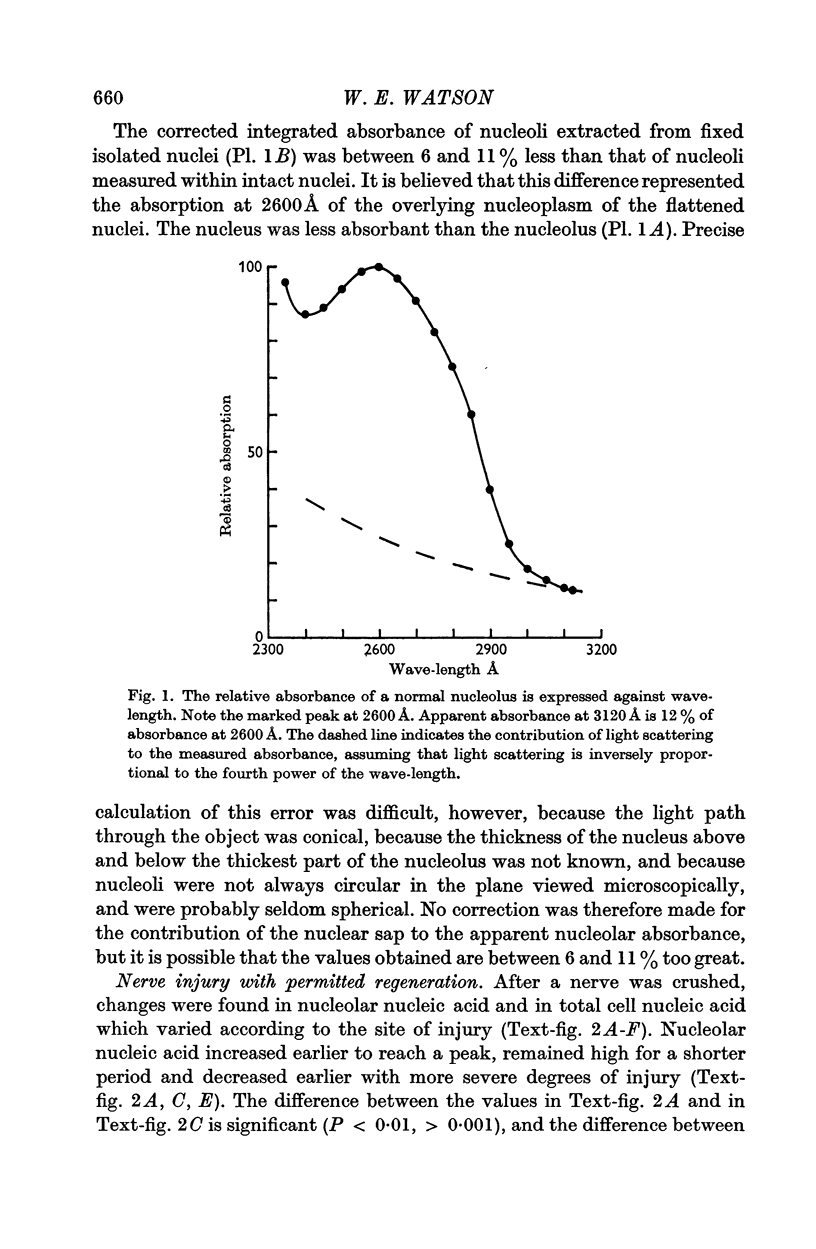
Abstract
1. The nucleic acid content of neuronal nucleoli and the total cell body nucleic acid content of neurones of the hypoglossal nucleus were measured by ultraviolet absorption microspectrography.
