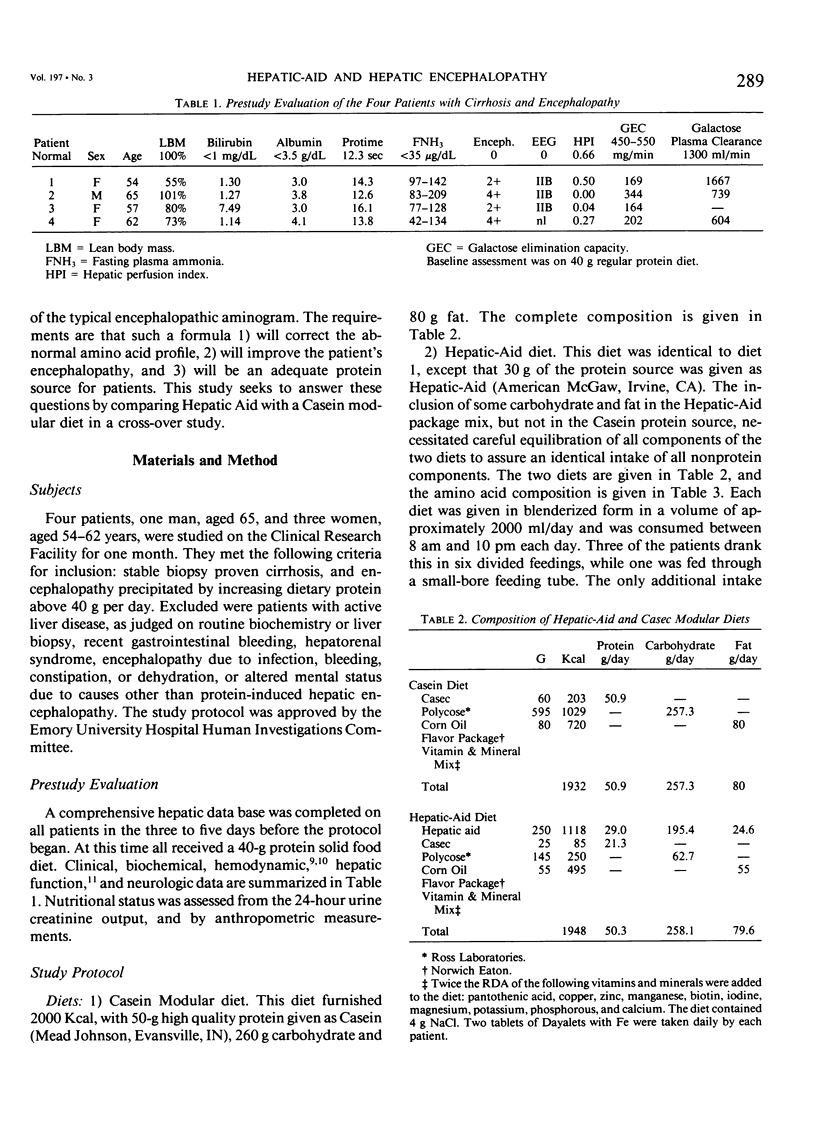
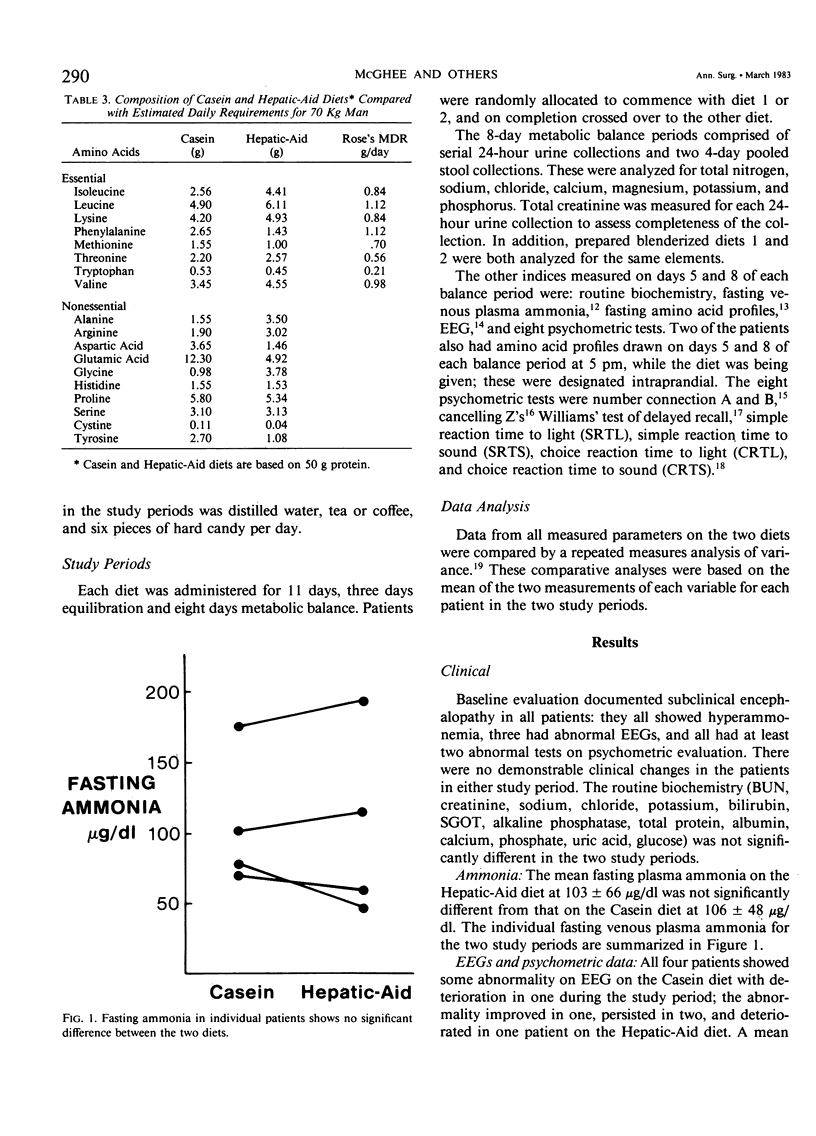
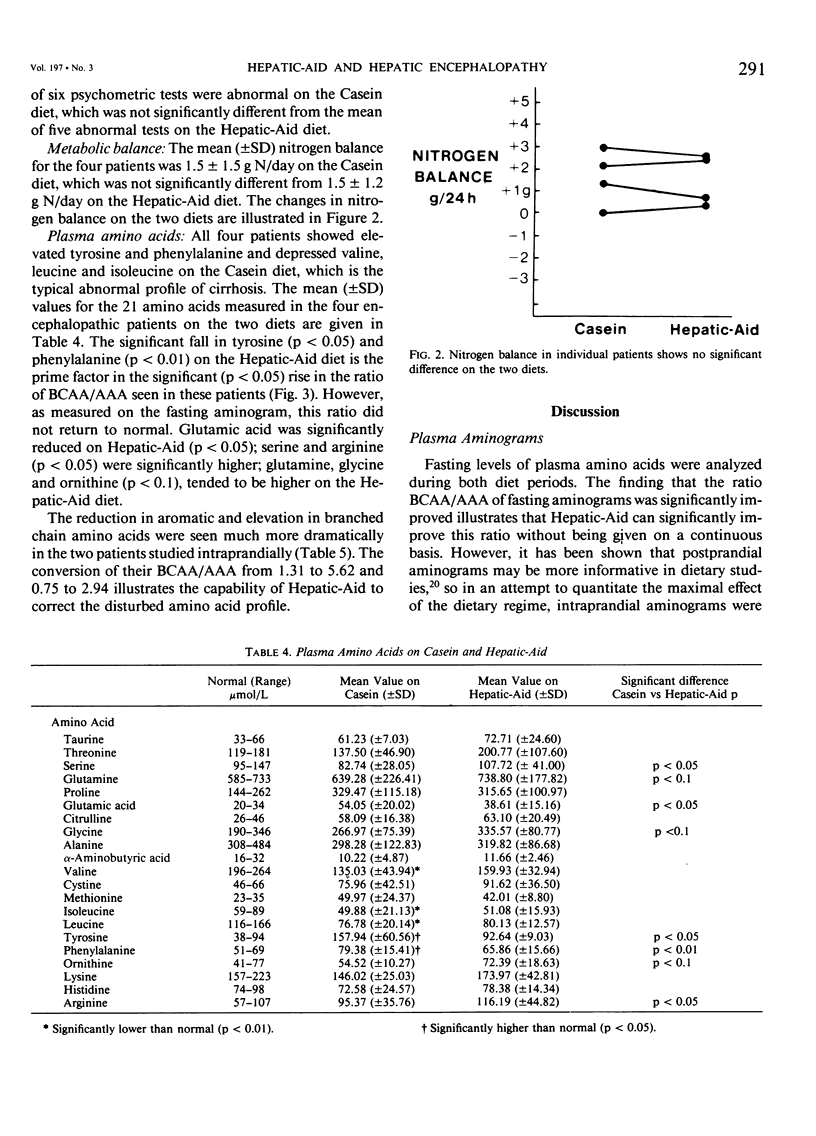
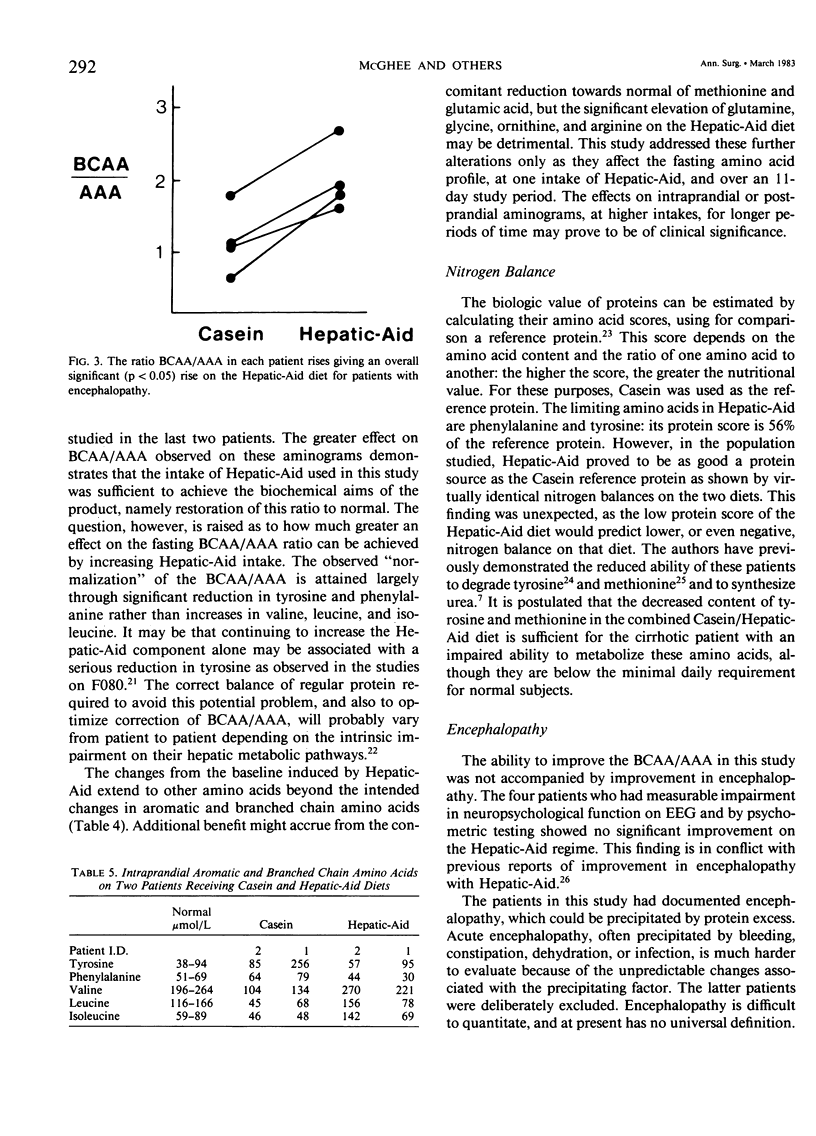
Abstract
Hepatic-Aid is purported to ameliorate encephalopathy and promote positive nitrogen balance in protein-intolerant, cirrhotic patients by correcting their imbalanced amino acid profile. This study evaluated Hepatic-Acid by comparing a 50-g Casein diet with an identical diet with 20-g Casein/30-g Hepatic-Aid per day in a cross-over study. Four patients with biopsy-proven stable cirrhosis, encephalopathy, and under-nutrition were studied. Each study period included three days of equilibration and eight days of metabolic balance, with the following measured at baseline and on balance days 5 and 8: routine biochemistry, fasting ammonia, psychometric tests, EEG, and plasma amino acid profiles. There was no significant change in clinical status, routine biochemistry, fasting ammonia, psychometrics or EEG between the two study periods. Mean (+/-SD) nitrogen balance on the Casein diet at 1.5 +/- 1.5 g/day was not significantly different from that on the Hepatic-Aid diet at 1.5 +/- 1.2 g/day. Plasma amino acid profiles showed a significant fall (p less than 0.05) in fasting and intraprandial tyrosine (tyr) and phenylalanine (phe) on Hepatic-Aid, but only intraprandial leucine (leu), isoleucine (ile), and valine (val) were significantly increased (p less than 0.05) on Hepatic-Aid. The ratio leu + ile + val to tyr + phe was significantly increased (p less than 