Abstract
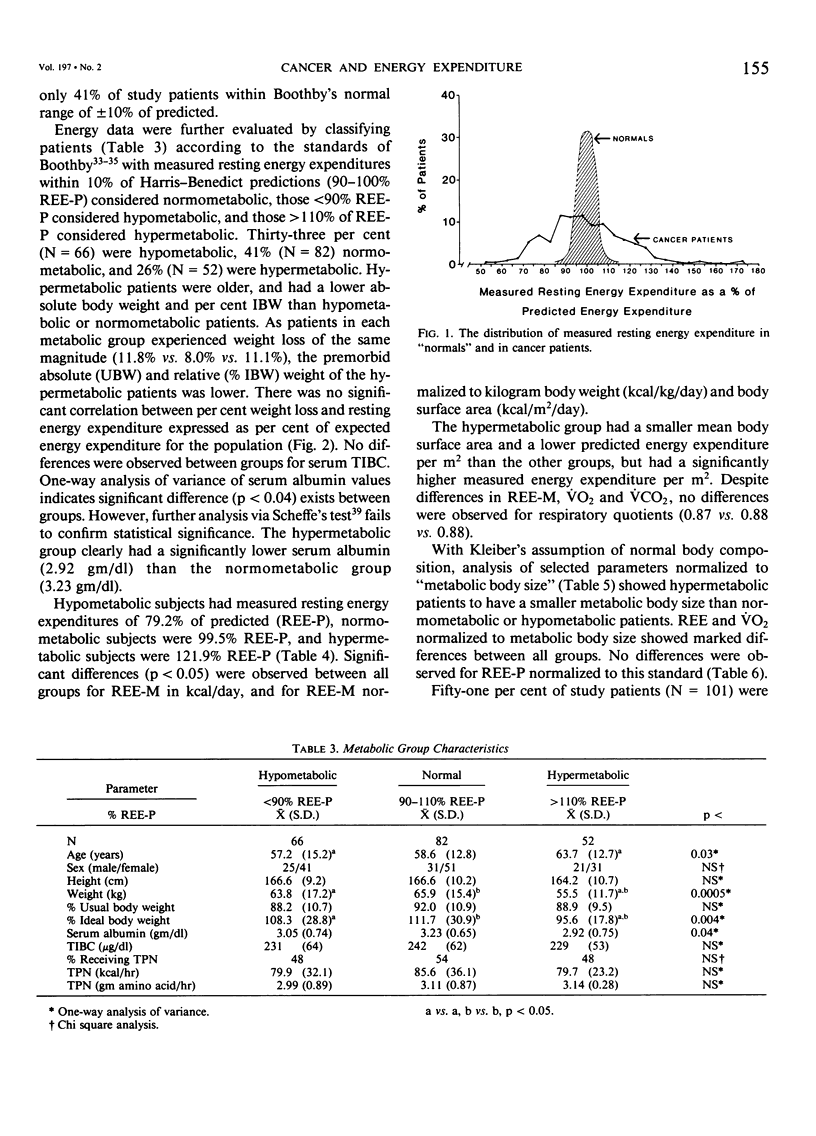
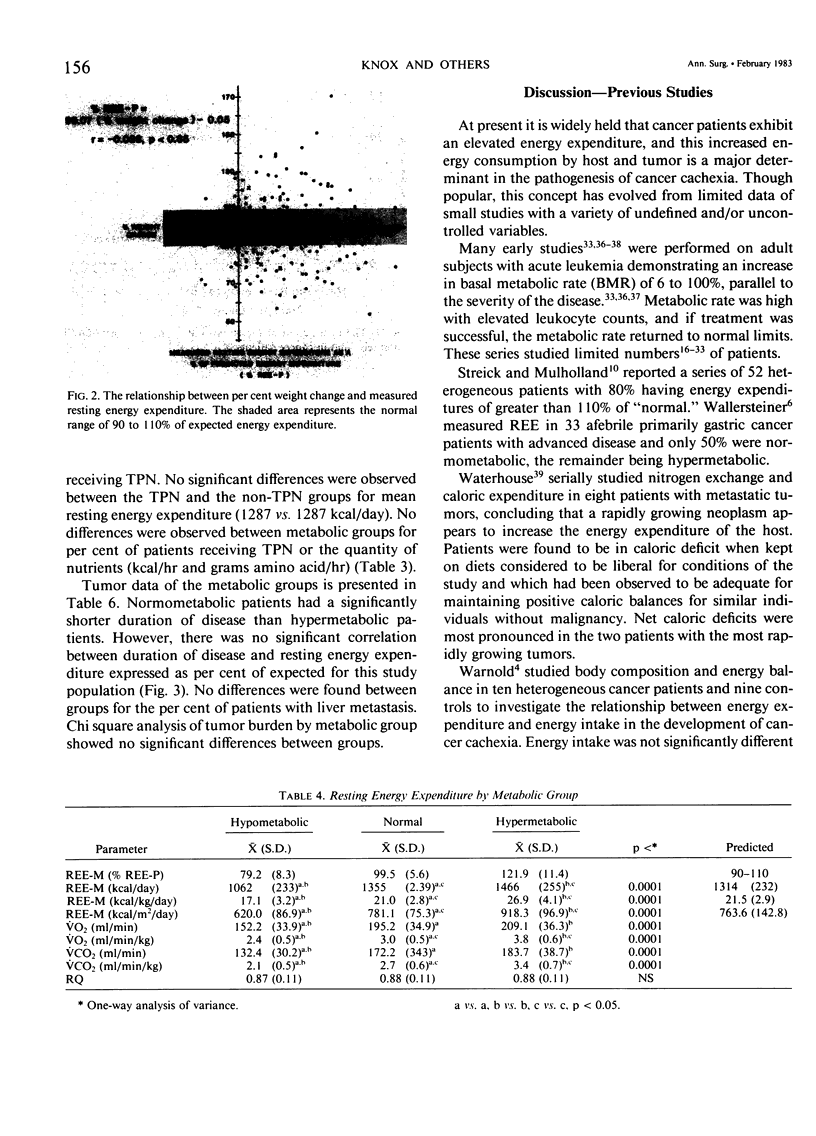
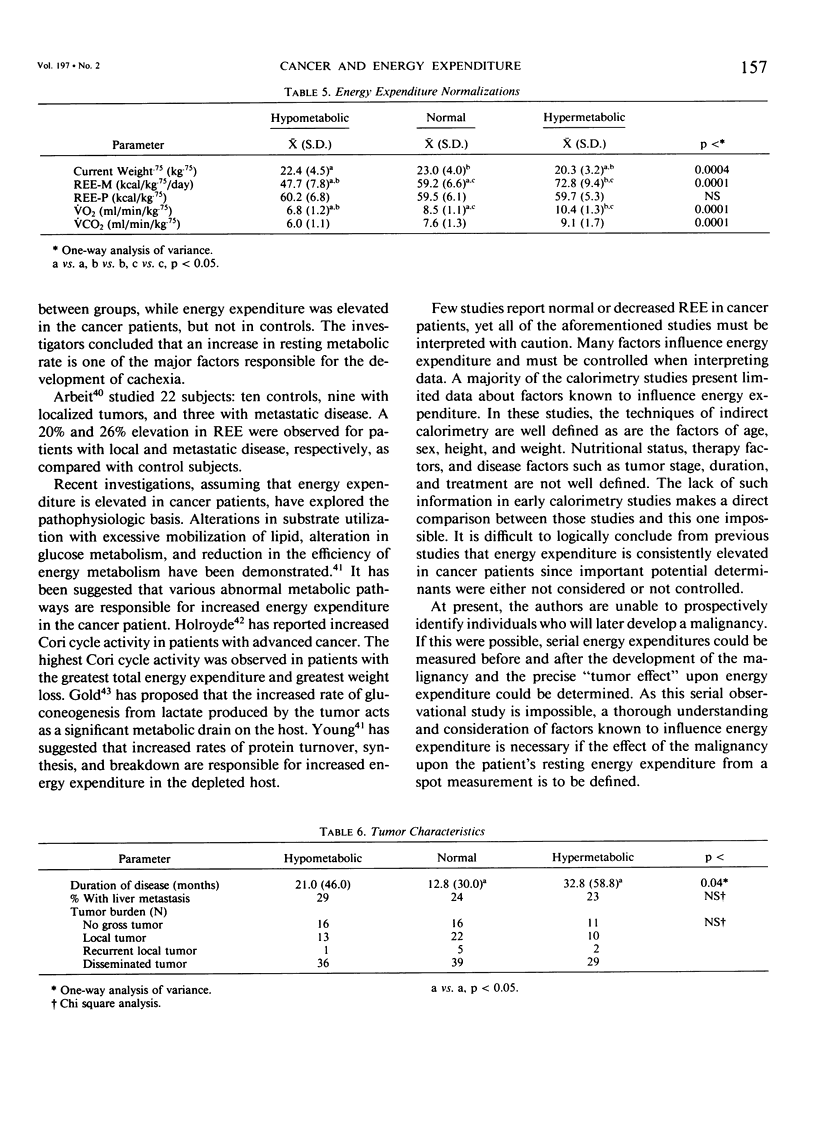
It is widely believed that the presence of a malignancy causes increased energy expenditure in the cancer patient. To test this hypothesis, resting energy expenditure (REE) was measured by bedside indirect calorimetry in 200 heterogeneous hospitalized cancer patients. Measured resting energy expenditure (REE-M) was compared with expected energy expenditure (REE-P) as defined by the Harris-Benedict formula. The study population consisted of 77 males and 123 females with a variety of tumor types: 44% with gastrointestinal malignancy, 29% with gynecologic malignancy, and 19% with a malignancy of genitourinary origin. Patients were classified as hypometabolic (REE less than 90% of predicted), normometabolic (90-110% of predicted) or hypermetabolic (greater than 110% of predicted). Fifty-nine per cent of patients exhibited aberrant energy expenditure outside the normal range. Thirty-three per cent were hypometabolic (79.2% REE-P), 41% were normometabolic (99.5% REE-P), and 26% were hypermetabolic (121.9% REE-P) (p less than 0.001). Aberrations in REE were not due to age, height, weight, sex, nutritional status (% weight loss, visceral protein status), tumor burden (no gross tumor, local, or disseminated disease), or presence of liver metastasis. Hypermetabolic patients had significantly longer duration of disease (p less than 0.04) than normometabolic patients (32.8 vs. 12.8 months), indicating that the duration of a malignancy may have a major impact upon energy metabolism. Cancer patients exhibit major aberrations in energy metabolism, but are not uniformly hypermetabolic. Energy expenditure cannot be accurately predicted in cancer patients using standard predictive formulae.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askanazi J., Carpentier Y. A., Elwyn D. H., Nordenström J., Jeevanandam M., Rosenbaum S. H., Gump F. E., Kinney J. M. Influence of total parenteral nutrition on fuel utilization in injury and sepsis. Ann Surg. 1980 Jan;191(1):40–46. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198001000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askanazi J., Carpentier Y. A., Jeevanandam M., Michelsen C. B., Elwyn D. H., Kinney J. M. Energy expenditure, nitrogen balance, and norepinephrine excretion after injury. Surgery. 