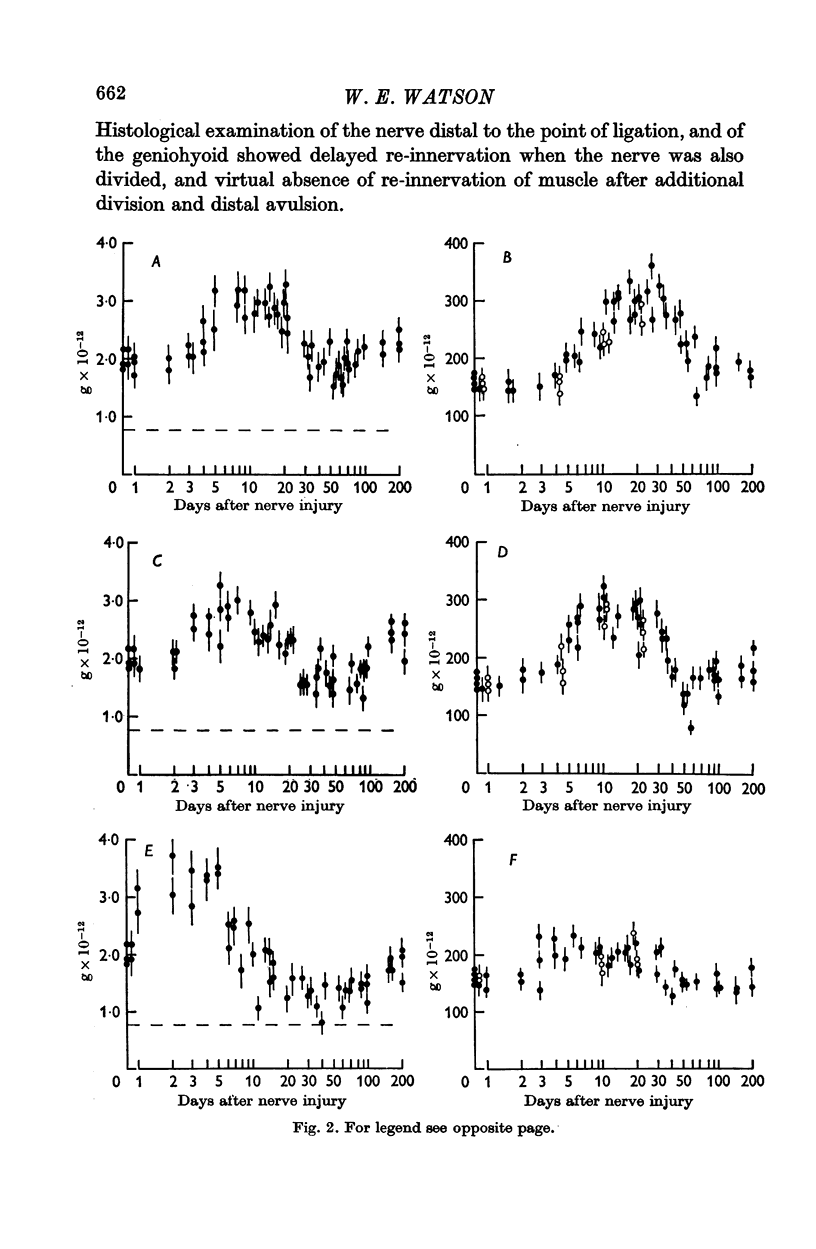
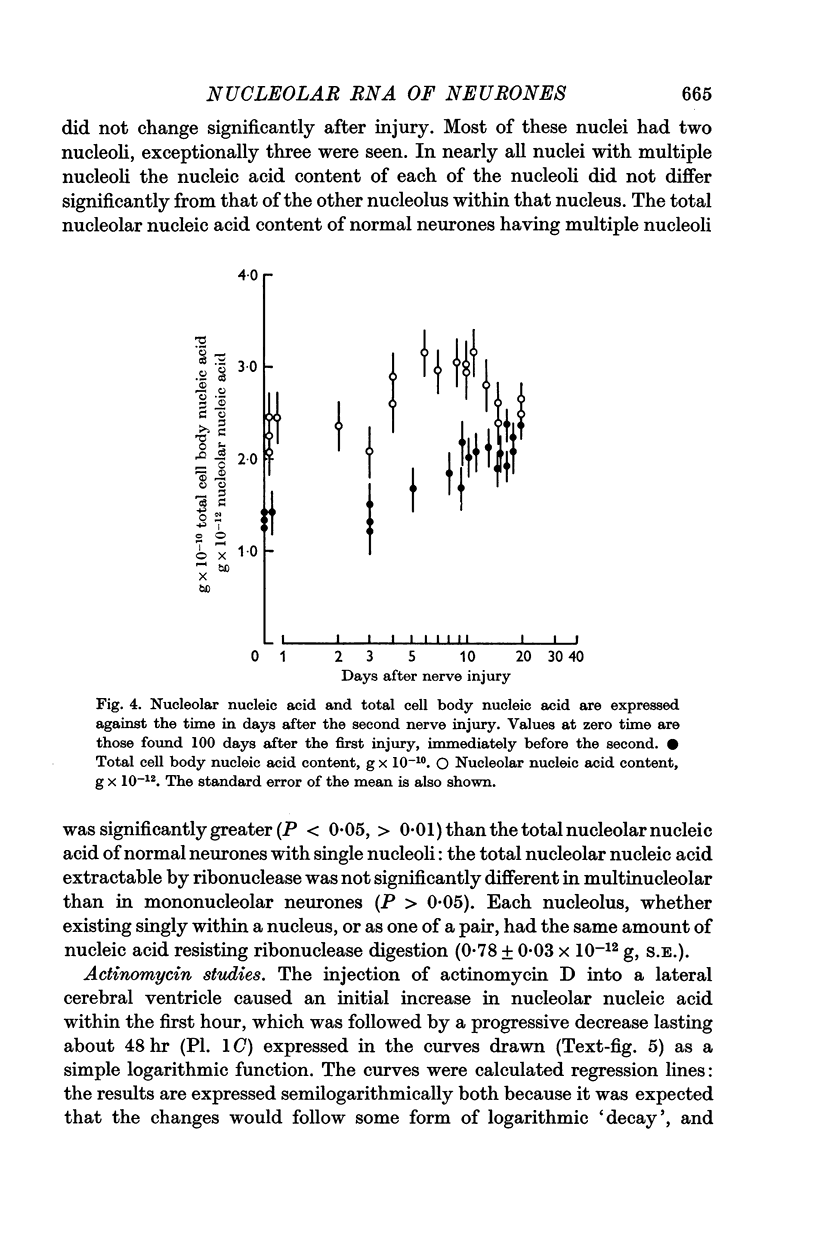
2. After nerve injury both the nucleolar nucleic acid and the total cell body nucleic acid increased: nucleolar changes preceded those of the cell body.
3. The closer to the nerve cell body that the axon was injured