Abstract
1. The time course and extent of changes in urinary flow and in the outputs of urea, Na+, K+, and NH4+ over a period of 7½ hr in conscious rats during water and osmotic (mannitol) diuresis were determined, and compared with spontaneous changes in non-diuretic animals.
2. In non-diuretic rats, a morning rise and subsequent decline in urinary osmolal, sodium, potassium and ammonium outputs occurred, possibly attributable to circadian rhythms.
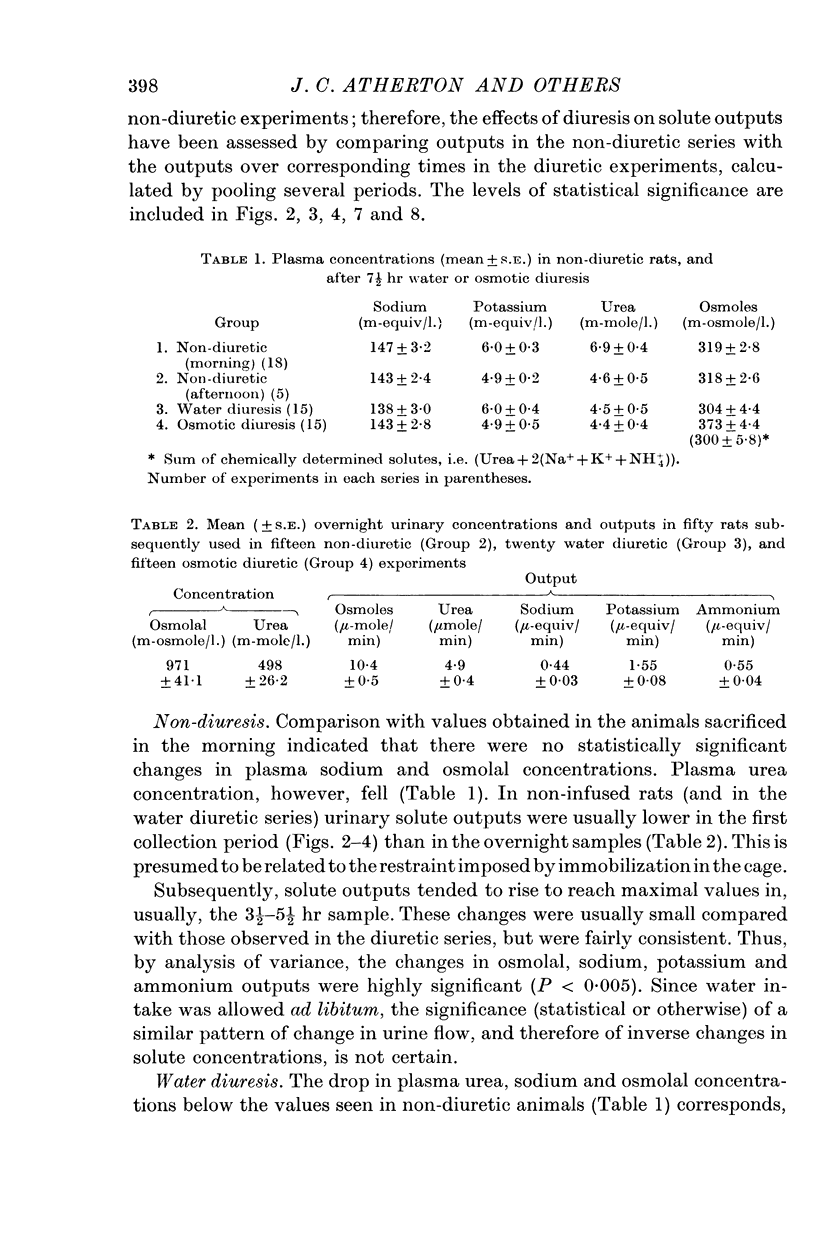
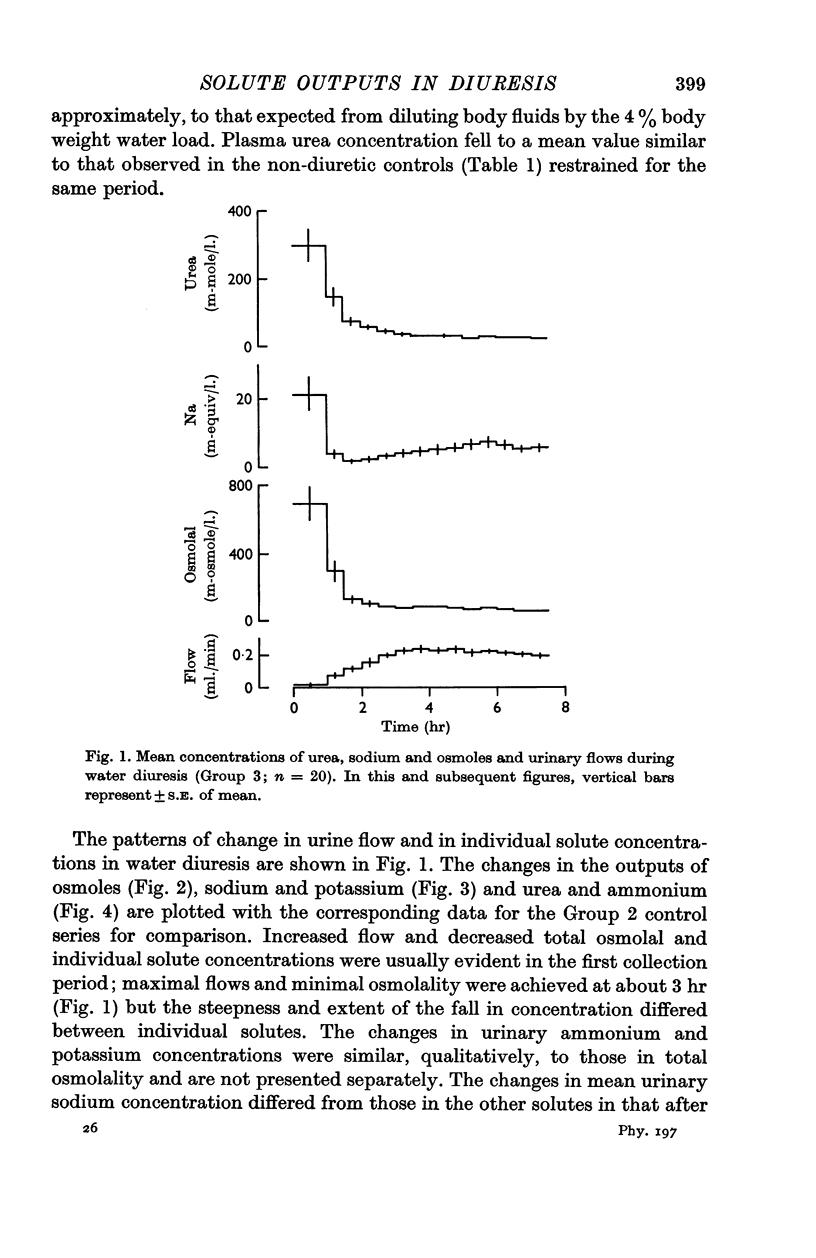
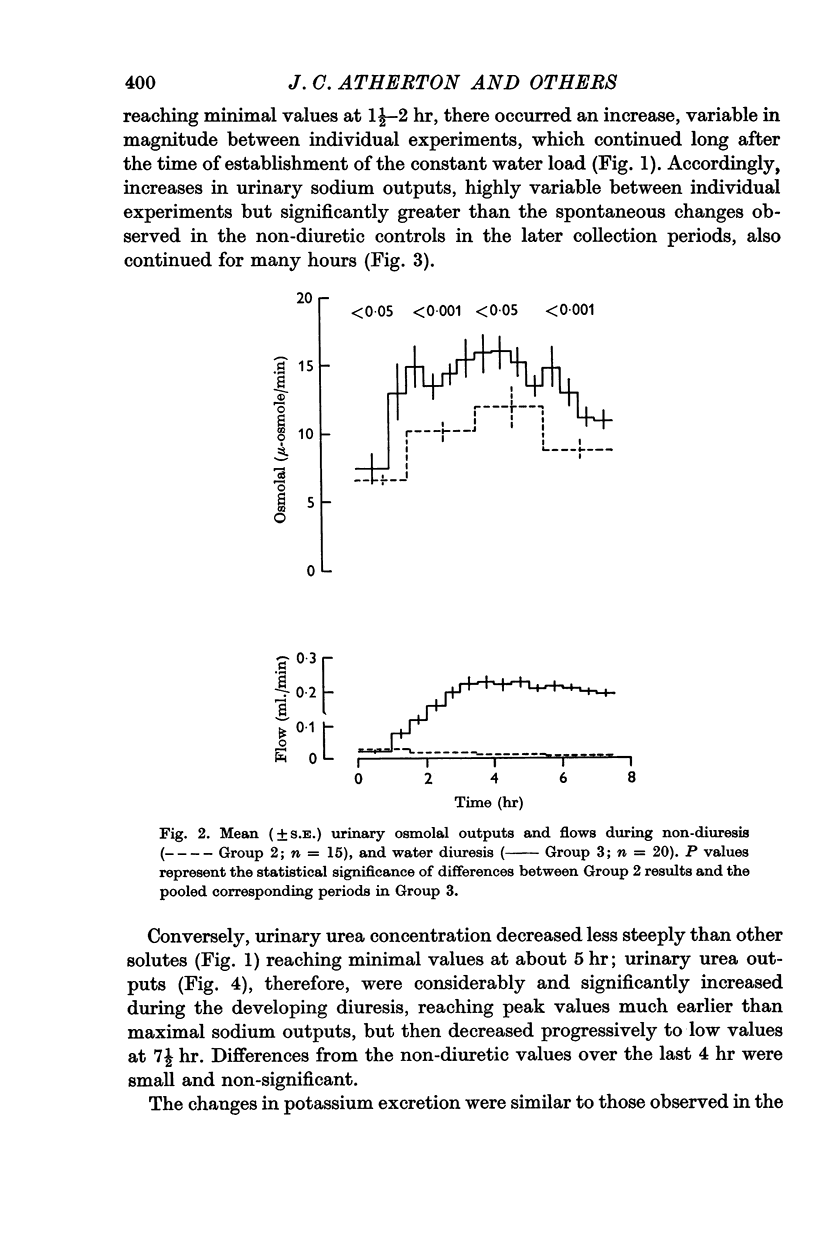
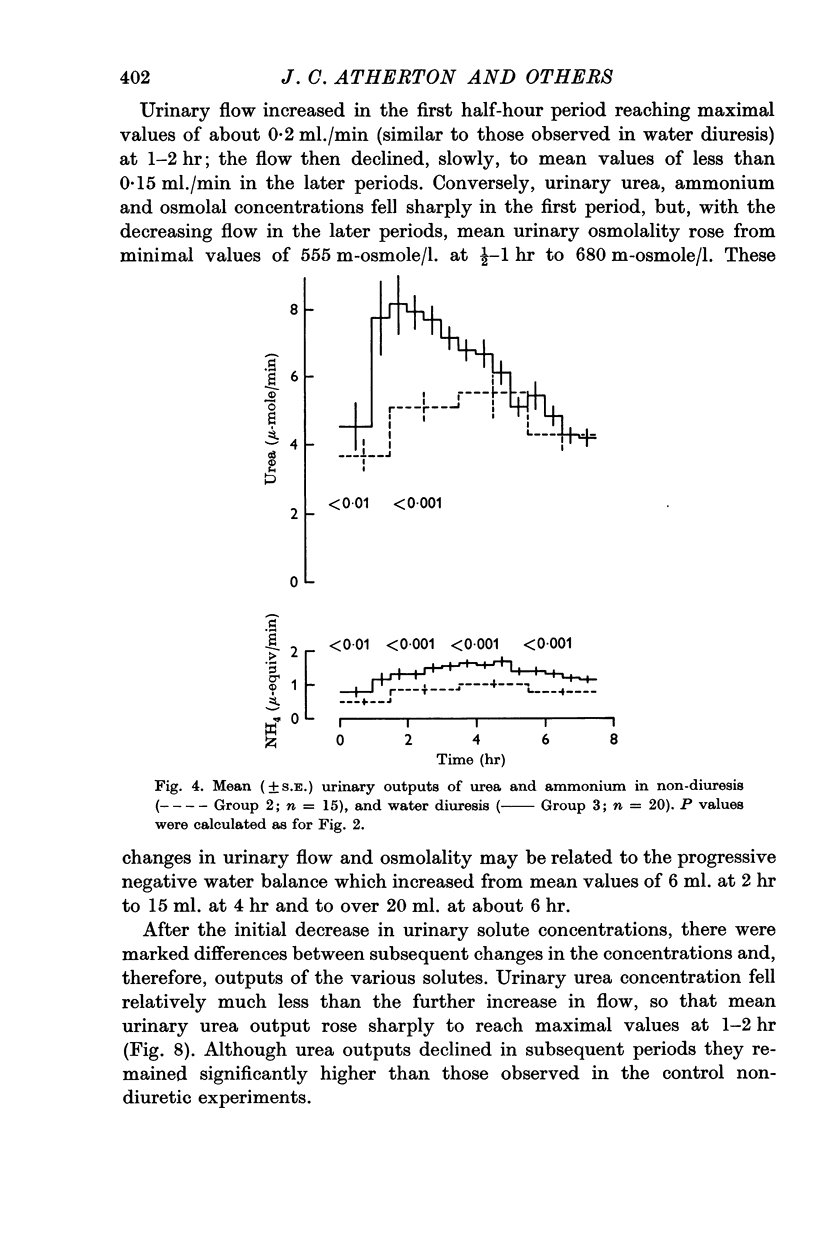
3. Water diuresis was accompanied by (i) a rapid increase in urea excretion during the phase of increasing urine flow, followed by a fall in later periods to values similar to those in non-diuresis, (ii) a slower increase in sodium output, continuing after the establishment of the constant water load, (iii) unchanged potassium excretion, but slightly increased ammonium outputs.
