Abstract
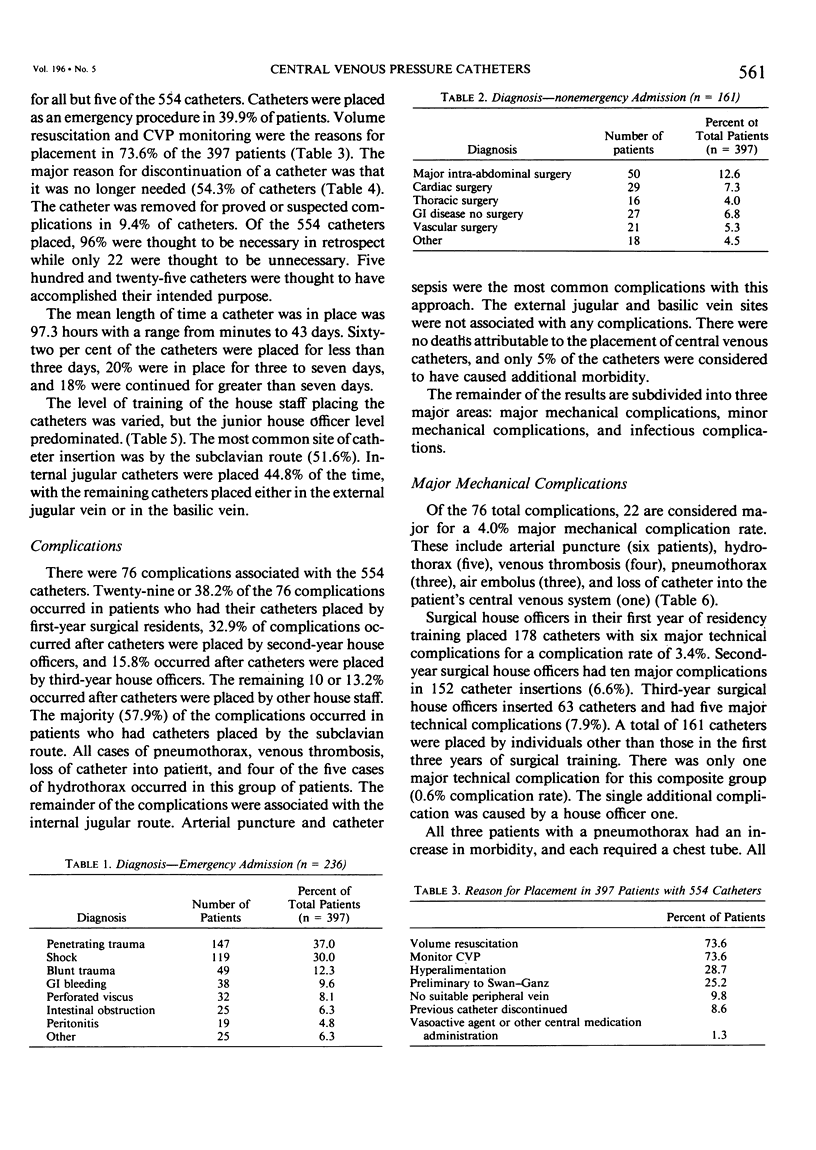
Over a 12-month period, this survey was conducted prospectively to examine the complication rate associated with the insertion and use of central venous catheters on the Louisiana State University Service at Charity Hospital, New Orleans. No attempt was made to alter or influence the current techniques and methods for catheter insertion. Three-hundred and ninety-seven patients received 554 catheters. The overall complication rate was 13.7%. Major mechanical complications occurred with 4.0% of catheters, and infectious complications occurred with 5.2%. Of the 22 major mechanical complications, 13 were associated with morbidity. Twelve of the 13 complications with morbidity occurred with 286 subclavian catheterizations (4.2%), while only 1 of the 13 complications with morbidity occurred with 248 internal jugular catheterizations (0.4%). Based on these data, it is recommended that the internal jugular approach be used in the majority of patients, reserving the subclavian approach for patients on long-term parenteral nutrition or when the internal jugular approach is not feasible technically.