the earlier was the onset and the decline of the nucleolar response.
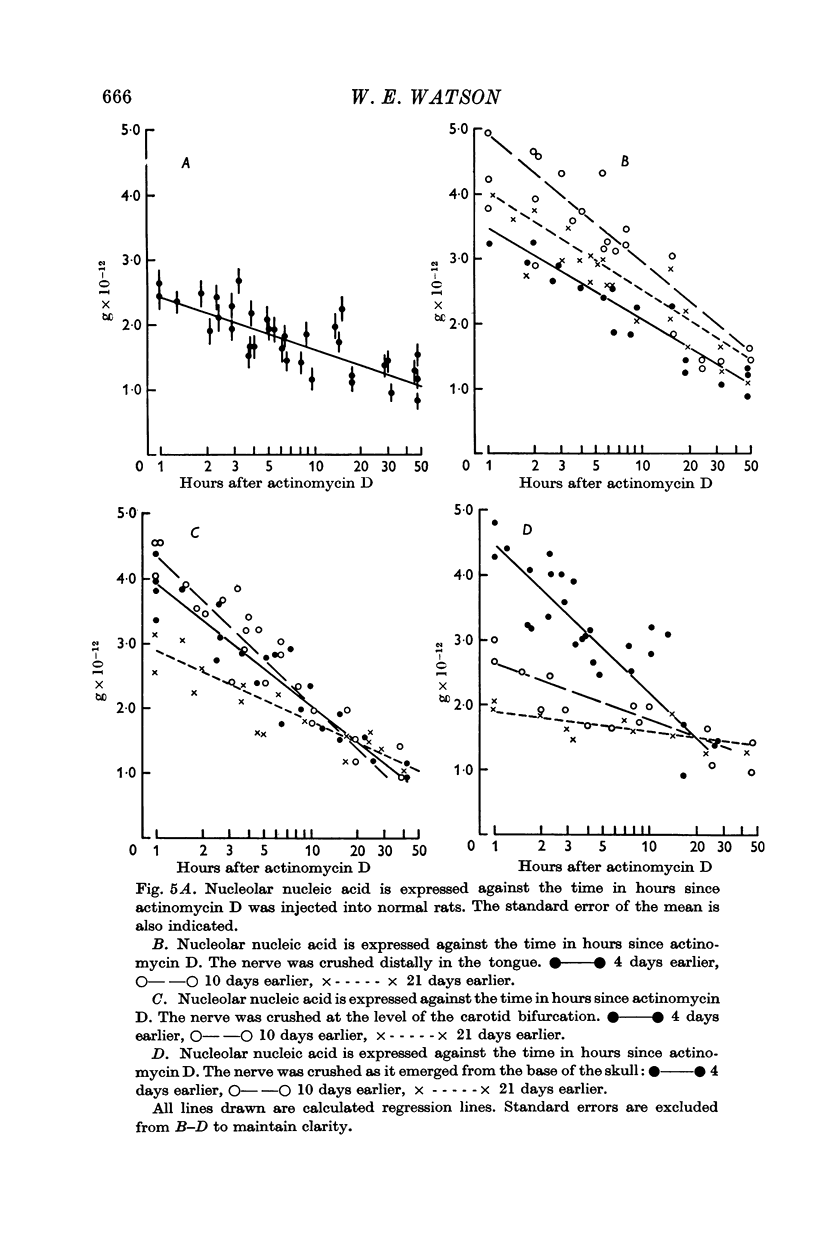
4. Actinomycin D was given to prevent DNA-primed RNA synthesis, and the rate of `decay' of nucleolar RNA was measured. This rate varied after nerve injury and was closely related to the nucleolar nucleic acid content.
