Abstract
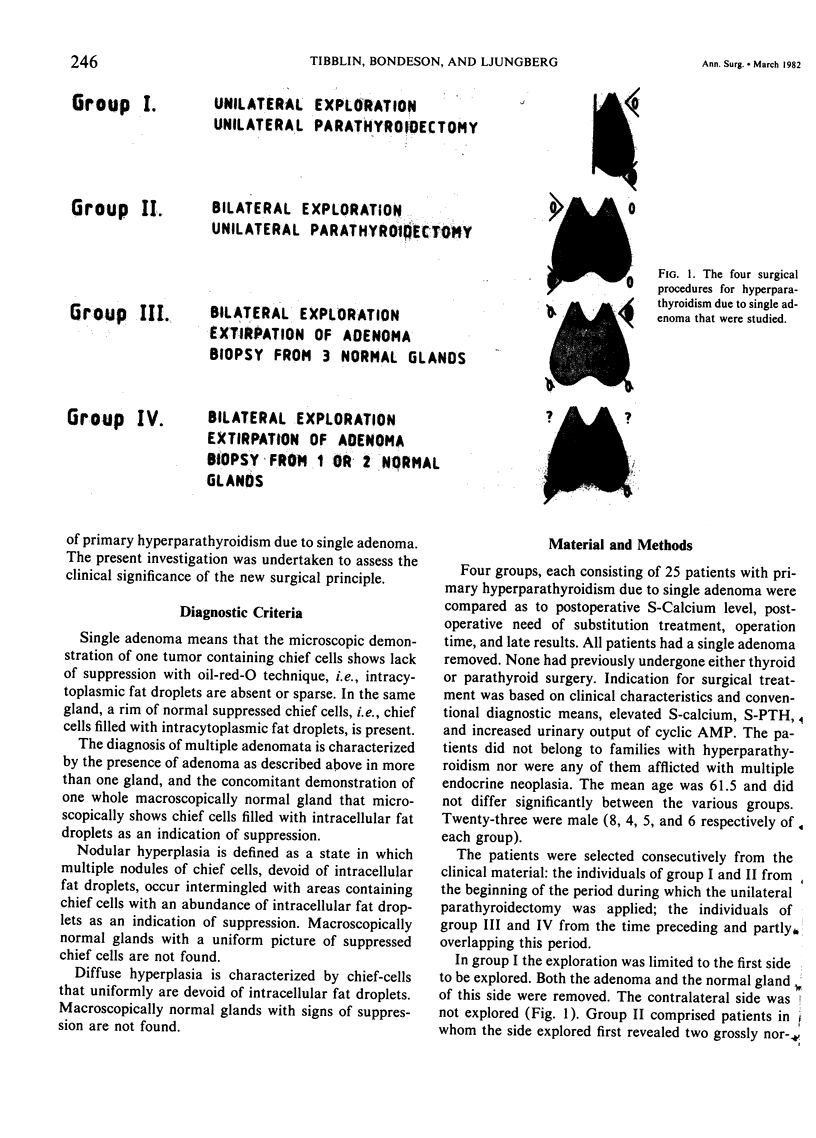
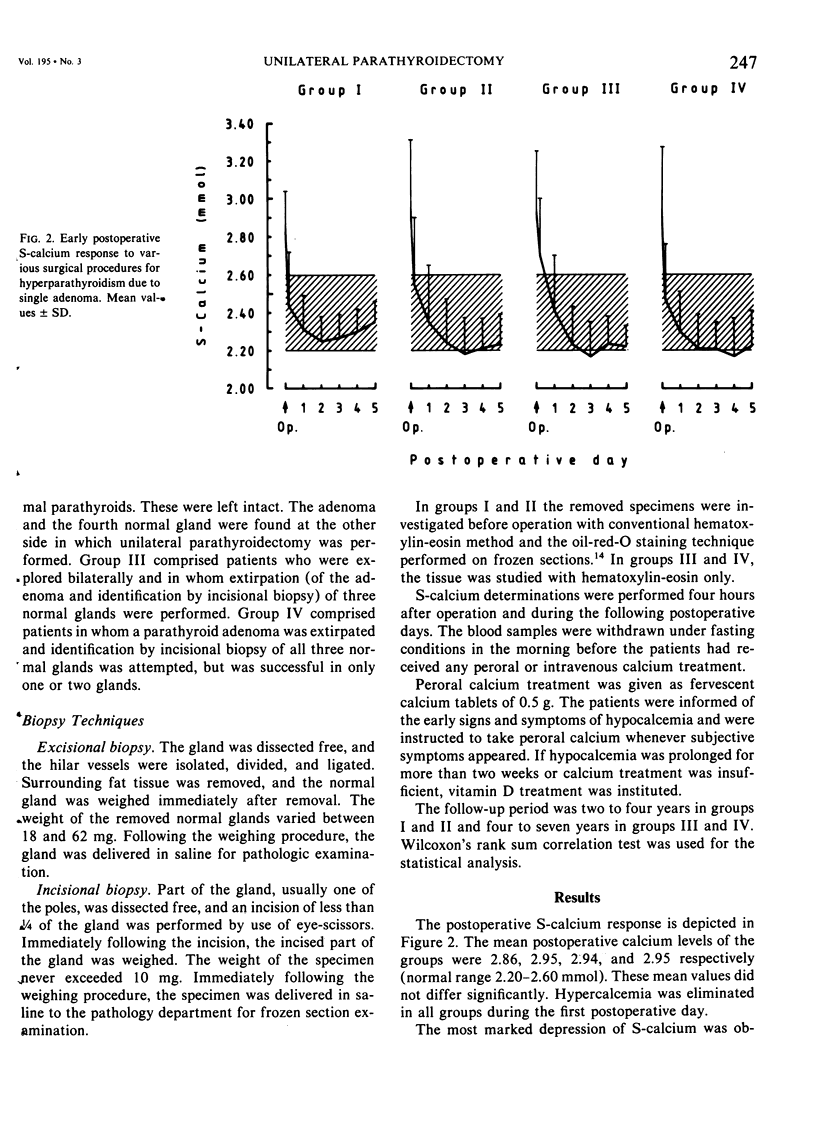
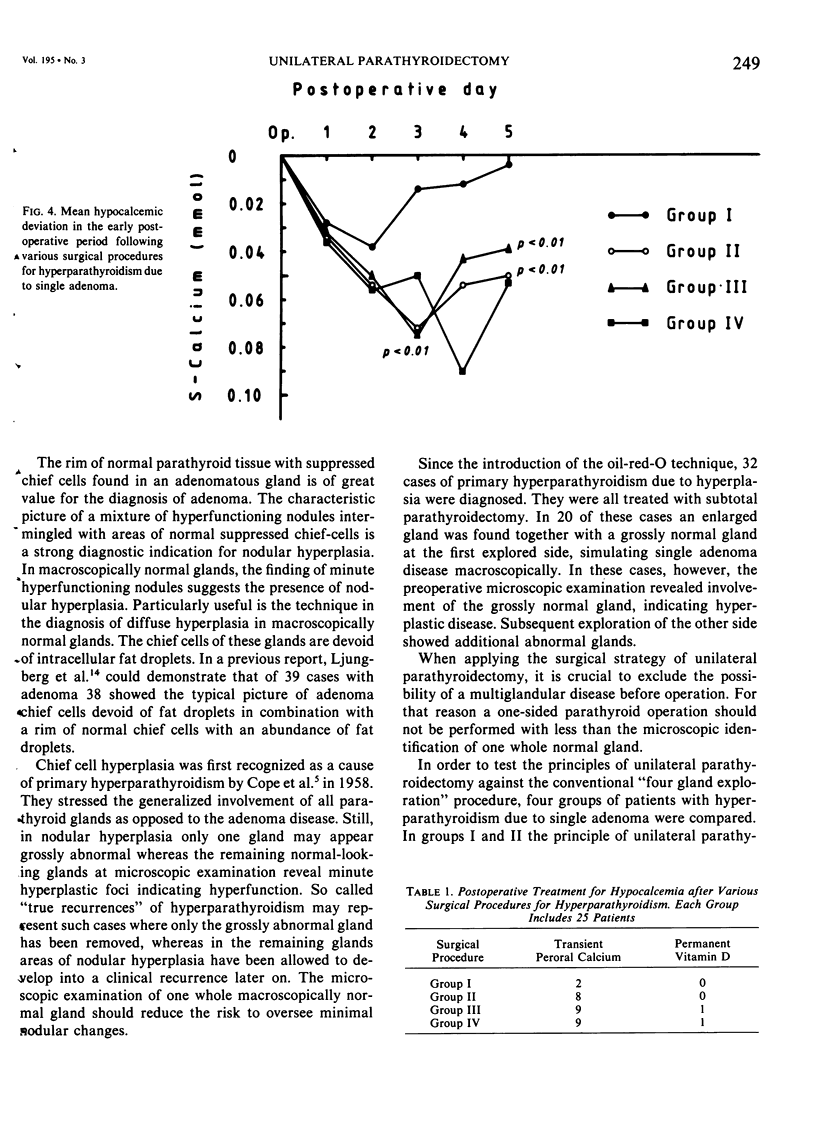
As a general principle in the treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism due to single adenoma, unilateral parathyroidectomy was applied to 50 patients and compared with another group of 50 conventionally explored patients. Twenty-five patients were explored only on the "adenoma" side. The other 25 patients were explored on both sides, avoiding biopsies at the first. In the conventionally explored patients, the adenoma was removed and one to three normal glands were biopsied. Oil-red-O technique was used in the intraoperative microscopical examination. The patients in whom the operation could be limited to the "adenoma" side had a statistically more favorable situation concerning early postoperative hypocalcemia, length of operation time, and need for calcium and vitamin D substitution. The principle of unilateral parathyroidectomy in conjunction with intraoperative oil-red-O staining technique is advocated in hyperparathyroidism due to single adenoma because it offers more reliable peroperative distinction between uni- and multi-glandular involvement, reduced operation time, decreased risk for complication, reduced early hypocalcemia, and more favorable technical conditions for reoperation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beazley R. M., Ketcham A. S. Surgical management of parathyroid disease. Am Surg. 1976 Oct;42(10):767–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. A., Frame B., Jackson C. E., Horn R. C., Jr The extent of operation for primary hyperparathyroidism. Arch Surg. 1974 Dec;109(6):798–801. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01360060068018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. A., Greenawald K., Horn R. C., Jr, Frame B. Involvement of multiple parathyroids in hyperparathyroidism. Surgical aspects. Am J Surg. 1967 Oct;114(4):530–537. