Abstract
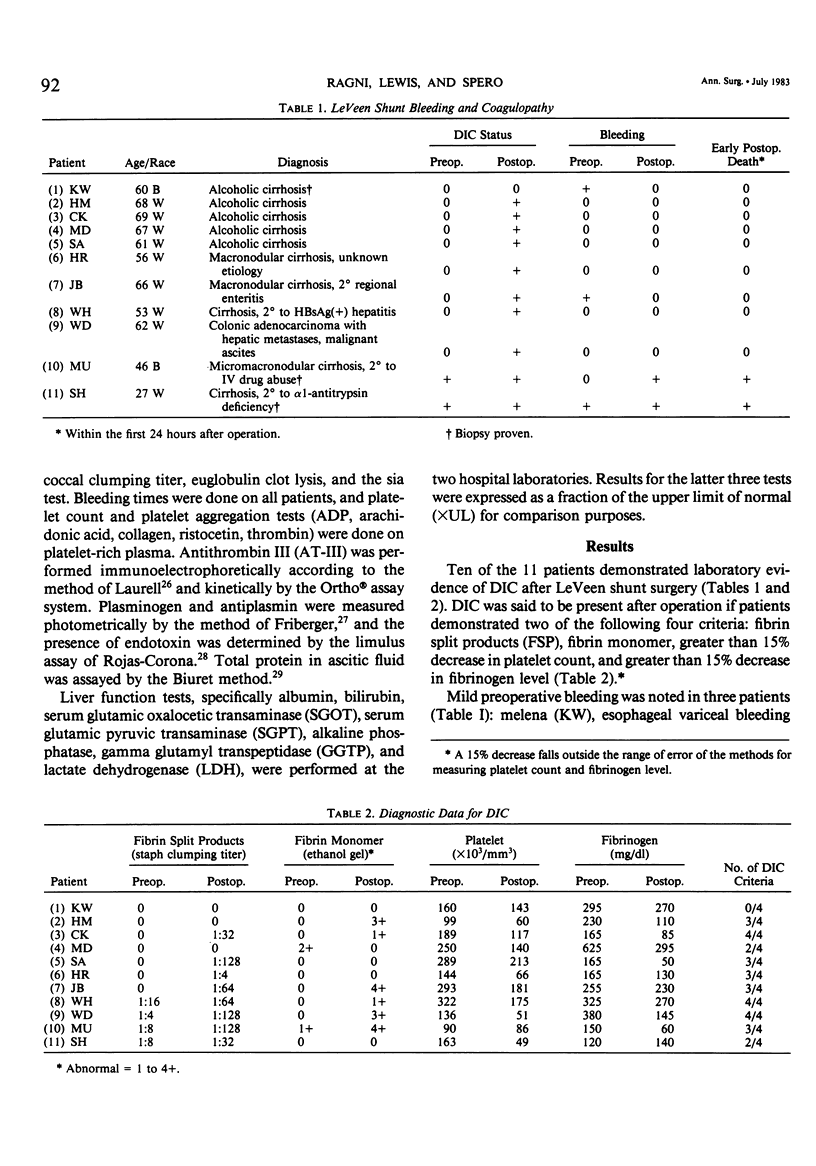
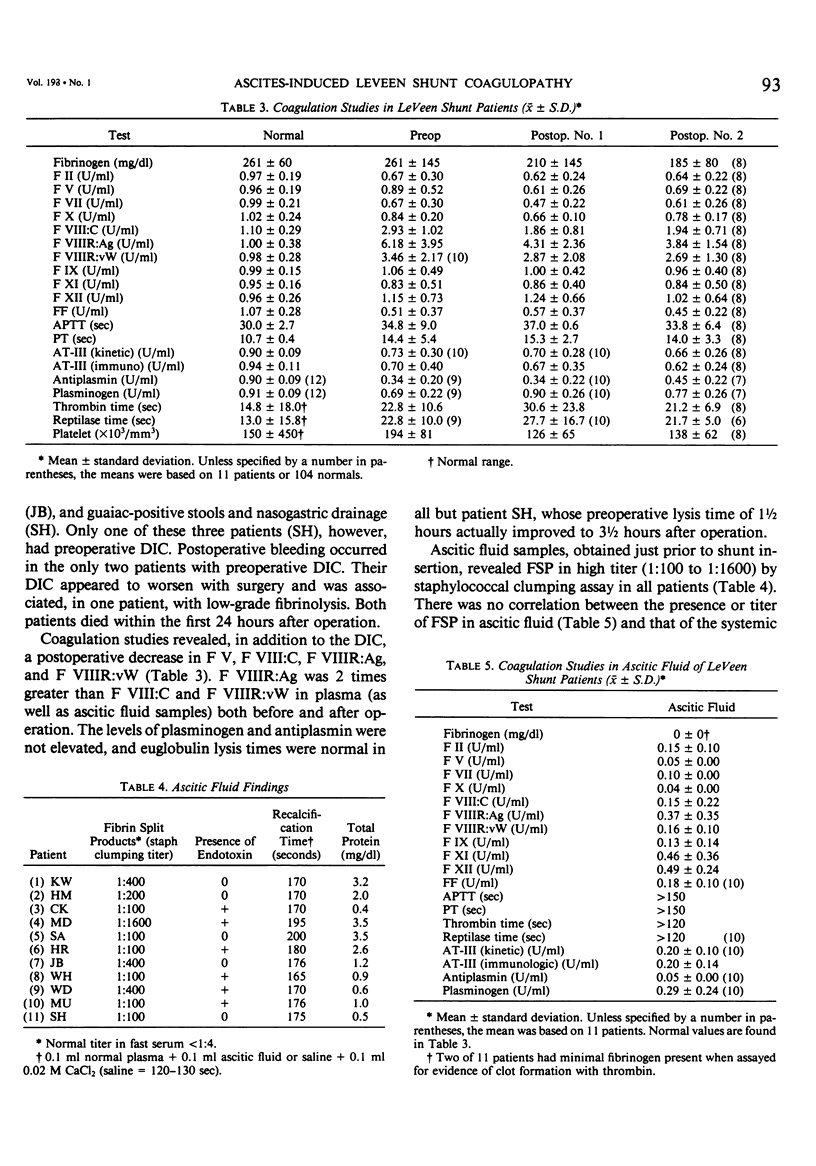
Ten of 11 patients undergoing peritoneovenous (LeVeen) shunt placement for intractable ascites had disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) following the shunt procedure. Intraoperative ascitic fluid specimens revealed fibrin split products (FSP) in high titer (1:100-1:1600) in all patients. Endotoxin was found in 6 of 11 ascitic fluid samples but in no plasma samples. Activated clotting factors, clot inhibitors, excess protein, and fibrinolytic activity were not found in ascitic fluid. Clotting factor levels were much lower than in plasma. Bleeding occurred after operation in two patients; this appeared to be related to the severity of liver dysfunction as demonstrated by elevations of bilirubin, serum glutamic oxalocetic transaminase (SGOT), serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), and preoperative DIC. It is concluded that the LeVeen shunt coagulopathy is DIC, and may be related to exposure of the systemic circulation to FSP-rich ascitic fluid that may activate the coagulation mechanism. Bleeding complications do not appear to be related to the severity of the post shunt coagulopathy, but rather to the severity of liver dysfunction and presence of preoperative DIC (probably caused by the liver disease).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansley J. D., Bethel R. A., Bowen P. A., 2nd, Warren W. D. Effect of peritoneovenous shunting with the Le Veen valve on ascites, renal function, and coagulation in six patients with intractable ascites. Surgery. 1978 Feb;83(2):181–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberger P., Knös M., Gustavsson S., Aurell L., Claeson G. Methods for determination of plasmin, antiplasmin and plasminogen by means of substrate S-2251. Haemostasis. 1978;7(2-3):138–145. doi: 10.1159/000214252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullen W. D. Hepatorenal syndrome: reversal by peritoneovenous shunt. Surgery. 