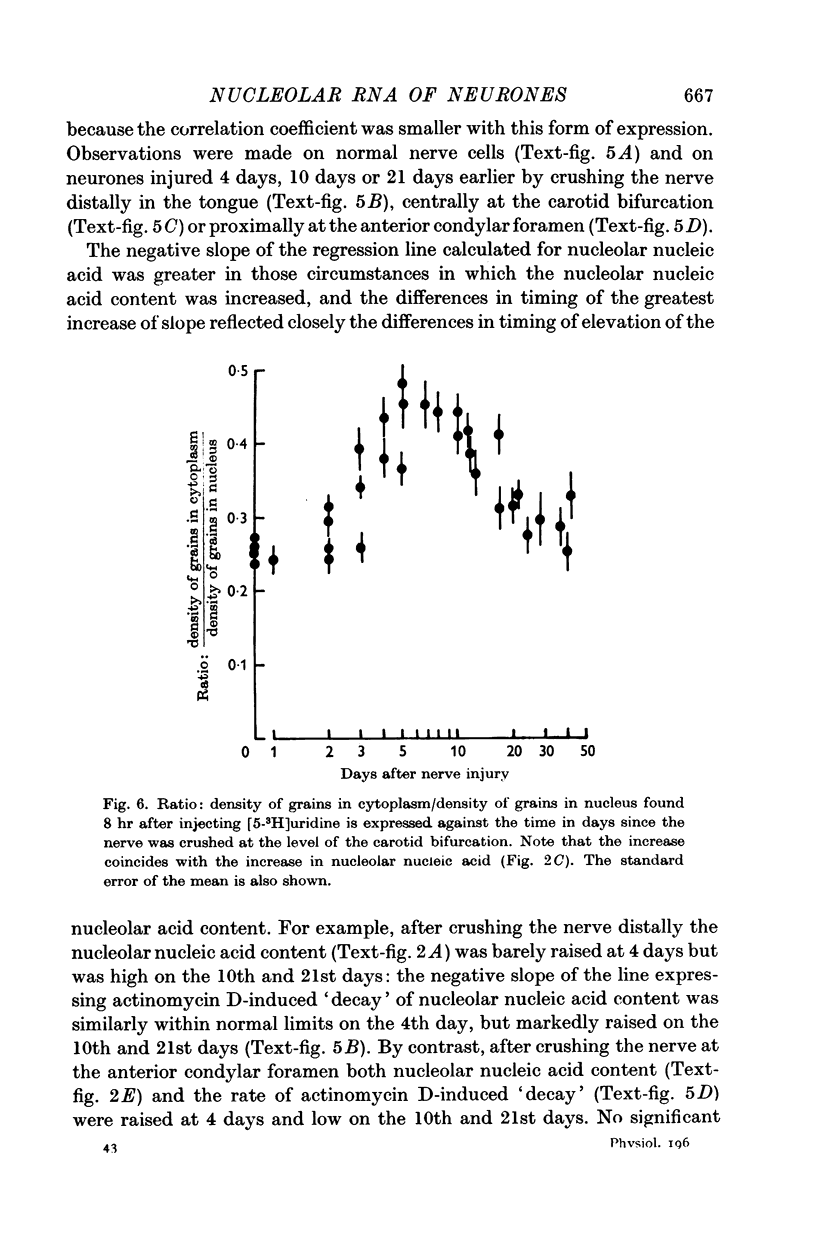
5. The apparent rate of transfer of labelled RNA from the neuronal nucleus into the cytoplasm changed after nerve injury in a manner closely related to the changes in nucleolar nucleic acid content.
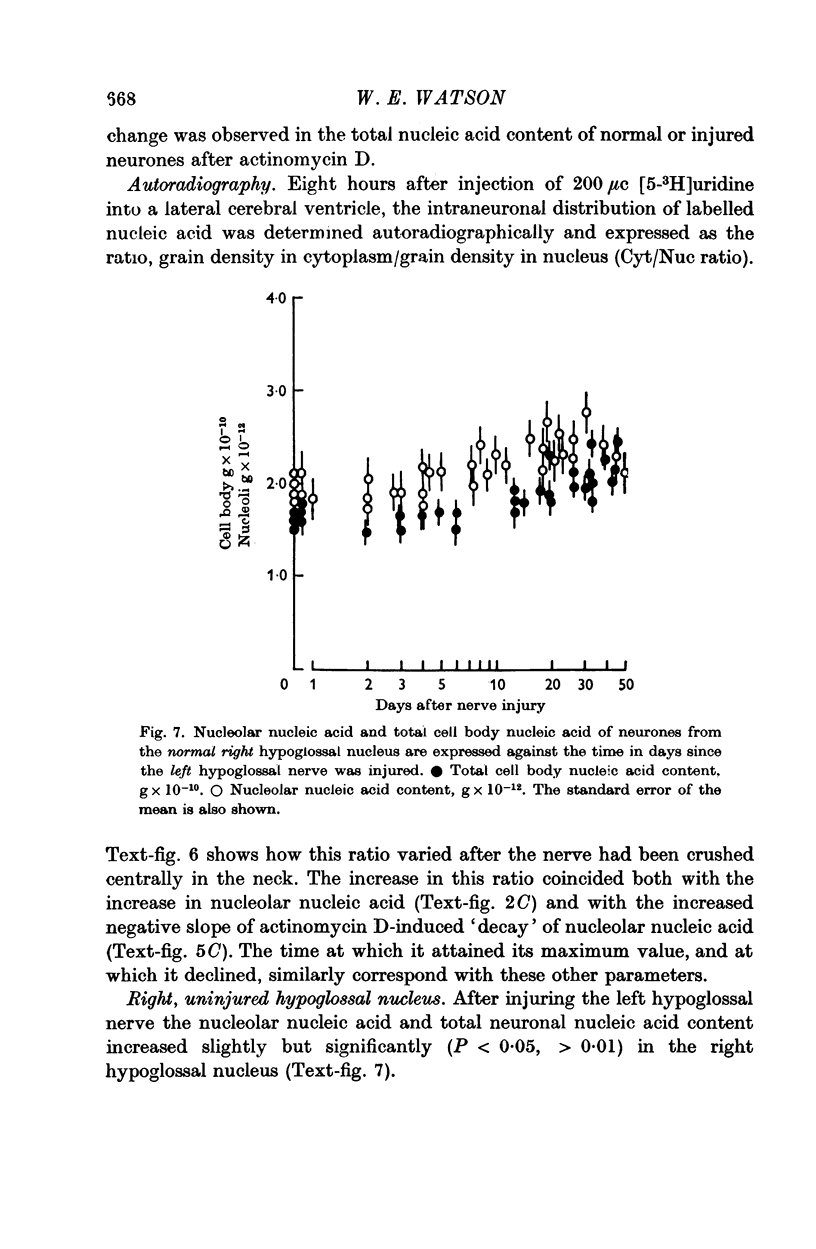
6. It was demonstrated by making consecutive nerve injuries or by preventing or delaying nerve regeneration, that the nucleic acid changes were not induced by removal of contact between the neurone and its motor end-plate, and were not repressed by the restoration of such contact.