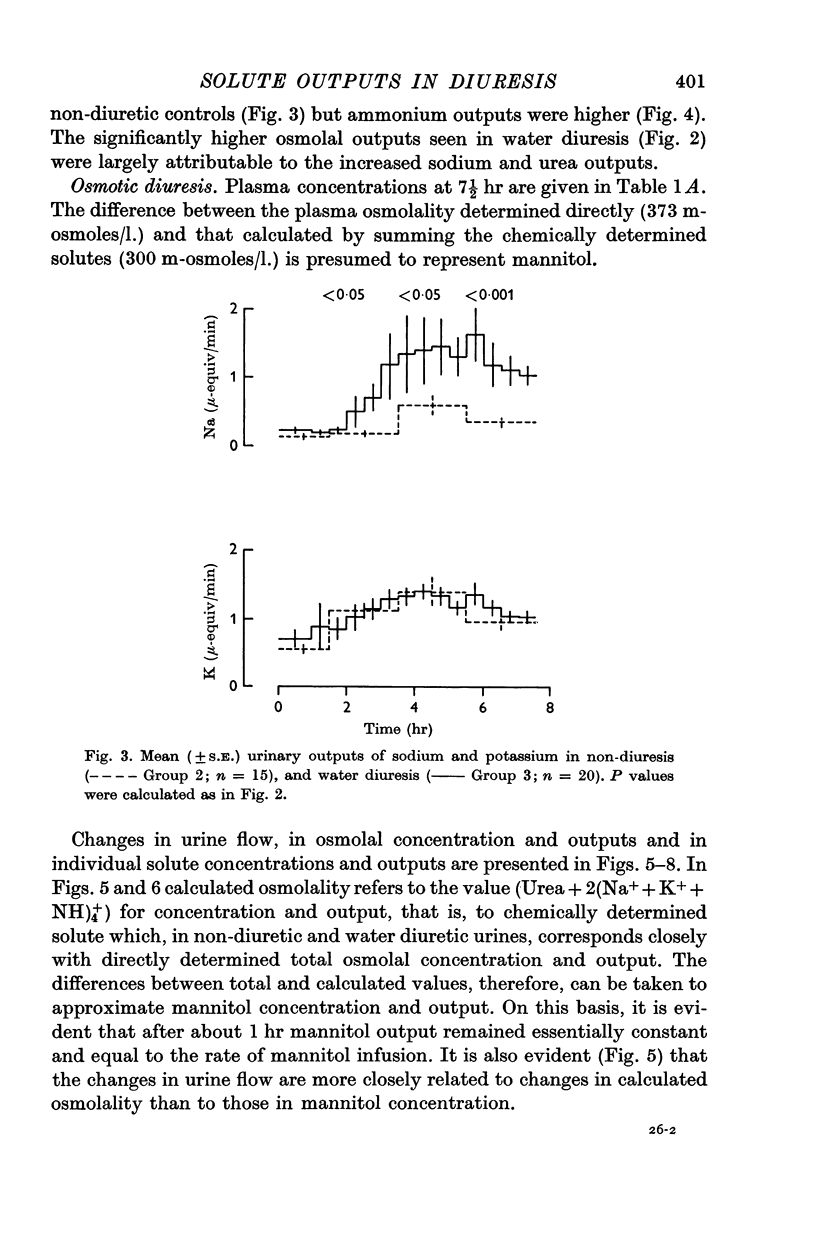
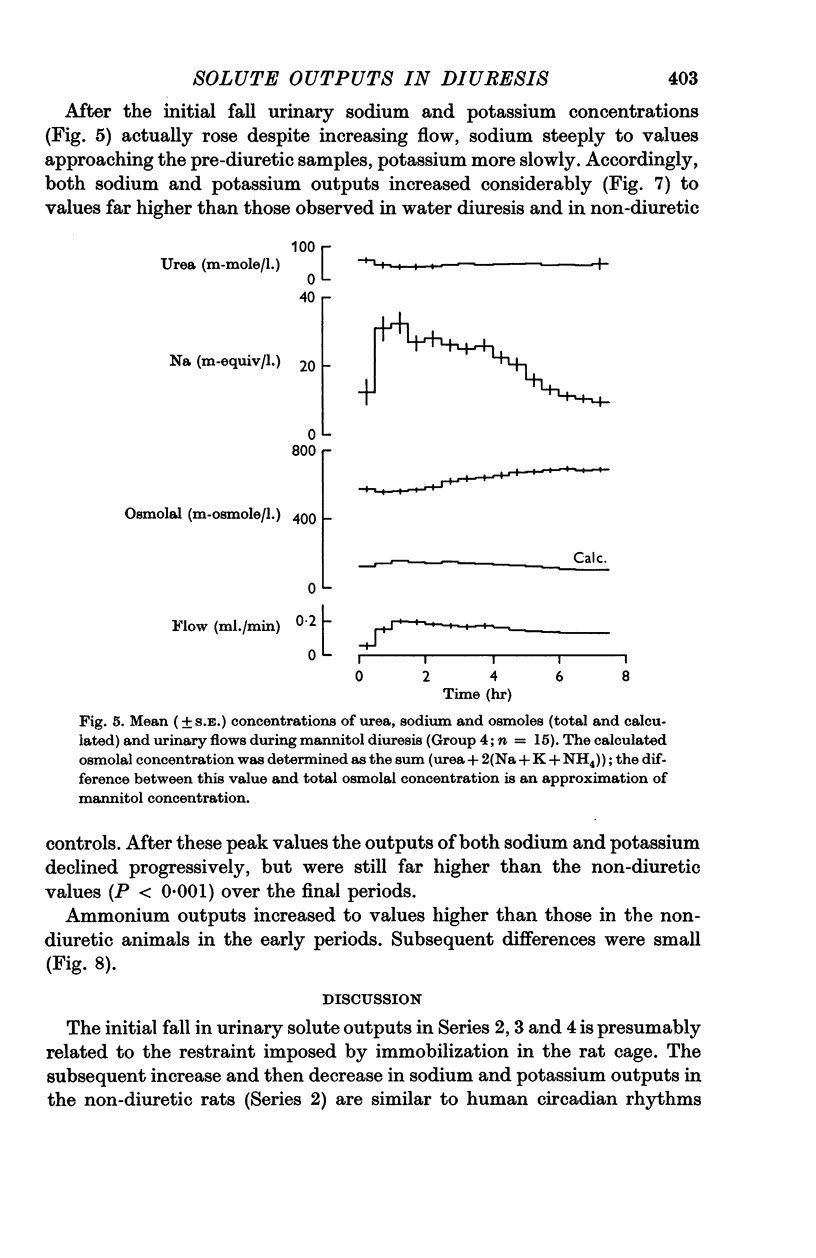
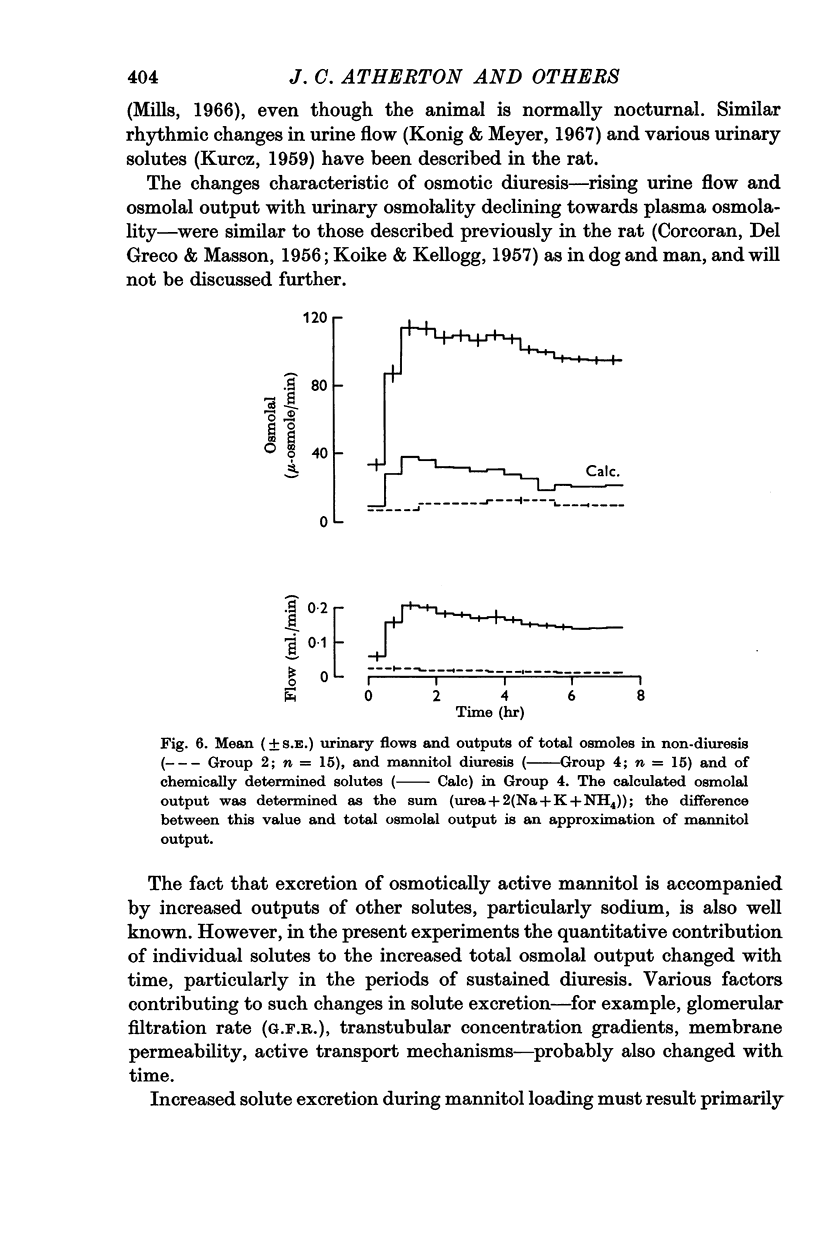
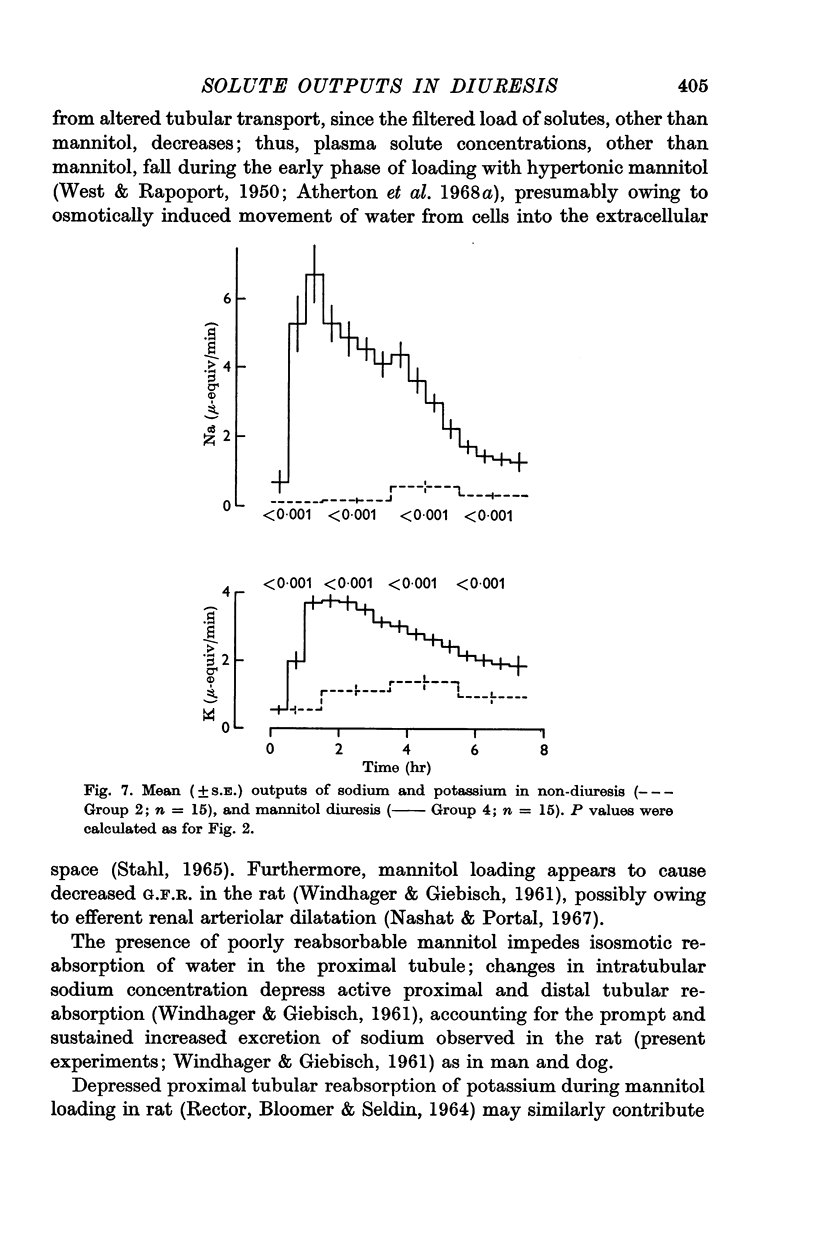
4. Mannitol diuresis was accompanied by (i) a rapid increase in urea outputs which subsequently fell but remained significantly higher, (ii) a steep rise in sodium and potassium outputs to values which remained far higher than those in non-diuretic and water diuretic animals.