0.05) on Hepatic-Aid. It is concluded that Hepatic-Aid, as given in this study, maintains N balance similar to Casein, alters the amino acid profile towards normal, but does not ameliorate encephalopathy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong M. D., Stave U. [A comparative evaluation of different methods of treating syringomyelia]. Metabolism. 1973 Apr;22(4):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O. Trailmaking and number-connection tests in the assessment of mental state in portal systemic encephalopathy. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Jun;22(6):541–550. doi: 10.1007/BF01072510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraj B. A., Bowen P. A., Isaacs J. W., Rudman D. Hypertyraminemia in cirrhotic patients. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 17;294(25):1360–1364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606172942502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. E., Funovics J. M., Aguirre A., James J. H., Keane J. M., Wesdorp R. I., Yoshimura N., Westman T. The role of plasma amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy. Surgery. 1975 Sep;78(3):276–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. E., Rosen H. M., Ebeid A. M., James J. H., Keane J. M., Soeters P. B. The effect of normalization of plasma amino acids on hepatic encephalopathy in man. Surgery. 1976 Jul;80(1):77–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund H., Yoshimura N., Fischer J. E. Chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Long-term therapy with a branched-chain amino-acid-enriched elemental diet. JAMA. 1979 Jul 27;242(4):347–349. doi: 10.1001/jama.242.