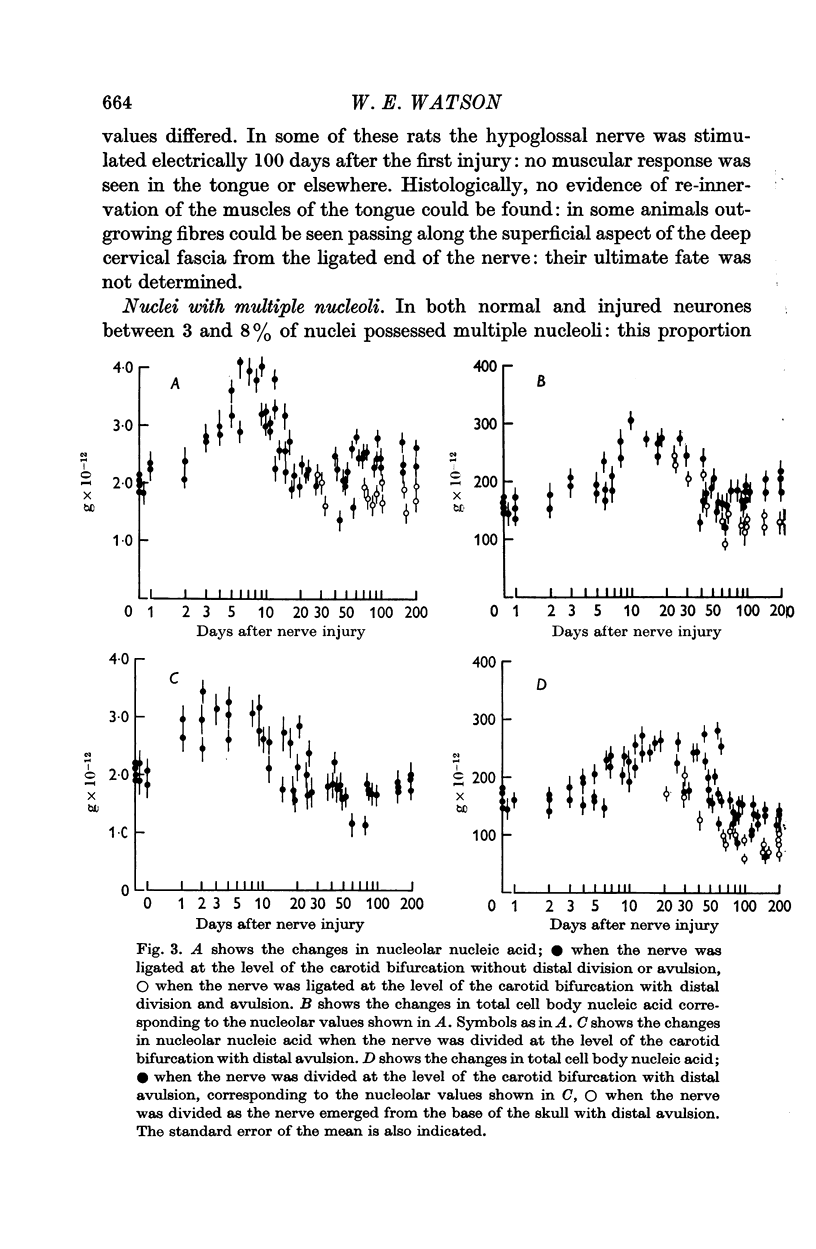
7. When regeneration was prevented the nucleolar nucleic acid content and the total cell body nucleic acid ultimately decreased to values less than normal: this decrease was greater when more of the axon was initially removed.
