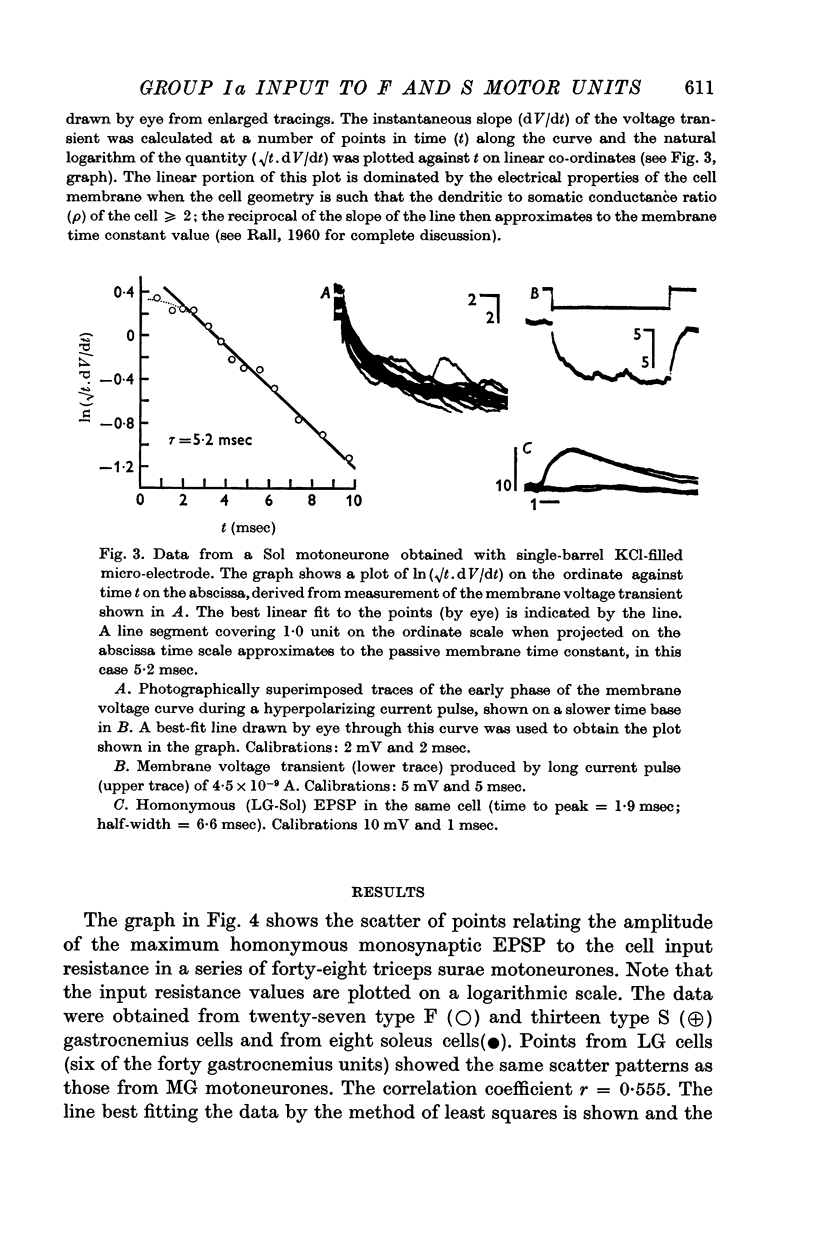








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke R. E. Composite nature of the monosynaptic excitatory postsynaptic potential. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1114–1137. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Firing patterns of gastrocnemius motor units in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):631–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Nelson P. G. Synaptic activity in motoneurons during natural stimulation of muscle spindles. Science. 1966 Mar 4;151(3714):1088–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3714.1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The interpretation of spike potentials of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Dec 3;139(2):198–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. Excitatory synaptic action in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):374–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The convergence of monosynaptic excitatory afferents on to many different species of alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Jun 18;137(1):22–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FADIGA E., BROOKHART J. M. Monosynaptic activation of different portions of the motor neuron membrane. Am J Physiol. 1960 Apr;198:693–703. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Stimulation of spinal motoneurones with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELFAN S., RAPISARDA A. F. SYNAPTIC DENSITY ON SPINAL NEURONS OF NORMAL DOGS AND DOGS WITH EXPERIMENTAL HIND-LIMB RIGIDITY. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Aug;123:73–96. doi: 10.1002/cne.901230108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HENATSCH H. D., STEG G. Tonic and phasic ventral horn cells differentiated by post-tetanic potentiation in cat extensors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Sep 26;37(2-3):114–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1956.tb01347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KELLERTH J. O., WILLIAMS T. D. INTRACELLULAR ASPECTS OF STIMULATING MOTONEURONES BY MUSCLE STRETCH. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:435–452. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PHILLIPS C. G., SKOGLUND S., STEG G. Differentiation of tonic from phasic alpha ventral horn cells by stretch, pinna and crossed extensor reflexes. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Sep;20(5):470–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E., OLSON C. B. RELATIONS BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN THE DESIGN OF SKELETAL MUSCLES. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:581–598. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E., SOMJEN G., CARPENTER D. O. FUNCTIONAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL SIZE IN SPINAL MOTONEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:560–580. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henneman E., Somjen G., Carpenter D. O. Excitability and inhibitability of motoneurons of different sizes. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28(3):599–620. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Stenhouse D., Eccles R. M. Origin of synaptic noise. Science. 1967 Jul 21;157(3786):330–331. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3786.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. A STUDY OF SPONTANEOUS MINIATURE POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:389–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. On the factors which determine the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):267–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLMODIN G. M., SKOGLUND C. R. Slow membrane potential changes accompanying excitation and inhibition in spinal moto- and interneurons in the cat during natural activation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 28;44(1):11–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. QUANTAL COMPONENTS OF EXCITATORY SYNAPTIC POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:81–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D. Input resistance, electrical excitability, and size of ventral horn cells in cat spinal cord. Science. 1966 Jun 17;152(3729):1637–1640. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3729.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Pollen D. A. Electrical constants of neurons in the motor cortex of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Mar;29(2):207–220. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCPHEDRAN A. M., WUERKER R. B., HENNEMAN E. PROPERTIES OF MOTOR UNITS IN A HETEROGENEOUS PALE MUSCLE (M. GASTROCNEMIUS) OF THE CAT. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Jan;28:85–99. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Frank K. Anomalous rectification in cat spinal motoneurons and effect of polarizing currents on excitatory postsynaptic potential. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1097–1113. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Branching dendritic trees and motoneuron membrane resistivity. Exp Neurol. 1959 Nov;1:491–527. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Membrane potential transients and membrane time constant of motoneurons. Exp Neurol. 1960 Oct;2:503–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(60)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Smith T. G., Nelson P. G., Frank K. Dendritic location of synapses and possible mechanisms for the monosynaptic EPSP in motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1169–1193. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Distinguishing theoretical synaptic potentials computed for different soma-dendritic distributions of synaptic input. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1138–1168. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling P., Kuypers H. G. Anatomical organization of the brachial spinal cord of the cat. I. The distribution of dorsal root fibers. Brain Res. 1967 Feb;4(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(67)90144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