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerron G. G., Ansley J. D., Isaacs J. W., Kutner M. H., Rudman D. Technical pitfalls in measurement of venous plasma NH3 concentration. Clin Chem. 1976 May;22(5):663–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. H., Rypins E. B., Henderson J. M., Heymsfield S. B., Moffitt S. D., Bain R. P., Chawla R. K., Bleier J. C., Rudman D. Evidence for impairment of transsulfuration pathway in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1981 Oct;81(4):668–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlinger B. M., Fulenwider J. T., Ivey G. L., Faraj B. A., Ali F. M., Kutner M., Henderson J. M., Rudman D. Tyrosine metabolism in cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Dec;94(6):832–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozalp I., Young V. R., Nagchaudhuri J., Tontisirin K., Scrimshaw N. S. Plasma amino acid response in young men given diets devoid of single essential amino acids. J Nutr. 1972 Sep;102(9):1147–1158. doi: 10.1093/jn/102.9.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARSONS-SMITH B. G., SUMMERSKILL W. H., DAWSON A. M., SHERLOCK S. The electroencephalograph in liver disease. Lancet. 1957 Nov 2;273(7001):867–871. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikkers L., Jenko P., Rudman D., Freides D. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy: detection, prevalence, and relationship to nitrogen metabolism. Gastroenterology. 1978 Sep;75(3):462–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Kutner M., Ansley J., Jansen R., Chipponi J., Bain R. P. Hypotyrosinemia, hypocystinemia, and failure to retain nitrogen during total parenteral nutrition of cirrhotic patients. Gastroenterology. 1981 Dec;81(6):1025–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rypins E. B., Henderson J. M., Fulenwider J. T., Moffitt S., Galambos J. T., Warren W. D., Rudman D. A tracer method for measuring rate of urea synthesis in normal and cirrhotic subjects. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jun;78(6):1419–1424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarper R., Fajman W. A., Rypins E. B., Henderson J. M., Tarcan Y. A., Galambos J. T., Warren W. D. A noninvasive method for measuring portal venous/total hepatic blood flow by hepatosplenic radionuclide angiography. Radiology. 1981 Oct;141(1):179–184. doi: 10.1148/radiology.141.1.6270726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYGSTRUP N. THE GALACTOSE ELIMINATION CAPACITY IN CONTROL SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER. Acta Med Scand. 1964 Mar;175:281–289. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1964.tb00576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. The measurement of memory in clinical practice. Br J Soc Clin Psychol. 1968 Feb;7(1):19–34. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1968.tb00538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