1981 Apr;89(4):478–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askanazi J., Elwyn D. H., Silverberg P. A., Rosenbaum S. H., Kinney J. M. Respiratory distress secondary to a high carbohydrate load: a case report. Surgery. 1980 May;87(5):596–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzetti F., Pagnoni A. M., Del Vecchio M. Excessive caloric expenditure as a cause of malnutrition in patients with cancer. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1980 Feb;150(2):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. F. Total parenteral nutrition in the cancer patient. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 13;305(7):375–382. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108133050705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwyn D. H., Kinney J. M., Askanazi J. Energy expenditure in surgical patients. Surg Clin North Am. 1981 Jun;61(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCH A. Le métabolisme basal standard et sa détermination au moyen du "metabocalculator". Helv Med Acta. 1951 Feb;18(1):23–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANDE F., ANDERSON J. T., KEYS A. Changes of basal metabolic rate in man in semistarvation and refeeding. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Mar;12(2):230–238. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.12.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. Cancer cachexia and gluconeogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;230:103–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holroyde C. P., Gabuzda T. G., Putnam R. C., Paul P., Reichard G. A. Altered glucose metabolism in metastatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1975 Dec;35(12):3710–3714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINNEY J. M., LISTER J., MOORE F. D. RELATIONSHIP OF ENERGY EXPENDITURE TO TOTAL EXCHANGEABLE POTASSIUM. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Sep 26;110:711–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb15793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keys A., Taylor H. L., Grande F. Basal metabolism and age of adult man. Metabolism. 1973 Apr;22(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. L., Schaffel N., Geiger J. W., Schiller W. R., Blakemore W. S. Metabolic response to injury and illness: estimation of energy and protein needs from indirect calorimetry and nitrogen balance. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1979 Nov-Dec;3(6):452–456. doi: 10.1177/014860717900300609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen J. L., Gertner M. H., Buzby G. P., Goodhart G. L., Rosato E. F. Implications of malnutrition in the surgical patient. Arch Surg. 1979 Feb;114(2):121–125. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370260011001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon G. F., Peterson S. R., Sanders R. Hepatic dysfunction during hyperalimentation. Arch Surg. 1978 Apr;113(4):504–508. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1978.01370160162028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEREPKA A. R., WATERHOUSE C. Metabolic observations during the forced feeding of patients with cancer. Am J Med. 1956 Feb;20(2):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologides A. Cancer cachexia. Cancer. 1979 May;43(5 Suppl):2004–2012. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197905)43:5+<2004::aid-cncr2820430708>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologides A. Pathogenesis of cachexia in cancer. A review and a hypothesis. Cancer. 1972 Feb;29(2):484–488. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197202)29:2<484::aid-cncr2820290238>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATERHOUSE C., FENNINGER L. D., KEUTMANN E. H. Nitrogen exchange and caloric expenditure in patients with malignant neoplasms. Cancer. 1951 May;4(3):500–514. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195105)4:3<500::aid-cncr2820040304>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATERHOUSE C. NUTRITIONAL DISORDERS IN NEOPLASTIC DISEASE. J Chronic Dis. 1963 Jul;16:637–644. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(63)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIR J. B. DE B. New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):1–9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnold I., Lundholm K., Scherstén T. Energy balance and body composition in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1978 Jun;38(6):1801–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse C. How tumors affect host metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;230:86–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young V. R. Energy metabolism and requirements in the cancer patient. Cancer Res. 1977 Jul;37(7 Pt 2):2336–2347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]