Full text
PDF
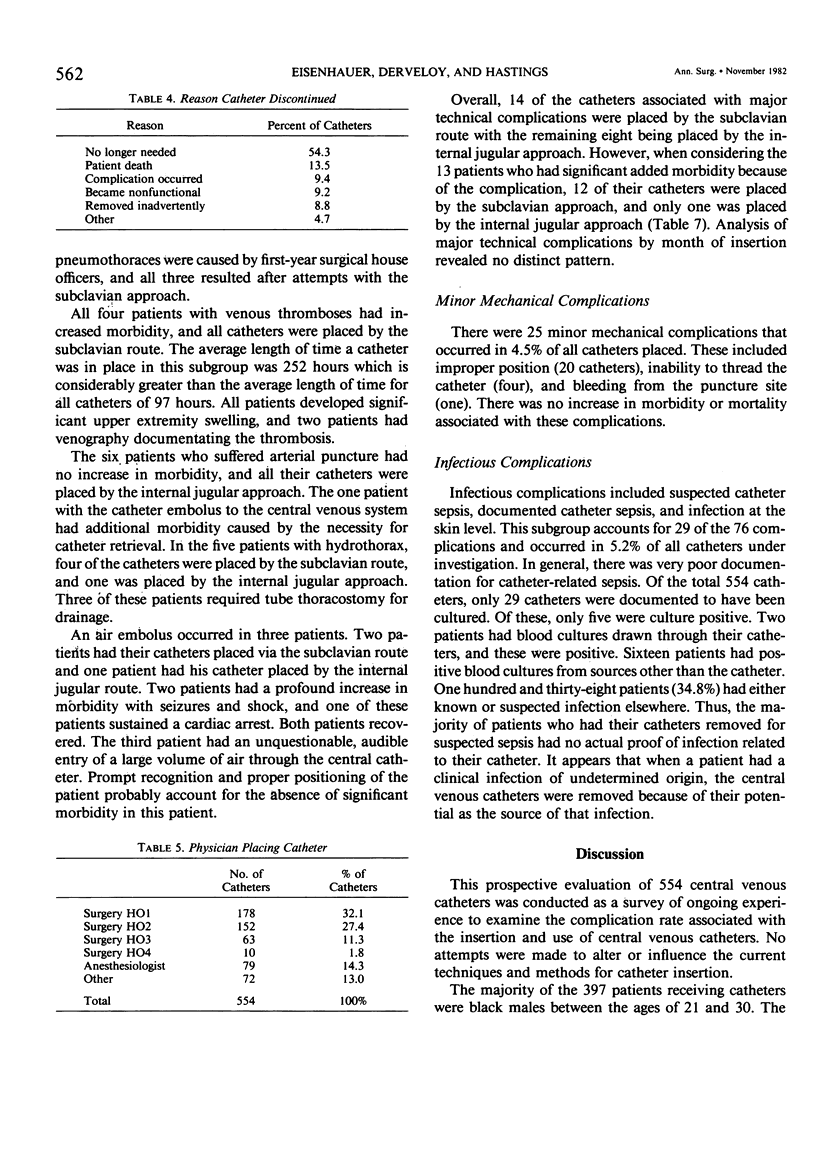


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adar R., Mozes M. Fatal complications of central venous catheters. Br Med J. 1971 Sep 25;3(5777):746–746. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5777.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard R. W., Stahl W. M., Chase R. M., Jr Subclavian vein catheterizations: a prospective study. II. Infectious complications. Ann Surg. 1971 Feb;173(2):191–200. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197102000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard R. W., Stahl W. M. Subclavian vein catheterizations: a prospective study. I. Non-infectious complications. Ann Surg. 1971 Feb;173(2):184–190. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197102000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen K. H., Nerstrom B., Baden H. Complications of percutaneous catheterization of the subclavian vein in 129 cases. Acta Chir Scand. 1967;133(8):615–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon J. D., Jr, Schaffner W., Van Way C. W., 3rd, Meng H. C. Septicemia and total parenteral nutrition. Distinguishing catheter-related from other septic episodes. JAMA. 1973 Mar 19;223(12):1341–1344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feliciano D. V., Mattox K. L., Graham J. M., Beall A. C., Jr, Jordan G. L., Jr Major complications of percutaneous subclavian vein catheters. Am J Surg. 1979 Dec;138(6):869–874. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst C. A., Jr Indications, management, and complications of percutaneous subclavian catheters. An audit. Arch Surg. 1978 Dec;113(12):1421–1425. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1978.01370240043006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merk E. A., Rush B. F., Jr Emergency subclavian vein catheterization and intravenous hyperalimentation. Am J Surg. 1975 Mar;129(3):266–268. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(75)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogil R. A., DeLaurentis D. A., Rosemond G. P. The infraclavicular venipuncture. Value in various clinical situations including central venous pressure monitoring. Arch Surg. 1967 Aug;95(2):320–324. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1967.01330140158036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt G. F., Gelbart S. M., Greenlee H. B. Catheter infection factors affecting total parenteral nutrition. Am Surg. 1978 Jul;44(7):401–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. A., Jr, Abel R. M., Abbott W. M., Hopkins C. C., Chesney T. M., Colley R., Phillips K., Fischer J. E. Catheter complications in total parenteral nutrition. A prospective study of 200 consecutive patients. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 4;290(14):757–761. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404042901401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDEGHEN P., DAIGNEUX D., MUTSERS A., VANDERHAEGHEN N. LE CATH'ETERISME VEINEUX PAR LA VOIE SOUS-CLAVICULAIRE (TECHNIQUE D'AUBANIAC MODIFI'EE) Rev Fr Gerontol. 1964 Oct;10:SUPPL–SUPPL:87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voegele L. D. Routine subclavian vein catheterization in thoracic surgical practice. Am Surg. 1978 Jul;44(7):448–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON J. N., GROW J. B., DEMONG C. V., PREVEDEL A. E., OWENS J. C. Central venous pressure in optimal blood volume maintenance. Arch Surg. 1962 Oct;85:563–578. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1962.01310040035005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