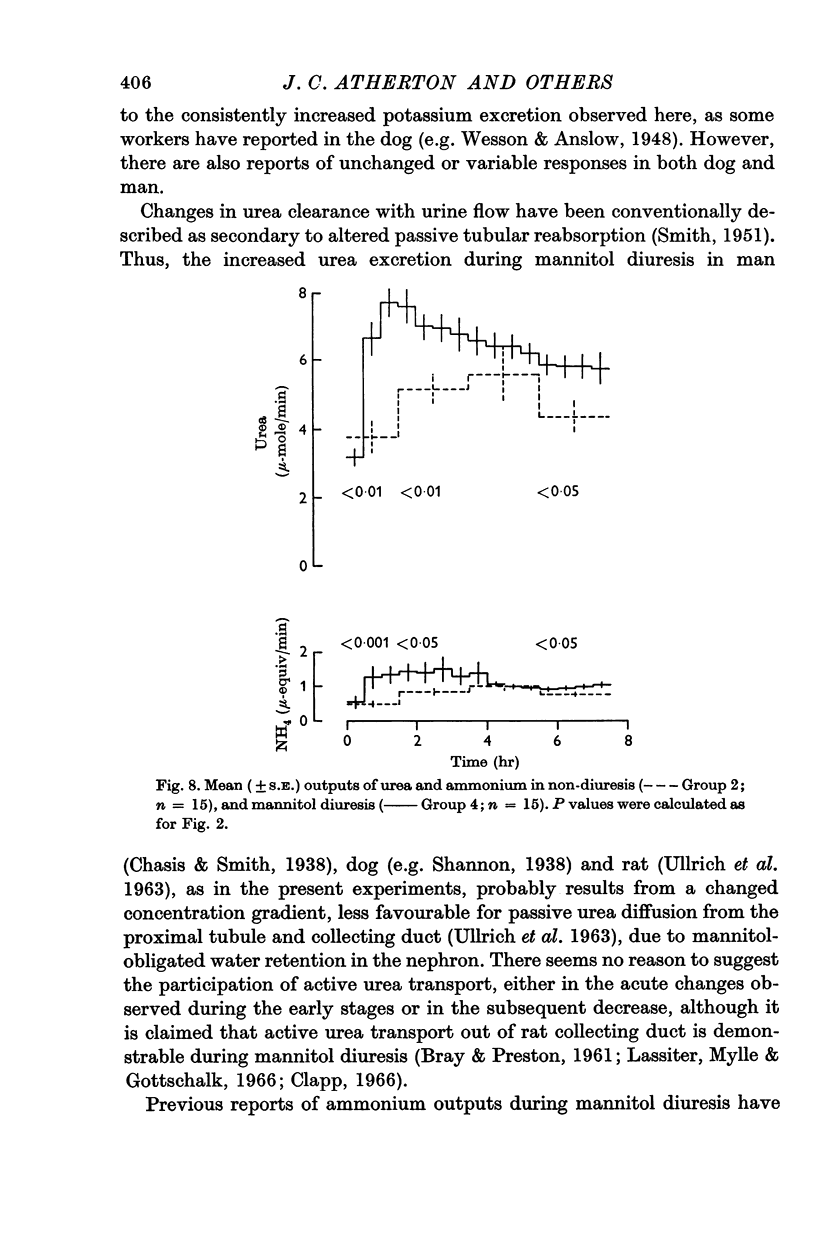
5. The changes in mannitol diuresis are considered to result mainly from decreased tubular reabsorption, due to the lowered intraluminal sodium, potassium and urea concentrations and increased intratubular fluid flow. Some of the acute increase in urea excretion may be due to washout of medullary urea into the tubular fluid.