8. The results are discussed in relation to the factor responsible for derepression and repression of DNA cistrons for ribosome synthesis in injured nerve cells.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken J. T., Sharman M., Young J. Z. Maturation of regenerating nerve fibres with various peripheral connexions. J Anat. 1947 Jan;81(Pt 1):1–22.2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRNSTIEL M. L., CHIPCHASE M. I., HYDE B. B. THE NUCLEOLUS, A SOURCE OF RIBOSOMES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 22;76:454–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRATTGARD S. O., EDSTROM J. E., HYDEN H. The chemical changes in regenerating neurons. J Neurochem. 1957;1(4):316–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1957.tb12088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN D. D., GURDON J. B. ABSENCE OF RIBOSOMAL RNA SYNTHESIS IN THE ANUCLEOLATE MUTANT OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jan;51:139–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch H., Desjardins R., Grogan D., Higashi K., Jacob S. T., Muramatsu M., Ro T. S., Steele W. J. Composition of nucleoli isolated from mammalian cells. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:193–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIPCHASE M. I., BIRNSTIEL M. L. ON THE NATURE OF NUCLEOLAR RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1101–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROUCH Y. F., BARR M. L. Behaviour of the sex chromatin during axon reaction. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1954 Apr;13(2):353–358. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195404000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSTROEM J. E., GALL J. G. THE BASE COMPOSITION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN LAMPBRUSH CHROMOSOMES, NUCLEOLI, NUCLEAR SAP, AND CYTOPLASM OF TRITURUS OOCYTES. J Cell Biol. 1963 Nov;19:279–284. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSTROM J. E., EICHNER D. Quantitative Ribonukleinsäure-Untersuchungen an den Ganglienzellen des Nucleus supraopticus der Albino-Ratte unter experimentellen Bedingungen (Kochsalz-Belastung). Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1958;48(2):187–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSTROM J. E., GRAMPP W., SCHOR N. The intracellular distribution and heterogeneity of ribonucleic acid in starfish oocytes. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:549–557. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSTROM J. E., PIGON A. Relation between surface, ribonucleic acid content and nuclear volume in encapsulated spinal ganglion cells. J Neurochem. 1958 Oct;3(1):95–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSTROM J. E. The content and the concentration of ribonucleic acid in motor anterior horn cells from the rabbit. J Neurochem. 1956 Dec;1(2):159–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1956.tb12068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H., RABINOWITZ M. Actionmycin D inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent synthesis of ribonucleic acid. Science. 1962 Apr 27;136(3513):315–316. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3513.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURDON J. B., BROWN D. D. CYTOPLASMIC REGULATION OF RNA SYNTHESIS AND NUCLEOLUS FORMATION IN DEVELOPING EMBRYOS OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:27–35. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAEMMERLING J., CLAUSS H., KECK K., RICHTER G., WERZ G. Growth and protein synthesis in nucleated and enucleated cells. Exp Cell Res. 1959;Suppl 6:210–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Tencheva Z. S., Bojadjieva-Mikhailova A. G. Isolation and some characteristics of cell nuclei from brain cortex of adult cat. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):383–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. M'ECANISMES BIOCHEMISQUES ET G'EN'ETIQUES DE LA R'EGULATION DANS LA CELLULE BACT'ERIENNE. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1964;46:1499–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob M., Stevenin J., Jund R., Judes C., Mandel P. Rapidly-labelled ribonucleic acids in brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):619–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG E. SYNTHETIC MECHANISMS IN THE AXON. I. LOCAL AXONAL SYNTHESIS OF ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE. J Neurochem. 1965 May;12:343–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG E. SYNTHETIC MECHANISMS IN THE AXON. II. RNA IN MYELIN-FREE AXONS OF THE CAT. J Neurochem. 1965 May;12:357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROEGER H. CHEMICAL NATURE OF THE SYSTEM CONTROLLING GENE ACTIVITIES IN INSECT CELLS. Nature. 