1977 Sep;82(3):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig P. D., Langer B., Blendis L. M., Taylor B. R., Glynn M. F. Complications after peritoneovenous shunting for ascites. Am J Surg. 1980 Jan;139(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon D. C., Demirjian Z., Ellman L., Fischer J. E. Disseminated intravascular coagulation with the peritoneovenous shunt. Ann Intern Med. 1979 May;90(5):774–776. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. M., Stein S. F., Kutner M., Wiles M. B., Ansley J. D., Rudman D. Analysis of Twenty-three plasma proteins in ascites. The depletion of fibrinogen and plasminogen. Ann Surg. 1980 Dec;192(6):738–742. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198012000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS J. H. Coagulation defects. JAMA. 1961 Dec 9;178:1014–1020. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.73040490010008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeVeen H. H., Wapnick S., Grosberg S., Kinney M. J. Further experience with peritoneo-venous shunt for ascites. Ann Surg. 1976 Nov;184(5):574–581. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197611000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. G., Nelson J. C., Corines P., del Guercio L. R. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Complication of LeVeen peritoneovenous shunts. JAMA. 1978 Nov 3;240(19):2064–2066. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.19.2064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveen H. H., Christoudias G., Ip M., Luft R., Falk G., Grosberg S. Peritoneo-venous shunting for ascites. Ann Surg. 1974 Oct;180(4):580–591. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197410000-00023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy V. G., Buffet C., Conard J. Trobules de la coagulation au cours de réinjections continues du liquide d'ascite. Fibrinolyse ou coagulation intra-vasculaire. Nouv Presse Med. 1973 Feb 17;2(7):446–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. T. Severe coagulopathy following insertion of the LeVeen shunt: a potentially fatal complication. Can J Surg. 1979 Jul;22(4):361–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matseshe J. W., Beart R. W., Bartholomew L. G., Baldus W. P. Fatal disseminated intravascular coagulation after peritoneovenous shunt for intractable ascites. Mayo Clin Proc. 1978 Aug;53(8):526–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. L., Rodgers J. B. Procoagulant activity of ascitic fluid in hepatic cirrhosis: in vivo and in vitro. Surgery. 