Abstract
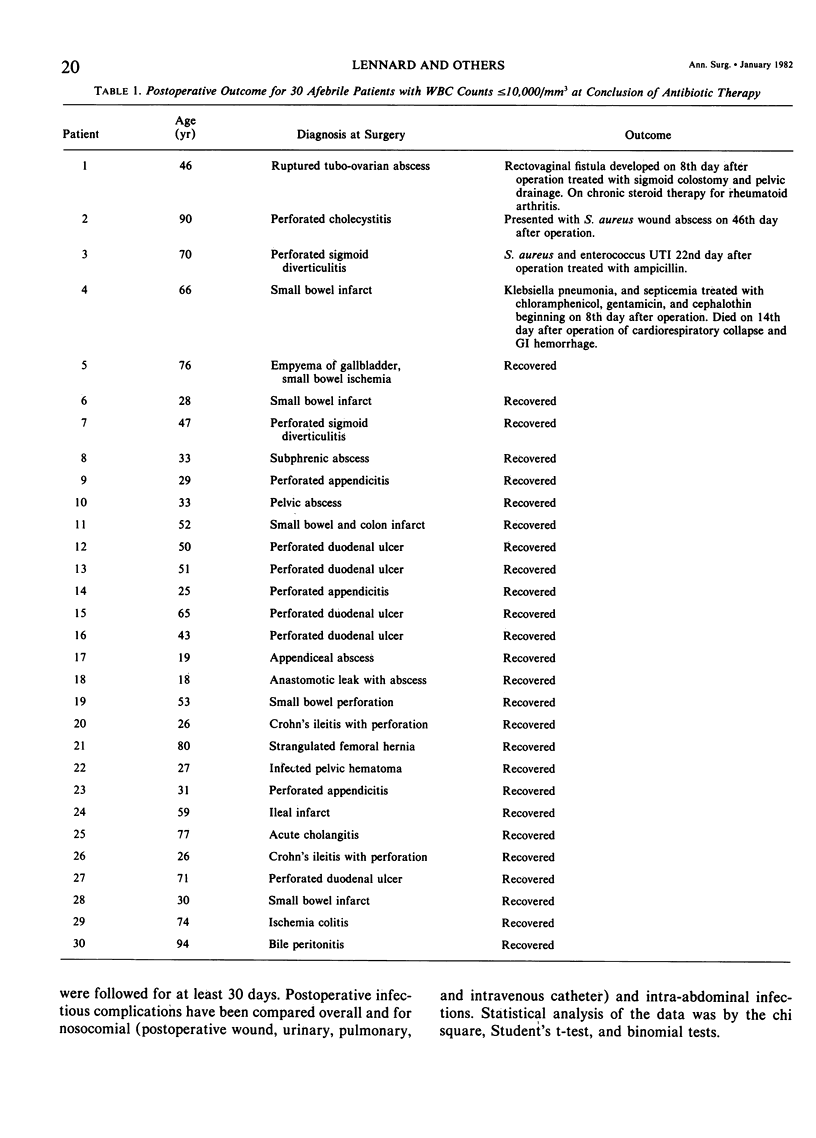
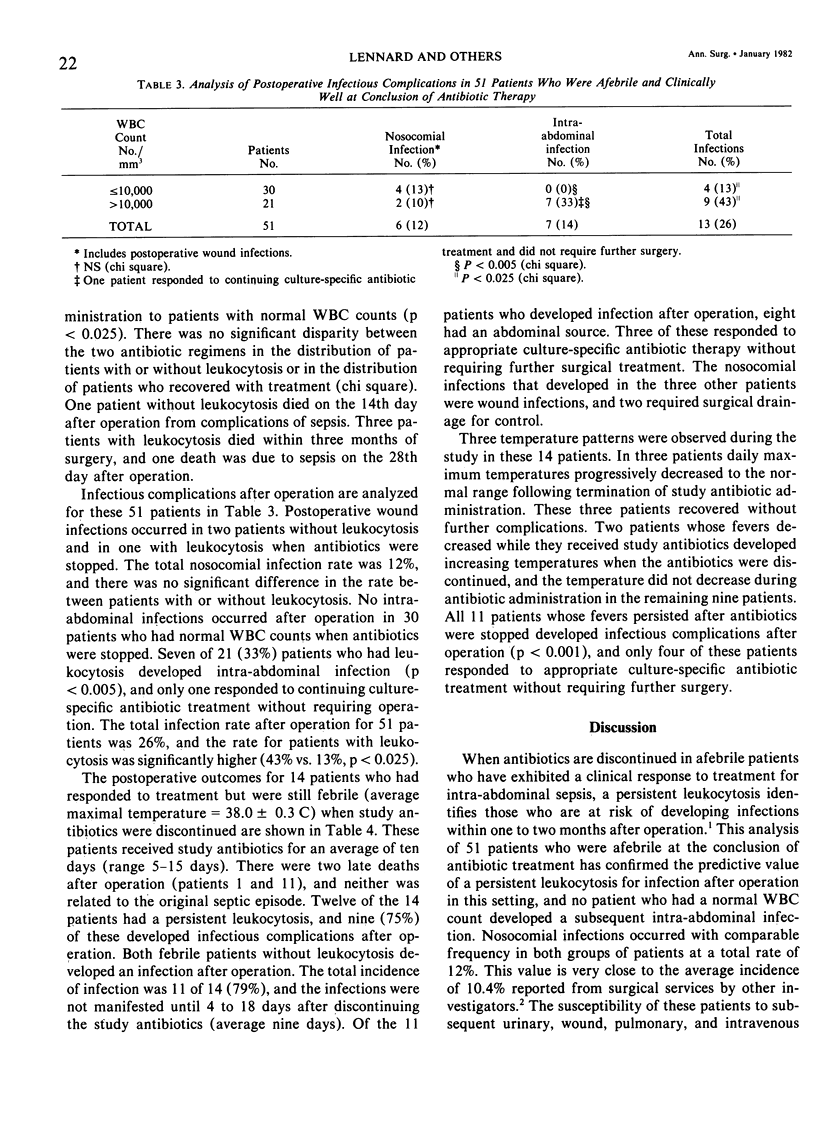
Outcomes of 65 patients after operation who had exhibited a clinical response to treatment for intra-abdominal sepsis were compared based on the presence or absence of leukocytosis and fever at the conclusion of antibiotic therapy. Fifty-one patients were afebrile when antibiotics were stopped. Intra-abdominal infection developed in 7 of 21 (33%) who had a persistent leukocytosis, but no intra-abdominal infections developed after operation in 30 patients who had normal WBC counts at the end of antibiotic treatment (p less than 0.005). Nosocomial infections developed in 6 (12%) of the 51 patients, and there was no difference in the incidence between patients with or without leukocytosis. Eleven of 14 (79%) patients who were still febrile when antibiotics were discontinued developed infections after operation. Nosocomial infections occurred in three (21%) and intra-abdominal infections in eight (57%). Of the 15 patients who developed intra-abdominal infection after operation, only four responded to appropriate antibiotic treatment without requiring further surgery. The other patients required surgical management for definitive control within two months of the initial operation. In conclusion, patients at risk of developing infection after operation after exhibiting a clinical response to treatment of intra-abdominal sepsis are those who are afebrile with a persistent leukocytosis or who are still febrile when antibiotics are stopped.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borsook D., Laburn H., Mitchell D. The febrile responses in rabbits and rats to leucocyte pyrogens of different species. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:113–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikkappa G., Chanana A. D., Chandra P., Commerford S. L., Cronkite E. P. Granulocytopoiesis: studies on leukocytosis-inducing and colony-stimulating factors. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Feb;154(2):192–197. doi: 10.3181/00379727-154-39635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Cline M. J. Endotoxin-induced release of colony-stimulating activity in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Sep;149(4):845–848. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F. Leukocytic endogenous mediator. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Apr;23(4):287–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard E. S., Minshew B. H., Dellinger E. P., Wertz M. Leukocytosis at termination of antibiotic therapy: its importance for intra-abdominal sepsis. Arch Surg. 1980 Aug;115(8):918–921. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380080016003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oken M. M., Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J. Endogenous pyrogen production by human blood monocytes stimulated by staphylococcal cell wall components. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):208–213. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.208-213.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powanda M. C., Bostian K. A., Dinterman R. E., Fee W. G., Fowler J. P., Hauer E. C., White J. D. Phagocytosis and the metabolic sequelae of infection. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Jan;27(1):67–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesenberry P., Morley A., Stohlman F., Jr, Rickard K., Howard D., Smith M. Effect of endotoxin on granulopoiesis and colony-stimulating factor. N Engl J Med. 1972 Feb 3;286(5):227–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197202032860502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. A., Entringer M. A., Bolin R. W., Stonington O. G., Jr Bacterial stimulation and granulocyte inhibition of granulopoietic factor production. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 24;297(21):1129–1134. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711242972101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. A. White blood cell interaction in granulocyte regulation. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Nov;24(5):583–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINSTEIN L., GOLDFIELD M., CHANG TE-WEN Infections occurring during chemotherapy; a study of their frequency, type and predisposing factors. N Engl J Med. 1954 Aug 12;251(7):247–255. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195408122510701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L., Musher D. M. Antibiotic-induced suprainfection. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jun;119(6):662–665. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.6.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