1963 Dec 21;200:1234–1235. doi: 10.1038/2001234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROEGER H. ZELLPHYSIOLOGISCHE MECHANISMEN BEI DER REGULATION VON GENAKTIVITAETEN IN DEN RIESENCHROMOSOMEN VON CHIRONOMUS THUMMI. Chromosoma. 1964 Apr 1;15:36–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00326914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEUCHTENBERGER C., KLEIN G., KLEIN E. The estimation of nucleic acids in individual isolated nuclei of ascites tumors by ultraviolet microspectrophotometry and its comparison with the chemical analysis. Cancer Res. 1952 Jul;12(7):480–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C. The distribution of cholinesterase in cholinergic neurons demonstrated with the electron microscope. J Cell Sci. 1966 Sep;1(3):381–390. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström M., Zetterberg A., Carlson L. Quantitative microspectrophotometric analysis of nucleic acids in concentrated solutions, in solid droplets and in lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Oct;43(3):537–545. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miani N., Di Girolamo A., Di Girolamo M. Sedimentation characteristics of axonal rna in rabbit. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):755–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PELLING C. RIBONUKLEINSAEURE-SYNTHESE DER RIESENCHROMOSOMEN. AUTORADIOGRAPHISCHE UNTERSUCHUNGEN AN CHIRONOMUS TENTANS. Chromosoma. 1964 Apr 1;15:71–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00326915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY R. P., ERRERA M. The role of the nucleolus in ribonucleic acid-and protein synthesis. I. Incorporation of cytidine into normal and nucleolar inactivated HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:47–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90868-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY R. P. On the nucleolar and nuclear dependence of cytoplasmic RNA synthesis in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Jun;20:216–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. On ribosome biogenesis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:527–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M., SHATKIN A. J., TATUM E. L. Effect of actinomycin D on cellular nucleic acid synthesis and virus production. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):556–557. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITOSSA F. M., SPIEGELMAN S. LOCALIZATION OF DNA COMPLEMENTARY TO RIBOSOMAL RNA IN THE NUCLEOLUS ORGANIZER REGION OF DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:737–745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROOTS B. I., JOHNSTON P. V. NEURONS OF OX BRAIN NUCLEI: THEIR ISOLATION AND APPEARANCE BY LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Apr;10:350–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritossa F. M., Atwood K. C., Lindsley D. L., Spiegelman S. On the chromosomal distribution of DNA complementary to ribosomal and soluble RNA. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:449–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanes G. J. Motor localization and the effects of nerve injury on the ventral horn cells of the spinal cord. J Anat. 1946 Jul;80(Pt 3):117–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENRAM U. Interferometric determinations of the ribose nucleic acid concentration in liver nucleoli of protein-fed and protein-deprived rats. Exp Cell Res. 1958 Aug;15(1):174–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(58)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent W. S., Baltus E., Lovlie A., Mundell R. E. Proteins and nucleic acids of starfish oocyte nucleoli and ribosomes. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:235–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER P. M. B., YATES H. B. Nuclear components of dividing cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1952 Oct 16;140(899):274–299. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1952.0062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson W. E. An autoradiographic study of the incorporation of nucleic-acid precursors by neurones and glia during nerve regeneration. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):741–753. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson W. E. An autoradiographic study of the incorporation of nucleic-acid precursors by neurones and glia during nerve stimulation. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):754–765. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson W. E. Quantitative observations upon acetylcholine hydrolase activity of nerve cells after axotomy. J Neurochem. 1966 Dec;13(12):1549–1550. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]