1979 Nov;86(5):714–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puig J. G., Antón F. M., González J. M., Vázquez J. O. Peritoneovenous shunt and bacterial endotoxin. Mayo Clin Proc. 1979 Feb;54(2):133–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raaf J. H., Stroehlein J. R. Palliation of malignant ascites by the LeVeen peritoneo-venous shunt. Cancer. 1980 Mar 1;45(5):1019–1024. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800301)45:5<1019::aid-cncr2820450531>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragni M. V., Lewis J. H., Spero J. A., Hasiba U. Bleeding and coagulation abnormalities in alcoholic cirrhotic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1982 Spring;6(2):267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1982.tb04973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Corona R. R., Skarnes R., Tamakuma S., Fine J. The Limulus coagulation test for endotoxin. A comparison with other assay methods. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):599–601. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Swaim W. R., Vogel S. B. Coagulopathy following peritoneovenous shunting. Surgery. 1979 Jun;85(6):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley M. M. Treatment of intractable ascites in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis by peritoneovenous shunting (LeVeen). Med Clin North Am. 1979 May;63(3):523–536. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31685-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S. F., Fulenwider J. T., Ansley J. D., Evatt B. L., Nordlinger B., McLemore P., Schwotzer L., Wideman C. S. Accelerated fibrinogen and platelet destruction after peritoneovenous shunting. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Aug;141(9):1149–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S. F., Harker L. A. Kinetic and functional studies of platelets, fibrinogen, and plasminogen in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Feb;99(2):217–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