6. In water diuresis, some of the changes in solute excretion may similarly result from altered tubular reabsorption, perhaps influenced by suppression of anti-diuretic hormone (A.D.H.). In addition, the slower changes in sodium output may be related to several consequences of change in body fluid volume.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atherton J. C., Hai M. A., Thomas S. The time course of changes in renal tissue composition during mannitol diuresis in the rat. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(2):411–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton J. C., Hai M. A., Thomas S. The time course of changes in renal tissue composition duruig water diuresis in the rat. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(2):429–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton J. C., Hai M. A., Thomas S. Transient saluresis due to lysine-vasopressin administration in the conscious water diuretic rat. J Physiol. 1967 May;190(2):30P–31P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER J. K., BARTTER F. C., DELEA C., DUNCAN L. E., Jr, LIDDLE G. W. The regulation of aldosterone secretion in man: the role of fluid volume. J Clin Invest. 1956 Nov;35(11):1306–1315. doi: 10.1172/JCI103386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECK R. N. Osmotic diuresis and the base sparing function of the kidney. Clin Sci. 1958 Feb;17(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAY G. A., PRESTON A. S. Effect of urea on urine concentration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1952–1960. doi: 10.1172/JCI104420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORCORAN A. C., DEL GRECO F., MASSON G. M. Osmotic (mannitol) diuresis in the anesthetized rat; effectiveness of water conserving mechanisms. Am J Physiol. 1956 Dec;187(3):515–519. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.3.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasis H., Smith H. W. THE EXCRETION OF UREA IN NORMAL MAN AND IN SUBJECTS WITH GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. J Clin Invest. 1938 May;17(3):347–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI100959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp J. R. Renal tubular reabsorption of urea in normal and protein-depleted rats. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1304–1308. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coxon R. V., Ramsay D. J. The effect of water diuresis on electrolyte excretion in unanaesthetized dogs. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):123–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker S. E., Heller H. The mechanism of water diuresis in normal rats and rabbits as analysed by inulin and diodone clearances. J Physiol. 1945 Mar 28;103(4):449–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1945.sp004090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes E. C. The action of pitressin on solute permeability of the rabbit nephron in vivo. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Sep;50(1):1–8. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES C. P., Jr, MAYSON J. S., OWEN E. E., ROBINSON R. R. A MICROPUNCTURE EVALUATION OF RENAL AMMONIA EXCRETION IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:77–83. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAENIKE J. R. The influence of vasopressin on the permeability of the mammalian collecting duct to urea. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:144–151. doi: 10.1172/JCI104228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIKE T. I., KELLOGG R. H. Osmotic diuresis in the unanesthetized hydropenic rat. Am J Physiol. 1957 Oct;191(1):45–49. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.191.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König A., Meyer A. Tagesperiodische Schwankungen der Urinausscheidung und des Adiuretingehaltes im Hypophysenhinterlappen männlicher Wister-Ratten. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Feb;54(2):275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassiter W. E., Mylle M., Gottschalk C. W. Micropuncture study of urea transport in rat renal medulla. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):965–970. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino J. A., Earley L. E. The effects of infusion of water on renal hemodynamics and the tubular reabsorption of sodium. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jul;46(7):1229–1238. doi: 10.1172/JCI105616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N. Human circadian rhythms. Physiol Rev. 1966 Jan;46(1):128–171. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.1.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nashat F. S., Portal R. W. The effects of changes in haematocrit on renal function. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):513–522. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPOPORT S., WEST C. D., BRODSKY W. A. Excretion of solutes and osmotic work during osmotic diuresis of hydropenic man; the ideal and the proximal and distal tubular work; the biological maximum of work. Am J Physiol. 1949 Jun;157(3):363–386. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1949.157.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, BLOOMER H. A., SELDIN D. W. PROXIMAL TUBUAL REABSORPTION OF POTASSIUM DURING MANNITOL DIURESIS IN RATS. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Jan;63:100–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTERICH R. Physico-chemical factors determining ammonia excretion. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1962;20:326–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B. Urea excretion in mammals. Physiol Rev. 1958 Apr;38(2):139–168. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAHL W. M. EFFECT OF MANNITOL ON THE KIDNEY: CHANGES IN INTRARENAL HEMODYNAMICS. N Engl J Med. 1965 Feb 25;272:382–386. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196502252720801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINMETZ P. R., BANK N. Effects of acute increases in the excretion of solute and water on renal acid excretion in man. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1142–1149. doi: 10.1172/JCI104799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS S. SOLUTE EXCRETION IN MAN DURING CHANGING URINE FLOW OCCURRING SPONTANEOUSLY AND INDUCED BY VASOPRESSIN INJECTION. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jan;43:1–10. doi: 10.1172/JCI104883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULLRICH K. J., SCHMIDT-NIELSON B., O'DELL R., PEHLING G., GOTTSCHALK C. W., LASSITER W. E., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of composition of proximal and distal tubular fluid in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1963 Apr;204:527–531. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSON L. G., Jr, ANSLOW W. P., Jr Excretion of sodium and water during osmotic diuresis in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1948 Jun;153(3):465–474. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1948.153.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST C. D., BAYLESS R. K. Relation of the saluresis of urea and mannitol loading to the normal excretion of electrolyte. Am J Physiol. 1957 Dec;191(3):512–524. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.191.3.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST C. D., RAPOPORT S. Urine flow and solute excretion of hydropenic dog under 'resting' conditions and during osmotic diuresis. Am J Physiol. 1950 Oct;163(1):159–174. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.163.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDHAGER E. E., GIEBISCH G. Micropuncture study of renal tubular transfer of sodium chloride in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1961 Mar;200:581–590. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain-ul-Abedin Effects of vasopressin upon the composition of rat's kidney. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Jul;52(3):285–292. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


