Abstract
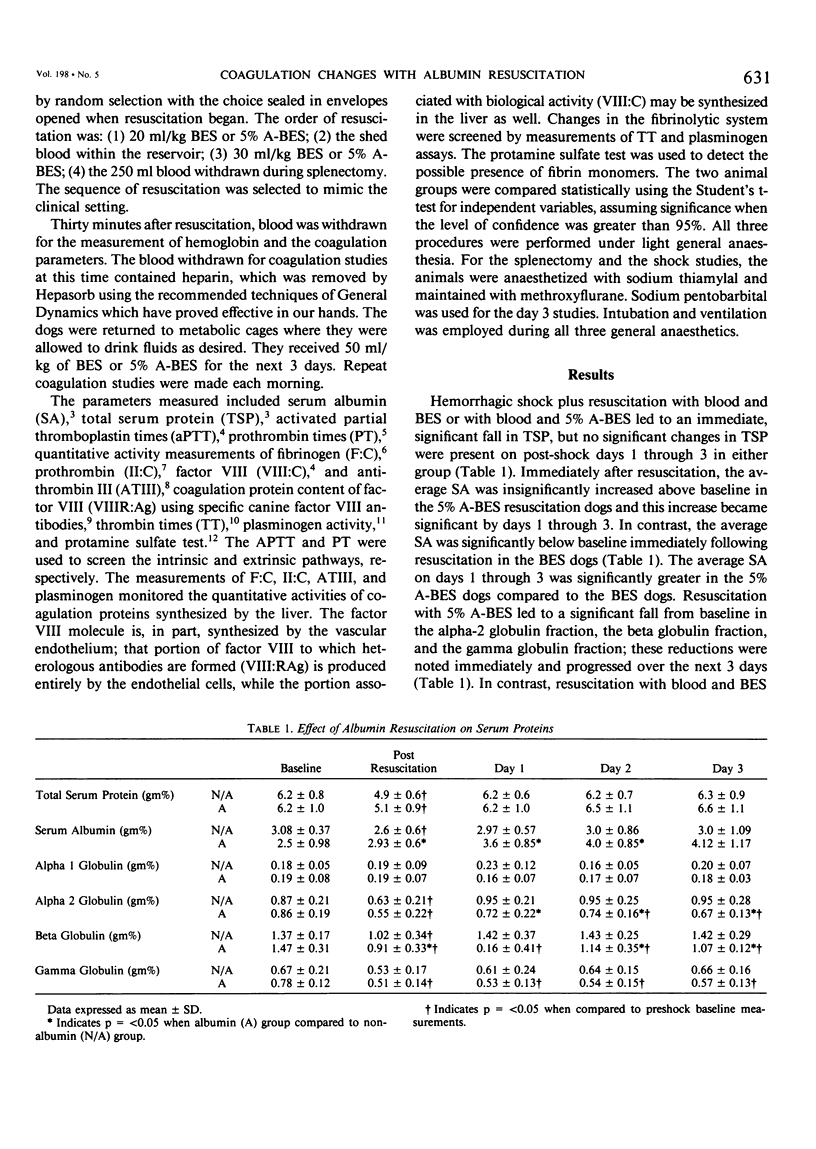
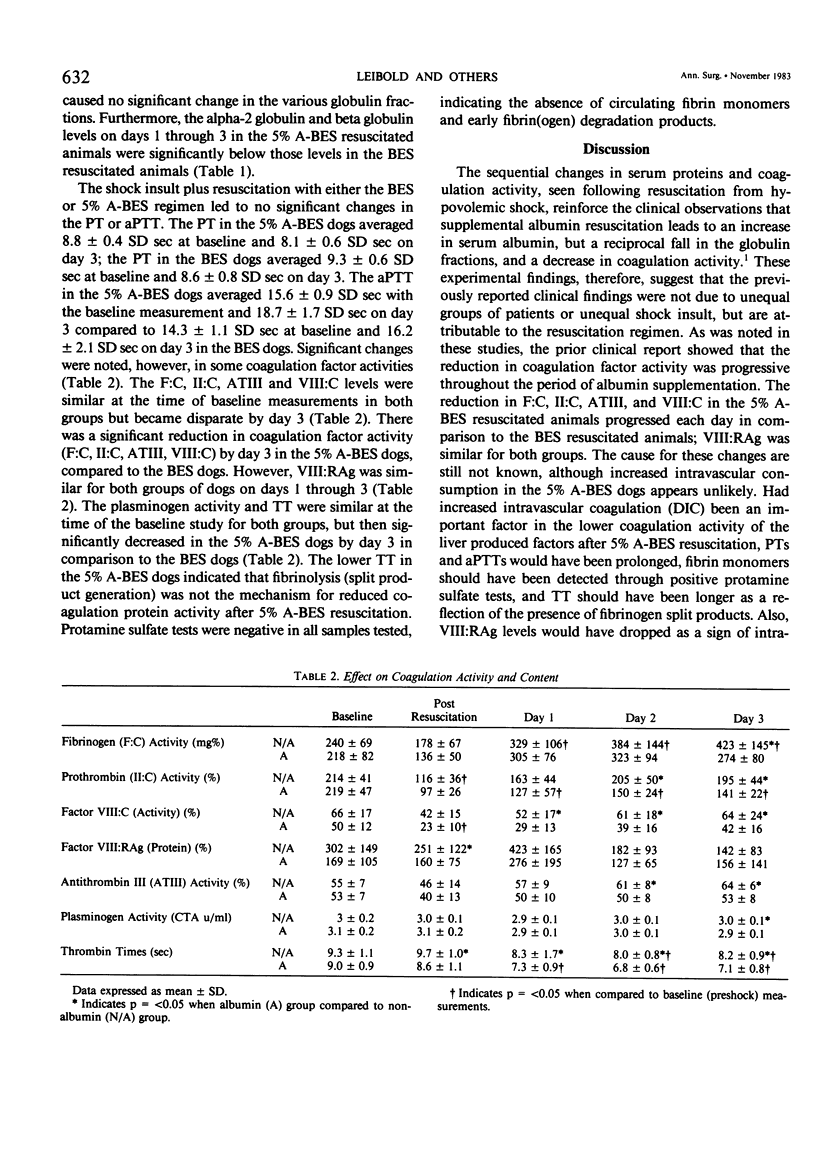
Prior work showed that albumin resuscitation in man leads to decreased coagulation activity and coagulation protein content. These observations were tested in 20 splenectomized dogs shocked by control hemorrhage and resuscitated with the sequential infusion of: (1) 20 ml/kg balanced electrolyte solution (BES) or 5% albumin/BES; (2) shed blood; (3) 30 ml/kg BES or 5% albumin/BES; (4) 250 ml blood stored from the time of splenectomy. Either BES or 5% albumin/BES was given for the next 3 days. Coagulation activity (fibrinogen, plasminogen, factor VIII, and prothrombin) and coagulation protein content (factor VIII by specific canine antigen) were measured preshock, post resuscitation, and daily for 3 days. Albumin resuscitation significantly (p = greater than 0.05) reduced coagulation activity of fibrinogen (423 +/- 145 vs. 274 +/- 80 mg/dl SD), factor VIII:C (64 +/- 24 vs 42 +/- 16% SD), prothrombin (195 +/- 44 vs. 141 +/- 22% SD) but did not alter CPC of factor VIII:RAg (142 +/- 83 vs. 156 +/- 141% SD). Lower coagulation activity after 5% albumin/BES resuscitation in conjunction with no change in factor VIII:RAg content which is produced by the vascular endothelium suggest that impaired hepatic synthesis may lead to the reduced coagulation activity after albumin resuscitation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Johnson S. D., Lucas C. E., Gerrick S. J., Ledgerwood A. M., Higgins R. F. Altered coagulation after albumin supplements for treatment of oligemic shock. Arch Surg. 1979 Apr;114(4):379–383. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370280033005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. E., Ledgerwood A. M., Mammen E. F. Altered coagulation protein content after albumin resuscitation. Ann Surg. 1982 Aug;196(2):198–202. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198208000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Gurewich V. Laboratory identification of intravascular coagulation. The serial dilution protamine sulfate test for the detection of fibrin monomer and fibrin degradation products. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Apr;77(4):665–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno T., Selenko V. Plasma fibrinogen determination by automated thrombin time. Am J Med Technol. 1972 Jun;38(6):196–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. A. Experience with a thrombin clotting time assay for measuring heparin activity. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 May;61(5):645–653. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.5.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Hoyer L. W., Dickson L., Edgington T. S. Determination of the von Willebrand's disease antigen (factor VIII-related antigen) in plasma by quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jul;86(1):152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