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(67)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COPE O., KEYNES W. M., ROTH S. I., CASTLEMAN B. Primary chief-cell hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands: a new entity in the surgery of hyperparathyroidism. Ann Surg. 1958 Sep;148(3):375–388. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195809000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark O. H., Way L. W., Hunt T. K. Recurrent hyperparathyroidism. Ann Surg. 1976 Oct;184(4):391–402. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197610000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. J., Boey J. H., Sweeney E. C., Gilbert J. M., Taylor S. Parathyroidectomy: extent of resection and late results. Br J Surg. 1977 Mar;64(3):153–157. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800640302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope O. Endocrine surgery. Surg Clin North Am. 1978 Oct;58(5):957–966. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)41636-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker A., Watson C. G., Barnes E. L., Jr The pathologic assessment of primary hyperparathyroidism and its impact on therapy. A prospective evaluation of 50 cases with oil-red-O stain. Ann Surg. 1979 Nov;190(5):671–675. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197911000-00020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edis A. J., Beahrs O. H., van Heerden J. A., Akwari O. E. "Conservative" versus "liberal" approach to parathyroid neck exploration. Surgery. 1977 Oct;82(4):466–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esselstyn C. B., Jr, Levin H. S. A technique for parathyroid surgery. Surg Clin North Am. 1975 Oct;55(5):1047–1063. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)40732-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimelius L., Johansson H., Ljunghall S., Thorén L., Akerström G. Controversies in the treatment of hyperparathyroidism. Acta Chir Scand. 1979;145(5):355–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harness J. K., Ramsburg S. R., Nishiyama R. H., Thompson N. W. Multiple adenomas of the parathyroids: do they exist? Arch Surg. 1979 Apr;114(4):468–474. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370280122018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungberg O., Tibblin S. Peroperative fat staining of frozen sections in primary hyperparathyroidism. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jun;95(3):633–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. T. Followup study of surgically-treated primary hyperparathyroidism. Ann Surg. 1974 May;179(5):729–733. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197405000-00027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. A., Brown W. A., Kerr W. H., Rosen I. B., Watters N. A. The surgical aspects of hyperparathyroidism. Arch Surg. 1975 Aug;110(8):1004–1007. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360140148028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purnell D. C., Scholz D. A., Beahrs O. H. Hyperparathyroidism due to single gland enlargement: prospective postoperative study. Arch Surg. 1977 Apr;112(4):369–372. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1977.01370040021003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanus R., Heimann P., Nilsson O., Hansson G. Surgical treatment of hyperparathyroidism. Prog Surg. 1973;12:22–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. I., Gallagher M. J. The rapid identification of "normal" parathyroid glands by the presence of intracellular fat. Am J Pathol. 1976 Sep;84(3):521–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. I., Wang C. A., Potts J. T., Jr The team approach to primary hyperparathyroidism. Hum Pathol. 1975 Nov;6(6):645–648. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(75)80073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. A., Rieder S. V. A density test for the intraoperative differentiation of parathyroid hyperplasia from neoplasia. Ann Surg. 1978 Jan;187(1):63–67. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197801000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. A. Surgery of the parathyroid glands. Adv Surg. 1971;5:109–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



